Coronary insufficiency coronary artery disease. Causes of coronary heart disease. Causes of ischemia of the heart
The prevalence of the disease ranks first in the world. From ischemic heart disease does not exist pharmaceuticals, which would effectively eliminate the cause of the disease - the narrowing of the coronary artery.
Causes of the disease
The widespread prevalence of the disease is due in most cases to the “vices of society”. Consumption of products with great content rich fatty acids and carbohydrates (all kinds of hamburgers, belyashi, fast foods) leads to the deposition of cholesterol in the wall of blood vessels. Over time, its "layers" inside blood vessel lead to narrowing of the lumen. If such a plaque is localized in the coronary artery, symptoms of coronary artery disease appear.
The cause of IHD can be a neurogenic spasm of this vessel. If a person has experienced severe stress or often nervous, he has pain behind the sternum. Such symptoms indicate a violation of blood supply in the myocardium.
Other causes of CAD:
- Raise blood pressure over 140/90 mm. rt. st;
- Overweight;
- Diabetes;
- Cholelithiasis;
- Excessive consumption of high-calorie foods;
- Smoking;
- Atherosclerosis (deposition of cholesterol in the vessels).
Symptoms "on the shelves"
The classic symptom of coronary artery disease is chest pain. They occur due to lack of blood to the heart muscle (myocardium). At the same time, a person feels discomfort in the chest and upper back. fear for own life compels him to seek medical help.
IHD is characterized by tingling behind the sternum during exercise and walking, which disappear on their own during rest. These symptoms pass 10-15 minutes after taking nitroglycerin.
Interruptions in cardiac activity are observed with advanced pathology, when some parts of the myocardium die, and the heart cannot fully function. Against this background, synchronicity is broken. heart rate(arrhythmias) and interruptions in the frequency of its contractions.
Depending on the severity of the pathology, there are several forms of the disease:
- Arrhythmic - with predominant symptoms of cardiac arrhythmias;
- Heart failure is characterized by the appearance of congestion in lower limbs and other organs due to a violation of the pumping function of the heart;
- Sudden cessation of blood supply - a sharp cessation of the functioning of the "motor of the body", requiring emergency assistance;
- - death of cardiac muscle cells;
- Angina pectoris (stable and unstable) - sudden pain behind the sternum due to lack of oxygen to the myocardium.
Most common symptoms due to the development of angina pectoris. It can appear during psychophysical stress (angina pectoris), at rest or not be accompanied by pain behind the sternum. The “silent” form of the pathology is manifested only by numbness of the hand with slight shortness of breath.
In some cases, the symptoms of coronary disease may be atypical: pain in the abdomen, left side, heartburn, vomiting, and digestive disorders. They are similar to diseases. gastrointestinal tract, but IHD "give out" associated markers of pathology:
- Feeling of fear of death;
- causeless anxiety;
- inexplicable apathy;
- Severe lack of air;
- mental manifestations.
In some cases, CAD symptoms are difficult to diagnose because the classic nitroglycerin test does not work correctly. So in the presence of angina pectoris with chest pain, the doctor gives the patient a nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue. If the pain syndrome disappears in 15 seconds, the person has coronary heart disease.
Atypical forms of pathology may not disappear after taking this tool, which causes diagnostic difficulties for doctors. For example, acute pain syndrome under the scapula after sleep should not be a manifestation of coronary artery disease, since the heart muscle did not experience physical activity. However, such forms of the disease exist.
How to identify the symptoms of coronary heart disease early
Early detection of symptoms of coronary disease and their timely treatment helps prevent myocardial infarction (death of the heart muscle). If the normal blood supply is not returned to the myocardium, its cells gradually die off.
In most cases, the cause of the disease is an atherosclerotic plaque that closes the lumen of the vessel. Medications it cannot be removed, so doctors resort to surgical intervention.
To establish the location of its location, and to identify the degree of narrowing of the coronary artery, angiography is performed (X-ray examination of the vessel after the introduction into it contrast medium). Contrast agent - special chemical compound, which "lights up" when X-rays are taken.
Angiography - invasive procedure. With it, the doctor inserts a special narrow tube into the femoral artery, which is used as a catheter to inject contrast. The doctor observes the progress of the contrast agent through the vessel on the monitor screen. 
The functioning of the heart muscle can be monitored using electrocardiography. The method allows you to register electromagnetic oscillations hearts.
Operational IHD treatment involves the elimination of the site of narrowing of the coronary vessel with the help of its plastics or shunting (creation of a bypass path of blood supply). The most technologically advanced and high-quality way surgical treatment pathology is transluminal percutaneous balloon coronary angioplasty. Percutaneous - the introduction of a catheter into the vessel through a puncture in skin. Balloon - restoration of the narrowed lumen of the coronary artery with the help of an expanding balloon. Coronary - an artery that supplies blood to the heart. The term "angioplasty" means that the manipulation is carried out with the vessel.
Therefore, the symptoms of coronary disease should be identified as early as possible. Only timely treatment of pathology will save a person's life.
What is IBS?
Ischemic disease heart (CHD) - damage to the heart muscle (myocardium), due to a decrease or cessation of blood delivery to the myocardium, as a result of pathological processes in the coronary arteries (arteries supplying the heart).
The basis of pathological processes in the coronary arteries is an atherosclerotic lesion (atherosclerosis) - the deposition of cholesterol on inner wall vessels. Coronary artery disease is called the “No. 1 killer” in the world - in developed countries, mortality from coronary artery disease exceeds that of oncological diseases. Men get sick 2 times more often than women; the frequency of coronary artery disease increases sharply with age.
Why is IBS dangerous?
The main function of the heart muscle is to pump oxygenated blood from the lungs to organs and tissues, and to pump blood from the organs to the lungs so that it can be oxygenated again.
With a lack of blood flow to the heart muscle itself, a gradual (with chronic course) or instantaneous (when acute course) deterioration in the activity of the heart muscle. The myocardium suffers from a lack of oxygen, nutrients, the amount of which gradually and steadily (in the absence of treatment) decreases. Suffering by itself, the heart can no longer perform its function effectively. As a result, in pathological process are involved internal organs, to which blood ceases to be effectively delivered and removed.
What is the cause of IBS?
The cause of CAD is an atherosclerotic lesion of the arteries supplying the heart ( coronary arteries).
Formation occurs on the inner wall of the coronary artery atherosclerotic plaque, which subsequently causes blockage (occlusion) of the vessel. Consequently, the volume of blood flowing through such an artery to the heart decreases sharply, the heart muscle begins to suffer. The first symptoms of coronary artery disease appear when the artery lumen decreases by more than 50%, severe attacks of the disease occur when the diameter decreases by more than 80%.
Ischemia (lack of blood supply and oxygen supply) also occurs due to the following reasons:
- Spasm of the coronary arteries. This reason most characteristic of young people with atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, but not to a large extent expressiveness. Spasm of the arteries can develop in response to psycho-emotional and physical overload of an untrained heart.
- Violation of the violation of the coagulation / anticoagulation function of the blood (med. rheological properties blood) - the presence of atherosclerosis contributes to increased blood clotting and the development of blood clots in the coronary arteries, which also impede blood flow.
- In some heart diseases, there is an increase in its size, and the growth of the vascular network, to ensure the blood supply to the enlarged heart, lags behind. It turns out that the heart large sizes is supplied with the same amount of blood as before its increase. And this volume of blood is not enough, the heart muscle suffers, develops pathological condition.
- During physical exertion, blood flow in the heart increases, but in the presence of a narrowed section of the vascular network, blood is coming bypassing this area, through the vessels normal size(“the way it is easier”). As a result, the area of the heart muscle, to which the constricted vessel approaches, does not receive enough blood. Again, the heart suffers a lack of oxygen and nutrients.
- Other causes of ischemia are low blood pressure ( arterial hypotension), increased blood pressure (hypertension), rhythm disturbance (arrhythmias), diseases thyroid gland(thyrotoxicosis), infectious diseases With high fever and etc.
What does the concept of IBS include?
According to the classification, IHD includes the following conditions:
- sudden coronary death(primary cardiac arrest) - non-violent death caused by heart disease, manifested sudden loss consciousness within 1 hour of onset acute symptoms, while the previous heart disease may or may not be known, but death is always unexpected.
- Angina pectoris is one of the forms of coronary artery disease, manifested by paroxysmal pain or discomfort in the region of the heart, caused by myocardial ischemia (but without the development of necrosis - "death" of the heart muscle), which is associated with a decrease in blood flow and an increase in myocardial oxygen demand.
- Acute infarction myocardial infarction is a form of coronary artery disease characterized by the development of limited myocardial necrosis due to an acute discrepancy between coronary blood flow and the needs of the myocardium.
- Postinfarction cardiosclerosis - replacement of areas of necrosis of the heart muscle with connective tissue
- Heart rhythm disorders
- Heart failure is the loss of adequate "pumping" function of the heart, when the heart muscle can no longer cope with the volume of blood that it needs to pump.
What are the clinical manifestations of IHD?
Clinical manifestations of IHD depend on the form of IHD (see above), but the most characteristic are:
- Pain in the chest, most often (most typically!) Compressive, pressing in nature, occurs paroxysmal. However, many patients describe the pain as burning, shooting, twitching, stinging.
- The most typical retrosternal localization of pain, which can spread to the entire region of the heart. Localization of pain in the epigastric region (under the sternum) is possible.
- The pain radiates (spreads) most often in left shoulder, V left hand, possible irradiation in cervical area, lower jaw and teeth. Less often in right shoulder, right shoulder blade and even in the lumbar region
- The pain is quite intense.
- Low exercise tolerance (or decreased exercise tolerance).
Keep in mind that symptoms may vary from person to person. different patients. Diagnosis is made only by a doctor!
What risk factors contribute to the occurrence of coronary artery disease?
Risk factors are factors specific to a given individual that significantly increase the risk of developing coronary artery disease compared to individuals who do not have these factors. There are 4 categories of risk factors:
- Category 1: factors, the elimination of which significantly reduces the risk of developing coronary artery disease;
- Category 2: factors whose correction with highly likely reduces the risk of developing coronary artery disease;
- Category 3: factors whose correction is less likely to reduce the risk of developing coronary artery disease;
- Category 4: factors that cannot be corrected or that do not lead to a reduction in the risk of developing coronary artery disease.
Smoking has been found to increase mortality from cardiovascular vascular diseases by 50%, and the risk increases with age and the number of cigarettes smoked.
- High cholesterol.
Elevated blood cholesterol is always associated with an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Starting from the cholesterol level of 4.65 mmol/l, its further growth continuously and proportionally correlates with the frequency of IHD complications. The optimal cholesterol level is up to 5 mmol / l!
- Arterial hypertension.
There is a strong correlation between systolic (“upper”) and diastolic (“lower”) pressure levels and the incidence of CHD. An increase in diastolic pressure by 7 mm Hg compared with the norm increases the risk of developing coronary artery disease by 27%.
- Diabetes.
In patients diabetes at the age of 40 years and older, coronary artery disease is the leading cause of death. Atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease develop 10 years earlier in patients with diabetes mellitus compared to people who do not suffer from this disease.
- Lowering lipoprotein cholesterol levels high density(HDL cholesterol) and increased blood levels of triglycerides (TAG)
Normally, the level of HDL cholesterol should be more than 1.45 mmol / l. TAG level ≤1.7 mmol/l
- Low physical activity(physical inactivity)
The risk of developing coronary artery disease is almost twice as high in people who sedentary image life compared to active people.
- Overweight (obesity)
To determine the degree of obesity, the Quetelet index (body mass index) is used - the ratio of body weight, expressed in kilograms, to height, expressed in meters and squared. Normally, the Quetelet index is from 18.5 to 25. From 25 to 30 - overweight, 30-35 - obesity of the 1st degree, 35-40 - obesity of the 2nd degree, 40-50 - obesity III degree, more than 50 - obesity of the IV degree.
Excess body weight is significantly associated with the risk of coronary artery disease and mortality. Among women who have significant excess body weight, the risk of coronary artery disease increases by almost 3 times, and with a moderate increase in body weight - by 80% compared with women of normal weight.
- Menopause and postmenopausal period.
After the onset of menopause, the risk of developing coronary artery disease in women increases. This is due to changes in lipid (fat) metabolism and in the cardiovascular system.
- Alcohol consumption
- Stress
- A diet high in calories and high content animal fats.
- Elevated levels of homocysteine in the blood
- Elderly age
- Male
- Family history (history) early development coronary artery disease - the development of coronary artery disease in the father or blood relatives a male under 55 years of age, or from a mother or other female blood relatives under 60 years of age.
What are the principles of IHD treatment?
Treatment of CAD should begin with changing risk factors that can be influenced (see above)
- Smoking cessation
- lowering cholesterol (diet, drug treatment)
- Increase physical activity
- The fight against obesity
- Treatment of concomitant arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus (as well as other pathological conditions)
- Drug therapy for coronary heart disease (nitrates, antiplatelet agents, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors (angiotensin-converting enzyme), calcium antagonists, antiarrhythmics, etc.)
- Surgery
IHD TREATMENT IS A CONTINUOUS PROCESS OF DOCTOR AND PATIENT INTERACTION. ONLY THE DOCTOR DETERMINES THE TACTICS OF TREATMENT!
Photos of Nolipida
Site search
Cardiac ischemia
Many people begin to experience pain or a feeling of pressure around the heart as they age. At first, they appear only with significant physical or emotional stress. But over time, the load at which these sensations arise becomes less and less. Usually people tend to think that it is "ageing", that there is nothing to be done about it, and do not seek medical help. This opinion is erroneous, since often such pain is a manifestation of coronary heart disease.
Ischemic heart disease (CHD) is an insufficient supply of blood to the heart muscle. Blood that carries oxygen and nutrients does not pass into the right amount through the vessels of the heart (coronary or coronary arteries) due to their narrowing or blockage. Depending on how pronounced the "starvation" of the heart, how long it takes, and how quickly it occurred, several forms of coronary heart disease are distinguished.
Asymptomatic, or "silent" form of coronary artery disease, when the "starvation" of the heart is not manifested by clinical symptoms.
Angina pectoris (angina pectoris) - with this form of coronary artery disease, malnutrition of the heart is manifested by severe pain behind the sternum during exercise, stress, exposure to cold or overeating.
An arrhythmic form of coronary heart disease, in which insufficient blood supply to the heart is manifested by heart rhythm disturbances, most often atrial fibrillation.
Myocardial infarction is the death of a section of the heart muscle caused by its "starvation".
Sudden cardiac death is a cardiac arrest, in most cases caused by a sharp decrease in the amount of blood supplied to it. The patient can be brought back to life only by immediate resuscitation.
If IHD is left untreated, due to oxygen deficiency, the heart ceases to perform its normal function, which leads to insufficient blood flow to all other organs. This condition is called chronic heart failure.
What causes coronary artery disease and why is it dangerous?
Ischemic heart disease usually occurs due to atherosclerosis of the heart (coronary) vessels. In this condition, so-called plaques form on the walls of the arteries, which either narrow the lumen or completely clog the vessels. At first, as a rule, the narrowing of the lumen of the coronary vessels is insignificant, it is manifested by pain behind the sternum (angina pectoris). If the plaque is destroyed, blood clots appear in the narrowed vessels, which lead to myocardial infarction. Spasm or inflammation of the coronary vessels can also be the cause of insufficient blood flow to the heart. These are the immediate causes of coronary heart disease. They, in turn, appear due to smoking, obesity, high blood pressure, uncontrolled medication, hormonal disorders, malnutrition and so on.
Among the complications of coronary artery disease - a violation of the rhythm of heart contractions or blockade. For severe angina or after massive heart attack heart function is disturbed - chronic heart failure occurs.
Coronary heart disease can develop in adults regardless of gender at any age, but most often in men aged 40-65 years. The development of atherosclerosis of the cardiac arteries is facilitated by such common factors in our time as malnutrition and as a consequence, increased content blood fat, hypertension, smoking, physical inactivity and stress.
In developed countries, coronary heart disease has become the most common cause death and disability - it accounts for about 30 percent of deaths. It is far ahead of other diseases as a cause sudden death and occurs in every third woman and half of men. This difference is due to the fact that female sex hormones are one of the means of protection against atherosclerotic damage to the vessels. In connection with the change hormonal background with menopause, the likelihood of a heart attack in women after menopause increases significantly.
Diagnosis ischemic heart disease
In order to suspect coronary artery disease, the doctor, as a rule, has enough complaints from the patient about pain behind the sternum, heart rhythm disturbances, and shortness of breath. For accurate diagnosis electrocardiography is used, and it most often needs to be carried out either during physical exertion or in the form of Holter monitoring using a special sensor that the patient wears for a day. Get the image of the heart needed for IHD diagnostics, you can use echocardiography or isotope scanning (myocardial scintigraphy), which also help to identify defects in the heart valves or abnormalities in the functioning of the heart muscle caused by its "starvation".
The final diagnosis can be made using contrast x-ray examination- cardioangiography, which allows you to see the vessels of the heart, the places of their narrowing or blockage on a special monitor.
Treatment ischemic heart disease
Most often, coronary heart disease is treated with medication, and combinations of drugs are used. different action. There are drugs that dilate the blood vessels of the heart, other drugs reduce the load on it, lowering blood pressure and equalizing the heart rate. There are also drugs that fight the main cause of coronary artery disease - lower blood cholesterol levels.
It is also possible to expand the narrowed arteries with the help of a simple operation - the method of coronary angioplasty, often with fixing their lumen with a metal insert - a stent. This treatment is more common in the West, and Russian doctors prefer therapeutic methods. In serious cases, cardiac surgeons resort to bypass surgery, in which clogged heart vessels are replaced with well-passable "new" ones - usually "made" from the veins of the limbs.
Ischemic heart disease: what is dangerous?
Heart - unique organ performing the pumping function. It provides blood circulation, making 100,000 strokes per day, 3 million strokes per month, pumping 170 liters of blood per day.
Heart is the main organ of the complex cardiovascular system, its average weight is 300 grams. During the contraction of the heart, the right ventricle pushes blood into the lungs in order to saturate it with oxygen, and from the left ventricle, oxygenated blood flows to all organs of our body. An uninterrupted supply of oxygen to the heart is provided coronary vessels. These arteries deliver oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle, without which our heart cannot function.
Usually, a well-functioning heart practically does not bother us, and we even forget about its existence. But here comes the moment when your heart makes itself felt.
Heart diseases vary, but the most common and serious of them is ischemic (coronary) heart disease. (IHD).
What is coronary heart disease and angina pectoris, what are the reasons for their origin?
IHD is based on the narrowing and blockage of the main coronary arteries by atherosclerotic plaques. On the inner surface of the arteries (normally very smooth and even), peculiar outgrowths appear - plaques protruding into the cavity of the blood vessel, like "rust in the pipes." Over time, they become more and more, and when the lumen of the vessel narrows to 70%, there is a difficulty in blood flow, and as a result of this, the balance between the delivery of oxygen to the heart muscle and the need for it is disturbed. At the same time, it develops oxygen starvation(hypoxia) cells.
While in this state, cells also suffer from nutrient deficiencies and are exposed to accumulated waste products. The whole complex of violations of the vital activity of heart cells in conditions of insufficient blood supply to it is commonly called ischemia. The degree of ischemia depends on the size of atherosclerotic plaques - the larger the size of the plaque, respectively, the narrower the lumen of the vessel, the less blood passes through it, which means that the tissues will receive less oxygen and nutrients, the more pronounced the manifestations of angina will be. The plaque can completely block the lumen of the vessel and block the blood flow. The mechanism of occurrence of ischemia with spasm (sharp narrowing) of the coronary arteries is similar.
How is IBS manifested?
So, if the heart muscle receives an insufficient amount oxygen and nutrients, then angina pectoris develops. If the delivery of oxygen and nutrients is completely stopped, then myocardial infarction develops.
Most often, the disease manifests itself against the background of physical activity or emotional stress. At this moment, there is pain or a feeling of pressure, heaviness behind the sternum - the first signal of the possible development of heart disease.
The most common form of coronary artery disease is angina pectoris. Angina pectoris (formerly called "angina pectoris") is a disease, the main manifestations of which are compressive pains behind the sternum, giving (irradiating) to the left hand, left half lower jaw, teeth, shoulder and so on. You may also be disturbed by a feeling of heaviness, burning, pressure behind the sternum, a feeling of lack of air, sometimes pain in the upper abdomen may bother you. Such pains are shown in the form of short (5-10 min.) attacks which can be repeated with various frequency. Physical exertion can provoke an attack of angina pectoris, emotional stress, cold air, smoking. Attacks can develop at any time of the day. But most often develop in the early morning hours.
Despite the fact that angina attacks have many manifestations, in the same person, attacks proceed in the same way.
Angina may be:
- stable;
- unstable.
stable angina- when angina attacks for a long time appear after an equal load and with the same frequency and have the same character.
Unstable angina- is manifested by an increase in seizures, which can occur at lower loads, become stronger and longer in time. Unstable angina - warning: “Caution, the risk of myocardial infarction! See a doctor immediately!"
Unstable or progressive angina is characterized by both an increase in the frequency of attacks and their severity, a reduction in the usual distance while walking. Pain can occur even at rest, and usual dose nitroglycerin does not always give an effect, you have to increase it. The risk of myocardial infarction and other severe complications increases!
If the pains become more intense and last more than 20-30 minutes, they repeat in waves at rest, severe weakness and a feeling of fear, the pulse quickens and blood pressure fluctuates sharply, an urgent consultation with a doctor is necessary or an appeal to ambulance. In such a situation, first of all, myocardial infarction should be suspected.
How to detect angina pectoris?
The diagnosis of angina pectoris is made mainly on the basis of a detailed questioning of the patient, a thorough analysis of the patient's complaints and the characteristics of the course of the disease. However, to confirm the diagnosis and clarify the severity of the disease, the doctor may prescribe additional research methods: recording an ECG at rest and at the height of a pain attack. ECG recording is extremely important role when examining elderly patients. Often, an ECG can reveal a previous myocardial infarction or heart rhythm disturbances.
A special place in the diagnosis is occupied by stress tests, while the ECG is monitored during the patient's exercise (treadmill, bicycle ergometer). However, you need to know that outside of an angina attack, the ECG may be normal.
A lot of useful information can be obtained with a 24-hour ECG recording (Holter ECG monitoring), when in living conditions a permanent ECG recording is being made.
If these studies are not enough, then the doctor may prescribe more complex methods diagnostics: coronary angiography (contrast study of the main coronary vessels) and perfusion scintigraphy (radio-nuclide study of the heart muscle).
Risk factors
Numerous scientific studies carried out have made it possible to identify the factors contributing to the development and progression of coronary artery disease. They are called risk factors.
At the same time, the main risk factors for coronary artery disease, which are causally associated with this disease and are widespread among the population, are distinguished:
- disorders of fat (lipid) metabolism, elevated cholesterol levels;
- high blood pressure (more than 140/90 mm Hg);
- smoking;
- diabetes mellitus, violation of carbohydrate metabolism.
Among the risk factors, there are those that you can influence:
- smoking;
- arterial hypertension;
- high cholesterol;
- stress;
- excess body weight;
- physical inactivity.
As practice has shown, patients with IHD usually have several risk factors at the same time. In this case, they negative impact summed up and, as a rule, increased by several times.
Risk factors contribute to the onset and progression of coronary heart disease, and their correction is the basis for the prevention of coronary artery disease.
IHD treatment
There are two main approaches to the treatment of coronary heart disease.
First aimed at prolonging the life of the patient by preventing fatal dangerous complications diseases. This approach is rightfully considered the main one. It includes:
- correction of risk factors;
- the use of drugs that lower the level of cholesterol in the blood - statins;
- the use of medicinal substances that prevent intravascular thrombosis - antiplatelet agents;
- the use of drugs that protect vascular wall from damage;
- the use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors), beta-blockers, calcium antagonists, nitrates, cytoprotectors.
Risk factor correction
First, smoking, here the answer is unequivocal: health and nicotine are not compatible. Nicotine is one of the main enemies of the cardiovascular system, it has a number of negative effects on the patient's body: it increases blood pressure, constricts blood vessels, provokes arrhythmias, promotes the deposition of "bad" cholesterol on the walls of blood vessels, increases blood clotting, reduces the percentage of oxygen in the blood. All this can provoke the appearance of cardiovascular complications in patients with coronary artery disease, including myocardial infarction. Therefore, it is advisable to quit smoking.
Secondly, it is necessary to follow a diet, to develop a certain character of nutrition. Some products are known to contain a large number of cholesterol. A high level of blood cholesterol leads to the development of atherosclerosis.
Therefore, it is necessary to exclude or sharply limit the use of such products. High cholesterol foods include: fatty meats, liver, butter, sour cream, cream, egg yolks, whole milk, fatty cheeses. It is more useful to introduce more vegetables into the diet, sour-milk products with a low fat content, vegetable oil, lean varieties meat, fish, poultry, flour bread coarse grinding or with bran, cereals with a high content of vegetable fibers (oatmeal, bran flakes). Butter should be replaced with soft margarine such as RAMA Vitality and RAMA Olivio. They are based on a mixture of oils: sunflower or soybean and vegetable solid fats, which are produced from the seeds of special oil palms. All of these ingredients do not contain cholesterol.
Thirdly, it is important to fight overweight. Being overweight is not a cosmetic problem. This is the risk of developing many diseases: diabetes mellitus, hypertension, gallstone disease and other diseases that can aggravate the course of coronary artery disease.
Fourth, lead an active lifestyle, engage in physical education. We offer you 9 tips for increasing physical activity, which of course it is better to discuss with your doctor again:
- 1. Use the stairs instead of the elevator.
- 2. Go to work and go shopping on foot.
- 3. Get out of the vehicle.
- 4. Do more chores around the house.
- 5. Work in the garden and in the country to the best of your ability.
- 6. Use your bike wisely.
- 7. Walk for your lunch break.
- 8. Do it regularly useful exercises: therapeutic physical education, breathing exercises.
- 9. Combine physical activity with positive emotions: music, art, hobbies, socializing with friends, etc.
Fifth, try to avoid stressful situations or learn to deal with them. It's about about measures to prevent or reduce psycho-emotional overstrain. We must learn to manage our emotions and correctly assess this or that situation, taking into account its true significance.
Recommended to avoid if possible conflict situations, acquire positive emotions. good effect also renders occupation by favorite business (hobby). The arsenal of health-improving means can include a system of psychological training (auto-training) and relaxation techniques that increase stability nervous system to stressful situations.
Statins
When the level of cholesterol is significantly elevated, even careful dieting will reduce it by no more than 5-15%. Therefore, if, with the observance of such a diet, cholesterol indicators remained at an unsatisfactory level, the use of lipid-lowering preparations is required. There are currently several various groups lipid-lowering agents, but proven to reduce the level of "bad" cholesterol and the risk of developing complications of atherosclerosis, only drugs from the group of statins: fluvastin, atrovastin, simvastin, pravastin.
Antiplatelet agents
Prevention of acute vascular thrombosis protects the patient from developing unstable angina and myocardial infarction - the most dangerous, acute, forms of coronary heart disease. Therefore, the appointment of drugs that affect the processes of thrombosis - important component prevention of complications of coronary artery disease. The main antiplatelet drugs in modern practice are aspirin, ticlopidine, clopidogrel.
ACE inhibitors
Most widely in contemporary practice for the treatment of hypertension and heart failure, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, the so-called ACE inhibitors, are used.
Nitrates
Nitrates are used to relieve and prevent angina attacks. These drugs have been used for many years. It is very important to have nitroglycerin tablets with you at all times, and they must be protected from heat and light. Nitrates are prescribed in various forms ah: tablets, capsules, spray, ointment, plaster.
How to relieve an angina attack
If you have an attack of angina pectoris, use nitroglycerin, put one tablet under the tongue.
- before taking nitroglycerin, you should sit down, the drug may cause dizziness;
- let the tablet dissolve completely. Do not crush the tablet, the drug will not work;
- you should wait 5 minutes and if angina persists, you need to take another tablet of nitroglycerin;
- you should wait another 5 minutes, if angina pectoris does not disappear, take the third tablet of nitroglycerin.
Attention: if the pain in the heart area lasts more than 15 minutes and does not go away after taking three tablets of nitroglycerin, contact an ambulance and take 1/2-1 tablet of aspirin - you may develop a myocardial infarction!
Beta blockers
These drugs reduce the amount of oxygen needed by the heart during physical or emotional stress. They also slow down the heart and lower blood pressure. It is very important to take them constantly and not stop taking them without consulting your doctor. These drugs are used to reduce the mechanical work of the heart, prevent angina attacks, heart rhythm disturbances, excessive increase blood pressure during physical or psycho-emotional stress. In cases where a beta-blocker cannot be prescribed due to contraindications or intolerance (for example, with concomitant bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, peripheral arterial disease, hypotension or normal blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, etc.), it is recommended to prescribe Coraxan (ivabradin).
calcium antagonists
Calcium antagonists prevent the development of angina attacks. These drugs dilate the arteries, including the coronary ones. As a result, blood flow is facilitated, a large amount of blood flows to the myocardium. The drugs also lower high blood pressure.
Cytoprotectors
A special group is represented by myocardial cytoprotectors (Preductal MB). These drugs directly protect myocardial cells at the time of ischemia with a lack of oxygen. They do not affect the heart rate and blood pressure, and, as a rule, their intake is not accompanied by the development of side effects. In addition, while maintaining angina attacks against the background of drugs of a hemodynamic type of action, Russian and European experts recommended the appointment of Preductal MV to enhance antianginal efficacy.
Surgical methods for the treatment of coronary heart disease
If the course of coronary artery disease, despite taking medication, progresses and limits the patient's normal life, there may be a need for surgical treatment.
What are the methods of surgical treatment?
Coronary bypass surgery is the most common operation for the treatment of angina pectoris. In this case, the patient's own vessel is used, with the help of which blood flow is restored, bypassing the clogged artery. The number of bypasses depends on the number of affected arteries.
Coronary angioplasty (balloon dilatation) is a procedure in which the lumen of the vessel is restored using an inflated balloon inserted into the artery.
Stenting is a procedure in which a coil is inserted into the lumen of the vessel, expanding the affected artery.
However, you should know that a surgical operation is milestone treatment coronary disease, but it does not cure completely, therefore, even with good health, the patient must comply with measures to prevent the progression of atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels, and receive maintenance therapy.
How to live with angina?
The quality of life of a patient with angina pectoris and life expectancy depends on:
- early detection of the disease;
- compliance with the regimen medicines;
- lifestyle changes and elimination of risk factors.
Lilia ADONINA.
Not every person knows why IHD develops, what it is and how to treat it. This abbreviation stands for coronary heart disease. This pathology is very common among the adult population. The basis of the development of coronary disease is a violation of the blood supply to the myocardium. Such a diagnosis worsens the prognosis for health and shortens the life expectancy of a sick person.
Development of coronary heart disease
IMPORTANT TO KNOW Means for cleaning blood vessels and reducing pressure, which is recommended by doctorsCirculatory system man is very complex. It consists of the heart and blood vessels. The myocardium itself constantly needs oxygen and nutrients. They enter there through the coronary (coronary) arteries. The latter nourish the heart itself, maintaining its functions at the proper level. Ischemic disease is a pathological condition in which the blood supply to the myocardium is disturbed or completely stopped.
This pathology can be organic or functional. With IHD, the percentage of deaths is high. Poor prognosis is most often associated with acute (myocardial infarction). IHD is the most common cause of sudden death. This is a serious medical social problem. In Russia, more than 1 million people die every year from vascular diseases. Most of the working population. Increasingly, IHD develops in young people.
The incidence rate is higher in men. This is due to active smoking, alcoholism and addiction to fatty foods. Many people become disabled. This happens as a result of myocardial infarction and the development of heart failure. Modern healthcare is not yet able to cope with similar problem and change the environment. The only way reduce mortality and morbidity - change lifestyle.
Varieties of ischemic disease
WHO (World Health Organization) considers coronary artery disease as general concept. It combines several diseases. The IBS group includes:
- sudden coronary death (with and without fatal outcome);
- angina (tension and spontaneous);
- painless variant of IHD;
- myocardial infarction;
- disorder of rhythm and conduction;
- heart failure;
- postinfarction cardiosclerosis.
 More common painful forms ischemic disease. The most common pathology is angina pectoris. It is stable and unstable. Separately, Prinzmetal's angina pectoris was singled out. Many specialists use the concept of acute coronary syndrome. It includes a heart attack. This includes unstable angina. Do not confuse coronary heart disease and stroke. This different concepts. A stroke is an acute disorder cerebral circulation.
More common painful forms ischemic disease. The most common pathology is angina pectoris. It is stable and unstable. Separately, Prinzmetal's angina pectoris was singled out. Many specialists use the concept of acute coronary syndrome. It includes a heart attack. This includes unstable angina. Do not confuse coronary heart disease and stroke. This different concepts. A stroke is an acute disorder cerebral circulation.
Etiological factors
Risk factors for coronary artery disease are known to every cardiologist. The development of this cardiac pathology is based on a lack of oxygen. The cause may be damage to the coronary arteries. Highest value in the development of coronary artery disease have the following factors:
- atherosclerosis coronary vessels;
- smoking;
- thrombosis;
- hyperlipidemia;
- diabetes;
- high blood pressure;
- alcoholism;
- malnutrition;
- physical inactivity.
Ischemic disease often develops against the background of atherosclerosis. The reason is a violation of lipid metabolism.
Cholesterol is produced in the human body. It is associated with blood proteins. There are low, high and very low density lipoproteins. Atherosclerosis increases the content of LDL and VLDL. Over the years, lipids are deposited on the walls of the coronary arteries.
 Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis Initially, there are no symptoms. Gradually, the lumen of the vessels decreases and in certain moment obstruction of blood flow. Dense plaques are formed. The situation is aggravated by smoking, unhealthy diet and physical inactivity. The risk factor for the development of coronary artery disease is hypertension. It increases the likelihood of myocardial ischemia several times.
IHD often develops in people suffering from endocrine pathology(obesity, diabetes, hypothyroidism). This form of coronary disease, such as a heart attack, may be due to acute thrombosis(blockage) coronary arteries. Causes of CHD include smoking. This is very serious problem which is almost impossible to solve.
dangerously active and passive smoking. Substances contained in the smoke contribute to arterial spasm, which leads to hypertension. Carbon monoxide helps to reduce the level of oxygen in the blood. All tissues of smokers experience oxygen starvation. Another risk factor that can be eliminated is stress. It leads to an increase in blood pressure due to the production of catecholamines (adrenaline and norepinephrine) and oxygen deficiency.
 With IHD, every doctor should know the etiology. Risk factors for this pathology include elderly age, genetic predisposition, nutritional errors and male sex. Symptoms of coronary artery disease often occur in people who abuse animal fats (they are found in meat, fish, butter, mayonnaise, sausage) and simple carbohydrates.
With IHD, every doctor should know the etiology. Risk factors for this pathology include elderly age, genetic predisposition, nutritional errors and male sex. Symptoms of coronary artery disease often occur in people who abuse animal fats (they are found in meat, fish, butter, mayonnaise, sausage) and simple carbohydrates.
The development of angina pectoris in humans
Of all forms of coronary artery disease, angina pectoris is the most common. This pathology is characterized by the occurrence acute pain in the region of the heart against the background of circulatory disorders. There are angina pectoris and spontaneous (variant). They have fundamental differences from each other.
Angina occurs predominantly in humans middle age. The risk of developing this pathology in a person under 30 years of age is less than 1%.
The prevalence of angina among adults reaches 15-20%. The incidence rate increases with age. The most common cause is atherosclerosis. Symptoms appear when the lumen of the arteries narrows by 60-70%.
With angina pectoris (stress), the following clinical manifestations are observed:
- chest pain;
- dyspnea;
- pale skin;
- increased sweating;
- change in behavior (feelings of fear, anxiety).
The main symptom of this form of IHD is pain. It occurs as a result of the release of mediators and irritation of receptors. The pain is paroxysmal. It occurs during physical exertion, quickly increases, is eliminated by nitrates, pressing or squeezing and is felt in the chest on the left. The attack lasts a few seconds or minutes. If it is delayed for 20 minutes or more, then myocardial infarction must be excluded.
 Pain radiates to left side torso. Angina pectoris can be stable or unstable. The first is different in that the attacks occur with the same physical activity. The pain syndrome is felt for less than 15 minutes. The attack disappears after taking 1 tablet of nitrates. Pain in unstable angina is longer.
Pain radiates to left side torso. Angina pectoris can be stable or unstable. The first is different in that the attacks occur with the same physical activity. The pain syndrome is felt for less than 15 minutes. The attack disappears after taking 1 tablet of nitrates. Pain in unstable angina is longer.
Each subsequent attack is provoked by a smaller load. Often it occurs at rest. Signs of CAD include shortness of breath. Such patients feel short of breath. Often it occurs during an attack of angina pectoris. Its appearance is due to a decrease in heart function, stagnation of blood in the small circle and an increase in pressure in the pulmonary vessels.
The patient's breathing becomes deep and frequent. With angina pectoris, the heart rhythm is often disturbed. This is manifested by frequent or rare palpitations, dizziness and even loss of consciousness.
With angina pectoris, a person's behavior changes: he freezes, bends down, tries to take a relieving position. Often there is a fear of death.
Variant and rest angina
Classification of coronary artery disease highlights angina that occurs at rest. This form of cardiac ischemia is characterized by the occurrence pain attack regardless of physical activity. This is one of the varieties of unstable angina. This pathology occurs in acute, subacute and chronic forms. Often it develops 1-2 weeks after myocardial infarction myocardium.
 Causes of rest angina include atherosclerosis, narrowing of the aortic orifice, inflammation of the coronary arteries, hypertension, cardiomyopathy with left ventricular hypertrophy. This form of IHD is characterized by the appearance pain syndrome at rest, when a person is in a prone position. Often this happens during sleep. The attack lasts up to 15 minutes and is severe. This is different from exertional angina. The pain is eliminated after taking 2-3 tablets of nitrates.
Causes of rest angina include atherosclerosis, narrowing of the aortic orifice, inflammation of the coronary arteries, hypertension, cardiomyopathy with left ventricular hypertrophy. This form of IHD is characterized by the appearance pain syndrome at rest, when a person is in a prone position. Often this happens during sleep. The attack lasts up to 15 minutes and is severe. This is different from exertional angina. The pain is eliminated after taking 2-3 tablets of nitrates.
Many people lose value as they get older. pain symptoms in the region of the heart, considering them a natural manifestation of the aging of the body.
Meanwhile, these signs may indicate the development of coronary disease, which is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. How to recognize formidable symptoms? And most importantly, what causes heart disease?
Ischemic disease is called functional or organic changes in the heart muscle leading to restriction or complete cessation of blood flow to certain areas.
That is, the main manifestation of the disease can be called an imbalance of the actual blood flow and the heart's need for blood supply.
The heart muscle, more than other organs, suffers from a shortage of incoming blood. This is due to the isolation of the heart by the inner shell - the muscle does not receive oxygen from the pumped blood, but is supplied with blood through the coronary arteries. Their defeat or narrowing leads to the onset of the disease.
The main causes of coronary heart disease and the occurrence of its first signs:
- the development of atherosclerosis, narrowing the lumen of blood vessels due to cholesterol plaques;
- thrombosis of the feeding vessel;
- prolonged spasm caused by a violation of nervous regulation;
- defective functioning of the mechanisms that expand the arteries;
- metabolic changes.
What does the medical treatment of myocardial infarction include? Read about it in our next one.
From what arises
There are quite a few reasons that can cause the development of pathology:
- high levels of harmful lipids in the blood, which we get mainly from animal products;
- arterial hypertension ( upper indicator pressure from 140 can be called a harbinger of the disease);
- sedentary lifestyle;
- obesity, which significantly increases the load on the heart;
- diabetes mellitus (it has been proven that in patients with diabetes for more than ten years, coronary artery disease develops in most cases);
- smoking, leading to chronic vasoconstriction and oxygen deficiency in the blood;
- alcohol abuse;
- excessive physical activity;
- constant stress leading to increased pressure;
- increased blood clotting, provoking the formation of blood clots.
At-risk groups
In the development of coronary artery disease, factors play an important role, which we cannot change. To the group high risk the occurrence of ischemia can be attributed to those who meet the following characteristics:
![]()
- Male. Before reaching old age Men are significantly more likely to experience ischemia than women. This is explained high level estrogen in female body that resist atherosclerotic changes. After the onset of menopause, the difference in the incidence of the disease disappears.
- hereditary predisposition. It has long been known that diagnosing cases of ischemia in the family significantly increases the risk of developing pathology in other family members.
- Elderly age. In men, the critical age occurs after 55 years; women are characterized by a sharp increase in the number of cases after 65 years.
- Long-term use hormonal drugs . Contraceptives increase the risk of blood clots, so with long-term use, the frequency of thrombosis increases significantly.
Complications of IHD
Statistics show that even with a half-constricted heart vessel, a person may not feel signs of cardiac pathology. Chest pain can only appear during moments of increased physical exertion and quickly pass in a calm state.
Such weak severe symptoms and lack timely therapy can lead to the progression of the disease or its transition to an acute form:
- chronic heart failure;
- angina;
- Heart arythmy;
- myocardial necrosis;
- sudden death.
The prognosis largely depends on the severity of the disease - with myocardial infarction, mortality is much higher than with angina pectoris. In the same time it is not uncommon for a disease that did not bother a person to become sharply aggravated. Lethal outcome with a small lesion of the arteries of the heart is more than half of sudden deaths caused by coronary artery disease.
The ongoing therapy is also of great importance - regular intake of the drug prescribed by the doctor and compliance with other recommendations reduce the chances of an unfavorable outcome by half.
Ischemia prevention
Disease prevention can only be achieved integrated approach and major lifestyle changes. These preventive measures shown not only to those who have been diagnosed with ischemia, but also simply included in the risk group.
If you have several factors at once that can provoke the development of pathology, then prevention is a must for you:

- give up nicotine, which contributes to the formation of blood clots and plaques;
- reduce alcohol consumption;
- get rid of extra pounds that increase the load on all body systems;
- reduce the consumption of animal products, high in cholesterol;
- increase the intake of potassium and magnesium - minerals vital for the full functioning of the heart muscle;
- increase the physical activity necessary to strengthen the heart muscle;
- avoid stress that causes jumps blood pressure;
- you can resort to, but only with the permission of a doctor;
- be observed by a cardiologist to recognize deviations from the norm at the initial stage.
If you are diagnosed with coronary heart disease, do not forget that The diagnosis is not yet the final verdict. elimination adverse factors, causes and management of symptoms of coronary artery disease will help prevent dangerous consequences. Be examined by a specialist: after all, the sooner treatment is started, the better the result will be.
Ischemic heart disease is not in vain considered one of the most common and dangerous heart diseases. Unfortunately, it knows no boundaries, neither age, nor geographical, nor economic.
Ischemic heart disease can strike by surprise
Sometimes, instead of the term "coronary heart disease", the names "ischemia", "coronary disease" or "coronary sclerosis" are used, these terms were in the list of diseases of the WHO in the last century. But even now, in some sources, and in medical practice, there are these names of a disease that has different stages requiring various techniques treatment, and therefore bearing various names.
signs
Most often, ischemia signals its presence periodic attacks burning pains in the chest. The pain is severe, its character is oppressive.
Sometimes signs of coronary heart disease are complaints of patients about a feeling of general weakness, nausea and unpleasant feeling lack of air. Pain in this case can be localized between the shoulder blades, felt behind the sternum, in the neck or left arm.
Painful sensations are the first signs of this disease. You should listen carefully to your own well-being, and as soon as the slightest suspicion of heart problems is felt, it is better to immediately contact a cardiologist.
If before such reactions of the body did not occur, this is the first sign of the need for a cardiological examination.
Chest discomfort too alarm signal organism.
In some people suffering from this ailment, it manifests itself as pain in the back, left arm, mandible. Other symptoms of coronary heart disease include changes in heart rate, shortness of breath, heavy sweating, nausea.
If none of the listed signs of the disease is present, it is still sometimes important to be examined, albeit with a preventive purpose, because coronary heart disease in a third of patients does not manifest itself at all.
Causes
Clinically, ischemic heart disease (CHD) characterizes the pathological process chronic nature caused by insufficient blood supply to the myocardium, or heart muscle.
Violation of the blood supply to the myocardium occurs due to damage to the coronary arteries, and can be absolute or relative.
The reason for the lack of oxygen in the myocardium is the blockage of the coronary arteries, which can be caused by a thrombus formed, a temporary spasm of the coronary artery, or atherosclerotic plaques accumulated in the vessel. Sometimes the reason lies in their fatal combination. Violation of normal blood flow in the coronary arteries and causes myocardial ischemia.
Throughout life, each person to some extent has deposits of cholesterol and calcium, in the walls of the coronary vessels there is an overgrowth of connective tissue, which leads to a thickening of their inner membrane and a narrowing of the total lumen of the vessel.
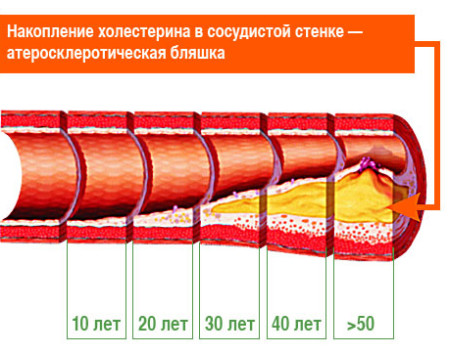
As you can see, the risk of the disease increases with age.
Narrowing of the coronary arteries, which leads to a partial limitation of the blood supply to the heart muscle, can cause angina attacks. These attacks most often occur with a sharp increase in the workload on the heart and its need for additional oxygen.
The occurrence of thrombosis of the coronary arteries is also caused by the narrowing of their lumen. The danger of coronary thrombosis is that it is the cause of myocardial infarction, leading to necrosis and further scarring of the affected area of the heart tissue.
In addition, it also leads to arrhythmia or heart block, in itself worst case dynamics of disease progression.
Classification
In accordance with the clinical manifestations, causes of occurrence and degree of progression, IHD has several clinical forms that occur in patients individually or in combination: angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, cardiosclerosis.
Currently, physicians use the modern classification of coronary heart disease, adopted in 1984 by the WHO with amendments and additions by the VKSC.
According to this classification, all the various features of the clinical manifestations of cardiac ischemia, as well as the corresponding prognosis and treatment methods, can be combined into the following groups:
- sudden coronary death, or primary cardiac arrest - according to the results of treatment, two groups of primary cardiac arrest are distinguished - with the practice of successful resuscitation or with a fatal outcome;
- angina pectoris, which in turn is subdivided into angina pectoris, unstable and vasospastic angina pectoris;
- myocardial infarction;
- postinfarction cardiosclerosis;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- heart failure.
In addition to this systematizing picture of the various manifestations of coronary artery disease, until recently there was another classification recommended by WHO experts in 1979.
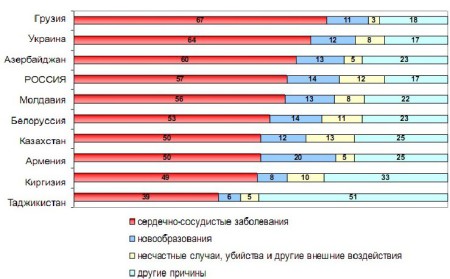
Death statistics
According to the then method of dividing coronary artery disease into classification groups, in the clinical form "angina pectoris" a subgroup "coronary syndrome X" was distinguished, unstable angina pectoris was considered in three different clinical manifestations. Also, such a picture of the disease as “painless form of coronary artery disease” was allocated to a separate diagnosed group.
Compliance with the classification of the disease when making a diagnosis is of paramount importance for the success of all further treatment patient.
It is unacceptable to formulate a diagnosis of coronary artery disease for a patient without subsequent decoding of the form, because in general view such a diagnosis does not at all clarify the real information about either the nature of the disease or the selection criteria best method treatment.
Correctly formulated diagnosis, in which the clinical form of the disease through the colon follows common diagnosis IHD is the first step to choosing a further course of treatment.
Acute and chronic forms
The course of cardiac ischemia is undulating, alternating periods of acute coronary insufficiency (coronary crises) that occur against the background of chronic, or relative, insufficiency. coronary circulation. Accordingly, acute and chronic forms of coronary artery disease are distinguished.
The acute form of IHD is manifested by ischemic myocardial dystrophy and myocardial infarction. Often, ischemic myocardial dystrophy leads to acute heart failure, a complication that often becomes direct cause sudden death.
![]()
myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction is the necrosis of the heart muscle caused by coronary artery disease. As a rule, this ischemic infarction with hemorrhagic corolla.
In the systematization of IHD, the forms that characterize chronic coronary heart disease are diffuse small-focal cardiosclerosis or large-focal post-infarction. The latter in some cases is complicated by chronic aneurysm of the heart.
Both acute ischemic heart disease and chronic form This disease can cause irreparable damage to the health and life of the patient.
The impact of bad habits
According to WHO statistics, among various reasons occurrence of coronary artery disease and other cardiovascular diseases, there are most often leading to the development of cardiac pathologies.
Risk factors for CAD include:
- increased blood cholesterol, or hypercholesterolemia;
- violations carbohydrate metabolism, especially diabetes mellitus;
- arterial hypertension;
- prolonged use of alcohol;
- smoking;
- obesity;
- physical inactivity against the background of stress instability;
- individual characteristics of behavior.
As can be seen from the listed reasons leading to the occurrence of coronary artery disease, this disease often has whole line reasons, being complex. Therefore, measures for its prevention and treatment should also be comprehensive. Patients suffering from ischemia of the heart, you must first get rid of bad habits.
Smoking
One of the habits that most often lead to coronary atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction is smoking. Long-term smoking has a narrowing effect on the coronary vessels, and also leads to increased blood clotting and slowing of blood flow.
smoking is poison
Another reason harmful effects nicotine on the heart is that nicotine causes an increased flow of adrenaline and norepinephrine into the blood, substances that large quantities are released during emotional and physical overload, or stress.
Their excessive concentration leads to insufficiency of the coronary circulation due to an increase in the demand of the heart muscle for oxygen. Adrenaline and norepinephrine also have a damaging effect on inner surface vessels.
Newly established similarity negative impact on cordially- vascular system prolonged negative emotions and nicotine proves how erroneous is the habit of many smokers to drag on another cigarette to calm down.
Alcohol
It is the second most destructive bad habit for patients diagnosed with CAD. According to statistical medical data, among men, about a third of patients with myocardial infarction abuse alcohol. Drinking alcohol often causes an attack of angina pectoris.
A feature of coronary artery lesions in alcohol-dependent patients is a high degree of development of the disease process. Among non-alcoholic patients of the same age, this process is much less associated with pain.
The insidiousness of alcohol is that immediately after taking it, a slight narcotic effect occurs, the disappearance pain and the appearance of a false impression of the vasodilating effect of alcohol on the heart. Very soon, however, there is a rapid vasospasm, an increase in blood viscosity leads to impaired blood flow.
Therefore, in the stage of intoxication of patients, there are so many heart attacks and brain attacks that are very difficult to stop, especially if you take into account wrong action cardiac glycosides against the background of the presence of alcohol in the blood.
Obesity
Obesity is another scourge that whips up the heart muscle. It renders Negative influence on the cardiovascular system by directly affecting the heart muscle (muscle obesity), as well as setting in motion complex mechanism nervous and hormonal effects.
Hypodynamia
Physical inactivity is now recognized as one of the most influential factors triggering the occurrence of coronary heart disease.

Passive lifestyle - Right way to coronary artery disease
A sedentary lifestyle is a serious reason for the development of atherosclerosis, thrombosis and other disorders. normal functioning of cardio-vascular system.
A global problem
The dynamics of the cure of patients with coronary artery disease is largely determined by the timeliness and quality of diagnosis of the clinical form of the disease, the adequacy of the prescribed outpatient treatment, as well as the timeliness of urgent hospitalization and emergency cardiac surgery.
Sad European statistics claim that coronary artery disease, together with a stroke of the brain, make up a catastrophic majority, namely 90% of all diseases of the cardiovascular system.
This indicates that ischemic heart disease is one of the most frequent illnesses, as well as the most common causes of death of modern man.
It often leads to long-term and permanent disability of the active population, even in the most developed countries of the world. All this characterizes the problem of finding more effective methods treatment of coronary artery disease as one of the leading tasks among the first medical problems XXI century.
Signs of coronary heart disease
In this article, we will look at the main signs of coronary artery disease in adults.
Symptoms
To the main clinical forms ischemic heart disease include: angina pectoris (the most common initial form), acute myocardial infarction. cardiac arrhythmias, heart failure. as well as sudden coronary cardiac arrest. Everything above listed stages coronary artery disease differ from each other in their severity and the presence of secondary complications.
The main signs of coronary artery disease, which should alert the patient and force him to consult a doctor for medical help, are: frequent shortness of breath, weakness, periodic pain V chest, vertigo, sweating. These symptoms occur in more than 80% of all initial stages development of ischemic disease.
In most cases, patients report a significant deterioration general well-being as a result of increased physical stress on the body, which aggravates the course of the disease.
As coronary artery disease progresses, there may be a significant aggravation of the resulting angina attacks, which indicates a fairly rapid deterioration of the underlying disease.
It should also be noted that in Lately there is a fairly large number of cases of the development of painless forms of coronary artery disease, which are quite difficult to identify in the early stages of development, and which are much less treatable. Therefore, it is very important at the slightest disturbance of the heart to consult a cardiologist in a timely manner to prevent the development of undesirable consequences.
angina pectoris is early and initial sign ischemic heart disease, which is manifested by periodic pain in the region of the heart, chest, extending under the left arm, shoulder blade, in the jaw. The pain may be accompanied by tingling, squeezing, be quite pressing, and generally last no more than 10-15 minutes. then remissions are possible again.
Angina pectoris or, as the people say, "angina pectoris" can be of 2 types: tension and calm. The first occurs under the influence of physical stress on the body, can develop as a result of stress or psychoemotional disorders. Rest angina mostly occurs without cause, in some cases an attack can occur during sleep.
Both types of angina pectoris are very well removed by taking 1-2 tons of nitroglycerin under the tongue with a minimum interval between doses of at least 10 minutes.
Remember: this species ibs requires mandatory consultation a cardiologist with a cardiogram of the heart and the appointment of an appropriate treatment, so as not to provoke further progression of the disease and its possible transition to a more severe, life-threatening stage for the patient.
Advanced myocardial infarction is very serious complication ischemic disease requiring emergency medical care. The main signs of a heart attack are severe, pressing and compressive pain in the region of the heart, which is not relieved by nitroglycerin preparations. In addition, a heart attack may be accompanied by shortness of breath, weakness, nausea, or vomiting, mostly yellowish in color.
The attack causes a feeling of fear, anxiety, general weakness, dizziness, in the area of \u200b\u200bthe heart there may be a strong contraction, tingling.
In some cases, a feeling of severe pain can cause the patient sudden loss consciousness.
Therefore, in cases of acute myocardial infarction, the patient should be immediately admitted to the hospital in order to avoid lethal outcome, and prevent possible development unwanted complications.
Chronic heart failure is one of the main signs of coronary heart disease, which is manifested by constant shortness of breath, the patient complains that he does not have enough air, he begins to periodically suffocate, the upper and lower tissue covers of the body become cyanotic, as a result acute violation blood circulation, local stagnation of blood occurs, the patient's chest becomes barrel-shaped.
With all the data, the above signs of coronary artery disease, it is necessary to go to the hospital as soon as possible with a cardiologist in order to timely diagnose the disease, since coronary heart disease development at its first stage, it is possible to stop at least a little in its further progression.
Sudden cardiac arrest(coronary death) is a formidable complication of acute myocardial infarction, as a result of not timely provision emergency medical care for him. It is manifested by a sharp cessation of cardiac activity with a stop to the further functioning of all vital - important organs and systems.
If in the next 2-3 minutes. the patient will not be provided with urgent resuscitation, then after 4-6 minutes. irreversible processes occur in the cerebral cortex and central nervous system, which leads to complete biological death.
Attention: early diagnosis of the disease early stage its development will allow you to carry out a fairly effective treatment, as well as prevent further development unwanted complications.
Diagnostics
- examination of the patient by a doctor, patient complaints of pain in the chest area;
- obligatory electrocardiogram of the heart;
- coronary angiography (makes it possible to determine the state of the coronary arteries of the heart, as well as to identify the presence of pathological changes in them);
- computed tomography of the chest cavity;
- angiography of the main arteries of the heart.
In this article, we found out the main signs of coronary heart disease.
Manifestations of coronary heart disease
The word heart attack means the necrosis of a part of the tissue of any organ due to a violation of the patency of the vessel that feeds this tissue. In addition to myocardial (heart) infarction, there are lung infarcts, kidneys, spleen and other organs. All of them arise in cases where one of the relatively large arteries supplying this body blood, and a part of the tissue that received oxygen and all the substances necessary for its vital activity from this artery undergoes dystrophy and dies. Due to morphological and functional features the heart muscle and the arteries supplying it, the frequency of myocardial infarction is incomparably higher than the frequency of lesions of this kind of other organs. At the site of the formed myocardial infarction (Fig. 4), cicatricial connective tissue, which is functionally unequal to the heart muscle. In this regard, if the myocardial infarction is large in area, heart weakness and other complications occur, leading to adverse consequences.
Man with absolutely healthy heart may suffer from a myocardial infarction due to damage to one of the coronary arteries that feed the heart.
So, myocardial infarction is a catastrophe caused by complete or partial blockage of the coronary artery. When the lumen of the vessel is partially closed, the possibility of infarction will be determined by how large the discrepancy between the needs of the myocardium in
oxygen (which depends on the intensity of the work of the heart) and the actual supply of the heart muscle with arterial blood.
With complete blockage of the coronary artery, energy-rich phosphorus compounds - ATP and CF - are quickly consumed in the heart muscle. This leads to the fact that the part of the heart muscle, the supply of which has stopped due to arterial patency, through a short time stops shrinking and muscle cells in this place without recovery of ATP and CF
soon die. As a result of the cessation of contractions of a relatively large part of the left ventricle, cardiac weakness (failure) develops, which sharply aggravates the condition of a sick person.
In most cases, the lumen of the coronary artery narrows gradually as a result of the formation of one or more atherosclerotic plaques in one of the sections of the vessel, which we will discuss in more detail below. Sometimes the plaque itself is small, but a blood clot forms on its rough or ulcerated surface, which completely or partially closes the lumen of the artery. An increase in blood pressure contributes to an additional narrowing of the artery at the location of the atherosclerotic plaque. With excessive physical stress even a small plaque can be an obstacle to a sharply increasing blood flow through the coronary arteries and cause the development of myocardial infarction. It is very likely that known to us from history Ancient Greece the episode of the messenger from Marathon, who ran 42 km to Athens and fell dead, provides such an example.
Close to a heart attack is another manifestation of atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries - angina pectoris, characterized by pain in the region of the heart, behind the sternum, often radiating to the left arm or shoulder blade. Just like myocardial infarction, angina is the result of insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle (ischemia).
By the proposal World Organization Healthcare approved the term "coronary heart disease", which refers to all conditions accompanied by insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle.
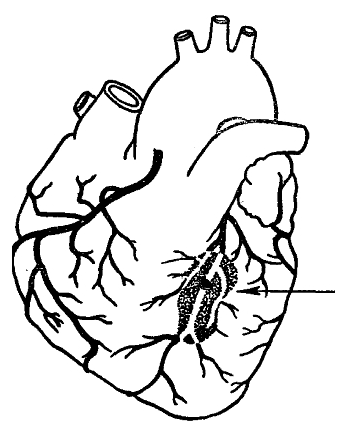
Rice. 4. Myocardial infarction, which developed as a result of blockage of one of the branches of the left coronary artery (indicated by an arrow)
Thus, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, very often various violations rhythmic work of the heart (arrhythmias), as well as cases of sudden death (see below) are manifestations of the same disease - coronary heart disease (CHD).
In coronary artery disease, the supply of oxygen to the heart muscle lags behind the actual need for oxygen, while normally, the supply of oxygen to the myocardium exceeds the need for it. As a result of myocardial ischemia, signs characteristic of IHD appear (Fig. 5).
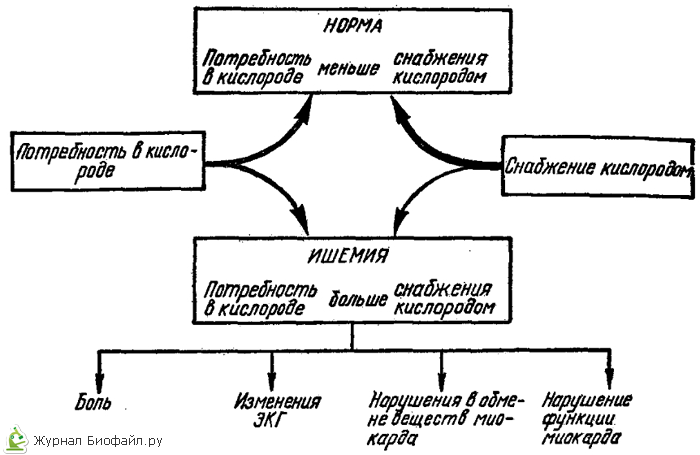
Rice. 5. Scheme of the occurrence of myocardial ischemia and some of its manifestations
Of course, there are many different forms of myocardial infarction and angina pectoris. Sometimes it is difficult to draw a clear clinical line between a prolonged attack of angina pectoris and a non-severe myocardial infarction. Some patients suffer from angina pectoris for many years without causing severe consequences. However, more often angina pectoris serves as a prelude to myocardial infarction or eventually leads to cardiac weakness or irregular work of the heart.
There are many cases when a myocardial infarction is preceded by only a few attacks of angina pectoris, to which a person did not attach any importance and did not consider it necessary to consult a doctor.
In close connection with the problem of finding out the causes of myocardial infarction, there is the problem of studying the causes of the so-called sudden death that occurs a few hours after the first manifestations of the disease (in a practically healthy person). The basis of sudden death, as a rule, is a rapidly occurring coronary insufficiency due to a sharp and prolonged spasm of one of the coronary arteries or acutely developed macrofocal infarction myocardium. And the immediate cause of death is deep heart rhythm disturbances: instead of ordered effective contractions of the heart muscle, chaotic twitches of individual muscle bundles begin, the so-called ventricular fibrillation, or cardiac asystole, develops, effective work heart stops. Similar state if it drags on for a few minutes, it becomes incompatible with life.
In order to seek help in a timely manner and develop the correct line of one's behavior, it is important to know well how IHD manifests itself.
Signs of angina pectoris and myocardial infarction. First classic description attack " angina pectoris”(as angina pectoris is called) was made by V. Heberden in 1768 at a lecture at the Royal College of Therapeutics in London.
During an attack of angina pectoris, a person has a feeling of pressure, heaviness, mixed with a feeling dull pain in the central part of the chest, behind the sternum, sometimes somewhere deep in the throat. Some people have relatively strong pain accompanied by fear, weakness, the appearance of cold sweat, but after 2-3 minutes the pain disappears and the person feels healthy again. In other people, this is not pain, but a kind of burning sensation, pressure behind the sternum or in the neck. (Fig. 6)
Usually these short-term attacks occur in the morning when a person is in a hurry to work, especially in cold windy weather This is a typical exertional angina
Often, angina attacks develop after a hearty meal, during physical exertion, or shortly after a big meal. emotional tension, negative mental influences or other unrest.
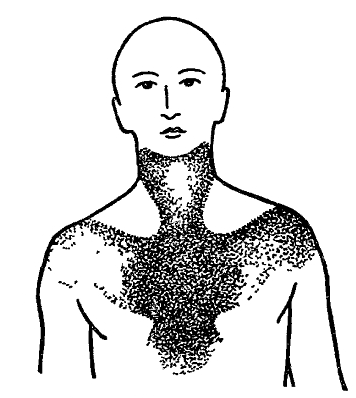
Figure 6. The area of distribution of pain in angina pectoris
With rest angina, often occurring at night or early in the morning, when the patient is at rest, a large role is played by the factor of vascular spasm (one of the sections of the coronary artery). As a rule, such spasms occur in patients arterial hypertension or with atherosclerotic coronary arteries.
IN last years the term "unstable angina" has become widespread. It is opposed to the definition of "stable angina", which is understood as a condition characterized by bouts of short-term retrosternal pain habitual to the patient, which occur when certain situations(fast walking against the wind, especially after eating, during unrest, etc.). sick stable angina systematic treatment should be carried out. There are no indications for his urgent hospitalization. Another thing is if angina pectoris appeared for the first time in life or its attacks became more frequent, if, along with angina pectoris, angina pectoris appeared at rest, attacks began to be worse removed by nitroglycerin, became sharper or longer. This type of angina is called unstable. Patients with unstable angina pectoris should be taken under special supervision, sharply limit their physical and emotional stress, monitor their ECG, strengthen treatment vasodilators. In most cases, such patients need to be hospitalized for intensive monitoring of them and active treatment. Attacks of unstable angina are also harbingers of myocardial infarction.
As already noted, it is not always easy to define a clear line between angina pectoris and myocardial infarction. Sometimes patients endure non-severe myocardial infarction "on their feet", without medical care. However, for myocardial infarction initial period more typically violent and severe course. Acute myocardial infarction most often occurs as an attack of sharp, piercing, lingering pain or as a very painful feeling of squeezing the chest, as if someone is squeezing it in a vise. The patient is frightened, restless, he has difficulty breathing, he rushes about the room, not finding a place for himself. Excitation is replaced by weakness, cold sweat, especially if the pain lasts more than 1-2 hours.
During such an attack, nitroglycerin, which previously relieved the condition, almost does not reduce pain or has only a short-term effect. In the midst of pain, the patient becomes pale, his pulse is weak and frequent, the rise in blood pressure is replaced by its fall. This is the most dangerous period illness. Immediate medical intervention is required. Only by administering special medicines to an emergency doctor or emergency care it is possible to cope with an attack, and sometimes it is necessary to urgently hospitalize the patient.
If a person has a first attack of angina or develops an attack of chest pain accompanied by weakness, cold sweat, nausea and vomiting, dizziness, or short-term loss consciousness, it is extremely important to immediately call a doctor. Only a doctor is able to assess the characteristics of certain manifestations of the disease and prescribe additional research, according to the results of which it is possible to put accurate diagnosis decide on the need for hospitalization and recommend the correct treatment.
All patients who are suspected of having a myocardial infarction should be in a hospital where it is possible thorough examination, observation and ‘intensive treatment. In specialized departments there are wards where especially seriously ill patients are sent to establish for them constant electrocardiographic monitoring, enhanced monitoring of medical and secondary medical personnel and, as a result, to timely recognize and treat such complications of myocardial infarction, which 10-15 years ago were considered incompatible with life.
In some patients, myocardial infarction develops suddenly, almost without any precursors, among the apparent full health. However, if such “healthy” people are examined before myocardial infarction, then the vast majority of them can detect certain signs of atherosclerosis of the heart vessels or metabolic disorders that developed long before the heart attack.
Establishing a diagnosis of myocardial infarction is sometimes difficult. An electrocardiogram, the results of a study of cellular and biochemical composition blood and data from other auxiliary diagnostic methods.
In many countries of the world, preventive examination of the population to detect latent IBO and underlying atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries. But so far, such inspections are not widespread. To prove that active prevention of myocardial infarction is necessary, we will provide some information about the spread of coronary artery disease and some of its complications.
Prevalence of coronary heart disease
It cannot be assumed that atherosclerosis did not occur in old times. Thus, atherosclerotic vascular lesions were found in Egyptian mummies. In the surviving ancient manuscripts of the Egyptians, in the Bible, heart pains are described, similar to those of angina pectoris. Hippocrates mentioned cases of blockage of blood vessels. The descriptions of the narrowed, tortuous sections of the vessels that Leonardo da Vinci left are interesting. He also noted that such changes are most often manifested in older people and suggested that they adversely affect the nutrition of tissues.
Since the 18th century, Italian anatomists began to describe cases of myocardial rupture in the dead, who during their lifetime suffered from pain in the heart. Correspondence of English scientists W. Heberden and E. Jenner (70s of the XVIII century) is known, in which E. Jenner gave examples of blockage of the coronary arteries in patients who died from an attack of angina pectoris (angina pectoris).
Russian doctors V.P. Obraztsov and N.D. Strazhesko in 1909 created contemporary performance O clinical picture and the nature of acute coronary heart disease. The doctrine of coronary disease began to develop especially rapidly with the introduction of clinical researches method of electrocardiography (ECG). In 1920, X. Purdy demonstrated ECG changes characteristic of myocardial infarction. Since 1928, the ECG method has been widely used in advanced cardiology clinics around the world. In our time, an electrocardiological study in 12-15 leads has become an integral method for diagnosing heart disease, not only in hospitals, but also outpatient settings. According to the results of an ECG examination of people during physical activity it is often possible to reveal hidden coronary disorders. Others are improving subtle methods diagnosis of myocardial infarction according to the determination of the activity of certain blood serum enzymes, for example, creatine phosphokinase, etc.
Thus, it is safe to say that myocardial infarction did not appear in the 20th century. However, there are a number of reasons why widespread this disease in our time.
Many do not realize the danger sharp increase cases of myocardial infarction and angina pectoris, as human psychology is rebuilt gradually. Meanwhile, there are indisputable statistics showing that myocardial infarction and other "coronary catastrophes" have become main reason death of the population of most of the most economically developed countries.
World Health Organization experts concluded that in the 70s of the XX century, mortality from cardiovascular diseases among men over 35 worldwide increased by 60%. At an international symposium in Vienna in 1979, it was reported that. out of 2 million deaths, annually registered in the United States, more than half are due to cardiovascular diseases, including more than a third is accounted for by coronary artery disease. In the US, about 650,000 people die from coronary artery disease every year.
The mortality rates of the population from cardiovascular diseases, including coronary artery disease, for a number of countries are shown in Fig. 7.
In general, in highly developed countries, out of ten people over 40 years old, five die from cardiovascular diseases. In Germany, about 250 thousand cases of myocardial infarction are registered annually, and the number of deaths from this disease from 1952 to 1974 increased by 5 times. In the Soviet Union, 514.4 thousand people died from atherosclerotic heart disease in 1976, in 1977 - 529.9 thousand people. According to the Central statistical office In the USSR in 1981, mortality from cardiovascular diseases in the country stabilized, and in some Union republics there was a tendency to decrease it.
Rice. 7. Mortality of men aged 35-74 from various diseases per 100 thousand inhabitants in different countries
A population survey of large groups of residents of the largest cities of our country - Moscow, Leningrad and Kyiv - was carried out in order to identify the prevalence of coronary artery disease among them and the factors contributing to its development. As expected, there was a regular increase in the prevalence of coronary artery disease with an increase in the age of the examined. So, among men of the city of Leningrad at the age of 20-29 years, the prevalence of coronary artery disease is less than 1%, 30-39 years - 5%, 40-49 years - 9%, 50-59 years - 18% and at the age of 60-69 years - 28 %. In general, it can be said that every sixth man aged 50-59 and every fourth man aged 60-69 are mountains. Leningrad suffer from coronary artery disease. Among women, the prevalence of coronary artery disease was about the same as among men, but severe forms IHD was less common in them. According to the medical statistics of many countries, women in the premenopausal period get myocardial infarction incomparably less often than men. Therefore, the main attention was paid to the prevention of this disease among the male part of the population, although, as the results of population studies carried out during the USSR, it is necessary to carry out appropriate preventive measures among women.
It has already been noted above that coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction arise on the basis of atherosclerotic lesions of the coronary arteries of the heart. Modern medical literature is full of descriptions of the so-called CHD risk factors that contribute to the onset and progression of this disease. But first of all, we will try to tell you what atherosclerosis is and what its essence is.

