How to treat endometrial hyperplasia of the uterus. Endometritis: causes, types, symptoms and treatment. Symptoms of a chronic course
By modern ideas, endometritis, or inflammation of the uterine lining, is referred to as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women. According to doctors, in recent times worldwide there is a clear trend towards an increase in the incidence of PID, including endometritis.
Of particular danger is the chronic course of the disease, the prevalence of which, according to various sources, is from 10 to 85%. Such a wide range is due to the difficulty of diagnosis and the low severity of symptoms. chronic endometritis. The disease is often detected already at the stage of complications: for example, miscarriage or infertility. In this regard, the question becomes especially relevant: is it possible to cure endometritis and prevent the development of its consequences?
Endometritis does not predict reproductive morbidity after pelvic inflammatory disease. Endometrial microlips on liquid hysteroscopy suggest the existence of chronic endometritis. Correspondence between hysteroscopic and histological findings in women with chronic endometritis. Chronic endometritis due to common bacteria is common in women with recurrent miscarriage, as evidenced by improved pregnancy outcome after antibiotic treatment. Hysteroscopy and histological diagnosis and treatment of chronic endometritis in patients with recurrent implantation.
A bit of anatomy
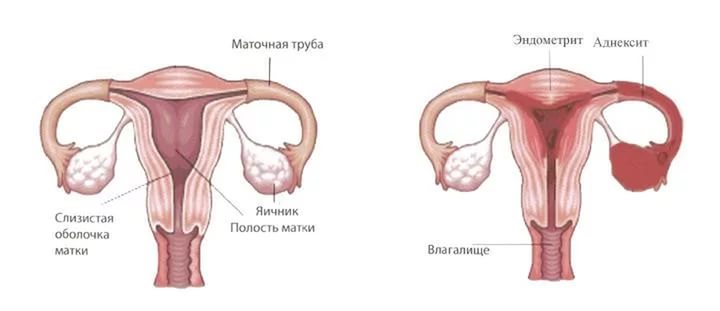
Before answering the question: what is endometritis, it is necessary to briefly dwell on anatomical features walls of the uterus. As you know, three layers or shells are distinguished in its structure:
- External (perimetry).
- Muscular (myometrium).
- Internal (endometrium).
The endometrium is abundantly supplied with blood and is a hormonally dependent tissue. It, in turn, is formed by two layers:
Efficiency of the Isaac cell sampler for endometrial cultures. Sterility of the uterine cavity. Bacterial colonization non-pregnant uterus: Examination of premenopausal abdominal hysterectomy specimens. Elevated vaginal pH and neutrophils are strongly associated with early spontaneous preterm birth.
Antibacterial activity of the mucous membrane of the human cervix. Antimicrobial factors in the cervical mucosa. differential expression of natural antimicrobials, beta-defensins 3 and 4, in human endometrium. Menstruation as a defense against pathogens transported by semen.
- Superficial or functional. It consists of a cylindrical epithelium and many glands. This part of the endometrium of the uterus is “responsible” for the normal attachment (implantation) of the embryo. If conception does not occur, this layer falls off and is removed from the uterus during menstrual bleeding.
- Basal or growth. Connects to the underlying muscle layer. Causes the restoration of the superficial part of the endometrium.
The thickness of the endometrium directly depends on the effect of female sex hormones during menstrual cycle reaching its maximum in the luteal phase. At the same time, its structure also changes.
Applying biofilm science to study and control chronic bacterial infections. Enterococcus Entococcal endocarditis in a patient with transposition of great vessels. Is the otitis media shedding a biofilm? Direct evidence of bacterial biofilms in the otitis media.
Plaque biofilm control. Pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. The role of growth factors and cytokines during implantation: endocrine and paracrine interactions. Expression of macrophage inflammatory protein-1beta in human endometrium: its role in the endometrial recruitment of natural killer cells. The answer is not easy.
Thus, the uterus prepares for possible pregnancy, causing everything the necessary conditions for normal attachment and further development embryo.
Endometritis - what is it?
This term literally means "inflammation of the endometrium (the inner lining of the uterus)." Endometritis in women usually develops in childbearing age, causing the emergence of many problems that affect the possibility of conception and pregnancy in the future.
Infection concept lower divisions genital tract with chlamydia or gonorrhea, causing cervicitis and vaginal discharge, is familiar to most sexual health practitioners. What is less known, and where there is no clear indication at this time, is whether this intermediate stage of endometritis is self-limiting. clinical condition and if so, how it should be diagnosed and treated. Endometritis is pathological diagnosis with normal infiltration vascular system inflammatory cells.
Endometrial sampling is usually done using an endometrial suction biopsy device, which is inserted through the cervix to obtain a small piece of endometrial tissue. This is usually a simple, well-tolerated procedure performed in outpatient settings. Unfortunately, fixation, staining, and reporting of the endometrial sample takes several days, and even slight delays in confirming the diagnosis and initial therapy pelvic infection may have serious consequences for future fertility.
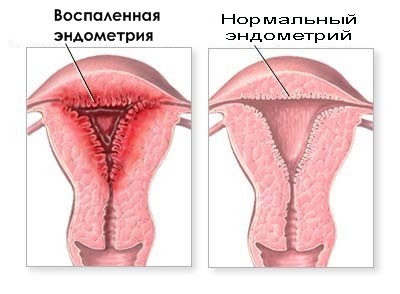
Inflammation of the uterine mucosa, both in acute and chronic variant of the course of the disease, usually affects both layers of the endometrium. The prevalence of the inflammatory process is:
- Diffuse (the entire mucous membrane is affected).
- Focal.
In addition, chronic endometritis is often combined with inflammation of other structures of the female genital tract, such as the fallopian tubes. Also pathological process can spread to the deeper layers of the uterus (myometrium), changing the normal cellular structure of the uterine wall. All this ultimately leads to serious violations menstrual and reproductive function women.
This limits the clinical applicability of this approach for diagnosis, as well as theoretical risk introducing an infection into the upper genital tract when taking an endometrial biopsy. A faster assessment of endometrial inflammation can be obtained by looking at a gram-stained smear or wet mount of vaginal discharge. An increase in the number of polymorphs in a discharge is associated with endometritis, although the correlation is not particularly strong. In other words, the absence of pus cells makes endometritis very unlikely, but their presence is not specific.
Therefore, it is possible to characterize the chronic course of endometritis as immediate cause female infertility.
The reasons
The main causes of endometritis are infection in combination with certain risk factors. Inflammatory process can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa and other infectious agents.
Other Features vaginal smear, such as a decrease in lactobacilli, may also support the diagnosis of endometritis but have not been rigorously evaluated. Endometritis usually occurs in women who have otherwise had an uncomplicated lower genital tract infection. About a quarter of women with cervical gonorrhea or chlamydia will also have endometritis on an endometrial biopsy, as will 15% of women with bacterial vaginosis. Predicting that women will have endometritis, as opposed to an infection limited to the lower genital tract, is difficult.
According to statistics, a sexually transmitted infection (STI) plays a large role in the occurrence of endometritis. It is detected in more than 70% of cases. The most common STD pathogens are:
- Gonococcus.
- Chlamydia.
- Urea and mycoplasmas.
- Genital herpes virus.
- Cytomegalovirus and others.
Also, the inflammatory process in the uterine cavity can also be caused by opportunistic flora, the pathogenic properties of which are activated under the influence of various adverse factors. In this case, an important role is played anaerobic bacteria(bacteroids, coli, some types of streptococci and others.).
The presence of endometritis is not associated with behavioral or demographic characteristics such as age, ethnicity, condom use, or sex during menstruation. Oral use birth control pills by itself does not increase the risk of developing endometritis, but appears to increase the risk of asymptomatic endometritis.
One of the few features that have been associated with endometritis is the phase of the menstrual cycle. This suggests that women are most at risk inflammation of the infection and cause inflammation of the endometrium only after their period, possibly due to loss of cervical mucosa or hormonal changes affecting the local immune function. It also raises the possibility that endometritis may, at least in a subgroup of women, be a temporary phenomenon with spontaneous clearance occurring within a few weeks.
In a significant number of cases with endometritis, an association of microorganisms is isolated, that is, the inflammatory process is caused by several infectious agents at once.
How does the infection enter the uterus?
The main routes of entry infectious agent in the uterine cavity are:
How to treat the disease in the acute phase?
Vaginal douching was associated with a higher incidence of endometritis, but only in those women who had recently shrouded or given a history of frequent douching. It has been suggested that douching "washes away" the normal vaginal flora, increasing the risk bacterial vaginosis which in turn predisposes to endometritis. Interestingly, the association between douching and endometritis is only seen in those who do not have bacterial vaginosis, somewhat contradicting this theory.
- Sexual. special role plays an active transfer by spermatozoa of some STI pathogens, for example, chlamydia.
- Ascending (from the vagina through the cervix).
In a healthy woman, the uterine cavity is sterile. This condition is caused, first of all, by the normal function of the cervix, which is a barrier between aggressive external environment and internal structures female genital tract. If the cervical barrier is violated, the infection gains free access to the uterine cavity and other internal genital organs of a woman.
This highlights the difficulties in interpreting the relationship between infection upper divisions genital tract and douching, because until recently the studies were all retrospective and therefore unable to explain cause and effect. Recently, putative data have been presented indicating that women who are not at risk of more high risk upper genital tract infections than those who do not.
Acute endometritis: symptoms
Endometritis is associated with abdominal pain, as well as with vaginal discharge, cervical tenderness, and pyrexia, although at a slower rate than with salpingitis. Endometritis also leads to increased levels peripheral blood and erythrocyte sedimentation rate, which indicates its clinical relevance. The presence of endometritis on endometrial biopsy correlates well, although not completely, with salpingitis—its positive and negative predictive values are about 90%.
In other cases, the infection can penetrate in the following ways:
- Hemato- or lymphogenous (respectively, through the blood or lymphatic vessels).
- From adjacent purulent foci along the peritoneum (for example, with appendicitis).
Sexual and ascending path infections are leading in the development of the disease and occur in more than 90% of women.
Thus, endometritis is usually associated with salpingitis but may occur in isolation. Does endometritis need treatment? Nearly half of the patients in the study failed to clear their initial endometritis despite a good clinical response, and no correlation was found between the absence of endometrial inflammation and subsequent symptoms. In addition, the presence of endometritis at initial diagnosis did not negative influence on subsequent long-term outcomes such as pregnancy, infertility and chronic pelvic pain.
Risk factors
Acute endometritis most often occurs after mechanical trauma to the endometrium or damage to the cervical barrier. This is found in postpartum period or after some medical manipulations:
- Curettage of the uterine cavity (diagnostic, for the purpose of abortion).
- Hysteroscopy.
- The introduction of an intrauterine contraceptive ("spiral").
- Probing of the uterine cavity.
- Carrying out the procedure of in vitro fertilization.
Endometritis after curettage of the uterine cavity or other medical and diagnostic manipulations may occur due to non-compliance with sterile conditions during the procedure.
Indeed, the trend has been that endometritis improves these outcomes. Endometritis can be defined based on histopathological findings and appears to be common in women with asymptomatic lower genital tract infections. Endometritis can be great clinical syndrome requiring treatment in those women who are symptomatic but currently lacking evidence or against active screening and treatment asymptomatic women in the absence of infection of the lower genital tract.
The development of inflammation of the endometrium in the postpartum period is primarily affected by the nature of childbirth. So, the risk of developing endometritis increases in such conditions:
- Delivery by caesarean section, imposing obstetric forceps.
- Bleeding.
- preterm birth
- Chorioamnionitis.
- Injuries of the birth canal.
- Manual examination of the uterine cavity (for example, with a delay in the separation of the placenta) and other pathologies.
In addition to direct mechanical impact on the uterine mucosa, other factors are also related to the development of endometritis. These include:
Uterine infection is referred to in jargon as endometritis. It can spread to different layers of the body and be taken seriously. Especially after childbirth, mothers are especially vulnerable, so more attention needs to be paid. When in doubt, you should not wait too long for a doctor's visit.
Basics: The structure of the uterus
To understand the condition of endometritis, you must first get to know the anatomy of the uterus better. The mother is pear-shaped. It belongs to the sexual organs of a woman. The uterus consists of an overlying body and a short narrowing called the isthmus. The narrowing separates the cervix from other parts of the uterus.
- Extragenital diseases.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- immunodeficiency states.
- Endocrine diseases (especially diabetes mellitus).
- Chronic inflammatory pathology.
- Anomalies in the development of the genital organs.
- sexual behavior ( frequent change partners, neglect barrier means protection, sex during menstruation, etc.).
- Prolonged stress, malnutrition, physical overload, bad habits and others external influences reducing immune resistance.
Chronic endometritis often develops as a result of inadequate treatment of an acute inflammatory process.
Symptoms of a chronic course
The uterine wall is part of the body of the uterus and consists of the following layers. The symptoms that cause endometritis depend on the inflamed uterine lining. However, mild bleeding disorders, prolonged periods, and bleeding after intercourse are the first warning signs. When exposed to muscle layer myometrium causes abdominal pain and sometimes fever. In these cases, the doctor speaks of myometritis. The uterine lining was called the gynecologist's perimetric.
Therefore, there are often complaints about vaginal area. These include, in particular, itching and unpleasant burning in the genital area. Another characteristic feature is a change in vaginal discharge, which usually smells and is colored in a yellowish-purulent condition.
Manifestations

Symptoms and treatment of endometritis directly depend on the phase of the inflammatory process (acute or chronic), as well as the root causes of the disease.
It is often possible to trace a direct relationship between previous intrauterine intervention and manifestations of the disease. Remains placental tissue, parts of the fetus (with incomplete abortion) serve as an excellent nutrient medium for pathogenic bacteria and contribute to the development of inflammation in the uterus.
Causes and risk factors - How does a uterine infection develop?
If you notice any symptoms, see your doctor as soon as possible. Infection of the uterus occurs whenever natural defense mechanisms organs are damaged. Accordingly, various triggers are taken into account. The most common causes are the effects of birth. Even after the birth process is completed, the cervix remains slightly open for the next six to eight weeks. In this phase of postpartum bacteria more easily enter the weakened body of a woman and cause inflammation.
Chronic endometritis is often diagnosed in women with miscarriage, a history of unsuccessful IVF attempts, and other pathologies. And to establish the true duration of the disease is sometimes simply impossible.
Spicy
Symptoms of endometritis in women with it acute course usually develop within a few days after infection. Acute endometritis is manifested by the following symptoms:
If the resulting endometritis is left untreated, it develops life threatening turtle fever. In this case, the pathogens have spread through the bloodstream, so this happens with blood poisoning. Therefore, you must be careful when you notice nausea or similar symptoms in the postpartum period.
Especially in older women hormonal change as a reason. Estrogen deficiency, as is common during menopause, adversely affects the stability of the endometrium. It is less stable and therefore more susceptible to germs. In addition, the age of formation of uterine secretion decreases, so that another protective mechanism is weakened.
- A sharp increase in body temperature, often up to high numbers (39-40 degrees).
- Severe intoxication manifestations: increased heart rate, chills, weakness, headache etc.
- Sharp pains in the lower abdomen.
- Vaginal discharge with endometritis becomes sanious or purulent, has an unpleasant odor.
- Often there is frequent and painful urination.
During the examination, the doctor reveals an enlarged and painful uterus, purulent discharge from cervical canal. Palpation of the side walls of the uterus also becomes painful, which is associated with damage to the lymphatic vessels.
Acute endometritis usually lasts up to ten days. With insufficient or ineffective treatment endometritis in this phase, it acquires a chronic course.
Chronic

This form of the disease is sometimes called "sluggish endometritis", which accurately characterizes its course. Signs of chronic endometritis are usually mild and, in most cases, are nonspecific.
Often there is an asymptomatic course of the disease, in which signs of endometritis can be detected only during additional methods examinations. In such women, the disease is often diagnosed already at the stage of complications (most often infertility).
Chronic endometritis is most often characterized by the following symptoms:
- Intermittent or permanent pain in the lower abdomen (sometimes in the lower back).
- Pathological vaginal discharge which have a mucopurulent or serous character.
- Menstrual disorders. Frequent uterine bleeding, intermenstrual bloody issues, prolonged and / or heavy menstruation.
- Discomfort or even pain during sexual intercourse.
Chronic endometritis is not accompanied by an increase in body temperature, manifestations of intoxication and other symptoms characteristic of the acute phase. And the above signs of endometritis may be unexpressed or absent altogether. This fact greatly complicates the timely diagnosis and treatment of chronic endometritis.
Diagnostics
correct and timely diagnosis significantly increases the success of the treatment of endometritis in women. For this, the following methods are used:
- Collection of anamnesis. In most cases, the onset of the disease is preceded by intrauterine interventions, childbirth (especially pathological ones), the introduction of an IUD, etc.
- General clinical and gynecological examination.
- Ultrasound scanning using dopplerography (usually performed at the beginning and end of the menstrual cycle).
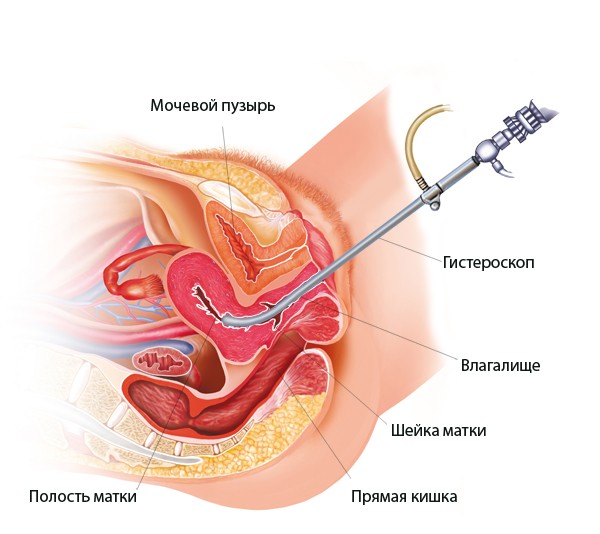
- Endometrial biopsy or diagnostic curettage followed by mandatory histological examination received material.
- Hysteroscopy.
- Identification of an infectious agent (bacteriological, bacterioscopic method, ELISA, PCR, etc.).
Usually, all these activities are carried out in a complex, which allows you to more accurately establish the diagnosis and find out how to treat uterine endometritis.
Endometritis on ultrasound is characterized by an increase in the uterus, pronounced changes in the thickness of the endometrium, and the unevenness of its contours. There are areas of different echogenicity and density.
In addition, the echo signs of chronic endometritis often include the detection of gas bubbles in the uterine cavity and its expansion, clear hyperechoic inclusions in the endometrium (calcifications) and other symptoms.
Instrumental examination (biopsy, hysteroscopy, curettage of the uterus) is usually carried out in the first phase of the cycle for the purpose of diagnosis chronic course diseases. Based on the histological findings, morphological changes endometrium, active or inactive endometritis, etc.
Treatment
![]()
Therapy of inflammatory lesions of the endometrium is a rather difficult task. Acute endometritis requires urgent hospitalization and treatment in a hospital setting. In the chronic course of the disease, therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis.
How to cure endometritis? First of all, you should carefully follow all the doctor's prescriptions. For example, incomplete course antibiotic therapy often a major transition factor acute form disease into a chronic one.
Basic principles of treatment:
- Antibacterial therapy. Antibiotics for endometritis are always used, given the infectious and inflammatory genesis of the disease. Such drugs are prescribed taking into account the sensitivity of the selected microflora. Usually used cephalosporins, semi-synthetic penicillins, aminoglycosides and other groups of antibacterial drugs.
- Be sure to prescribe agents that affect the anaerobic flora (for example, metronidazole).
- Drugs with detoxifying and immunomodulatory effects.
- Local preparations ( vaginal suppositories with antibiotics and metronidazole).
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Prevention of dysbacteriosis - antifungal drugs.
- Surgical treatment for acute endometritis (removal of remnants gestational sac, placental tissue, etc.) is carried out only against the background of massive antibiotic therapy.
In order to completely cure endometritis, successfully applied various methods physiotherapeutic influence, sanatorium-and-spa treatment. AT acute phase endometritis physiotherapy should be used only after the inflammatory manifestations subside.
Chronic

Given the "insidiousness" of the course of this disease, the question is natural: is it possible to cure chronic inflammation of the endometrium?
The treatment regimen for chronic endometritis is determined only by the attending physician. In this case, morphological changes in the structure of the endometrium, the presence of synechia in the uterine cavity and associated disorders are necessarily taken into account. reproductive system women. Therefore, it is possible to cure chronic endometritis only with integrated approach to therapy, and the patient's compliance with all doctor's prescriptions.
Treatment chronic inflammation endometrium in most cases produced in several stages. The goals of this therapy are:
- Elimination of a bacterial or viral factor that damages the endometrium.
- Recovery normal function damaged endometrium.
At the first stage, antibacterial or antiviral drugs according to the identified infectious agent. If it is impossible to determine the type of microbe, then the so-called empirical antibiotic therapy is used. a wide range actions. Antibacterial drugs applied both systemically and locally (by introduction into the uterine cavity).
Restoration of the impaired function of the uterine mucosa takes quite a long time. The following treatments are commonly used:
- Enzyme therapy.
- Fortifying drugs, vitamins, immunostimulants, etc.
- desensitizing therapy.
- Physiotherapy - exposure to magnetic fields, electrophoresis, UHF, ultrasound, infrared rays, etc.
- Mud therapy and balneotherapy (baths, irrigation).
- Surgical intervention is used only in the presence of synechia (fusions or adhesions) in the uterine cavity.
With a broken menstrual function appointed hormonal preparations, for example, combined oral contraceptives or monopreparations (estrogens, progesterone).
Effects

The inflammatory process in the uterine mucosa, especially with its prolonged course, can provoke the development serious complications. These include:
- Spreading infectious process on other structures of the female genital tract.
- Infertility.
- Increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Miscarriage.
- Pathology of placenta attachment.
- Complicated course of pregnancy: placental dysfunction, fetal hypoxia, etc.
- premature birth.
- Infection of the fetus and newborn.
- Stillbirth.
- Autoimmune pathology.
- Menstrual disorders, uterine bleeding.
- antiphospholipid syndrome.
- Syndrome of chronic pelvic pain.
- Adhesions in the uterine cavity (Asherman's syndrome).
- Leiomyoma of the uterus.
- Endometriosis.
- Dyspareunia (pain during intercourse) and other disorders.
Development prevention inflammatory lesions the endometrium is simple. It consists, first of all, in elementary rules sexual hygiene (permanent sexual partner, the use of barrier methods to protect against genital infections). It is also important to visit your gynecologist regularly for early detection and treatment of latent infections of the female genital tract.
You have disabled java script in your browser, you need to enable it or you will not be able to get all the information on the article "Endometritis and manifestation symptoms".
Endometritis - the main symptoms:
What is endometritis? This is a disease characterized by an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the uterus. This process does not affect the muscle layer of the affected organ. Very often this disease is confused with metroendometritis, although these are completely two various diseases. In the second option, a much sadder prognosis is observed, because after suffering metroendometritis, it is not always possible to get pregnant.
The reasons
The root cause of the formation of the disease is damage to the mucous membrane of the uterus, which contributes to the formation of the inflammatory process. But by itself, such a pathology cannot provoke endometritis. Important role this process is played by reduced immunity, non-compliance with sanitary standards when performing manipulations. In addition, the following common causes are distinguished:
- curettage of the uterine cavity;
- probing the uterine cavity;
- hysterosalpingography;
- endoscopic diagnosis of the uterine cavity;
- installation of intrauterine contraceptives;
- careless douching.
Today, postpartum endometritis has become of particular importance. They are associated with restructuring. immune system female body. The inflammatory process very quickly affects the muscular layer of the uterus and serves dangerous complication postpartum period.
Endometritis refers to polyetiological diseases, the occurrence of which is influenced by many pathogens:
- group B streptococci;
- coli;
- klebsiella;
- enterobacter;
- Proteus;
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasmas;
- diphtheria bacillus;
- tuberculosis mycobacterium.
Chronic endometritis occurs due to improper acute therapy, as well as in the case when the infection settles in the tissues for a long time. The causative agents of the disease can be listed above.
How does the disease manifest itself?
Symptoms of endometritis are not pronounced, so a woman cannot immediately detect them. This phenomenon contributes to the development of inflammation in severe form, as a result of which it also affects the muscle layer of the organ. This situation requires immediate hospitalization and inpatient treatment.
A timely visit to the doctor will allow timely treatment of endometritis and avoid its transition to metroendometritis.
There are chronic endometritis and acute. If the diagnosis and treatment of acute endometritis is not difficult, then chronic form causes many difficulties. This is another factor that requires careful diagnosis if there are symptoms of endometritis.
Acute manifestations of the disease
Acute endometritis is formed due to artificial termination of pregnancy. In most cases, this is due to non-compliance with all necessary sanitary standards. Acute endometritis manifests itself as follows:
- increase in body temperature up to 38–39 ° C;
- the occurrence of serous and bloody-purulent discharge from the vagina;
- pain in the abdomen, radiating to the sacrum;
- general malaise.
In the current situation it is required immediate help specialist and it is forbidden to self-medicate, since acute endometritis is inflammatory disease, so it can affect various tissues located near the primary focus.
When postponing a trip to the doctor, each woman increases the risk of severe purulent-septic complications that require careful treatment. The result of this kind of complications will be sepsis with a fatal outcome.
Manifestations of a chronic disease
Chronic endometritis has almost the same symptoms as acute. The manifestations in this case are blurred. Chronic endometritis manifests itself as follows:
- Elevated body temperature that lasts for a long time.
- Irregular bleeding from the uterus. This process is also typical for healthy women, but blood cells are invisible in the secretions. Contribute to the formation of uterine bleeding such factors as a decrease contractile activity penis and violation of platelet aggregation properties.
- Discharge from the vagina, having a putrefactive character.
- Pain during defecation.
Are chronic endometritis and pregnancy compatible concepts? As a rule, such an ailment does not prevent conception, which occurs in the presence of ovulation. Another thing is when chronic endometritis is combined with other genital pathologies. In this case, you can get pregnant, but most often this leads to spontaneous miscarriages.
Endometritis and childbearing
Endometritis and pregnancy - these words are very scary for many women who decide to become mothers? You can get pregnant, but only if the treatment was started on time and there were no complications. Although it is impossible to say for sure. Many doctors on the issue of pregnancy and endometritis are inclined to believe that it will be impossible to conceive and bear a baby, since this disease causes adhesions leading to infertility. As practice shows, during pregnancy and endometritis, this disease does not affect the functioning of the ovaries, but the question of engraftment of the embryo and its further bearing remains relevant.
Most patients refuse to take antibiotics and in vain, since after conceiving a baby, and even more so, it will be much more difficult to endure it. You can take antibiotics even during gestation, since pregnancy after treatment of acute or chronic endometritis will last until the end of the term without pathologies for the child.
Diagnostic study
Diagnosis of the presented disease should begin with the doctor carefully listening to all the complaints of the patient. There are situations when, on the basis of the manifestations of acute endometritis, a diagnosis can be made. However, to confirm the disease, the doctor must perform next row actions:
- Examine the woman gynecological chair. Such a diagnosis will allow him to evaluate the present secretions: color, smell and quantity.
- Take swabs and send them for research. The results of smears will help to find out about the presence of pathogens of endometritis. The doctor takes smears for culture for more exact definition the nature of the pathogen and its reaction to certain drugs.
- General blood analysis.
- Ultrasound of the uterus. Such a study is appointed if necessary. With the help of ultrasound, it is possible to detect thickening of the mucous membrane, characteristic blood and purulent clots, and affected the fallopian tubes, ovaries.
Therapy
After the diagnosis has been made, you can proceed to the treatment of endometritis. It is the gynecologist who, on the basis of the results of the tests, will be able to draw up an effective treatment regimen.
Endometritis and pregnancy may not depend on each other if therapeutic measures were started on time and there were no complications. Treatment of endometritis should take place in outpatient under the direct supervision of the attending physician. The therapy scheme provides for the following action plan:
- antibacterial drugs;
- antibiotics;
- mechanical cleaning of the uterine cavity;
- cleansing the plasma from harmful toxins and bacteria.
How to treat the disease in the acute phase?
Early diagnosis of acute endometritis and modern therapy You can prevent all complications and get pregnant safely. Acute endometritis can be treated with the following action plan:
- Immunomodulators and vitamins.
- Antibiotics. The following drugs are prescribed: Metril in combination with Cephalosporins intravenously. The course of therapy is 5-10 days.
- If, after an abortion, the remains of the fetus or placenta were found, then it is advisable to repeat the curettage of the uterine cavity.
- Treatment of endometritis with physiotherapeutic methods.
How to treat a disease in the chronic phase?
Chronic endometritis has its own symptoms, different from the acute form. Therefore, the treatment of chronic endometritis is to stop specifically the causative agent of the disease.
First of all, the doctor should take smears for culture and check the susceptibility a certain kind pathogen for various antibiotic drugs. After that, he will be able to draw up a specific treatment regimen for chronic endometritis. Next is assigned efficient scheme therapy, including joint reception antibiotics and antiviral drugs.
Most effective treatment chronic endometritis is an input medicinal medicines into the lining of the uterus. This approach contributes to the concentration of the maximum amount medicines at the site of inflammation. In addition to the above, the following therapeutic methods are used to treat chronic endometritis:
- hormone therapy. This is where oral contraceptives come into play. Such events should be carried out in the case when a woman dreams of pregnancy and chronic endometritis will not interfere with this.
- Separation of formed adhesions by the surgical method.
- Physiotherapy for the treatment of chronic endometritis. If the patient's condition has returned to normal, then it is advisable to use physiotherapeutic methods of therapy. They increase the outflow of mucus and pus from the uterine cavity, and also improve local reparative functions.
Therapy of purulent endometritis
Treatment of chronic endometritis of a purulent nature includes mechanical cleaning of dead tissues and pus of the uterine cavity. This manipulation is characterized unpleasant sensations, so they perform it under general anesthesia. After that, hormonal drugs are prescribed.
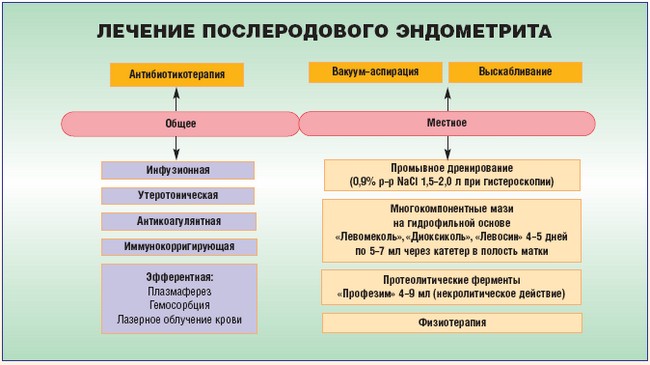
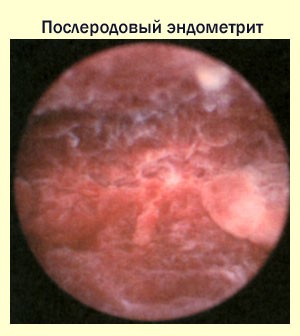
Postpartum endometritis occurs after unsuccessful removal of the placenta after delivery. Therapy for this form of the disease includes taking antibiotics. The treatment regimen is compiled individually for each breastfeeding woman. Timely diagnosed postpartum endometritis does not need a rehabilitation course. In order for postpartum endometritis to disappear, it is necessary to be under the supervision of a doctor all the time and fulfill all his appointments.
Preventive methods
If there is a possibility that postpartum endometritis will form, then prevention includes taking antibacterial medications. Prevention after therapy is based on the implementation of all sanitary standards during uterine bleeding, abortion, childbirth. A prerequisite is a regular visit to the gynecologist, who would be able to timely identify all pathologies. To protect yourself from exacerbations of endometritis, you need to constantly strengthen your immune system.
Endometritis is dangerous female disease, which most often occurs due to non-compliance with sanitary standards during such manipulations as childbirth and abortion. characteristic symptoms pathologies are purulent discharge from the genitals and fever. Treatment of the disease is selected individually, taking into account the form of the disease: chronic or acute.
If you think you also have symptoms that are characteristic of this disease, then a doctor can help you.

