The size of the thyroid gland in men table. Normal size of the thyroid gland. Dimensions are normal on ultrasound.
A healthy thyroid gland is a guarantee good mood, normal weight, healthy nerves, wellness. But this system in the human body often fails, and this can manifest itself in a change in the size of the nodes thyroid gland. What diagnostics is needed to identify deviations, and what exactly is meant by them?
Thorough examination of the thyroid gland to make an accurate diagnosis
Thyroid nodules are rounded inflammatory foci of thyroid tissue. Sometimes they have a capsule that separates them from the surrounding tissue, or a colloidal fluid. In most cases, the nodes are benign, so they do not pose a danger to human life. Such formations do not manifest themselves, do not affect the well-being of a person.
Thyroid nodes form in many people, and the frequency of their occurrence increases with age. Nevertheless, there is a risk that the nodes will turn out to be malignant, because such diagnoses are made, albeit not very often, but the number similar diseases slowly growing. Therefore, it is very important to identify the node in time and monitor how it behaves.
The main feature of the nodes is that a person cannot independently determine their presence, and often the doctor cannot do this in relation to the patient. The person feels good, he has no special complaints, discomfort. External examination, palpation does not allow you to feel the presence of formations, because they have small size. If their size increases, the owner begins to feel a foreign body. It may be difficult for him to even swallow food. IN rare cases nodes are visible when swiping hygiene procedures with oral cavity.
Read also:
But these and some other signs are not enough in order to make a diagnosis, we need instrumental methods research.
- ultrasound. This is the most available method, which makes it possible to explore the thyroid gland in a non-invasive way. It gives an excellent effect and does not bring any pain. If ultrasound is performed using a device that has a good throughput, then nodes are determined, the size of which is only one millimeter. Modern devices make it possible to accurately determine the size, structure, outlines and other characteristics of formations, as well as to examine the state of organs located in the neighborhood.
- Fine needle aspiration biopsy(TAB). It is prescribed if, according to the results of ultrasound, the size of the formations exceeds 1 cm. This is a procedure during which the doctor extracts cells from the thyroid gland for further research, which helps to understand the nature of the formation and its cytological structure. Patients easily tolerate the procedure, it causes almost no pain, and even less harm to the thyroid gland.
- Hormone tests. They are also appointed if there is any suspicion. Checking the level thyroid-stimulating hormone, tetraiodothyronine and triiodothyronine. Its level decreases or increases, that is, it does not correspond to the norm in accordance with age, the size of the formations may begin to increase.
- Multispiral CT scan. It is especially needed if the nodes are located behind the sternum, in which case ultrasound provides little information. Multislice CT allows you to determine with high accuracy where the formations are located, what is their structure, and so on.
If the hormonal situation is unfavorable or the level of one hormone is very high, it is important to determine the cause of this. There are three possible options here.
- Age norm in terms of physiology. They may seem high when compared with other indicators.
- The hormone is too actively produced by the thyroid gland itself. In this case, the reason lies in the internal regulatory circuit and it must be found.
- Active production of the hormone is associated with the work of nodes or other pathologically altered sources.
In the latest development of events, scintigraphy based on the use of iodine 121 or technetium 99 is used.
Only a thorough diagnosis allows the doctor to put accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
Normal size of thyroid nodes
Now it remains to understand when there are reasons for concern. What are the norms for the size of thyroid nodules today? In this regard, everything is simple. If the knot is no more than 1 cm, it is considered harmless, but it is necessary to check regularly with a specialist. If the size of the formation exceeded 1 cm, further examination is necessary.
Of course, when examining the thyroid gland, its size also matters. The rules are:
- for women no more than 18.6 cm 3;
- for men no more than 25.5 cm 3;
- for teenagers (15 years old) no more than 16, 2 cm 3.
For children, the rules are different depending on their age.
Ultrasound today - standard method diagnostics, which not only allows you to judge the size, location and structure of internal organs, but is also absolutely safe and comfortable for the patient. In our detailed review and the video in this article, we will analyze what can be found out with the help of an ultrasound of the thyroid gland: the norm in women + a table of the main indicators that the doctor pays attention to during the examination.
Thyroid- important endocrine organ, which regulates the activity of the digestive, cardiovascular, nervous, reproductive and other systems. If the doctor suspects hormonal imbalance caused by a lack or, conversely, an excess of thyroid hormone synthesis, the patient in without fail an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland will be ordered.
Note! average price procedures in private clinics - 800 rubles.
When can a doctor prescribe an ultrasound?
Indications for a diagnostic procedure:
- nodes, formations in the thyroid gland, which the patient determines when examining the neck with his own hands;
- complaints about chronic cough, choking, discomfort or foreign body in the throat;
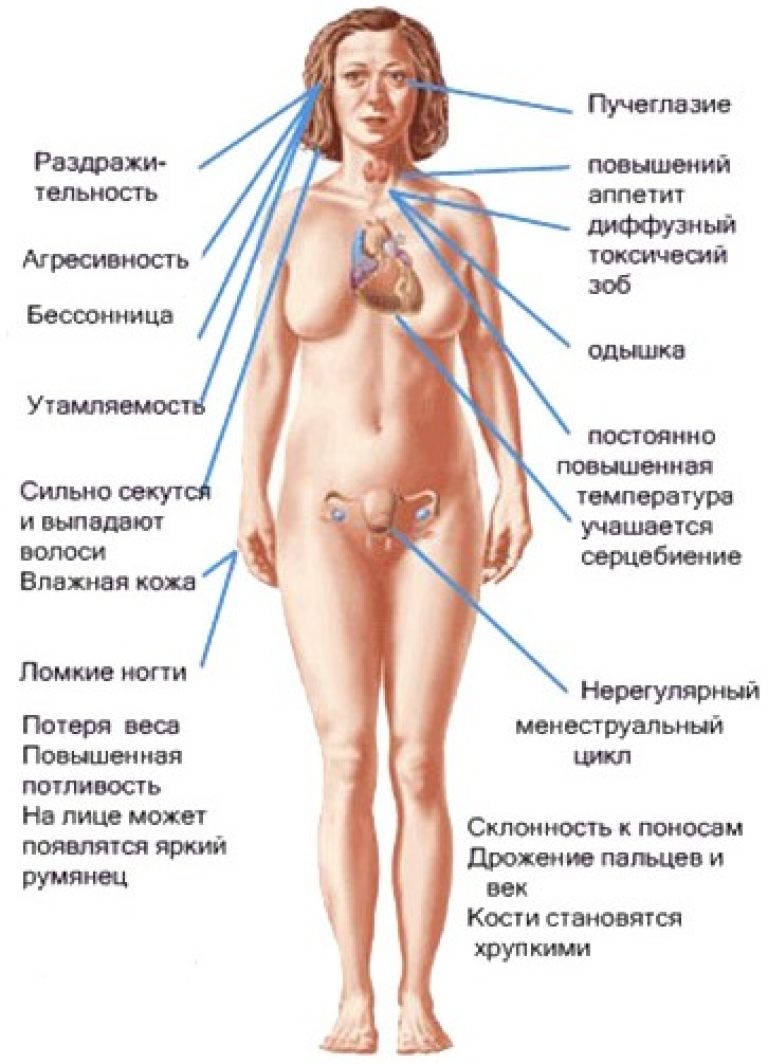
- increased nervous excitability, anxiety, insomnia, acceleration of metabolism (sudden weight loss) - symptoms of hyperthyroidism;
- drowsiness, fatigue, rapid weight gain, arrhythmia, puffiness of the face and upper body are signs of hypothyroidism;
- hereditary predisposition to thyroid diseases;
- harmful production factors;
- treatment with hormonal drugs;
- control of therapy of diagnosed thyroid disease;
- pregnancy planning (see).
Note! Due to the widespread endocrine pathology, including women reproductive age, medical instruction recommends taking preventive examination thyroid gland for all healthy women over 35 years old 1 time in 3-5 years.
Research objectives
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland is prescribed to determine:
- the location of the organ and its anatomical structure;
- contours of the thyroid gland;
- longitudinal and transverse dimensions of both lobes of the organ and isthmus;
- internal structure of the thyroid gland;
- presence or absence focal formations- knots, cysts, calcifications;
- degree of echogenicity and "response" of thyroid tissues to ultrasound;
- availability, size and internal structure regional lymph nodes.
Preparing for an ultrasound
Doctors often hear from their patients the question of when is the best time to do a thyroid ultrasound: women are worried about the impact hormonal fluctuations the genital area to the work of the body. In fact, fluctuations in the level of estrogens and progestogens do not have a significant effect on the ultrasound picture when examining the thyroid gland, so the procedure can be performed on any day of the menstrual cycle.
There is no specific preparation for the procedure. If you have elevated vomiting reflex, it is better to perform an ultrasound examination on an empty stomach due to possible pressure neck sensor.
Research algorithm
The ultrasound procedure does not take much time and consists of a few simple steps:
- The patient lies on the couch and slightly unbends the neck for better access to the thyroid gland.
- On the front surface of the neck, the doctor applies a small amount of a special gel with high electrical conductivity.
- With a sensor producing ultra sound waves, the specialist examines the thyroid gland, receiving a two- or three-dimensional image of the organ on the screen.
- The uzist evaluates all the data received and gives his medical opinion.
This is interesting. The mechanism of operation of the ultrasound machine is based on the action of short-wave sound. The machine generates and, with the help of a sensor, acts ultrasonic waves on the tissue of the thyroid gland, and then receives the "reflected" sound waves, digitizes the received information and displays it on the screen.
By the way, similar action possesses a sense organ in bats that use ultrasound to determine the distance to surrounding objects.
Medical opinion is an important document
Upon completion of the study, all patients are provided with a medical report, which contains all the necessary data and a photo of the ultrasound picture. This paper is important. medical document allowing the endocrinologist to make the correct diagnosis.
It is not surprising that each person wants to understand the conclusion himself and understand what changes in the thyroid gland he has found. This will help deciphering the ultrasound of the thyroid gland in women, presented below.
Before determining the pathology, you need to find out what are the norms of ultrasound of the thyroid gland in women.
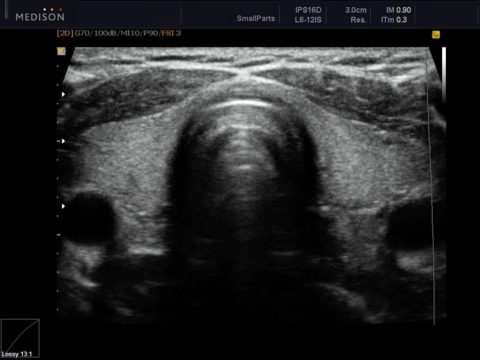
Table: Normal and pathological parameters of the thyroid gland on ultrasound:
| Index | Norm | Options for pathology |
| Contours of the thyroid gland | Clear | Fuzzy contours indicate:
|
| Dimensions | The size of each lobe is on average 4 × 2 × 2 cm, the thickness of the isthmus is 4-5 mm. The right lobe should be approximately the same size as the left lobe. The normal volume of an organ has the following values:
|
Diffuse (uniform) increase in the thyroid gland - goiter occurs with endemic iodine deficiency, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism. A decrease in the size of an organ - hypoplasia - can be congenital or acquired (for example, in autoimmune diseases). |
| Structure | Homogeneous, granular. | The heterogeneity of the structure of the thyroid gland indicates inflammatory diseases organ. |
| echogenicity | Satisfactory, equal to echogenicity parotid gland patient. | A decrease in echogenicity indicates inflammatory changes, neoplasms in the structure of the organ. |
| Focal nodes | None. | Any node in the thyroid gland, the size of which is more than 2-3 mm, requires careful attention from the doctor. The specialist must describe:
|
| Tissue blood supply | No features: during Doppler study several color signals are determined on the surface of the thyroid gland. | Increased blood flow is a typical sign of inflammation. |
| Regional l / s | Not enlarged, with clear contours and a homogeneous internal structure. Solbiati index (ratio of longitudinal and cross dimension l / y) must be at least 2. |
An increase in the size of regional lymph nodes, increased blood flow and the presence of cysts in their internal structure - typical manifestations cancer metastases. |
What diseases can be diagnosed by ultrasound
In case of deviation from the standard values, typical signs allow the doctor to suspect the following diseases:
- Thyroiditis. It can be acute (infectious), subacute and chronic (autoimmune). It is manifested by an increase in the size of the thyroid gland, a change in the contours of the organ, and the heterogeneity of its internal structure.
- Nodular goiter. The node in the thyroid gland is visualized as a site high density, which has clear boundaries.
- . The thyroid gland is enlarged evenly, and its internal structure remains normal.
- thyroid cyst. It is visualized as a limited cavity filled with liquid. Its echogenicity is usually increased.
- Malignant formations. They are high-density knots with fuzzy contours. Typically also the defeat of regional l / y.
Note! With the help of ultrasound, one can only assume the presence. A biopsy confirms or refutes the diagnosis - the sampling is not a large number node cells with their subsequent microscopy.
Thus, the norm of the thyroid gland in women is an ultrasound picture that the doctor takes as a standard and is based on it when examining each of his patients. Of course, in addition to ultrasound diagnostics, it is important to take into account complaints and anamnesis, data clinical examination And laboratory tests. Comprehensive examination will allow the endocrinologist to make the correct diagnosis and start timely treatment.
The normal size of the thyroid gland in men depends on body weight, age and other individual features of the body structure, for clarity, a table has been compiled. Scientists endocrinologists in the study of the state of the thyroid gland proceed from the normal size of the organ. Any deviation becomes an object of close study for them.
The volume of the thyroid gland in men is under the close attention of the attending physician. Endocrinologists compare the patient's thyroid volume with normal sizes. There are deviations from established norm, values of boundary states.
The thyroid gland, which has dimensions that meet the standards, does not bother a person, does not cause discomfort, deterioration in health. The specialist will analyze the picture of the disease, listen to the patient's complaints. One of the doctor's first appointments will be an ultrasound. It will give a picture of the state endocrine system. The description obtained in the form of a snapshot can only be disassembled by a specialist. The patient himself will not be able to figure it out; special medical knowledge and possession of a conceptual set are required.
Doctors use two concepts:
- norm;
- deviations from the norm.
The norm of the thyroid gland in a man differs from the volumes female organ. The size of the male thyroid gland depends on the weight of the patient, age. normal volume male organ should not be more than 25.5 cubic meters. cm.
Limit deviations are the allowable changes in volume. You can consider the size of a healthy organ depending on weight according to medical data:
| Patient body weight/kg | The volume of the gland in a healthy state / cc |
| up to 40 | 12,5 |
| 41-50 | 15,5 |
| 51-55 | 17 |
| 56-65 | 20 |
| 66-75 | 25 |
| 76-85 | 28 |
| 86-95 | 30 |
| over 100 | 34 |
Dimensions may be within, may be increased, but this is not always an indicator of the onset of the disease. The specialist will be able to make a diagnosis by examining the causes of changes in volumes, deviations from the normal state.
The thyroid gland has a specific structure.
 Its parts experts consider:
Its parts experts consider:
- right lobe;
- left lobe;
- isthmus.
Ultrasound examination will provide data on the state of the gland. If the organ is healthy, then both lobes are approximately equal in volume. Dimensions: height is 4 cm, width and thickness - 2 cm.
The isthmus is not more than 5 mm wide.
Doctors say that if deviations vary from 1 to 5 mm, these are individual structural features of a human organ. Such a deviation is possible because each organism is unique.
If the deviations are greater, this is a symptom or signal of the development of pathology. Only a doctor can determine it. Other indicators include: contours, echogenicity, tissue structure.
According to the results of ultrasound, conclusions are drawn about the state of the thyroid gland:
- The picture shows the outline of the thyroid gland. They are viewed on the monitor during the session. laboratory examination. Clear contours are considered normal, without breaks and breaks in its parenchyma. Parenchyma - medical term denoting a collection of tissue formations. Inflammation is characterized by blurred outlines, fuzzy boundaries. The picture displays this information by changing the color of the thyroid tissue. The difference and heterogeneity of color indicate different density of fabrics. healthy organ has a uniform composition.
- Echogenicity shows the level of reflection of the signal of the ultrasound machine from the studied tissues of the thyroid gland. It is studied if there are deviations in size and volume. Normal level confirms the absence of pathological formations. Echogenicity will be disturbed when examining contours if nodular seals are found. A reduced level signals the formation of nodal and cystic formations. You can see them on the ultrasound. Enhanced Level shows the predominance of connective tissues. This signals a decrease in the functionality of the organ. Connective tissue does not produce hormones, glandular tissue formations do this. Zero level does not sound signal ultrasound equipment. In conclusion, the doctor will write what kind of echogenicity he revealed during the study.
- The structure of tissue formations. The normal structure has a homogeneous granular mass. Grains at the rate correspond to 1 mm in diameter. Pathologies are detected with deviations from normal sizes. If the thyroid gland is affected by macrofollicles, the diameter will be larger.
 The male thyroid gland is located below the top of the sternum. The body changes its size during maturation. In a newborn, the weight of the thyroid gland is only 2 grams. Most active period growth - from 5 to 15 years. The decrease starts around the age of 55. The reason is the atrophy of the follicles. The functionality of the thyroid gland does not deteriorate.
The male thyroid gland is located below the top of the sternum. The body changes its size during maturation. In a newborn, the weight of the thyroid gland is only 2 grams. Most active period growth - from 5 to 15 years. The decrease starts around the age of 55. The reason is the atrophy of the follicles. The functionality of the thyroid gland does not deteriorate.
TO individual characteristics buildings, scientists attribute the following characteristics:
- The presence of an additional thyroid gland.
- Greater development of the right lobe.
- The absence of an isthmus.
- Duality.
- Availability of additional shares.
To establish a diagnosis, the endocrinologist considers anatomical structure, then compares with the norms and only then draws conclusions about the state of the thyroid gland in a man.
Today, many experts consider the most informative method study of the state of this body. Moreover, ultrasound diagnostics is one of the most affordable today. Its undoubted advantage should be considered the ability to examine patients at any age.
Why is research needed?
Ultrasound (normal for healthy people will be given below) can be used when preventive examinations and dispensaries. Timely completion ultrasound often allows you to identify organ defects, tumor changes, minimal foci of inflammation. However, at the same time, it is not possible to identify the very cause of the occurrence of violations using only this method. In the process of research, the specialist also studies the structure of paired formations - parathyroid glands. They are located on the left and right lobes organ. The lymph nodes that are located on the front of the person's neck are also examined. As a matter of fact, ultrasound of the thyroid gland, the volume of which is different for women and men, is considered the first additional diagnostic method prescribed by an endocrinologist. In accordance with the data obtained, a correction of the patient examination scheme can be carried out. 
What exactly is studied during an ultrasound examination?
When performing an ultrasound of the thyroid gland, the norm and deviations are evaluated according to several parameters. First of all, the structure of the organ is studied. At the same time, the ability to reflect the signal of the sensor in the thyroid gland and the salivary parotid gland is compared. The study allows you to study the echogenicity of the body. This parameter indicates the uniformity of the fabric. As mentioned above, the examination parathyroid glands and lymph nodes. In addition, the condition is assessed large vessels, which are located near the body. In particular, they study jugular veins, external The volume of the organ is studied, as well as the structure of the isthmus, which unites the lobes, the size of the thyroid gland. The norm of linear values depends on the age and sex of the patient. If necessary, other anatomical structures can be examined: soft tissue neck, larynx and others.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland. Decryption
The norm of volume in men is up to 25 ml, in women - up to 18. The description of the conclusion might look like in the following way: "The location of the organ is correct, the shape is normal, the contours are clear, even, there are no nodes, the echostructure is not changed, it is homogeneous. The lymph nodes of the subclavian, submandibular region are not enlarged." However, with certain pathologies, the size of the thyroid gland according to ultrasound does not deviate from the generally accepted parameters. These diseases include, in particular, 
Pathologies that are detected by ultrasound
When suspected of what diseases, an ultrasound of the thyroid gland is prescribed? Dimensions, the norm of which is individual for each person, may indicate the presence or absence of thyroiditis. In the structure of the organ, seals, diffuse or local changes can be detected. In the latter case, small compacted nodes of various sizes are revealed. In some cases, during a routine examination by an endocrinologist, they are not noticeable. In this regard, the doctor (to clarify the diagnosis) prescribes an ultrasound of the thyroid gland, the norm of volume and linear parameters which is indicated above.
Tumor diagnostics
In most cases, during the study, a specialist can identify and distinguish between benign and malignant neoplasms in the thyroid. The latter are characterized by reduced echogenicity, the presence of calcium salts in the tissue, and heterogeneity of the structure. Neoplasm can be of different sizes, including very small. After removal of the tumor, ultrasound of the thyroid gland is re-assigned. The norm will testify to the effectiveness of the measures taken. The study is recommended to be carried out regularly to exclude recurrence. 
In what cases is an examination necessary?
Who is assigned to ultrasound of the thyroid gland? How to prepare for research? First of all, the examination is necessary for people who are in "risk groups". These, in particular, include people over forty years of age, since it is at this age that the likelihood of the occurrence of neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature increases. Examination is necessary for patients working in hazardous industries, spending a lot of time at a computer, often staying in stressful conditions. Ultrasound is recommended for patients who, throughout their lives, due to certain pathologies, have been prescribed hormonal agents. Unfavorable heredity is also an indication for the purpose of the study. Pregnant women need to be screened.  Ultrasound is recommended in this case both at the planning stage and during the term for any deviations.
Ultrasound is recommended in this case both at the planning stage and during the term for any deviations.
Who else is being tested?
Diagnosis is recommended for people who have symptoms of thyroid pathologies. In particular, with unclear weight fluctuations, changes in heart rate, unexplained irritability or lethargy, which are not provoked by the use of medications or violations of thermoregulation. Additionally, ultrasound is recommended if the thyroid hormone levels are reduced or increased, the norm for total thyroxine is 60.0-160.0 nmol / liter, and for T3 (free) - 1.2-2.8 mIU / liter. If there are deviations, then additional research will help clarify the diagnosis. Before carrying out the method, the patient does not require special preparation.
Additional options for ultrasound examination
If autologous changes are detected, the specialist may recommend an ultrasound with CDC (digital Doppler mapping). This method research allows not only to study the features of the structure and structure of the organ, but also to assess the nature of interstitial blood flow. Based on all the data, a more accurate diagnosis is established. Especially often, CDI is used when tumor nodes are detected in the gland. When studying the characteristics of blood flow, a specialist has the opportunity to understand real reasons development of pathology, the probability and direction of metastases against the background of a malignant process. Under the control of ultrasound, a fine-needle biopsy of tissues from pathological foci detected during a preliminary examination is performed. 
Features of diffuse changes detected by ultrasound
These violations usually lead to inflammatory processes in the thyroid. These include, in particular, chronic thyroiditis. During the examination, there is a reduced echogenicity of the organ, its increase in all directions. Typical signs is also diffuse inhomogeneity of the tissue. With thyroiditis, several indistinctly demarcated nodes may be found. Their internal structure is similar to that of the surrounding tissue. When a large node is detected, the shape of the gland changes (becomes diffuse-nodular).
Differential Diagnosis
Ultrasound can distinguish multinodular goiter from chronic thyroiditis. This is especially important, since the choice will depend on the diagnosis. therapeutic measures. So, autoimmune thyroiditis treated conservatively, and multinodular goiter - surgical method. diffuse changes may accompany (diffuse toxic goiter). They manifest themselves in the form of a uniform increase in the thyroid gland, in some cases by 2-3 times in comparison with the norm. However, in many cases, the severity of the pathology does not affect the size of the thyroid gland. The norm, as already mentioned above, is individual for each patient. At pronounced manifestations thyrotoxicosis in men, for example, there is a slight deviation from the generally accepted parameters. As a rule, the tissue structure is homogeneous, may be slightly dense, and echogenicity is increased. In some cases, against the background of the considered changes, secondary nodules, accumulations of calcium salts and cysts may be detected. 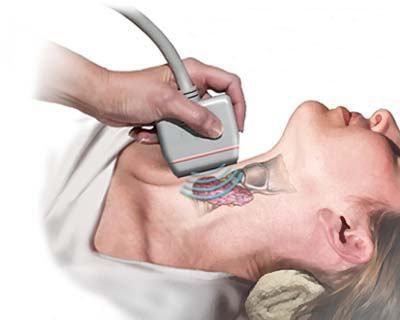
Conclusion
Unfortunately, not every person is able to notice violations in metabolic processes. Most people realize that they are sick when serious problems with appetite or weight. Tendency to consume large amounts of sweets frequent drops moods, hair loss - all these are signals about the presence of any disorders in the body. With such manifestations, you should consult a specialist. The endocrinologist will examine and prescribe necessary tests and research, including ultrasound of the thyroid gland. Where to do an ultrasound? It is carried out in special rooms in which the appropriate equipment is installed. Diagnosis is carried out by a specialist - an uzist. Today, ultrasound, as mentioned above, is the most informative diagnostic method. This is mainly due to its popularity. In addition, the study is accessible to a large mass of the population. The cost of the examination is much lower, and its information content is higher than that of thyroid radiography. Moreover, when conducting an ultrasound examination, there is no radiation exposure to the patient's body. The undoubted advantage of the method is the possibility of its repeated use by patients at any age, including newborns, as well as pregnant women. Before conducting a study, the doctor should be informed about all the drugs taken by the patient, including vitamins. However, despite all the information content of ultrasound, making a diagnosis, taking into account only the results of ultrasound of the thyroid gland, will be wrong. Great importance has all clinical picture, medical history information. The results of other studies are also taken into account, including indicators of thyroid hormones (the norm for them is indicated above). Only on the basis of an assessment of all the data obtained in a complex during an ultrasound examination, the doctor can make a conclusion about the presence or absence of pathological changes and make an accurate diagnosis, in accordance with which treatment will be prescribed.
The thyroid gland regulates the work of a large number of human internal organs. If the normal volume of the thyroid gland is exceeded, the gland does not work properly.
However, many diseases early stages are asymptomatic. In some cases, violations can be regarded as the natural course of things.
For example, in a number of diseases of the thyroid gland, human performance deteriorates.
A person may think that he is tired because the boss has increased the load. But in fact, the work of the thyroid gland is disrupted in humans.
In many countries, doctors advise once a year to undergo an examination of the thyroid gland for diseases using ultrasound, because diseases in the early stages are very easy to treat.
Certainly, modern medicine allows in the later stages.
But why take the risk and spend extra money if you can go to the hospital once a year and, right?
In some cases, an unhealthy thyroid gland can be detected by the following symptoms:
- Pain in the muscles.
- Sudden weight loss for no apparent reason.
- High sweating.
- Extremely high fatigue, as a result - loss of working capacity.
If you have these symptoms, be sure to visit.
To clarify the diagnosis, he will send you for an ultrasound examination. After passing the ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland, you will be given a special document.
Although your attending physician should definitely deal with its decoding, you can understand something yourself.
The conclusion of the ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland
You can read the paper on thyroid research yourself. The main thing here is not to add anything in the conclusion, and also not to self-medicate.
When examining the gland, the following parameters are taken into account:
- Structure and volume of the thyroid gland. It also indicates its homogeneity.
- Dimensions of the right and left halves of the gland.
- Isthmus structure.
- The structure of the larynx and cervical tissues.
- The general condition of the lymph nodes located near the thyroid gland.
What parameters are considered normal
For a healthy thyroid, the following will be true:
- The echostructure is homogeneous, there are no features.
- The size of the thyroid gland ranges from 18 cubic centimeters (in women) to 25 cubic centimeters (in men). However, at big people the size of a normally functioning thyroid gland will be larger. To take into account this measurement defect, doctors use a table of normal thyroid sizes, taking into account weight.
The table of the size of the thyroid gland is normal in women by ultrasound:
Note: The size of the thyroid gland in the norm in women and men differs slightly (adjusted for weight). But in children, the size of the thyroid gland varies significantly. To find out what size of the thyroid gland in children is considered normal, use: The thickness is normal no more than 0.4-0.5 cm.
- The right lobe of the thyroid gland is normally about 4x2x2 cm.
- The left share is equal to the right. Its volume is normally the same - 4x2x2 cm.
- Lymph nodes near the thyroid gland should be of normal size.
- The contours of the gland on ultrasound should be clear and even.
- If no changes in the size of the thyroid gland and adjacent organs are found, it will be written in the certificate - “ pathological changes organs are missing.
Table of norms for the size of the thyroid gland in children:
What parameters are considered abnormal
However, the results may not always please the patient. You need to be wary if the following results:
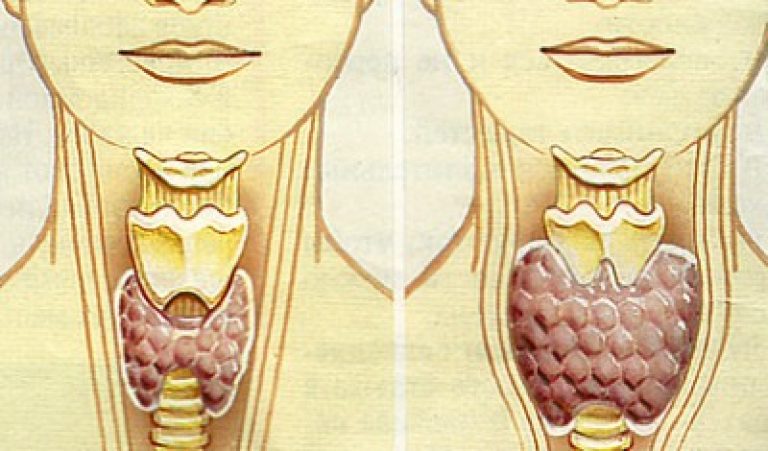
- The maximum volume of the thyroid gland has been exceeded. There is a suspicion of diffuse toxic goiter. However, some people naturally have an enlarged thyroid gland.
- Structure is heterogeneous. It can talk about inflammatory processes going on inside the organ.
- There are seals in the tissues of the body. This suggests that a benign or malignancy. The first is called, the second - cancer. To, the doctor sends for additional research.
- Inside the organ there is a cavity in the form of a circle. The edges of the circle are clear, without teeth; the cavity has normal structure, there is liquid inside it. This indicates the presence
- The size of the thyroid gland is very small. There is hypothyroidism of the thyroid gland (reduced work).
- If the thyroid gland not only exceeds the maximum volume, but also the presence of edema, the organ suffers.
It is important not to forget that only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. An amateur can easily make mistakes while parsing a document.
In what cases is an ultrasound analysis of the thyroid gland prescribed?
Thyroid diseases Lately occur more and more frequently. Thyroid disease is often accompanied by an increase in the size of this organ.
Even an amateur eye can notice an enlarged human thyroid gland.
However, in some cases, the detection of violations is difficult. by the most in a simple way The diagnosis of the thyroid gland is an ultrasound.
The procedure is absolutely safe. Ultrasound helps to determine the size of the thyroid gland and its shape.
If something bad happened to the organ, it will be noticeable on the ultrasound test.
Before testing, a person can conduct his normal image life, because for the test you do not need to first refuse food, drink, or even.
Usually, an ultrasound test is accompanied by blood donation. She is sent to a laboratory where the amount of hormones in the blood is determined. This helps clarify the ultrasound test.
When doctors prescribe an ultrasound test of the thyroid gland
Doctors themselves may send you for an ultrasound test if:
- showed strange results.
- The patient complains of pain during swallowing.
- Sudden obesity. Less often -.
- Complaints of headaches and weakness.
- A high temperature that does not go away on its own.
- If a girl is expecting a baby, she can be sent to inspect the work of all internal organs.
- It was found that the patient eats food with reduced.
- The patient works in hazardous "environmental" industries.
What diseases can ultrasound detect?
The ultrasound test is extremely effective.
It helps to identify such diseases:
Thyroiditis . It is a consequence of the harmful activity of bacteria and viruses in the body. The thyroid gland increases in size, and the temperature of the whole body rises. Edema may also be observed.
. This violation can be determined by touch. By pressing on the glands, you will feel the compaction of the thyroid tissue. On an ultrasound test, the goiter looks like it borders on healthy tissue.
Cancer. They are neoplasms of high density. The contours of the neoplasms are ragged, indistinct. In the case of cancer, the lymph nodes also enlarge.
Conclusion
The thyroid gland is involved in the regulation of work internal organs. At healthy woman weighing 60 kilograms, the thyroid gland normally does not exceed 19 centimeters cubic.
If the size of the thyroid gland is larger, they speak of an increased volume of the thyroid gland.
This may indicate the presence pathological processes in organism. To confirm or refute fears, doctors prescribe ultrasound examination thyroid glands.

