How to improve placental circulation during pregnancy. Types of disorders of the uteroplacental blood flow, what it is, what to do
During pregnancy female body starts to rebuild. Therefore, during this period it is so important to keep under control the condition of both the woman and the fetus. According to medical statistics, a fairly large number of pregnant women have impaired blood flow. An additional one that has arisen in the body requires constant monitoring by specialists. Its violation can lead to the death of the fetus, and this can happen at any stage of pregnancy. Let's try to figure out why blood flow is disturbed during pregnancy.
A bit of theory
Everyone knows that the placenta acts as a link between the woman's body and the fetus. In this complex system, two types of blood circulation are distinguished - placental and fetal. Any violation of one of them can lead to enough sad consequences including the development of various diseases. The severity of the problem is assessed only by the doctor.
In this case, a woman who is at the 30th week of pregnancy must necessarily undergo a special ultrasound diagnostics, which clearly shows the vessels of the placenta in a three-dimensional image. If there is any violation, the doctor will definitely see it, as there is a change in the spatial ratio of the uterine and fetal-placental circulation. This is very dangerous state organism, as oppression occurs respiratory function, and the development of the fetus is suspended.
Degrees of violation
Medicine distinguishes three degrees of severity of this pathology. The first degree is considered the easiest, when insufficient blood circulation has not yet reached its critical values. In this case, the hemodynamics of the fetus is in a satisfactory condition. There is a violation of the uteroplacental blood flow of 1 A degree and insufficient fetal-placental blood circulation of 1 B degree.
The second degree is characterized by a deterioration in the blood supply to the fetus. In 50% of cases, there is a decrease in the maximum velocity of blood moving through all the valves of the heart, and such a violation is observed both in the fetus and in the uterine arteries.
Quite often for short span time the second degree passes into the third. In this case, the blood flow practically ceases to flow to the fetus, which can cause its hypoxia. There is a high probability of a decrease in diastolic blood flow in the aorta, and in some cases it may disappear completely.
The reasons
If there is a violation of the blood flow of the 1st degree during pregnancy, the reasons leading to this may be different. Numerous adverse factors able to affect the placenta not only during its formation, but also at a later date. medical practice allocates primary and secondary, which disrupts the functioning of the placenta, which acts as a transport, protective, immune, metabolic and endocrine organ.
Thus, impaired blood flow of 1 A degree during pregnancy can occur for the following reasons:
- tumor of the uterus;
- genetic defects;
- consequences of abortion;
- infectious diseases;
- hypertonic disease;
- diseases of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland;
- structural anomalies;
- hormonal dysfunctions;
- thrombosis, atherosclerosis;
- diabetes.
If this pathology is not eliminated in a timely manner, then after 6 weeks a slight violation of blood flow can go into the third stage. If a problem is detected at the 30th week, the doctor still has enough time to take appropriate measures to restore normal blood circulation.
Symptoms
Any pathology is characterized by its clinical picture so that the doctor can make an appropriate conclusion. The lack of hemodynamics leads to a change in the functioning of the placenta, because of which the fetus begins to suffer. The necessary nutrients and oxygen, and there is a slowdown in the excretion of metabolic products. Signs begin to appear, as a result of which its intrauterine development stops.
Thus, if there is a violation of blood flow during pregnancy, the symptoms of this condition are manifested as follows:
- cardiopalmus;
- decrease or increase in fetal motor activity;
- discrepancy between the volume of the abdomen for a specific gestational age.

Such signs usually occur with a decompensated form. If a violation uterine blood flow during pregnancy of 1 A or 1 B degree, then these symptoms do not yet appear, since hemodynamics is compensated. It is usually detected during diagnostic studies.
Diagnostics
In order to identify a violation of blood flow of 1 A degree during pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo a series of examinations, with the help of which the type and degree of changes that have occurred are established, and the condition of the fetus is also determined. In this case, the doctor prescribes the following procedures:
- blood test for hormones such as estrogen, chorionic gonadotropin, progesterone;
- cardiotocography;
- ultrasound procedure;
- dopplerometry.
In some cases, the doctor, already during the examination, is able to determine the violation that has arisen, focusing on the child's heart rate, which are counted during auscultation. But the most reliable results usually obtained after laboratory and instrumental studies.
Treatment
Impaired uteroplacental blood flow of any degree must be treated. Mostly medical measures aimed at preventing the pathology from progressing in the future. Hemodynamics normalizes only if a violation of blood flow of 1 B degree is detected.
In pregnancy that occurs with deviations, are used various means improving the condition of the fetus. Mainly used conservative methods treatment. Surgical intervention possible only in case of complications and life important indications. When normalizing blood flow disorders, a set of measures is used - pathogenetic, etiotropic and symptomatic treatment.
Medical treatment
Most often, impaired blood flow of 1 A degree during pregnancy is corrected with the help of medications. When identifying initial signs disorders are treated on an outpatient basis. More severe circulatory failure requires hospitalization.

The following drugs are used for treatment:
- antispasmodics - "Eufillin", "No-shpa";
- vascular - "Actovegin";
- antiplatelet agents - "Kurantil";
- vitamins and microelements - "Ascorbic acid", "Magne B6";
- hepatoprotectors - "Hofitol", "Essentiale";
- tocolytics - "Partusisten", "Ginipral";
- improving blood microcirculation - "Trental";
- antihypoxants - "Instenon";
- metabolic - "ATP".
Usually, to improve the condition, two courses of therapy are carried out - immediately after the diagnosis was made and at a period of 32-34 weeks. After that, the doctor decides on the method of delivery. This is especially important if the circulatory disorder is severe. In case of violation of the blood flow of the 1st degree, childbirth is carried out naturally.
Surgery

If the violation of blood flow is pronounced, an emergency delivery is performed. In case of failure conservative treatment, even in lung case violations, the decision is made within two days. Usually carried out C-section. If it is planned for a gestational age of less than 32 weeks, then the condition of the fetus and its viability are assessed.
Preventive measures
To avoid such pathological condition, as a violation of blood flow 1 A degree during pregnancy, preventive measures should be taken. A woman who is expecting a baby should eat foods that contain essential vitamins, micro and macro elements, fats, carbohydrates and proteins. Every day, at least 1.5 liters of fluid should be consumed, but only if swelling does not torment.

It is also important to keep your weight under control. During pregnancy, the recommended weight gain should not exceed 10 kg. Women at risk are given prophylaxis with drugs to interact with the systems of the body of the mother and fetus and prevent extremely dangerous dysfunction uteroplacental circulation. An important role is played by the timely corrected method of conducting childbirth. But it should be remembered that even compliance with these measures does not exclude the occurrence of severe neurological complications.
Conclusion
Thus, it is important to control blood flow during pregnancy. The reasons may be different. The main thing is to take care of your health, and timely detection pathology can help prevent severe consequences for the future child.
In this article we will talk about such a concern for many pregnant girls as a violation of the uteroplacental blood flow. Causes of circulatory disorders in the mother-fetus system, their symptoms, dangers such violations and opportunities for treatment.
Violations of the uteroplacental blood flow are much more correctly called the term "violation of the uterine-fetal blood flow", since the blood circulation in the "mother-fetus" system can be conditionally divided into two components:
- Uteroplacental circulation.
- Feto-placental blood flow.
Violations of blood flow in any of these systems or in both at once is called in obstetrics disorders of the uterine-fetal blood flow.
The conditional boundary between these two systems can be called the placenta - a temporary organ of pregnancy, formed by the growth of the chorionic villi of the embryo into the mucous membrane of the uterine wall. The placenta is a filter consisting of numerous weaves of different levels of vessels in which maternal blood, without mixing with the fetus, gives oxygen and nutrients to the fetal bloodstream, and takes back harmful substances and metabolic products.
The placenta is the most important organ for the fetus, which ensures its normal functioning.
Let's try to understand this most complex blood flow system:
- From the side of the uterus, the placenta is fed by the maternal arteries - uterine arteries and spiral arteries. They are the constituent component of the first level of blood supply to the pregnant uterus and fetus.
- The spiral arteries feed the placenta, forming directly the placental blood flow.
- The placenta forms the umbilical cord or umbilical cord - a complex of three vessels - two arteries and one vein, surrounded by a special jelly-like substance. By umbilical vein blood rich in oxygen and nutrients moves to umbilical ring fetus, further supplying blood to the liver and other vital organs of the fetus. The blood flow in the umbilical vessels forms the second component of the blood circulation in the "mother-fetus" system.
- Large fetal arteries in vital important organs- aorta, cerebral artery form the third component of blood circulation.
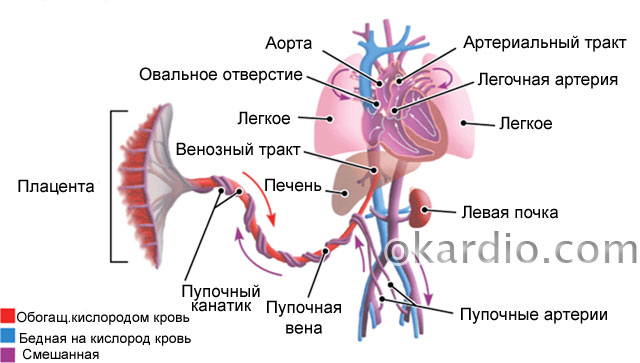 Fetal circulation. Click on photo to enlarge
Fetal circulation. Click on photo to enlarge If blood flow is disturbed at any level, the fetus receives less nutrients and oxygen - intrauterine hypoxia of the fetus or its oxygen starvation. Intrauterine hypoxia can be both acute and quickly leading to fetal death, and chronic - long and sluggish, the main symptom of which is fetal growth retardation (abbreviated as FGR).
Depending on the severity and degree of blood flow disorders, the condition can be observed and treated conservatively (when it is not very dangerous) or urgent delivery of a woman at any stage of pregnancy to save the life of the child.
The problem of blood flow disorders in the mother-fetus system is dealt with by obstetricians-gynecologists in close contact with perinatal ultrasound diagnostics doctors, since the main function for determining direct disorders and their degrees belongs precisely to ultrasound doctors.
Causes of circulatory disorders in the "mother-fetus" system
- Placentation disorders - the formation and functioning of the placenta. Such violations can be primary - at the stage of pregnancy formation - placental abruption, lack of progesterone, defective uterine mucosa. An already formed placenta may also suffer. This is caused by disturbances in the coagulation system, infections, trauma to the placenta.
- Coagulation system disorders - spontaneous and induced thrombosis. Thrombi block large and small branches of the vessels of the uterus and placenta.
- Intrauterine infections damage the placenta and trigger the formation of blood clots.
- Complications of pregnancy - Rh conflict, preeclampsia, twin steal syndrome, placental abruption, premature birth.
- Lack of nutrients and vitamins - in particular iron deficiency - anemia.
- Maternal diseases - diabetes mellitus, hypertension, thrombophilia, vascular defects and vascular wall, heart and lung diseases.
- Impact harmful factors external environment – harmful conditions at work, the effect of drugs, smoking, alcoholism, drug addiction.
- Stress and nervous strain.
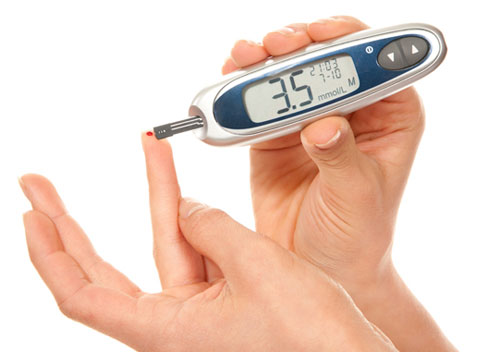 Glucometer for measuring blood sugar levels. The presence of diabetes in the mother can lead to circulatory disorders in the system "mother-fetus"
Glucometer for measuring blood sugar levels. The presence of diabetes in the mother can lead to circulatory disorders in the system "mother-fetus" The main symptoms of the disease
These symptoms are called external, because the main method for diagnosing disorders of placental and fetal blood flow is the Doppler ultrasound method, which will be discussed below in a separate section.
How can one suspect the suffering of the fetus before an ultrasound examination?
- Insufficient growth or complete absence the increase in the main indicators of measurements of the abdomen of a pregnant woman at the next admission - the height of the fundus of the uterus and the circumference of the abdomen. It is these two sizes that the doctor measures with a centimeter tape at each appointment of a pregnant woman.
- Unsatisfactory results of listening to the fetal heart by a doctor during examination. Each examination of the expectant mother is accompanied by listening to the heart sounds of the fetus using a special tube - an obstetric stethoscope. If the doctor notes a change in the fetal heart rate, muffled tones, lack of heart rate response to movements, then this should alert the physician.
- Unfavorable fetal movement profile. This symptom is clearly noted by the woman herself. A pregnant woman may complain of a weakening of movements, long periods of “silence” of the fetus, or excessively violent movement. The simplest test for motor activity fetus will test "Count to ten". In this case, a pregnant woman should count at least 10 separate fetal movements within 12 hours.
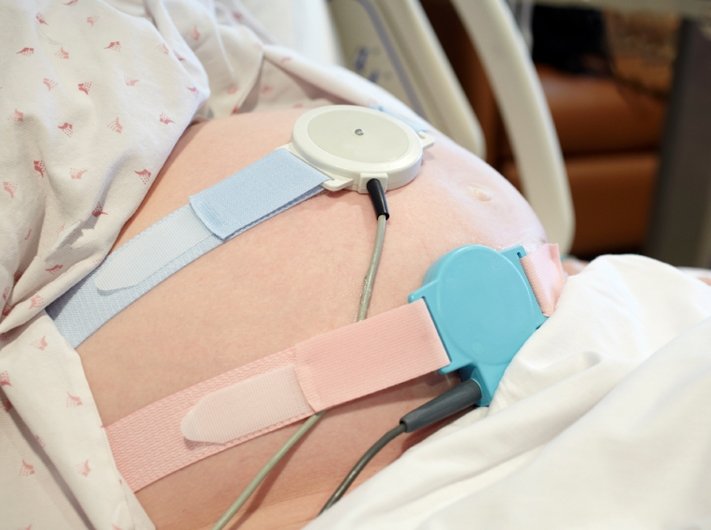
- Unfavorable or disturbing types of CTG - cardiotocography. This procedure for recording the electrical activity of the fetal heart is carried out each time in antenatal clinic starting at 28-30 weeks. CTG is a very sensitive method for assessing the condition of the fetus, therefore, in case of violations of the cardiotocogram, an obligatory ultrasound examination of the fetus and its blood flow is necessary.
These are the four main points at which there are objective reasons to suspect one or another violation of the blood supply to the uterus and fetus. There are more relative readings for additional diagnostic measures regarding uterine-fetal blood flow:
- Multiple pregnancy, especially in the presence of monochorionic twins. Such twins have one placenta for two, so the latter often cannot cope with such a load, especially in late pregnancy.
- Anomalies in the structure of the placenta - hypoplasia of the placenta, rolled placenta, as well as its premature aging.
- Anomalies in the structure of the umbilical cord or its presence true nodes- such nodes are formed during the active movement of the fetus.
- The presence of intrauterine infection - viral, bacterial or others.
- Rh-conflict of the mother and fetus according to the Rh factor or blood group. Such a conflict is primarily diagnosed by the presence of antibodies in the mother's blood.
- Maternal gestational diabetes mellitus that developed during an existing pregnancy, or pre-existing diabetes mellitus.
- Preeclampsia is a complication of late pregnancy, characterized by an increase in blood pressure, edema and the appearance of protein in the urine.
- Maternal hypertension.
- Any cardiac or vascular pathologies mother.
- Blood clotting disorders - especially the tendency to thrombosis. Such disorders include hereditary thrombophilia and antiphospholipid syndrome.
All these factors significantly increase the risk of developing blood flow disorders in the mother-fetus system, and therefore are subject to close monitoring.
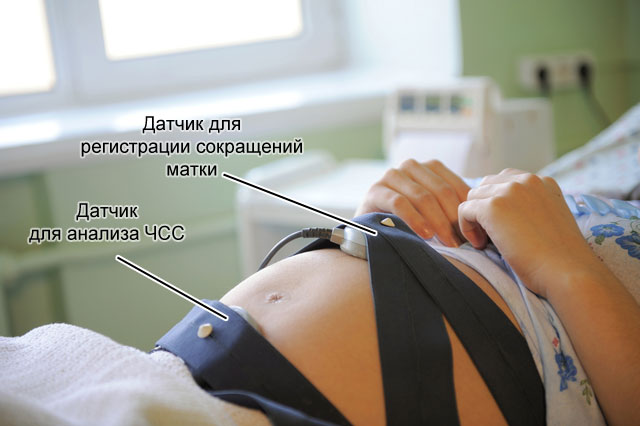 With the help of cardiotocography, it is possible to assess the fetal heartbeat at rest, movement and during uterine contractions.
With the help of cardiotocography, it is possible to assess the fetal heartbeat at rest, movement and during uterine contractions. Diagnosis of blood flow disorders
The gold standard for diagnosing disorders of perinatal blood flow is ultrasound examination of the fetus with obligatory dopplerometry. The Doppler method is based on the measurement of velocities, resistance indices and other indicators of blood flow in the vessels. The global medical community has developed great amount tables and diagrams of dopplerometry of each vessel.
In obstetrics, the assessment of fetal circulation is carried out in the following vessels:
- Uterine arteries - assessment of the first link of the "mother-fetus" system. Close attention is paid to the indicators of the uterine arteries in pregnant women with heart and vascular diseases, anemia, arterial hypertension, preeclampsia and gestational diabetes mellitus.
- Vessels of the umbilical cord - assessment of the "mother-fetus" system - indicators of blood flow from the placenta to the child. The most commonly assessed indicators of blood flow in the umbilical artery.
- The middle or median cerebral artery is a powerful vessel in the fetal brain. The indicators of blood flow in this vessel are extremely important and significant in the presence of a conflict in the Rh system or blood groups, fetal anemia, and also in case of suspected fetal malformations.
The doctor measures the blood flow indicators several times and correlates the obtained values \u200b\u200bwith the tables. These are extremely variable indicators, they can fluctuate significantly depending on external and internal factors:
- The gestation period is up to one week.
- The number of fetuses and placentas - for twins and triplets, their Doppler indicators.
- Maternal blood pressure - an ultrasound doctor is always interested in a pregnant woman with her pressure numbers.
- Maternal hemoglobin levels - with anemia, blood flow indicators can change significantly.
- Smoking and other bad habits of the mother.
- Medicinal preparations.
- The tone of the uterus - both the usual hypertonicity, and regular contractions, for example, in childbirth.
 Uterine tone (hypertonicity) - contraction of the muscular layer of the uterus
Uterine tone (hypertonicity) - contraction of the muscular layer of the uterus In addition to dopplerometry, the doctor performs the so-called fetometry - measuring the size of the fetus and calculating its estimated weight. If the fetus is significantly behind in development from the average, the doctor has the right to make a diagnosis of "fetal growth retardation", or FGR. A similar lag in fetal growth is observed during chronic hypoxia - that is, the fetus does not receive enough oxygen and nutrients for a long time several weeks and even months.
Based on the obtained indicators, the doctor of ultrasound diagnostics forms the diagnosis: “Violation of the utero-fetal blood flow” and indicates the degree. In the presence of fetal growth retardation, the diagnosis is supplemented by the wording "GRP".
Now we will talk in detail about the classification of the degrees of blood flow disorders.
Three degrees of pathology
There are three main degrees of utero-fetal blood flow disorders:
- I degree - minor violations of one of the conditional circulatory systems. The first degree has two sub-degrees:
- I A - violations of the utero-placental blood flow with preserved feto-placental blood flow. This means a violation of blood circulation in the system of uterine arteries.
- I B - violation of the feto-placental blood flow with preserved utero-placental blood flow. In this case, the uterine arteries fully perform their function, but there are violations at the post-placental level.
Treatment of fetal and uterine blood flow disorders
Mandatory treatment requires almost all degrees of blood flow disorders. The question is what degree of blood flow disturbances is detected, and whether it is accompanied by fetal growth retardation.
The most "harmless" are violations of the uteroplacental blood flow at 1a degree. It is important to understand that this type of violation is sometimes an accidental finding at the next ultrasound. This condition can occur against the background of an increase in the mother's blood pressure, her excitement, fatigue, and a decrease in hemoglobin levels. This degree does not always indicate the suffering of the fetus and often disappears on its own within a few hours after rest or walking on fresh air. However, this does not mean that you need to “give up” on the diagnosis. A pregnant woman must definitely undergo a control ultrasound in 5-7 days, and record CTG several times during the week.
The main methods of treatment of fetal blood flow disorders:
- Normalization of the lifestyle and nutrition of a pregnant woman. It is important to walk a lot in the fresh air, sleep at least 8 hours at night and try to rest at least an hour during the day, avoid long sitting in awkward posture, move a lot, eat normally and fully.
- Blood pressure control is one of the most important parameters that determine uterine blood flow. In the presence of arterial hypertension you need to constantly take the drugs prescribed by the doctor and independently monitor the pressure indicators.
- Treatment of intrauterine infection antiviral drugs and antibiotics.
- Treatment of extragenital pathology - normalization of sugar levels, normalization of hemoglobin levels, control of body weight, correction of the blood coagulation system. The latter includes medication low molecular weight heparins- Fragmina, Fraksiparina and others.
- The use of antispasmodics - No-shpy, Drotaverine, Papaverine. These drugs relax the wall of the uterus and spiral arteries, increasing blood flow.
- Taking magnesium preparations - magnesium has a relaxing effect on the uterine wall and a powerful protective effect on the central nervous system fetus. The last factor is important in the development of hypoxia.
- The use of "vascular" drugs - large group antiplatelet agents, angioprotectors and drugs that improve microcirculation and tissue trophism. The most common drugs in obstetrics are Pentoxifylline, Dipyridamole, Actovegin and their derivatives.
- In case of Rhesus conflict, plasmapheresis is prescribed - purification of the mother's blood on a special apparatus to reduce the amount of antibodies damaging the erythrocytes of the fetus.
- In the case of acute fetal hypoxia against the background of impaired blood flow II and III degree, inefficiency conservative therapy, as well as severe fetal growth retardation, early delivery is advisable, regardless of the gestational age. Most often, they resort to caesarean section, since the stimulation of childbirth is an additional burden on an already suffering fetus. The principle of “outside is better than inside” is the best fit for these situations.

Placenta - formed in the uterus after pregnancy. It is necessary for binding the body of mother and child with one blood circulation. With the help of the placenta, the fetus is supplied with oxygen, nutrients necessary for the development and formation of organs. AT reverse side unnecessary substances formed as a result of biochemical processes are removed.
Impaired uteroplacental blood flow causes a condition called placental insufficiency. This leads to the death of the fetus, miscarriage.
For 36 weeks, three mandatory ultrasound examinations are performed. It allows you to timely identify the violation, develop a plan for the management of pregnancy and childbirth, prescribe treatment, prevent the death and abnormal development of the child.
Modern requirements of obstetricians-gynecologists are aimed at examining pregnant women with the help of safe methods to evaluate uteroplacental blood flow by volume.
How does blood flow between mother and fetus work?
The mother-fetus circulatory system is based on such anatomical formations like placenta, umbilical arteries, veins.
Blood flows to the placenta through the uterine arteries. The structure of their walls is characterized by the presence of a muscle layer that can contract and block the lumen. Before pregnancy, this mechanism helps to reduce blood loss during menstruation.
At 4–5 weeks of fixation of a fertilized egg (gestation process), the muscle layer disappears. Blood flow to the placenta is no longer dependent on vascular contraction. And by the sixteenth week, the arteries are transformed for constant blood supply. This is dangerous when bleeding occurs, since it is impossible to stop it by reducing the lumen of the vessels.
AT normal conditions placenta attaches to inner surface uterus with the help of villi penetrating deep into the thickness of the mucosa. They grow into the walls of blood vessels and directly contact with maternal blood.
Here at the cellular level is happening:
- exchange between the maternal organism and the fetal blood flow;
- two oppositely directed streams meet;
- transition essential substances(diffusion).
another part general circulation provide vessels of the umbilical cord (normally there are 2 arteries and a vein). The main volume of blood flows to the fetus through the arteries, flows through the vein towards the placenta.
With the growth of the uterus, the arteries expand, form anastomoses
Violation of the fetal-placental blood flow is the most difficult to tolerate developing child. Creates conditions for an unsatisfactory build prediction internal organs and systems, birth healthy baby.
What causes can break the flow of blood between the mother, placenta and fetus?
The reasons for the violation of the circulatory system between the mother's body and the fetus (fetoplacental insufficiency) are well understood. Some of the factors are formed only against the background of pregnancy. The other one depends on general health women.
Pathologies of pregnancy include:
- Low attachment of the placenta (obstetricians say - presentation, "placentation") - lower divisions uterus are thinner muscle layer. Not enough blood flows through it to the fetus. A similar situation develops in the case of presentation in the zone postoperative scar(for example, from a caesarean section).
- Late toxicosis - accompanied by damage small vessels uterus, the complication is the most frequent violation blood flow.
- Anemia - low level hemoglobin causes a compensatory acceleration of the heartbeat, blood flow through the uterine arteries increases in order to compensate for the lack of oxygen. The circulation in the utero-placental circle also changes.
- Incompatibility between the blood of the mother and the fetus according to Rhesus - an immune conflict arises with the development hemolytic disease child, anemia. The same situation is possible when transfusing blood of different groups from a donor.
- The burden on the kidneys due to toxicosis can cause an increase in blood pressure. This contributes to the change in blood flow.
- Rarely, pathology of the umbilical arteries is detected. If there is only one umbilical artery, then the blood flow is insufficient for the fetus.
- Multiple pregnancy - the placenta is enlarged and requires enhanced nutrition. Sometimes blood flow passes from one fetus to another.
It turns out that the first child is a constant donor for the twin, develops worse, because he transfers blood to his brother, and he himself is “malnourished”
Such changes are called fetotransfusion syndrome. The donor has a smaller body weight. And the recipient has increased load to the developing heart. Both babies have problems.
Of the diseases of women, the most dangerous are:
- Acute infections during pregnancy - pathogens can penetrate the placental barrier and destroy the vasculature.
- Malformations of the uterus - the most significant is the "two-horned" uterus. Inside the cavity there is a partition dividing it into 2 parts. Pregnancy is possible only in one of them. The main violation is not the compression factor (the cavity has the ability to stretch enough), but the lack of communication between the uterine arteries, insufficient development of the vascular network, placental hypoxia.
- Endometriosis - changes in the inner lining of the uterus, occur after inflammatory diseases(including sexually transmitted infections), frequent abortions, diagnostic curettage. One reason is smoking and alcohol.
- Tumor of the uterus - if a woman has even a small fibroid ( benign tumor), then pregnancy stimulates the growth of nodes. They take over part of the blood supply, and the blood flow of the fetus is “robbed”. Deficiency directly depends on the size of the tumor.
- Diabetes mellitus - affects the walls of blood vessels, often occurs in women with risk factors during pregnancy.
What threatens the fetus with insufficient placental blood supply?
All disorders of both uteroplacental and fetal-placental nature lead to oxygen deficiency fetus (hypoxia). Complications are caused precisely by this mechanism:
- the formation of the internal organs of the fetus is disturbed, there is a lack of mass, this is called "delay prenatal development»;
- the heart reacts with rapid contractions (tachycardia) or arrhythmias, bradycardia;
- the composition of electrolytes and acid-base balance are disturbed;
- functioning is disrupted endocrine system, the fetus has a hormonal imbalance;
- fat depots are not formed.
Most severe complications- fetal death, threatened miscarriage.
Myomatous nodes take part of the vascular network in the fetus for its growth
Types of blood flow disorders in the placenta
There are fetoplacental (between the fetus and the placenta) insufficiency and uteroplacental insufficiency.
Fetoplacental hypoxia can proceed as:
- Acute deficiency- occurs in any period of pregnancy and during labor pains. calls premature detachment placenta, vascular thrombosis, heart attack in the area of the placenta, hemorrhage. Can cause the death of a child.
- Chronic - occurs more often, develops from the second trimester, but manifests itself only in the third. Placental changes are premature aging, fibrin is deposited on the surface of the villi. Permeability is sharply reduced, which provokes fetal hypoxia.
Against the background of the development of chronic placental insufficiency, stages can be distinguished:
- compensation - the course is favorable, because they work defense mechanisms the mother's body and compensate the baby for the missing nutrition, the treatment is effective, the child is born on time, healthy;
- subcompensation - the mother's body is not able to fully compensate for the "unprofitable" blood supply to the fetus, it is necessary complete treatment, the child may be born with complications, lag behind in development;
- decompensation - the pathology develops rapidly, compensatory mechanisms are not enough, the activity of the heart is disturbed in the fetus, intrauterine death is possible;
- critical stage- characterized by pronounced structural changes in the placenta, which violates its functions, therapy cannot change the state of the fetus, death is inevitable.
Degrees of impaired blood flow
In a joint violation of the fetoplacental and uteroplacental blood flow, 3 degrees are distinguished.
I - changes are compensated, do not threaten the fetus, they capture only the uteroplacental blood flow, the child develops normally. Depending on the level of change, there are:
- degree Ia - violation of uteroplacental blood flow is limited to one of the arteries of the uterus, all hemodynamic parameters are stable, within the normal range;
- degree Ib - the blood flow is disturbed at the level of communication between the fetus and the placenta due to the vessels of the umbilical cord, enough blood flows through the uterine arteries.
If small changes in the first stage were not detected and the woman did not receive treatment, then after 3-4 weeks, violations of the second degree occur.
II - the blood flow in the uterine and umbilical arteries changes.
III - indicators are critical, reverse blood flow in the arteries is possible.
How is the diagnosis carried out?
Most accurately helps to put correct diagnosis and to identify the level of impaired blood flow by Doppler sonography. The method is highly sensitive and very informative. Shows even small changes in the first stage to clinical manifestations. An important advantage is safety for the fetus and the expectant mother.
With the help of Doppler sonography, it is possible to examine the blood flow through the arteries and veins, obtain a color graphic image, and measure the hemodynamic parameters of the fetus.
This plays a significant role in predicting the course of pregnancy, creates conditions for making decisions on therapeutic measures.
To indirect methods diagnostics include:
- computed tomography,
Methods allow you to identify the lack of fetal weight, the placenta is not well. These signs may be evidence of the development of hypoxia.
What does the mother feel and the doctor determines during the examination?
Hypoxia stimulates the motor activity of the fetus.
At the appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist, the doctor listens to the fetal heartbeat, pays attention to a high frequency, arrhythmia or bradycardia. This necessitates referral for Doppler examination.

A pregnant woman pays attention to the increase in movements, tremors
Treatment of disorders
Establishing the degree of impaired uteroplacental blood flow is necessary for choosing the tactics of pregnancy management.
- It is believed that it is possible to maintain pregnancy in the first degree (a and b), treatment will still help.
- The second degree is considered as borderline, requiring constant monitoring, the effectiveness of treatment is unlikely.
- In the third degree, urgent delivery by surgical methods is required.
The possibilities of therapy are aimed at all parts of the pathology:
- to improve microcirculation, Pentoxifylline, Actovegin are used;
- Stabizol, Venofundin, Infucol are used as support for low blood flow velocity and pressure in the vessels (synthesized on the basis of a starch solution, capable of retaining fluid in the vessels);
- vasodilators medicines such as Eufillin, No-shpy eliminate spasm of medium and small arteries;
- by reducing the tone of the uterus, it is possible to influence vasospasm, reduce the degree of hypoxia, apply magnesium sulfate, Magne B6, Ginipral;
- antioxidants eliminate the effects of hypoxia, destroy decay products, prescribe Tocopherol, combinations of vitamin E and ascorbic acid, Hofitol;
- Essentiale renders protective action by increasing the level of beneficial phospholipids in the blood, improving liver function;
- Curantyl is prescribed during pregnancy against the background of uterine fibroids, it has been established positive action on microcirculation and prevention of thrombosis.
In the practice of obstetricians continue to use Cocarboxylase, which was abandoned by cardiologists. But gynecologists consider the drug effective for restoring tissue respiration.

For the treatment of newborns and care for them, according to indications, incubators are used
Forecast and consequences
For statistical studies such indicator as "perinatal mortality" is used. It includes all deaths in the fetus from the 22nd week of pregnancy and among newborns in the first week of life. It is believed that it fully reflects the influence of the factor of pregnancy and childbirth. The calculation is based on 1000 born children.
Currently, 13.3% of children die from the second degree of violation of the uteroplacental circulation, in the third - up to 47%. Timely caesarean section can reduce mortality.
AT intensive care need:
- 35.5% of newborns with the first degree;
- 45.5% - from the second;
- 88.2% - from the third.
The consequences of the preservation and treatment of children born in conditions of pathological hypoxia. Pediatricians and psychiatrists point to its unconditional influence on physical and mental development.
Diagnosis and treatment of conditions associated with a violation of the uteroplacental barrier can only experienced professionals. Cannot be taken on its own medications or use the advice of poorly educated people. The situation can become critical not only for the fetus, but also for the woman.
A well-functioning "mother-placenta-child" system is a guarantee of the health of a woman waiting for an addition to the family, and her baby. Failure in this system, expressed in impaired blood flow, can lead to negative consequences for a child, the reversibility of which is often simply impossible. Violation is fraught with a delay in the development of the fetus in the womb. The consequences of impaired blood flow during pregnancy also include hypoxia, malformations, and even death of the embryo.
An additional circle of blood circulation in a pregnant woman requires an additional examination by a specialist. This examination is called dopplerometry. Dopplerometry is an ultrasound diagnosis of the intensity of blood flow in different vessels. Diagnosis is carried out in the third trimester of pregnancy. It is at this time that the doppler shows almost 100% reliable results. In some cases, dopplerometry is performed for a period of twenty weeks.
Comparing the information received on the device and guided by the norms of blood flow, the diagnostician determines whether the child is experiencing oxygen starvation or not.
Dopplerometry has its own approved standards, which include: the resistance index of the vessels of the uterus, umbilical cord, aorta and cerebral artery fetus. Self decryption and comparison of the data obtained after the diagnosis and the norms of dopplerometry is a thankless task. Only a doctor can calculate the vascular resistance index using the appropriate formula.
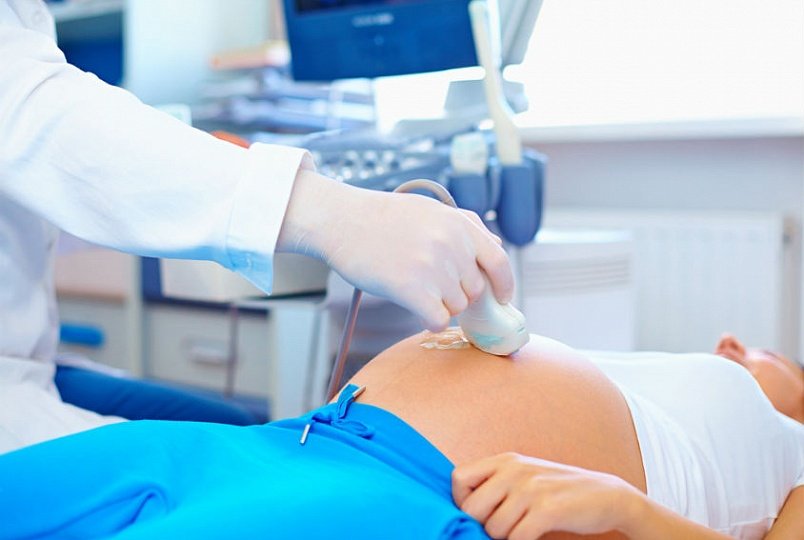
What to do if the doctor, having deciphered the Doppler data and compared them with the norms, states a violation of the blood flow of the pregnant woman? Well, do not panic and do not be nervous. It won't work for a child either. Timely prescribed treatment is quite effective in combating blood flow diseases.
Circulatory disorders in blood vessels during pregnancy vary in severity.
At the first degree, the violation of blood flow does not reach critical values. The hemodynamics of the fetus in this case is positive.
Hemodynamics of the fetus in the second degree of the disease is impaired. Half the time maximum speed blood flow through all heart valves is reduced. At the same time, blood circulation is disturbed both in the child and in the arteries of the uterus of the future woman in labor. In a very short period, the second degree can develop into the third.
The third degree is detrimental to the child. Her diagnosis states critical situation fetal blood supply. Intracardiac hemodynamics at this stage has profound changes. Hypoxia of the fetus is the most likely.
Can a pregnant woman feel blood flow disturbances? There are certain symptoms. But, for example, in the first stage, placental insufficiency does not manifest itself in any way. It can only be diagnosed by ultrasound. A symptom of the second degree is a change in the behavior of the baby. He is either too active or, on the contrary, inactive. Secondary signs of blood flow disease may be the excretion of protein in the urine, insufficient or excessive amount amniotic fluid, edema, preeclampsia (late toxicosis), pressure surges, sudden weight gain.
Bloody discharge from birth canal- most danger sign disorders associated with placental abruption. In such a situation, only Ambulance specialists.
The consequences of impaired blood flow are very sad if treatment is not prescribed in time. It is at least acute or chronic hypoxia and intrauterine growth retardation. More severe complications: premature birth; fading pregnancy; miscarriage; development congenital pathologies, including those incompatible with life; intrauterine fetal death.
In order to prevent the disastrous consequences of impaired blood circulation, we need, first of all, thorough prevention.
In order for the baby’s nutrition to be complete, in the process of bearing, a woman must consume a balanced diet. These are products with maximum possible number vitamins and microelements. Quality proteins, carbohydrates and fats. Frequent water consumption (more than one liter) is also required. Except in cases where the future woman in labor is prone to swelling.

Prevention of blood flow disorders involves monitoring weight changes during gestation. An increase of more than 10 kg by the end of pregnancy is already considered excessive.
If the pregnant woman is at risk (under 17 years of age or over 36 years of age; with bad habits; having chronic diseases and so on), then prevention should include taking medications preventing blood flow diseases.
A woman who dreams of becoming a mother of a healthy baby in the future should analyze her lifestyle during pregnancy planning and eliminate, if possible, potential risks.
Video on the topic of the article

