HDL cholesterol is lowered. High density lipoproteins (HDL) - what is it
Lipoproteins high density, called "good" cholesterol, are made in the liver. HDL cholesterol slows down the development of atherosclerosis. It removes "bad" cholesterol from all cells, including those responsible for the formation atherosclerotic plaques.
The study of HDL values is an integral part of the main preventive and therapeutic measures aimed at lowering the level of lipids in the blood.
HDL and LDL
HDL cholesterol is made in the liver. It arises as a particle, consisting mainly of protein, is transported by the blood to all tissues and "takes" lipids from them. "Accepted" cholesterol is transported to the liver, where it becomes part of the bile. Thanks to this mechanism, the body gets rid of excess fat.
LDL is a lipoprotein composed primarily of fats. It is responsible for excess cholesterol in tissues, as well as for the formation of atherosclerosis. Therefore, HDL particles act in the opposite way to LDL particles.
"Good" cholesterol - a protective effect
High density lipoproteins slow down the development of atherosclerosis. In addition, they have an antioxidant effect, which is to remove free radicals that cause damage to the LDL molecule. Damage to LDL particles causes them to stay in the blood for a long time, which contributes to the formation of atherosclerosis. HDL inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory particles in the vessel. It limits inflammatory processes in him. HDL molecules activate the regenerative potential of the cells lining the vessels. That is, they act:
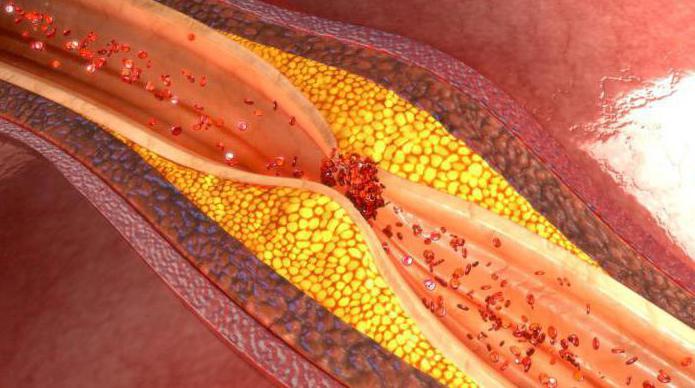
What lowers HDL levels?
If high-density lipoprotein cholesterol is lowered, this leads to adverse effects for good health. There is a gradual deprivation of the body of the mechanism that regulates the level of overall lipid balance.
Factors that reduce high-density lipoprotein levels:

These are basically the same factors that cause the increase LDL level. Therefore, dietary changes, increased physical activity, smoking cessation, appropriate treatment concomitant diseases should become the basis in the treatment of any lipid metabolism disorder. Improvement in lifestyle is necessary, also due to the fact that there is still no effective drug that raises the level of HDL in the blood. Medications can help lower the concentration of LDL fractions.
HDL cholesterol and cardiovascular disease
The concentration of "good" cholesterol below the limit values is synonymous with an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
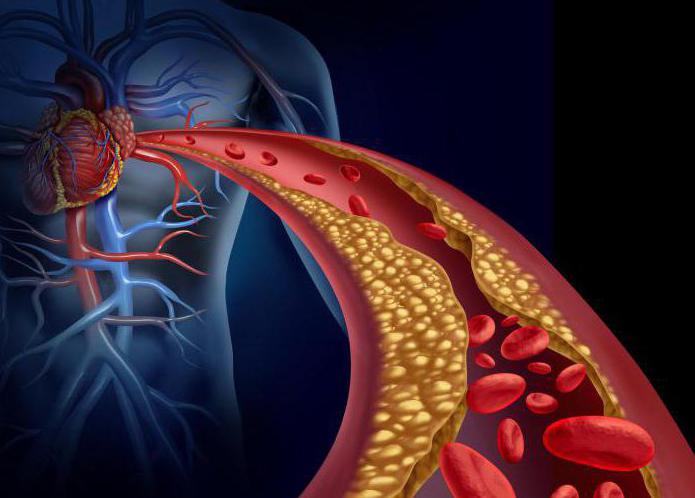
These include:
- arterial hypertension - pressure above 140/90 mm Hg. Art.;
- disease coronary artery, myocardial ischemia and insufficient supply of oxygen. Restriction observed physical performance, pain in chest myocardial infarction may occur;
- cerebral stroke - can lead to paresis of the limbs, muscle paralysis, limitation in normal functioning;
- renal ischemia, which increases with hypertension;
- ischemia lower extremities leads to pain in the limbs and difficulty in walking.
Low HDL cholesterol
The lower the concentration of HDL, the higher the risk of the diseases mentioned above. Cardiovascular disease is the second leading cause of death (after cancer) in highly developed countries. It should be borne in mind that lifestyle changes after the onset of diseases of the heart and blood vessels can lead to significant improvement well-being of the patient and the reduction of certain symptoms. If high-density lipoprotein cholesterol is elevated - the development of atherosclerosis is inhibited and even the size of atherosclerotic plaques is reduced. If you combine this with the corresponding pharmacological treatment and lower LDL, you can achieve really good therapeutic effect. And the risk, for example, of a second myocardial infarction, will decrease.
Indications for lipid profile testing
High-density lipoproteins are examined in the presence of any of the disease risk factors of cardio-vascular system, as well as the coexistence of diseases such as:
- diabetes;
- ischemic disease hearts;
- cerebrovascular disease;
- violations of blood flow in peripheral vessels;
- hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
The study is carried out within the framework of primary prevention health. This means that such a test should be carried out on everyone. healthy person at least once every 5 years. Standardly, four parameters are indicated in the study in aggregate:
- the level of total cholesterol;
- fractions of LDL;
- fractions of HDL;
- triglycerides.
Preparation and methodology for studying the lipid profile
 To explore HDL cholesterol in the blood, the patient needs to prepare in advance for the test. This is the application of a normal diet approximately 3 weeks before the study. It is necessary to avoid overeating, as well as reducing or changing typical eating habits. You should also take drugs that affect lipid metabolism and avoid alcohol completely.
To explore HDL cholesterol in the blood, the patient needs to prepare in advance for the test. This is the application of a normal diet approximately 3 weeks before the study. It is necessary to avoid overeating, as well as reducing or changing typical eating habits. You should also take drugs that affect lipid metabolism and avoid alcohol completely.
Immediately before donating a blood sample for research, the patient should refrain from eating for 12-14 hours. Intense physical activity should be avoided, and in case of illness or infection, the study should be postponed for 3 weeks.
After sampling venous blood in plasma, an enzymatic method (using esterase and oxidase) indicates "good" cholesterol. High-density lipoproteins (HDL) are noted in mg / dl or mmol / l.
High density lipoproteins - the norm
The normal level of the “good” cholesterol fraction is determined depending on gender and is:
- at least 40 mg/dl in men;
- at least 50 mg/dl in women.
Interpretation of research results
In the case of an incorrect HDL level, coexist also elevated level LDL and triglycerides.
You should know that the recommended form of treatment is always dietary restriction of animal fats and lifestyle changes, and only then drugs are applied.
The pharmaceutical products used are fibrates and nicotinic acid.
First control study blood lipids should not be carried out earlier than 4 weeks after the start of therapy. The optimal evaluation of treatment occurs after 3 months.
It is worth remembering that there are certain conditions, including completely physiological ones, that are associated with a change in the level of the HDL fraction:
- concentration can be increased in case of regular physical training;
- moderate alcohol consumption, mainly red wine;
- application hormone therapy estrogen.
A decrease in concentration occurs:
- in some genetically determined diseases, such as familial HDL deficiency;
- in patients diabetes;
- in people with metabolic syndrome;
- with obesity.
Diet - application rules
What to do if high density lipoproteins are below normal? How to increase HDL levels and reduce blood LDL levels with diet?
The rules for a balanced diet include:

Foods that increase HDL levels in the body
High-density lipoproteins can be increased in the blood if you include the following foods in your daily menu:

In the diet, you need to limit the intake of sugar, sweets, sugary sodas and processed foods. Do not over-consume foods that are a source of saturated acids, which are present in fatty meat, dairy products, butter, sour cream.
Lipoproteins (lipoproteins) of high and low density in the blood: what is it, normal, increase
Lipoproteins are complex protein-lipid complexes that are part of all living organisms and are essential integral part cell structures. Lipoproteins perform transport function. Their content in the blood is an important diagnostic test that indicates the degree of development of diseases of the body systems.
This is a class of complex molecules, which can simultaneously include free, fatty acid, neutral fats, phospholipids and in various quantitative ratios.
Lipoproteins deliver lipids to various tissues and organs. They consist of non-polar fats located in the central part of the molecule - the core, which is surrounded by a shell formed from polar lipids and apoproteins. The similar structure of lipoproteins explains their amphiphilic properties: simultaneous hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity of the substance.
Functions and meaning
Lipids play important role in the human body. They are found in all cells and tissues and are involved in many metabolic processes.
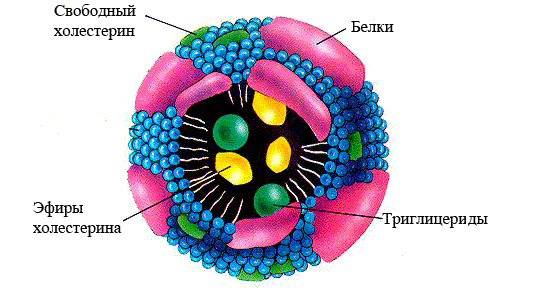
lipoprotein structure
- Lipoproteins are the main transport form of lipids in the body.. Since lipids are insoluble compounds, they cannot fulfill their purpose on their own. Lipids bind in the blood to proteins - apoproteins, become soluble and form a new substance, called lipoprotein or lipoprotein. These two names are equivalent, abbreviated - LP.
Lipoproteins occupy a key position in the transport and metabolism of lipids. Chylomicrons transport fats that enter the body with food, VLDL deliver endogenous triglycerides to the site of disposal, cholesterol enters cells with the help of LDL, HDL have antiatherogenic properties.
- Lipoproteins increase permeability cell membranes.
- LP, the protein part of which is represented by globulins, stimulate the immune system, activate the blood coagulation system and deliver iron to the tissues.
Classification
LP of blood plasma is classified by density(using the ultracentrifugation method). The more lipids are contained in the LP molecule, the lower their density. Allocate VLDL, LDL, HDL, chylomicrons. This is the most accurate of all. existing classifications LP, which was developed and proven using an accurate and rather painstaking method - ultracentrifugation.
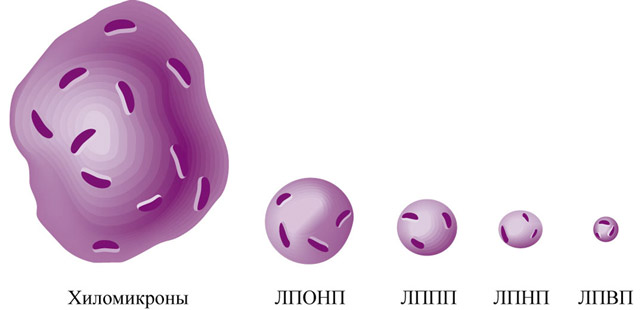
The size of the LP is also heterogeneous. The largest molecules are chylomicrons, and then in decreasing size - VLDL, HDL, LDL, HDL.
Electrophoretic classification LP is very popular among clinicians. Using electrophoresis, the following classes of LP were identified: chylomicrons, pre-beta lipoproteins, beta lipoproteins, alpha lipoproteins. This method based on introduction into a liquid medium active substance using galvanic current.
Fractionation LP is carried out in order to determine their concentration in blood plasma. VLDL and LDL are precipitated with heparin, while HDL remains in the supernatant.
Kinds
Currently allocate the following types lipoproteins:
HDL (high density lipoprotein)
HDL transports cholesterol from body tissues to the liver.
- An increase in HDL in the blood is noted with obesity, fatty hepatosis and biliary cirrhosis of the liver, alcohol intoxication.
- The decrease in HDL occurs when hereditary disease Tangier, caused by the accumulation of cholesterol in the tissues. In most other cases, a decrease in the concentration of HDL in the blood is a sign.
HDL levels are different for men and women. In males, the value of LP this class ranges from 0.78 to 1.81 mmol / l, the norm for women HDL is from 0.78 to 2.20, depending on age.
LDL (low density lipoprotein)
LDL are carriers of endogenous cholesterol, triglycerides and phospholipids from the liver to tissues.
This class of LP contains up to 45% cholesterol and is its transport form in the blood. LDL is formed in the blood as a result of the action of the enzyme lipoprotein lipase on VLDL. With its excess, they appear on the walls of the vessels.
Normally, the amount of LDL is 1.3-3.5 mmol / l.
- The level of LDL in the blood rises with hypofunction thyroid gland, nephrotic syndrome.
- Reduced LDL levels are observed with inflammation of the pancreas, hepatic-renal pathology, acute infectious processes, pregnancy.

infographics (click to enlarge) - cholesterol and LP, role in the body and norms
VLDL (very low density lipoproteins)
VLDL are formed in the liver. They carry endogenous lipids synthesized in the liver from carbohydrates into tissues.
These are the largest LPs, second in size only to chylomicrons. They are more than half made up of triglycerides and contain a small amount of cholesterol. With an excess of VLDL, the blood becomes cloudy and acquires a milky hue.
VLDL is a source of "bad" cholesterol, from which plaques form on the vascular endothelium. Gradually plaques increase, joins with the risk of acute ischemia. VLDL is elevated in patients with kidney disease.
Chylomicrons
Chylomicrons are absent in the blood of a healthy person and appear only in violation of lipid metabolism. Chylomicrons are synthesized in epithelial cells mucous membrane small intestine. They deliver exogenous fat from the intestines to peripheral tissues and liver. Most of the transported fats are triglycerides, as well as phospholipids and cholesterol. In the liver, under the influence of enzymes, triglycerides break down and fatty acids are formed, some of which are transported to the muscles and adipose tissue, and the other part binds to blood albumin.
![]()
what do major lipoproteins look like
LDL and VLDL are highly atherogenic- containing a lot of cholesterol. They penetrate the wall of the arteries and accumulate in it. When metabolism is disturbed, the level of LDL and cholesterol rises sharply.
The most safe against atherosclerosis are HDL. Lipoproteins of this class remove cholesterol from cells and contribute to its entry into the liver. From there, it enters the intestines with bile and leaves the body.
Representatives of all other classes of LP deliver cholesterol to cells. Cholesterol is a lipoprotein that is part of the cell wall. It is involved in the formation of sex hormones, the process of bile formation, the synthesis of vitamin D, which is necessary for the absorption of calcium. Endogenous cholesterol is synthesized in the liver tissue, adrenal cells, intestinal walls, and even in the skin. Exogenous cholesterol enters the body along with animal products.
Dyslipoproteinemia - a diagnosis in violation of lipoprotein metabolism
Dyslipoproteinemia develops when two processes are disturbed in the human body: the formation of LP and the rate of their excretion from the blood. H violation of the ratio of LP in the blood is not a pathology, but a development factor chronic disease, in which the arterial walls are compacted, their lumen narrows and the blood supply is disturbed internal organs.
With an increase in the level of cholesterol in the blood and a decrease in the level of HDL, atherosclerosis develops, leading to development of deadly diseases.
Etiology
Primary dyslipoproteinemia is genetically determined.

Causes secondary dyslipoproteinemias are:
- hypodynamia,
- Diabetes,
- Alcoholism,
- kidney dysfunction,
- hypothyroidism,
- hepatic-renal failure,
- Long-term use of certain medications.
The concept of dyslipoproteinemia includes 3 processes - hyperlipoproteinemia, hypolipoproteinemia, alipoproteinemia. Dyslipoproteinemia is quite common: every second inhabitant of the planet has similar changes in the blood.
Hyperlipoproteinemia - increased content LP in the blood due to exogenous and endogenous causes. The secondary form of hyperlipoproteinemia develops against the background of the underlying pathology. At autoimmune diseases LP are perceived by the body as antigens, to which antibodies are produced. As a result, antigen-antibody complexes are formed, which are more atherogenic than the drugs themselves.
Alipoproteinemia is a genetically determined disease with autosomal dominant inheritance. The disease is manifested by an increase in the tonsils with an orange coating, hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenitis, muscle weakness, decreased reflexes, hyposensitivity.
Hypolipoproteinemia — low blood levels of lipoproteins, often asymptomatic. The causes of the disease are:
- Heredity,
- malnutrition,
- Passive lifestyle,
- Alcoholism,
- Pathology of the digestive system,
- Endocrinopathy.
Dyslipoproteinemias are: organ or regulatory , toxigenic, basal - a study of the level of LP on an empty stomach, induced - a study of the level of LP after a meal, drugs or exercise.
Diagnostics
It is known that excess cholesterol is very harmful for the human body. But the lack of this substance can lead to dysfunction of organs and systems. The problem lies in hereditary predisposition, as well as in lifestyle and nutritional habits.

Diagnosis of dyslipoproteinemia is based on the history of the disease, complaints of patients, clinical signs- the presence of xanthoma, xanthelasma, lipoid corneal arch.
The main diagnostic method of dyslipoproteinemia is a blood test for lipids. Determine the coefficient of atherogenicity and the main indicators of the lipid profile - triglycerides, total cholesterol, HDL, LDL.
Lipidogram - method laboratory diagnostics, which reveals lipid metabolism disorders leading to the development of diseases of the heart and blood vessels. Lipidogram allows the doctor to assess the patient's condition, determine the risk of developing atherosclerosis of the coronary, cerebral, renal and hepatic vessels, as well as diseases of the internal organs. Blood is taken in the laboratory strictly on an empty stomach, at least 12 hours after the last meal. The day before the analysis exclude the intake of alcohol, and an hour before the study - smoking. On the eve of the analysis, it is desirable to avoid stress and emotional overstrain.
The enzymatic method for studying venous blood is the main one for determining lipids. The device fixes samples previously stained with special reagents. The diagnostic method allows you to conduct mass surveys and get accurate results.
Take tests to determine lipid spectrum with a preventive purpose, starting from youth, it is necessary 1 time in 5 years. Persons over the age of 40 should do this annually. Conduct a blood test in almost every district clinic. Patients suffering from hypertension, obesity, diseases of the heart, liver and kidneys are also prescribed a lipid profile. Burdened heredity, existing risk factors, monitoring the effectiveness of treatment are indications for prescribing a lipid profile.
The results of the study may be unreliable after eating on the eve of food, smoking, stress, acute infection during pregnancy, taking certain medications.
Diagnosis and treatment of pathology is carried out by an endocrinologist, cardiologist, therapist, doctor general practice, family doctor.
Treatment
plays a huge role in the treatment of dyslipoproteinemia. Patients are advised to limit the intake of animal fats or replace them with synthetic ones, eat up to 5 times a day in small portions. The diet should be enriched with vitamins and dietary fiber. Fatty and fried foods should be abandoned, meat should be replaced sea fish, eat a lot of vegetables and fruits. Restorative therapy and sufficient exercise stress improve general state sick.

figure: useful and harmful "diet" in terms of LP balance
Lipid-lowering therapy and antihyperlipoproteinemic drugs are designed to correct dyslipoproteinemia. They are aimed at lowering the level of cholesterol and LDL in the blood, as well as increasing the level of HDL.
Of the drugs for the treatment of hyperlipoproteinemia, patients are prescribed:
- - Lovastatin, Fluvastatin, Mevacor, Zocor, Lipitor. This group of drugs reduces the production of cholesterol by the liver, reduces the amount of intracellular cholesterol, destroys lipids and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Sequestrants reduce the synthesis of cholesterol and remove it from the body - Cholestyramine, Colestipol, Cholestipol, Cholestan.
- I lower the level of triglycerides and increase the level of HDL - "Fenofibrate", "Ciprofibrat".
- B group vitamins.
Hyperlipoproteinemia requires treatment with hypolipidemic drugs "Cholesteramine", " Nicotinic acid”,“ Miscleron ”,“ Clofibrate ”.
Treatment of the secondary form of dyslipoproteinemia is to eliminate the underlying disease. Patients with diabetes are advised to change their lifestyle, regularly take sugar-lowering drugs, as well as statins and fibrates. In severe cases, insulin therapy is required. With hypothyroidism, it is necessary to normalize the function of the thyroid gland. For this, patients undergo hormone replacement therapy.
Patients suffering from dyslipoproteinemia are recommended after the main treatment:
- Normalize body weight
- Dose physical activity,
- Limit or eliminate alcohol consumption
- Avoid stress and conflict as much as possible
- Give up smoking.
Video: lipoproteins and cholesterol - myths and reality
Video: lipoproteins in blood tests - the program "Live healthy!"
We will learn about the risks associated with low HDL cholesterol levels. We explore the symptoms and causes of low cholesterol values well, and we see how to return values to the level of a physiological diet.
What is HDL cholesterol
Low HDL is spoken of when it is concentration in peripheral blood turns out below 40 mg/dL for men and 50 mg/dL for women.
It would seem that, low level cholesterol can be interpreted as a sign good health however, the opposite is true for HDL.
Why Low Good Cholesterol Is Harmful
Of course, you know that high cholesterol levels are the enemy of cardiovascular health. But this axiom does not apply to all types of cholesterol. In fact, in the case of HDL, the higher its concentration, the lower the risk of developing atherosclerotic changes and, as a result, heart disease.
Cholesterol is a necessary component of the proper functioning of the body (a component of cell membranes, a precursor important hormones such as steroids). To move freely along with the bloodstream, cholesterol is packaged in special proteins that increase its solubility.
Basic information about lipoproteins:low density lipoproteins. Also known as "bad" cholesterol, they are produced in the liver. Under normal physiological conditions, this process is balanced. In the sense that each cell is able to maintain the level of cholesterol necessary for its functioning, and return the excess to the liver. If this natural balance is upset, then there will be an increase in the level of LDL in the blood, which can be deposited on the walls of the arteries and lead to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. L high density hypoproteins. Also known as "good" cholesterol. They are involved in the reverse transport of excess cholesterol. That is, excess lipoproteins circulating there are obtained from the cells and transferred to the liver. In addition, HDL perform other important features: protect the body from atherosclerotic deposits, from the occurrence of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack and stroke. |
High HDL values not only prevent plaque deposition by preventing LDL oxidation, but also promote the removal of existing plaques by preventing monocytes from adhering to the vessel wall and, as a result, preventing possible blood vessel obstruction.
Optimal Levels HDL concentrations are:
- Men: 60 mg/dl or more
- Women: 60 mg/dl or more
What are the symptoms of a decrease in HDL
A decrease in HDL values occurs asymptomatically and few people notice it, only with the usual periodic medical control.
Symptoms occur when health is already damaged and disease develops.
Reasons for lowering cholesterol values
But what are the reasons that can lead to decrease in HDL values?
There are many of them, and they are not always associated with diseases:
- Pregnancy and menopause are the most common causes of a physiological decrease in HDL cholesterol values. The reason is to be found in hormonal changes. Latest Research showed marked decline cholesterol is noted within two years after pregnancy.
- During menopause lower cholesterol is due to the lack of estrogen, which regulates cholesterol synthesis.
- Birth control pills can reduce HDL cholesterol levels, as they contain progestin, which leads to an increase in the level LDL cholesterol thus increasing the value of total cholesterol.
- Improper nutrition: rich fatty foods and poor in vegetables, fiber, and monounsaturated fats, leading to an increase in LDL cholesterol and a decrease in HDL.
- Misbehavior: sedentary image life leads to an increase in the level of "bad" cholesterol and reduces "good".
- Smoking: The mechanism that links smoking to HDL cholesterol is not entirely clear, but smoking cessation has been shown to markedly increase good cholesterol levels.
- Obesity: with obesity, an excess of triglycerides occurs, which leads to an increase in the concentration of very low density lipoproteins and a number of changes in the cholesterol chain: high density lipoproteins become smaller and lose their atherogenic functions.
Diseases leading to a decrease in the level of good cholesterol:
- celiac disease or food allergy reduce cholesterol levels, as the body does not absorb food, and therefore does not receive HDL from the diet.
- hypothyroidism and liver disease such as hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver; excess thyroid hormone leads to an increase in metabolism.
- Medications, such as beta-blockers, diuretics, interferons, or statins used to lower cholesterol levels.
Risks of Low HDL
Considering protective function HDL against arteries, low HDL cholesterol, exposes the body to high risk cardiovascular diseases.
When HDL cholesterol falls far below optimal levels, with a ratio of total cholesterol above 5, damage to the arteries can lead to:
- Atherosclerosis: body fat in the arteries, which entail a decrease in blood flow.
- Stroke: obstruction or rupture of an artery in the brain, resulting in the death of brain tissue.
- heart attack: reduction or cessation of blood flow, which leads to the death of the heart muscle.
- Cardiac ischemia: complete or partial cessation of blood flow to the heart.
What to do to increase HDL levels
Quit smoking. Exclusion of smoking entails an increase in HDL levels by about 10%. Especially if you add physical activity(at least 5 days a week for 30 minutes): Swimming, biking, running, brisk walking, gardening, anything that increases your heart rate.
Lose overweight . A 3 kg weight loss raises HDL levels by 1 mg/dl of blood.
Follow the rules rational nutrition . The basis of such a diet should be the consumption of healthy fats. In particular, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated, in the latter case it is omega 3, found in fruits with a hard shell and oily fish.
Drinking one or two glasses of red wine a day. Not everyone agrees with this recommendation, but wine certainly helps keep HDL values high. It is possible that this is the reason that explains the French paradox. The French, being heavy consumers of saturated fats ( butter, fatty meat) have a low prevalence of cardiovascular disease.
Taking drugs that increase HDL the most common is niacin. There are also supplements based on this ingredient. It should not be used without the advice of a doctor because it may cause side effects on liver function.
Diet to increase cholesterol values
To reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, you need to eat foods that help increase the proportion of HDL cholesterol and lower LDL.
In particular:
- Fish, rich in omega-3 (fats), such as salmon or swordfish.
- cereals, especially whole grains such as bread and pasta.
- Non-greasy boiled sausage or defatted ham.
- low fat cheese such as mozzarella, ricotta, goat cheese.
- Milk and yogurt.
- Lean meat such as turkey, chicken and rabbit.
- Dried fruits such as hazelnuts, walnuts and almonds because they contain omega-3s.
- Foods rich in antioxidants, such as vitamin C, which is abundant in kiwi, broccoli, oranges and lemons.
- Some legumes, such as soybeans, which contain phytoestrogens, substances that can mimic the effects of estrogen and lower cholesterol levels.
A diet that can help you keep your "bad" cholesterol levels low vegetarian diet , because it excludes the consumption of animal fats and involves the consumption of large amounts of fruits and vegetables rich in vegetable fats containing sterols, which have a structure similar to cholesterol and stimulate the reduction of total cholesterol.
Lipids are fats that do not dissolve in water, so clean mind they are not present in the blood, as they cannot move and be transported along with the bloodstream.
Therefore, nature provided a coherent substance, in which fats acquire solubility in the blood and greater mobility - these are lipoproteins (or lipoproteins). They are a complex consisting of fats and proteins, outwardly resemble a soft, waxy mass, which is found in almost all parts of the body, and is part of cellular structures. To many, this substance is better known as cholesterol.
It is not enough to know one concept, for diagnostic purposes, experts analyze the state of subclasses and fractions of this complex compound. One such subgroup is high-density lipoproteins (or HDL). Today we will tell you what is lpvp in biochemical analysis blood, what deviations signal, and what is the norm for a healthy person.
What cholesterol is good and what is bad?
No matter how surprising it may sound to some, but cholesterol does not always harm the body, in acceptable quantities it is even necessary for the body to build cell membranes, to participate in metabolic processes, the production of sex hormones and much more.
Scientists have long begun to divide cholesterol into "bad" and "good". Bad, we usually get along with food, along with fried sausages, sausages, canned food, smoked meats, fast food, mayonnaise, and other very fatty and heavy foods. This does not mean that the body does not need it at all, it is able to support and stimulate well. immune system, but only when it is in allowable amount.
Good, healthy cholesterol is produced human body to fight negative particles and normalize vital processes.
This is the considered high-density lipoprotein. He helps drive harmful substances back to the liver for processing, serves as a building material for cells, helps to establish the production of hormones by the adrenal glands, in addition, it is responsible for the psycho-emotional state of a person, prevents the occurrence depression and sudden mood swings. In layman's terms, HDL is the "good" cholesterol. And therefore, if the HDL is lowered, it is absolutely not good sign, in this case, the risk of atherosclerosis, heart attack, stroke and other diseases of the blood vessels increases significantly.
Thus, high and low density lipoproteins have almost opposite functions and the type of effect on the body, and therefore diagnostic value these substances are different.
Norm HDL
In order to evaluate possible risks the development of cardiac ischemia, or myocardial infarction, atherosclerosis or the appearance of blood clots, as well as to choose the right treatment tactics, cardiologists, therapists and endocrinologists often prescribe to the patient biochemical research blood.
The norm of lipoproteins may differ for people of different age category and gender. A normal HDL level for a healthy person is:
- for kids:
- up to 5 years - 0.98-1.94 mmol / l;
- 5-10 years - 0.93-1.94 mmol / l;
- 10-15 years - 0.96-1.91 mmol / l;
- more than 15 years - 0.91-1.63 mmol / l.
- for adults:
- from 20 years old - 0.78-2.04 mmol / l;
- from 30 years old - 0.72-1.99 mmol / l;
- from 40 years old - 0.7-2.28 mmol / l;
- from 50 years old - 0.72-2.38 mmol / l;
- after 60-65 years - 0.78-2.48 mmol / l.
It should be noted that the rate of the indicator may vary slightly, depending on the laboratory in which the study is carried out.
HDL norm in men is slightly lower than in women. A reading of less than 1.036 mmol/L for men and 1.30 mmol/L for women leads the doctor to believe that high-density cholesterol is lower allowable rate, which means the risk of cardiovascular disease is much higher.
Often, to assess the potential risk of developing ischemia, doctors analyze the HDL cholesterol level.
relative to the total amount of cholesterol in the blood. For this, an atherogenic coefficient was created, showing the balance between "good" and total cholesterol.
CA = Common cold - HDL / HDL.
Normally, this coefficient should be in the range of 2-2.5 (for newborns - no more than 1, for men after 40 years - no more than 3.5).
HDL cholesterol is low, what does it mean?
The level of useful cholesterol in the blood may differ from the normative values, in a number of ways. various reasons, for example malnutrition, bad habits, the rhythm of life, etc.
But, maybe HDL cholesterol is lowered and pathological reasons, these are:
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- endocrine diseases and violations;
- cholelithiasis;
- hepatic and kidney disease: cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome, etc.;
- type IV hyperlipoproteinemia;
- and etc. infectious diseases in the acute stage.
The level of “good” cholesterol may decrease due to long-term use some medicines transferred severe stress, or acute infectious exposure. In this case, the patient is scheduled for a second study, after about 1.5-2 months.
High density lipoproteins are elevated, what does this mean?
After reading the information about HDL, you might think that increased rate is a favorable sign for the body, because this substance prevents the formation of excess cholesterol, which means it reduces the risk of cholesterol plaques and the development of various diseases. This is true, but not always. High HDL cholesterol what does it mean?
Yes, of course, if high-density lipoproteins are elevated in the blood, doctors say that the likelihood of developing ischemia (CHD) is minimal, because. There are more than enough “useful” components and they are actively doing their job. However, when HDL cholesterol is elevated significantly, there is reason to suspect some abnormality in the body. Such pathological conditions, you can select a little, these include:
- hereditary boost lipoproteins in the blood - hyperlipoproteinemia;
- biliary (primary) cirrhosis of the liver;
- Hepatitis B chronic form;
- alcoholism or other chronic intoxication organism.
Also, I would like to note that there are some factors that can affect the result and provoke an increase in the indicator, for example:
- the period of pregnancy (therefore, it is recommended to take an analysis no earlier than after 6-8 weeks after childbirth);
- taking statins, estrogens, fibrates, holistyramines, or insulin.
How to increase HDL cholesterol?
As we said before unique feature HDL cholesterol fraction is that it is denser and is able to transfer cholesterol "excess" from organs and vessels back to the liver, from where it will subsequently be excreted from the body. Scientists have proven that an increase in HDL by only 0.02 mmol / l reduces the risk of onset heart attack more than 3%.

Therefore, the question often began to sound on the Internet, how to increase good cholesterol and lower bad.
It should be understood that the terms "bad" and "good" cholesterol are used to more easily explain the problem to patients. Well, based on the properties of various subclasses of cholesterol.
So, in order to level up good cholesterol, you must first of all follow the recommendations for lowering LDL, i.e. "bad" cholesterol. For this, you need:
- reduce the consumption of saturated trans fats, they are usually found in the maximum amount in animal products (meat, lard, cream, butter ...);
- decrease daily intake calories, the best option will include fiber-rich vegetables, berries and fruits in the menu;
- increase physical activity we are talking about useful gymnastic and cardio exercises;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- make it a habit to drink green tea, it contains substances polyphenols that help reduce general level cholesterol while increasing HDL. Cranberry juice has similar properties.
So that in the future you will not be overtaken by a whole “bouquet” of diseases and problems with blood vessels, think about your health and watch your diet now!
High-density lipoproteins are compounds made up of lipids (fats) and proteins. They provide the processing and removal of fats from the body, so they are called " good cholesterol».
Russian synonyms
HDL, high density lipoproteins, HDL, HDL cholesterol, alpha cholesterol.
SynonymsEnglish
HDL, HDL-C, HDL Cholesterol, High-density lipoprotein cholesterol, High density lipoprotein, Alpha-Lipoprotein Cholesterol.
Research method
Colorimetric photometric method.
Units
mmol/l (millimoles per liter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not eat for 12 hours before donating blood.
- Eliminate physical and emotional overstrain and do not smoke for 30 minutes before the analysis.
General information about the study
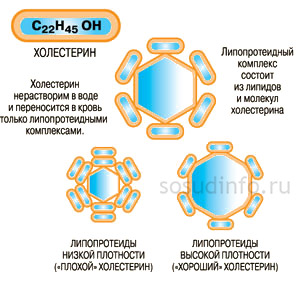
Cholesterol (CHC, cholesterol) is a fat-like substance that is vital necessary for the body. The correct scientific name for this substance is “cholesterol” (the ending -ol indicates belonging to alcohols), however, the name “cholesterol” has become widespread in the mass literature, which we will use later in this article. Cholesterol is formed in the liver, and also enters the body with food, mainly with meat and dairy products. Cholesterol is involved in the formation of cell membranes of all organs and tissues of the body. Based on cholesterol, hormones are created that are involved in the growth, development of the body and the implementation of the reproduction function. Bile acids are formed from it, due to which fats are absorbed in the intestines.
Cholesterol is insoluble in water, therefore, to move around the body, it is “packed” into a protein shell, consisting of special proteins - apolipoproteins. The resulting complex (cholesterol + apolipoprotein) is called lipoprotein. Several types of lipoproteins circulate in the blood, differing in the proportions of their constituent components:
- very low density lipoproteins (VLDL),
- low density lipoproteins (LDL),
- high density lipoproteins (HDL).
High-density lipoproteins consist mainly of a protein part and contain some cholesterol. Their main function is to carry excess cholesterol back to the liver, where it is excreted as bile acids. Therefore, HDL cholesterol (HDL-C) is also called "good cholesterol". About 30% of total blood cholesterol (cholesterol) is part of HDL.
If a person has hereditary predisposition to high cholesterol or he consumes too much fatty foods, then the level of cholesterol in the blood may rise, so that its excess will not be completely excreted by high density lipoproteins. It begins to be deposited in the walls of blood vessels in the form of plaques, which can restrict the movement of blood through the vessel, as well as make the vessels more rigid (atherosclerosis), which significantly increases the risk of heart disease (ischemic disease, heart attack) and stroke.
High HDL cholesterol values reduce the risk of developing plaques in the vessels, as they help to remove excess cholesterol from the body. Decreased HDL-C even with normal level total cholesterol and its fractions leads to the progression of atherosclerosis.
What is research used for?
- To assess the risk of developing atherosclerosis and heart problems.
- To monitor the effectiveness of a low-fat diet.
When is the study scheduled?
- Analysis for HDL is carried out during scheduled preventive examinations or with an increase in total cholesterol as part of the lipid profile. A lipid profile is recommended for all adults over 20 years of age at least once every 5 years. It may be given more frequently (several times a year) if the patient is on a low-fat diet and/or is taking cholesterol-lowering medications. In these cases, it is checked whether the patient reaches the target level of HDL cholesterol and total cholesterol and, accordingly, whether his risk of cardiovascular diseases is reduced.
- With existing risk factors for the development of cardiovascular diseases:
- smoking,
- age (men over 45, women over 55),
- promotion blood pressure(140/90 mm Hg and above),
- cases high cholesterol or cardiovascular disease in other family members (heart attack or stroke in the closest male relative under 55 years old, female under 65 years old),
- existing ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction or stroke,
- diabetes,
- overweight,
- alcohol abuse,
- reception a large number foods containing animal fats
- low physical activity.
- If a child in the family had a history of high cholesterol or heart disease in young age, then for the first time he is recommended to take a test for cholesterol at the age of 2 to 10 years.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: 1.03 - 1.55 mmol / l.
The concept of "norm" is not entirely applicable in relation to the level of HDL cholesterol. For different people with a different number of risk factors, the HDL norm will be different. To determine the risk of developing cardiovascular disease more accurately for a particular person, it is necessary to evaluate all the predisposing factors.
In general, we can say that a reduced level of HDL predisposes to the development of atherosclerosis, and a sufficient or high level prevents this process.
In adults, HDL cholesterol, depending on the level, can be assessed as follows:
- less than 1.0 mmol / l in men and 1.3 mmol / l in women - high risk development of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases, regardless of other risk factors,
- 1.0-1.3 mmol / l in men and 1.3-1.5 mmol / l in women - the average risk of developing atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases,
- 1.55 mmol / l and above - low risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases; while the vessels are protected from negative impact excess cholesterol.
The reasons reduced level HDL:
- heredity (Tangier disease),
- cholestasis - stagnation of bile, which can be caused by liver disease (hepatitis, cirrhosis) or gallstones,
- severe liver disease
- untreated diabetes,
- chronic inflammation of the kidneys leading to nephrotic syndrome,
- chronic renal failure.

