Uterine blood flow during pregnancy is increased. Violation of the uteroplacental blood flow during pregnancy
In the process of gestation, the mother's body is closely connected with the fetus through placental structures that provide a full fruitful development, and also carry out the delivery of nutrition and oxygen, produce hormonal components and remove metabolic products. In general, the placenta is responsible for everything critical processes during the gestation period. Sometimes, for various reasons, a woman develops a violation of blood flow during pregnancy. Such conditions are incredibly dangerous for gestation, they can provoke fetal pathologies and complications of gestation.
Scheduled ultrasound allows you to recognize any deviations in time
During gestation, a close relationship is established between the child and the mother, which is also called the fetoplacental system. It consists of several departments.
- The central role is given to the placenta, which grows with villi into the uterine wall and through them nourishes the fetus in the uterus. essential substances. Moreover, maternal blood does not mix with fetal blood, since there is a hematoplacental barrier through which the blood is filtered, returning back to the woman.
- Part of the fetoplacental system is and arterial network uterine body. Before conception, these arteries are spasmodic and twisted in the form of a spiral, but already from the first month of pregnancy muscle layer, providing a spasmodic state, resolves, and by the fourth month of gestation, the arteries are transformed into special trunks that carry blood to the placental structures, fully participating in the blood supply. A similar phenomenon was specially provided by nature for the best intrauterine nutrition of the child. If they start uterine bleeding, then vascular walls will no longer be able to contract, which is fraught with profuse blood loss, up to and including death.
- Another part of the blood supply system between the mother and the fetus is the umbilical vessels, which form another blood supply pathway. A vein and two arterial channels pass through the umbilical cord, which connect the fetus to the placenta. If blood flow disturbances occur in this part, then the fetus is subjected to severe lesions.
Causes of violation of the blood flow of the uterus
Fetoplacental insufficiency can provoke various reasons. The main thing is that such a state pathologically affects such placental functions as metabolic and trophic, endocrine, transport, etc. In such states, the material exchange processes between the fetal and maternal organisms are seriously disrupted, which leads to serious consequences.

If you have diabetes, check your blood sugar levels regularly
Intrauterine infectious lesions, pneumonia or fetal hypoxia, hypertensive disorders, etc. Also, normal blood supply is disturbed in pathologies such as asthma, cardiac pathological conditions type of low blood pressure, malformations, etc. Often the causes pathological disorders blood circulation is caused by neuroendocrine ailments such as hyperthyroidism or diabetes, hypothyroidism, as well as hypothalamic or adrenal pathologies. Provoke circulatory disorders, kidney failure or pyelonephritis.
Also, problems with blood supply can be caused by anemia or thrombosis, which is actually the norm for similar pathologies. Quite often, women suffer from exacerbations different kind infectious pathologies which also lead to placental changes. Various infectious agents cause inflammatory lesions, which in the first weeks of gestation can cause spontaneous interruption, and on later dates various deviations in fetal intrauterine development. No less dangerous are various uterine pathologies such as fibroids, endometriosis, hypoplasia or malformations, as well as pathological changes in the myometrial layer.
At the risk of encountering blood flow disorders are mothers after 35, pregnant women for the first time and having large fibroids. Also, placental or breech presentation, gestosis and multiple gestation, the presence of Rhesus conflict, abortions in the past and a tendency to unhealthy habits, social dissatisfaction and other factors.
Varieties of fetoplacental insufficiency
First of all, placental insufficiency is classified into chronic and acute forms. An acute pathology can occur at any time and even during delivery. AT placental tissues meanwhile, there is a violation of gas exchange, leading to acute fetal hypoxia or the death of the baby. Often similar phenomenon occurs against the background of premature placental infarction or detachment, bleeding or vascular thrombosis.
Chronic forms of placental insufficiency are diagnosed much more often and occur mainly during the second trimester of gestation, although they are found only in the third trimester. On the surface of the villi that grow into the uterine wall, fibrin begins to be deposited, which interferes with the normal course of material exchange processes. As a result, premature placental aging begins.
Chronic insufficiency of fetoplacental blood supply is divided into the following varieties:
- Critical. With this form, serious functional and morphological changes, which cannot be influenced in any way, so fetal death becomes inevitable.
- Subcompensated insufficiency. With such a violation, the female body cannot cope with violations of placental activity, therefore, fetal development is delayed, which leads to complications during gestation and fetal development.
- Decompensated - when compensation mechanisms lose their ability to deal with pathological placental changes, therefore, the norm of indicators during the development of pregnancy is violated, the fetus begins to suffer from hypoxia, cardiac disorders, developmental delays, etc. There is a high probability of intrauterine fetal death.
- Compensated insufficiency is considered the most favorable of all of the above, since the fetus continues to develop without suffering from various abnormalities. female body with such insufficiency, he is able to adapt and compensate for the deviations that have occurred to the child. If a woman gets proper treatment, then such deviations will not affect the health of the baby and the timing of delivery.
Degrees of hemodynamic abnormalities

Breathing exercises are useful for the expectant mother and baby
In addition to the types of disorders described above, there are various fetoplacental degrees during pregnancy. At elementary degrees pathological abnormalities, the fetus is in normal condition, blood flow deviations are not dangerous and affect only the uteroplacental sphere. It is important to detect such violations in a timely manner, if the patient does not receive necessary assistance, then within a month pathological abnormalities aggravated, moving to a more serious degree.
Blood flow disorders of the 1st degree are conventionally divided into two types: deviations of the 1A degree and 1B. In the latter case, the blood flow between the placenta and uterine tissues is normal, but there are deviations in the placental-fetal circulation. In about 80% of cases, the fetus with such disorders develops developmental delay. Deviations of the blood flow of the 1A degree are characterized by disturbances between the placental and uterine circulation, while in the placental-fetal blood flow the norm of indicators is observed. About 90% of cases such violations accompanied by a developmental delay.
In the second degree of pathology, there are serious violations in the bloodstream of the fetal vessels and the uterine body. This stage is usually short-lived, takes about a week and quickly moves on to the next stage of disorders. The third degree of hemodynamic disturbances is characterized by critical disturbances in the fetal blood supply or its complete absence. You can try to cure only the pathology of stage 1B, in other cases, the deviations are irreversible and often require premature birth.
Signs of pathology
The clinical picture of blood flow disorders is determined by their severity. Compensated disorders usually proceed latently and are detected only when ultrasound diagnostics. Decompensated and sharp forms placental insufficiency is usually accompanied by changes motor activity fetus, which is either minimized or becomes overly pronounced. Normally, the fetus should move at least ten times a day.
Sometimes such deviations are accompanied by insufficient growth of the tummy of a pregnant woman, polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios, severe preeclampsia or hyperedema, a sharp weight gain or pressure surges, the appearance of protein compounds in urine. Most dangerous manifestation insufficiency placental circulation uterine bleeding is considered, which usually occurs against the background of placental abruption. In such a situation meaningful help a woman can only get from specialists, so you need to call an ambulance.
What is the danger of a blood flow disorder
During gestation, problems with blood flow are dangerous, because even a slight violation of blood circulation reduces the amount of nutrition and oxygen supplied to the fetus. With prolonged fasting of this kind, complications are likely to develop, such as:

When identifying initial stage there are no particularly dangerous risks for the baby; with age, the child will catch up with the development of his peers. When more than heavy degrees violations of the forecasts are unfavorable, such pregnancies usually end in a frozen fetus or the appearance of a child with various anomalies, inferiority and other ailments.
Diagnosis of violations
If the development of placental blood flow disorders is suspected, the patient is comprehensive examination. The leading role in the diagnosis is given to dopplerometry in combination with ultrasound examination. Such techniques allow timely detection of pathological blood flow disorders and determine the degree of complications caused by them. Usually dopplerometry is prescribed for premature placental aging, deficiency or excess content amniotic fluid, congenital genetic pathologies or fetal defects, with hypoxic manifestations or intrauterine retention fruitful development.
How to normalize the blood supply in the uterus
The first stage of blood flow fetoplacental abnormalities responds most positively to treatment. In the second degree, therapy is practically ineffective, and in the third, emergency delivery through surgical intervention. In the process of therapy, it is necessary to influence all parts of the blood flow structures. With minor microcirculation disorders, to improve blood flow, patients are shown taking Hofitol, which belongs to the category homeopathic remedies. If the treatment does not provide the desired effect, then resort to medications such as Actovegin or Pentoksifarm.
To expand the vascular passages, No-Shpa or Drotaverine is used, and for thrombophlebitis, Curantyl is indicated. Improves blood flow and reduces the tone of the uterine muscles Magnesium B6 and magnesium infusion. And with an antioxidant purpose, reception is indicated ascorbic acid and vitamin E.
In order not to treat blood flow disorders or their consequences, it is necessary to take preventive measures in advance to prevent these conditions. Mom should eliminate all risk factors that provoke the development of placental insufficiency. Mommy needs to control body weight, spend more time on fresh air and complete all planned procedures on time, diagnostic studies, laboratory tests and gynecological examinations. This is the only way to detect deviations in time and prevent their further development.
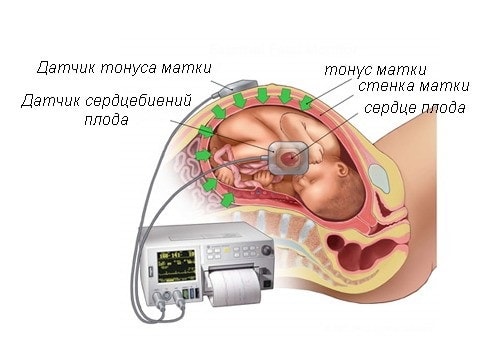
During pregnancy it is very important to constant surveillance for the state of the organisms of the mother and fetus and their performance of vital functions. One of the most significant research is an analysis of blood flow in the arteries of the uterus, the umbilical cord of a woman, as well as in the aorta and cerebral vessels child.
Among the main causes of perinatal mortality and morbidity is not the last place is the violation uterine blood flow(uteroplacental and fetal-placental).
Blood flow in the placenta
The placenta, in which the fetus is located, supplies it with nutrition and oxygen from the mother's blood and removes metabolic products. child's body. It is this organ that unites two complex vascular systems - the maternal, which connects the vessels of the uterus and the placenta, and the fetal, passing into the umbilical arteries and leading to the fetus.
The above circulatory systems separated by a membrane that prevents the mother's and baby's blood from mixing. The placenta acts as a kind of barrier that is resistant to many viruses and harmful substances.
In some cases, completely different reasons placental insufficiency may develop, which inevitably affects the performance of trophic, metabolic, transport, endocrine and other vital functions of the placenta. In this condition, the metabolism between the body of the mother and the child deteriorates significantly, which is fraught with consequences.
Causes of impaired uterine blood flow
Circulatory disorders in the uterus can be caused by increased pressure, pneumonia, intrauterine infection and insufficient supply of the fetus with oxygen ().
For diagnosing the circulatory system in obstetric practice applied three-dimensional ultrasound procedure(Doppler), with which the vessels are visible in the so-called 3D (three-dimensional) image. With this modern diagnostic method there was a prospect to diagnose retroplacental bleeding, to evaluate malformations of the heart by monitoring the blood flow. This method is indispensable, since with its help you can see defects even in the smallest vessels that form the microvasculature, monitor the development and formation of intraplacental hemodynamics, and also control the amount of oxygen and nutrients that must be ingested by the fetus. Opened up new opportunities for early detection obstetric complications, and if the correction or treatment is started without loss of time, then it is possible to practically avoid circulatory disorders and further pathologies associated with it.
Hemodynamic disorders during pregnancy
Hemodynamic disorders are divided into three degrees of severity:
First degree includes two subtypes:
- 1A - violation of uteroplacental blood flow, which is the easiest. The fetal-placental circulation is preserved with it. In most cases, intrauterine infection leads to this problem;
- 1B - uteroplacental blood flow is preserved, while pathologies occur in the fetal-placental one.
Second degree It is characterized by violations of both blood flow systems, while it does not carry cardinal changes.
Third degree is that a violation of the uteroplacental circulation leads to defects in the blood circulation at the uterine-fetal level.
With the first degree of violations, due to the timely detection and adequate treatment of cases of fetal death, it is possible to avoid. Perinatal mortality in the second degree is 13.3%, in the third - 46.7%. At the time, it was found that the correction of placental insufficiency in patients with hemodynamic impairment of the third degree was ineffective. In this case, perinatal mortality in conservative childbirth was 50%, while it helps to avoid losses. To the ward intensive care 35.5% of newborns fall with the first degree, 45.5% with the second and 88.2% with the third.
Prevention of blood flow disorders during pregnancy
Every woman who wants to give birth to a child must remember that the state of the mother is completely transmitted to the unborn baby. Therefore, in order for the fetus to develop without complications, she needs to make up her diet from food containing a maximum of vitamins, micro- and macroelements, as well as rich necessary quantity carbohydrates, proteins and fats. If the pregnant woman is not concerned about swelling, then fluid intake should be at least 1-1.5 liters.
It is important to control changes in body weight, since by the end of pregnancy, weight gain should not exceed 10 kg.
There are risk groups that need to be applied drug prevention, which promotes the interaction of the body systems of the fetus and mother and prevents dysfunction of the uteroplacental circulation.
Significantly reduce perinatal morbidity and mortality will help timely corrected methods of conducting childbirth and drug therapy. But high risk appearance of severe neurological complications still not excluded.
Specially for Elena Zhirko
After a woman finds out about her pregnancy, she must realize that now the body belongs not only to her, but also to her unborn child. Hormonal surges and a complete restructuring of the pelvic organs quite often end with a violation in the blood supply to the fetus. In this article, we will talk about impaired blood flow during pregnancy, what it is fraught with, what symptoms are inherent, what therapy can be used, and how to bear a healthy child.
How blood flow changes during pregnancy
Initially, let's figure out how everything works in mothers' tummies. During pregnancy for the transfer beneficial trace elements and oxygen to the baby is the placenta. It is the same unifier through which the vascular system of the pregnant woman is connected to vascular system fruit, becoming common. Any disturbances in the work of the placenta affect the condition of the baby, so it is necessary to monitor the blood flow during pregnancy. Diagnosis is made through a study - dopplerometry. About it, below we will talk in more detail.
What is blood flow disorder during pregnancy
Violation of blood flow can appear at any gestation period. A pregnant woman is diagnosed with placental insufficiency. This is one of the most common complications during pregnancy associated with dysfunction of the placenta. This pathology occurs in two forms:
- The acute form appears suddenly and is most often the result of placental abruption. May cause disruption of gas exchange this body and as a result, oxygen starvation in the fetus.
- Chronic, also called premature aging placenta. Most often detected in the third trimester of pregnancy. It is divided into the following types:
- compensated - is considered minimally dangerous, since with this form the child continues normal physiological development. In the mother's body "turn on" defense mechanisms that compensate for impaired blood flow;
- decompensated - the mother's body can not cope with the problem, there are pathological changes in the placenta. The first oxygen starvation fetus, entailing developmental delays, intrauterine death of the baby is possible;
- subcompensated - with this form, the condition of the fetus worsens, it lags far behind in development;
- critical - with this form of insufficiency, the death of the child is inevitable.
Diagnosis of pathology
It has already been said earlier that during pregnancy, a violation of blood flow can be diagnosed by means of dopplerometry. It is an ultrasound examination that can detect any pathological abnormalities in blood flow. During the diagnosis, a pregnant woman takes a horizontal position on her back or side. The specialist conducts a study by the transabdominal method. Usually dopplerometry is prescribed twice:
- at 20–22 weeks, in order to make sure that there are no deviations in the development of the fetus;
- at 32 weeks.
Degrees of blood flow disorders in pregnant women
Conventionally, the blood flow system during pregnancy can be divided into two subsystems:
- woman (womb) - placenta;
- placenta is a baby.
In medicine, there are norms for Doppler readings. They are applied from the second trimester. Doctors compare the obtained diagnostic data with the norms and identify the degree of blood flow disturbance during pregnancy.
I degree
When diagnosing, the presence of deviations in one of two forms is recorded:
- I-a degree - a violation of blood flow occurs in the area pregnant - placenta (utero-placental blood flow);
- I-b degree - pathological changes are observed in the placenta-child subsystem.
Violation of blood flow during pregnancy of the first degree does not affect the condition of the unborn baby and is easily amenable to medical correction.
II degree
In the second degree, both subsystems are affected. For 7–12 days, this condition threatens to develop into III degree which could end tragically.
III degree
The critical point at which the child's blood supply may be completely absent or reversed. If within 72 hours, with reverse blood flow, it is not possible to stabilize the condition, then a diagnosis is made to artificial childbirth or premature termination of pregnancy.
What is the danger of impaired blood flow during pregnancy
Complications and dangers that can develop as a result of impaired blood flow include:
- placental abruption;
- hypoxia;
- fetal hypotrophy;
- pathology of development;
- intrauterine death.
At I degree, if the fetus does not suffer from hypoxia, then the woman is allowed to give birth on her own. In other cases, delivery is carried out through C-section.
Why blood flow disorders occur during pregnancy
There are many reasons that contribute to impaired blood flow during pregnancy. Consider the most common factors that provoke a violation of blood flow.
- Diseases of the uterus: bicornuate uterus, endometriosis, uterine hypoplasia, the presence of fibroids, etc.
- Mother's health problems: kidney failure, diabetes, hypotension, pyelonephritis, diseases endocrine system, bronchial asthma and etc.
- Unfavorable conditions for gestation: Rhesus conflict, multiple pregnancy, preeclampsia, abnormal presentation of the fetus, etc.
- External factors: alcohol intake during pregnancy, smoking, constant being in a nervous environment, first birth (and a woman over 35), poor (limited) nutrition of the mother.
Symptoms of pathology
At the first degree of manifestation of the pathology, the symptoms do not manifest themselves in any way, therefore future mom learns about the problem by visiting the next scheduled ultrasound. If the pathology proceeds in an acute or decompensated form, then changes in the activity (movement, stirring) of the fetus can be noticed. Such states are characterized by changes too strong movements with lulls.
In addition to behavioral changes in the baby's abdomen, there may be:
- slow growth of the mother's abdomen;
- late toxicosis;
- increased swelling;
- oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios are diagnosed.
Treatment Methods
If the disease occurs in mild form(first degree), then the doctor may prescribe drugs that improve blood circulation.
The dynamics of the state of the fetus is carried out, weekly, until the indicators normalize, the pregnant woman is given dopplerometry and the fetal heartbeat is checked. If the indicators stabilize, then the woman will continue to bear the child further. In case of deterioration, it is recommended to perform a caesarean section (for a period of more than 25–28 weeks).
In the second degree, the pregnant woman is hospitalized and treated under the strict supervision of the medical staff. If the condition worsens, an unscheduled operation is performed.
As for the third degree, it is not amenable to treatment, since in the development of the fetus, irreversible changes. Therefore, in order not to risk the life of the child, doctors insist on an urgent cesarean.
In conclusion about prevention
Prevention actions should be aimed at creating conditions for healthy growth and prenatal development child. To do this, a woman must:
- watch your diet;
- rest more often;
- regularly visit the fresh air;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- minimize emotional stress.
The main thing is to regularly visit a doctor and follow his recommendations.
During the period of bearing a child, the body of the expectant mother is exposed to strong hormonal changes. In this regard, it is very important to constantly monitor the health of the woman and the condition of the fetus. AT medical practice very often there is a violation of blood circulation in women who are waiting for an addition to the family. The appearance of an additional circle of blood circulation in the body of the mother requires frequent examination at a specialist. After all, if blood flow is disturbed during pregnancy, then there is a risk of fetal death, and different terms its bearing.
Blood flow during pregnancy: normal
Many women, especially those who are carrying their first child, are unaware of the existence of such a study as dopplerometry. It consists in ultrasound diagnostics, which is able to assess the intensity of blood flow in different vessels. This study is mainly carried out in the third trimester of pregnancy. But in some cases, they resort to it even after the twentieth week of bearing a child. Doppler is considered serious research, which allows you to diagnose vascular pathology in the uterus and in the placenta, in the brain and carotid arteries and fetal aorta. Comparing the obtained numbers and the norms of blood flow during pregnancy, the specialist determines whether the child in the mother's womb suffers from lack of oxygen or not.
There are approved norms of dopplerometry, starting from the second trimester of pregnancy. These are the norms of the resistance index of the vessels of the uterus, umbilical cord, aorta and cerebral artery fetus. Doctors recommend not to try to decipher the results on your own. There is a formula for accurately calculating the vascular resistance index - only a doctor should do this procedure.
Violation of blood flow during pregnancy: degrees
For many expectant mothers, such a diagnosis leads to panic and confusion. Should I be nervous? Can this pathology have any consequences for the child? What are the degrees of this disease? Let's try to find answers to these questions.
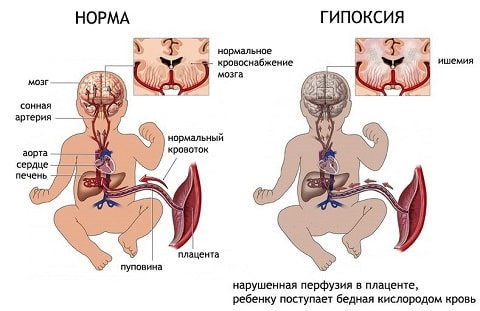
There are three degrees of violations of blood circulation through the blood vessels during gestation. The first is characterized by impaired blood flow, which does not reach critical values (in the umbilical cord and artery). At the same time, a positive state of fetal hemodynamics is observed. In both ventricles of his heart, there is a decrease in the diastolic function index, as well as an increase in the maximum blood flow velocity through all heart valves. The first degree of the disease is divided into 1-a, in which only the uteroplacental blood flow is disturbed, and 1-b degree, in which there is an inferior fetal-placental blood flow.
In the second degree, there is a violation of the hemodynamics of the fetus. Decreased in 50% of cases maximum speed blood flow through all heart valves. It should be noted that this phenomenon is less pronounced in the left sections. Blood flow disorders are observed both in the fetus and in uterine arteries. The second degree often passes into the third, and in a very short period.
The third degree signals critical condition fetal blood supply. At this stage, a deeper restructuring takes place. intracardiac hemodynamics. It is directly related to the centralization of blood circulation. Fetal hypoxia is not excluded. It is also possible to reduce diastolic blood flow in the aorta, up to its disappearance. There is a simultaneous defective movement of blood in the aorta and carotid artery.
What threatens blood flow during pregnancy: consequences
This pathology leads to placental insufficiency, which is observed in 25% of pregnant women.
It is known that the placenta is the main organ during the bearing of the unborn baby, with the help of which it breathes and feeds, as well as excretes its waste products. It is in the placenta that two systems of blood vessels converge, between which there is a membrane that provides a kind of barrier between the body of the child and the mother. Thanks to the membrane, the blood of the mother and the unborn child does not mix. The placenta is also a protective shield against viruses and bacteria. She performs immune function to protect the fetus.
With placental insufficiency, the uteroplacental and fetal-placental blood flow is disturbed, and the placenta itself does not mature properly. In connection with these changes, the unborn child does not receive enough useful material and oxygen. For this reason, its development and growth slows down, and the existing complications of pregnancy are exacerbated.
Naturally, due to the fact that the blood flow during pregnancy is low, such serious changes can even lead to the death of the fetus. But it happens in rare cases. Often this pathology detected at an early stage and successfully treated.
Violation of the uteroplacental blood flow
AT medical terminology violation of the uteroplacental circulation of blood is indicated by degree 1a. The occurrence of this pathology indicates dangerous complication pregnancy. It usually occurs at a later date.
Inadequate blood flow occurs between the uterus and the placenta. Similar state contributes to a significant deterioration in the metabolism between the body of a woman and the fetus. Naturally, such a state leads to certain consequences.
There are reasons that provoke the development of this condition. These include an increase blood pressure mothers, diabetes mellitus, pneumonia and kidney disease in a pregnant woman, as well as the presence of an infection in the fetus itself. It should be noted that timely detection possible groups risk is serious preventive measure. Therefore, it is important for a pregnant woman to monitor her health and seek medical help even with minor ailments.
What is the danger of impaired blood flow in a child
In a single functional system mother-placenta-fetus defective fetal-placental blood flow leads to placental insufficiency. After all, the placenta supplies the unborn baby with food and oxygen. It is she who is the link that unites two complex systems - maternal and fetal. When such a pathology occurs, a violation of the blood flow in the child is observed. It should be noted that inadequate movement of blood in the vessels of any degree leads to malnutrition of the fetus. His condition also depends on the stage of blood flow disturbance. Naturally, the third degree signals the critical condition of the child.
When early detection of this pathology, the doctor must determine the need for treatment in a hospital or at home. It all depends on the specific case and the duration of pregnancy.
In medical terminology, a violation of the fetal-placental blood flow is indicated by degree 1b.
How to treat blood flow disorders during pregnancy
For the treatment of defective blood flow during the period of bearing a child, apply various drugs, which contribute to increasing the resistance of the fetal brain to hypoxia, improving blood microcirculation and reducing its coagulability. If necessary, the doctor prescribes antibacterial and antiviral drugs, as well as immunomodulators.
A good tool to improve cerebral circulation, the work of the heart and metabolism in a child with hypoxia, is the drug Instenon. It is used in combination with other drugs.
The expectant mother is also credited with the use of Actovegin, a drug that helps to increase the resistance of tissues and the brain of the fetus to hypoxia. It also improves metabolism, stimulates the renewal of the cells of the unborn baby, improves blood circulation in the complex system - mother-placenta-fetus. As a result of treatment with Actovegin, blood flow indicators improve, and there is active growth baby in the mother's womb.
It is known that in placental insufficiency, as a rule, there is chronic disorder blood clotting. In this regard, experts recommend the use of drugs that prevent the formation of blood clots in the vessels (for example, Curantila).
In the case of the 3rd (most difficult) degree of blood flow disturbance, specialists cause premature birth.
Specially for -Ksenia Manevich
During pregnancy, the expectant mother should be observed by a gynecologist so that the fetus develops properly. In the process of the body's work, disturbances may occur that affect the formation of the fetus, the doctor helps the woman to avoid unpleasant consequences. An additional circle of blood circulation appears in the mother's body, and violations in this area can cause the death of the baby during pregnancy.
The circulatory system that connects the uterus, placenta and baby has a different functional value: supplies the baby with nutrition and oxygen, removes the metabolic products of the fetus. The placenta is an obstacle for viruses that can enter through the mother's blood. If there is a violation of the blood supply to the placenta, this leads to placental insufficiency and impaired functionality of the placenta.
Why is blood flow disturbed?
There are reasons for this:
- Due to high pressure.
- On account.
- With inflammation of the lungs.
- With hypoxia.
- due to thrombosis.
- The presence of gynecological disorders.
- Due to miscarriages, abortions.
Violations are of the following types:
- Utero-placental.
- Placental.
- Feto-placental.
Diagnostic methods
Are there? To answer this question, it is necessary to define blood flow disorders. Dopplerometry and ultrasound should be performed. Checking blood flow is carried out in different blood vessels mother and child.
What the doctor pays attention to when making a diagnosis: a thin placenta, the presence of infections, abnormalities in the amniotic fluid.
With the help of doplerometry, three degrees of blood flow disturbance can be determined:
1 degree - easy is divided into categories:
1B - fetal-placental - uteroplacental blood flow is preserved;
Grade 2 - both blood flow systems are disturbed.
Grade 3 - circulatory disorders in a critical stage.
Doppler is carried out at any stage of pregnancy, especially when there is a suspicion of circulatory disorders.
In addition, apply laboratory methods blood tests of pregnant women.
Therapeutic methods
Treatment of circulatory disorders is carried out in a complex, so that there are no complications. If a pregnant woman falls into a risk category (abortion, gynecological diseases), carried out preventive treatment, the future mother is constantly monitored. Methods of therapy are determined based on the degree of circulatory disorders.
The use of drugs that can reduce the tone in the uterus and improve blood circulation, for example, Magne-B6, depends on the individual state of the mother's body. No-shpa may also be prescribed in order to expand the vessels. In addition, the methods of therapy include drugs that help blood clotting, for example, Curantil.
A woman with impaired blood flow without fail at 36 weeks placed on hospital treatment for prenatal diagnosis. natural childbirth a pregnant woman with impaired blood flow of the 1st degree is carried out under special supervision. For grades 2 and 3, a caesarean section is performed.
Prevention to reduce the risk of blood flow disorders:
- Proper nutrition.
- Getting rid of stress.
- Walks in the open air.
- Vitamins.
Impaired blood flow should be treated under medical supervision. If a pregnant woman behaves incorrectly, is not treated - this may be the cause of premature birth, or complications in the development of the fetus.

