What is a Doppler study. Doppler sonography during pregnancy. Dopplerography of cerebral vessels
Doppler study is an ultrasound technique that allows you to measure the speed and determine the direction of blood flow in the cavities of the heart and blood vessels. The method is based on the effect described by K. Doppler in 1842. Its essence is as follows: when an ultrasonic beam of a known frequency (fo) is sent to the heart, it is reflected from the blood cells. The frequency of the reflected ultrasonic beam (fr) is equal to the frequency of the sent beam (fo) if the reflection is from a stationary object.
This is only done when the child is suspected of being anemic, in cases where your child is suffering from Rh antibodies, or if your child is suffering from a slap. This test gives an indication of whether the child's blood has sufficient oxygen carrying capacity or not, and whether the child needs any intervention, such as a blood transfusion.
What is cardiotocography or not a stress test?
Diagnosis of the ductus venosus This is rarely done. In the first trimester, along with other tests, he gives an indication of chromosomal abnormality The child has. In the third trimester, it helps determine if the baby is getting adequate nutrition and oxygen. You can ask your doctor to listen to your baby's heartbeat for early stage, but this may cause you anxiety. This is because your baby's heartbeat may be difficult to find before 13 weeks.
Frequency of the reflected ultrasonic beam(fr) increases if blood cells move towards the ultrasound source and decreases when they move away from the ultrasound source. The difference between the frequencies of the sent and reflected beams (Af) is called the frequency shift of the ultrasonic signal or the Doppler shift: Af=fr-fo.
Af depends on the frequency of the sent beam (fo), the speed of the particles from which it is reflected (blood flow velocity - V), the angle between the direction of the ultrasonic beam and the direction of blood flow, the speed of propagation of ultrasound in the blood (1540 m/s), which is expressed by the Doppler equation: Af \u003d 2fo x V x cos 9 / c.
Dopplerography of cerebral vessels
If you feel like your child moves regularly throughout the day, he will probably be fine. However, if your child's movements are slowing down, it is very important to contact your doctor immediately. This is because doctors have other, less invasive monitoring methods that should be enough to take care of you and your baby.
The readings can then be used as a baseline if required by hospital staff later in your work. One of the main goals of routine prenatal care is to identify babies who do not thrive in the womb. It is possible that medical interventions may improve outcomes for these children if they can be identified. Doppler ultrasound uses sound waves to detect the movement of blood in the vessels. It is used during pregnancy to study the circulation of the baby, uterus and placenta.
Thus, knowing Af, you can calculate the speed of movement of blood cells: V \u003d Af x c / 2fo x cos 9.
If a ultrasonic beam parallel to the direction of blood flow, then the angle 0=0, its cosine = 1. The value of the cosine of the angle 0 less than 20° is also close to 1 (cosine 20° = 0.94), so it can be neglected. If the direction of movement of the object is perpendicular to the direction of the emitted ultrasonic beam, then, since the cosine of the angle of 90° is 0, it is impossible to calculate such an equation and it is impossible to determine the speed of the object. Therefore, for correct definition velocity of blood flow, the direction of the long axis of the sensor should be close to the direction of its flow (angle 9 should be< 20°).
Its use during pregnancy high risk when there is concern about the child's condition, shows benefits. However, its value as a screening tool in all pregnancies must be assessed because of the potential for unnecessary interventions and adverse effects. there were no improvements seen for either the baby or the mother, although more data would be needed to prove whether or not it is effective in improving outcomes.
Existing evidence does not provide hard evidence that the use of a routine Doppler ultrasound Doppler ultrasound or a combination of Doppler ultrasound with a small or non-isolated umbilical and uterine arteries benefits the mother or child. Future studies should be designed to address small changes in perinatal outcome and should focus on potentially preventable deaths.
AT echocardiography The most commonly used options for Doppler studies are:
1) pulse (pulsed wave - PW);
2) constant wave (continuous wave - CW);
3) color (color Doppler);
4) tissue (tissue velocity imaging - TVI, tissue myocardial imaging, Doppler tissue imaging).
Its main varieties:
tissue color (color tissue velocity imaging),
tissue non-linear (C-mode),
tissue impulse (pulsed wave tissue velocity imaging),
tissue trace (tissue tracking),
assessment of myocardial deformation and its speed (strain, strain rate),
vector analysis myocardial movements (vector velocity imaging - VVI).
Rationale for the Doppler method
One of the main goals of routine antenatal care is to identify fetuses at risk for clinical interventions that can lead to a reduction in perinatal morbidity and mortality. Doppler ultrasonography of the umbilical artery helps to identify a compromised fetus in high-risk pregnancies and therefore deserves evaluation as a screening test in low-risk pregnancies.
Assess the impact on obstetric practice and pregnancy outcomes of routine fetal and umbilical Doppler ultrasound in unselected and low pregnancy risks. We searched the Cochrane Pregnancy and Birth Registry and reference lists of retrieved studies.
At pulse doppler study the same piezo element of the sensor sends a series of pulses with a certain frequency and receives signals reflected from moving blood cells. The advantage of the method is the possibility exact definition blood flow velocity in any selected area of the heart chamber or the main vessel, in which the control (trial) volume is set. At the same time, a graphic scan of the blood flow in the area of the control volume is recorded on the screen: the time is plotted along the abscissa axis, and the blood flow velocity is plotted along the ordinate axis.
Randomized and quasi-randomized controlled trials of Doppler ultrasound to investigate umbilical and fetal vessel signals in unselected pregnancies compared with Doppler ultrasound. Studies that evaluated uterine vessels along with fetal and umbilical vessels were included.
Two review authors independently assessed studies for inclusion, assessed the risk of bias, and performed data extraction. All trials had adequate concealment retention, but none had sufficient blinding of participants, staff, or outcome evaluators. Overall, and apart from the lack of blinding, the risk of bias for the included trials was considered low.
streams that moving towards the sensor, located above the isoline, the sender - below it. Since the same piezo element sends and receives ultrasound, the maximum frequency shift of the ultrasonic signal that can be measured using a pulse study is equal to half the frequency of the pulses sent, which is called the Nyquist limit. If the frequency shift of the ultrasound signal exceeds the Nyquist limit (at blood flow velocity > 2.5 m/s), Doppler spectrum distortion (aliasing) occurs and part of it is recorded at the top or bottom of the opposite side of the isoline. That is, in a pulsed study, the Doppler shift is limited by the Nyquist limit and the measurement of high blood flow velocities is impossible.
Overall, routine fetal and umbilical Doppler examination in patients with low or unselected populations has not resulted in an increase in antenatal, obstetric, and neonatal interventions. There were no differences in the groups that were noted for the primary results of monitoring perinatal mortality and newborns. Only one of these included a study assessing severe neonatal morbidity and found no evidence of group differences.
To compare a single Doppler score and Doppler, evidence of group differences in perinatal mortality was found. However, these results are based on a single trial and we recommend caution in interpreting this finding.
At continuous wave Doppler study The transducer sends and receives reflected ultrasonic signals continuously using two separate piezoelectric elements. Therefore, the recorded maximum frequency shift of the ultrasonic signal is not limited by the frequency of the sent pulses, or by the Nyquist limit. This allows accurate measurement of high blood flow velocities. In contrast to the pulsed mode, in a constant-wave Doppler study, all frequency shifts of the ultrasonic signal (velocity) along the ultrasonic beam are measured. Therefore, it is possible to determine the highest blood flow velocity along the ultrasound beam, but it is not possible to precisely locate the maximum measured velocity.
There was no evidence of group differences in outcomes caesarean section, tricks intensive care newborns or preterm births less than 37 weeks. Evidence for stillbirth outcomes was rated according to patient subgroups with a moderate quality rating for stillbirth and a low quality rating for stillbirth. Evidence for admission to the neonatal intensive care unit was rated as moderate quality, and data on outcomes for caesarean section and premature birth less than 37 weeks were evaluated for quality.
In this regard, in the presence of laminar low-velocity intracardiac flows(normally) it is advisable to use a pulsed Doppler study, with turbulent high-speed flows (with stenosis, valve insufficiency, intracardiac blood shunt) - a constant-wave study.
color doppler study is a variety impulsive, when not one control volume is applied, but a set (250-500), forming the so-called raster, resembling a truncated cone in shape. At the same time, the frequency shift of the ultrasonic signal is measured in each control volume, which is converted into a digital format, automatically compared with the specified color scheme and displayed on the screen against the background of a two-dimensional image. If the blood flow velocity does not exceed the Nyquist limit, then the flow directed to the sensor is usually coded in red, from the sensor - in blue and their shades.
There are no data available to assess impact on long-term long-term outcomes such as child neurodevelopment, and no data to assess maternal outcomes, especially maternal satisfaction. Using a special ultrasonic method, called Doppler sonography, we measure and determine the speed and direction of flowing blood in the arteries and veins. This gives us the opportunity to control the blood supply to certain organs and tissues that are important for the development of the unborn child. The blood flow between the uterus and the placenta, as well as between the fetus is the human embryo after the formation of internal organs.

When the blood flow above this limit (in case of turbulence), then the flow is encoded in shades of green and yellow flowers. The advantages of the method are the ability to quickly assess blood flow in the chambers of the heart and main vessels, detection and semi-quantitative assessment of the degree of valvular regurgitation, detection of intracardiac blood discharges.
The fetus and placenta can be assessed and assessed in this way. Like conventional ultrasound, Doppler sonography uses ultrasound as an imaging modality to study organic tissue. Doppler sonography is harmless to you and your baby.
In principle, we distinguish two coverage areas. The first area of care is the blood vessels that supply the uterus and placenta. The most important vessel is the umbilical artery, which indirectly shows how the baby is delivered through the placenta. With color Doppler sonographic vessels and vascular areas can be further stained. This is necessary, in particular, for the diagnosis of cardiac activity for an accurate statement. The exam is possible throughout the pregnancy. . Doppler sonography uses ultrasound as an imaging modality to study organic tissue.
Tissue Doppler- a type of Doppler study, in which the movement of the myocardium, cusps, valve rings or other tissues is recorded. In a Doppler study of blood flow, the velocities of erythrocytes are measured (more than 20 cm / s, reach 800 cm / s with valvular pathology). The speed of movement of the myocardium is less (usually 5-20 cm / s), but its amplitude is greater than that of erythrocytes.
Doppler sonography is based on. Hypertension, preeclampsia - a violation of high blood pressure during pregnancy, also known as pregnancy hypertension. The initial main symptom is the excretion of sugar in the urine. . Doppler ultrasound as a method of prenatal diagnosis.
Doppler ultrasound can monitor blood flow in the blood vessels of the unborn baby, uterus, and placenta. As a result of Doppler ultrasound, conclusions can be drawn about the care of the child, as well as the functioning of the internal organs. B. hearts are drawn.
At Doppler study of blood flow high-amplitude and low-speed (low-frequency) signal from the myocardium is considered noise and is removed by filters that pass only high-frequency signals (usually more than 400-500 Hz). In a tissue Doppler study, on the contrary, high blood flow velocities are cut off with the help of filters and low velocities of myocardial movement are recorded (frequencies 0-50 Hz).
Doppler ultrasound, also called Doppler sonography or duplex ultrasound, is a special form of ultrasound that can be used in the second half of pregnancy, among others. Doppler ultrasound scans specific blood vessels for the baby and mother, as well as blood flow between the baby and the placenta, and gives the attending physician answers to questions about whether the baby is adequately supplied. nutrients and oxygen and such internal organs as a child The heart develops according to plan.
tissue research can be represented by color mode. In this case, as in the color study of blood flow, the average speed of movement is reflected. Red indicates movement towards the sensor, blue indicates movement away from the sensor. Brighter shades correspond to more high speeds motion up to the Nyquist limit. The color image of the tissue Doppler study is superimposed on the image of the myocardium in B- or M-mode.
Doppler ultrasound uses the Doppler effect. The devices that are used for Doppler ultrasound use what is known as the Doppler effect, mothers-to-be may still be familiar with from physics classes. It is an acoustic phenomenon first described in this century by the Austrian Christian Johannes Doppler. If the transmitter and receiver of an acoustic signal move away from each other or towards each other, the Doppler effect causes expansion, or this is recognized by the receiver due to a significant frequency shift of the signal.
Doppler ultrasound indications during pregnancy
An example from Everyday life for this is Ambulance with a siren whose frequency audibly changes as soon as the car has passed and the noise goes away again. This effect is also exploited in Doppler ultrasound by emitting ultrasonic waves on the solid components of the blood using a transducer and makes the movement of blood visible on the basis of reflections. Thus, both the direction of blood flow and the velocity can be detected using Doppler ultrasound. They, in turn, provide information about the progress blood vessels, their diameter, as well as the condition of the inside of the vessel.
The advantages of the method are possibility rapid assessment of myocardial movement, including in subepicardial and subendocardial layers, as well as the possibility of simultaneous registration of the speed of movement of various segments of the myocardium and delayed assessment of the movement of individual segments. This method makes it possible to detect zones of impaired local contractility, to clarify the border of the endocardium in case of its poor visualization in the B-mode. The main limitation of this method is the possibility of overestimation or underestimation of velocities due to intraventricular block causing paradoxical movement of the heart walls, due to the Nyquist limit, and also due to complex mechanism heart contractions.
Doppler ultrasound is mainly used in the second half of pregnancy. In principle, examination with Doppler ultrasound is possible throughout the entire pregnancy. However, this is mainly done in the second half of pregnancy, because at this time the development of the child can already be assessed well. Since Doppler ultrasound is not a standard precaution during pregnancy, it is initiated by the attending physician. This is especially true in cases where anomalies were detected during conventional ultrasound, or the state of pregnancy makes it more likely organic disease or fetal malnutrition - for example, if there is multiple pregnancy, mother smokes during pregnancy or alone A high blood pressure disorder or blood type intolerance has been found between mother and child.
Tissue non-linear(C-mode) - color graphic image of movement interventricular septum, apex and lateral wall of the left ventricle in time. The advantage is the possibility of a detailed assessment of the direction of movement of the walls of the heart in various zones and detection of violations of local contractility. The limitation is intraventricular blockade, which causes paradoxical movement of the walls of the heart and makes diagnosis difficult.
Tissue Pulsed Doppler(pulsed wave tissue velocity imaging) - a graphical representation of the movement of heart structures in the area of the control volume: the time is plotted along the abscissa axis, the speed of movement of the heart structures is plotted along the ordinate axis. At the same time, systolic (Sm), early (Em) and late diastolic (Am - corresponds to atrial systole) components of the movement are distinguished. The diastolic movement of the myocardium is shaped like an inverted image of the transmitral blood flow, so the peaks are named similarly, but using the index m (Em, Am), an apostrophe (EA), or lower case(e, a).
Between end of systolic movement and the beginning of movement corresponding to early (rapid) relaxation of the myocardium, the time of isovolumic relaxation of the left ventricle (IVRT) is recorded, between the end of the late diastolic component and the beginning of the systolic component, the time of isovolumic myocardial contraction (IVCT) is recorded. The nature of the movement of the fibrous ring mitral valve used to identify and determine the type of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction.
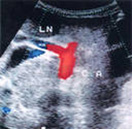 Doppler measures how sound waves bounce off moving objects. The computer processes the information and creates a two-dimensional color image showing whether there are obstructions in the blood flow, for example, due to cholesterol deposits - atherosclerotic plaques.
Doppler measures how sound waves bounce off moving objects. The computer processes the information and creates a two-dimensional color image showing whether there are obstructions in the blood flow, for example, due to cholesterol deposits - atherosclerotic plaques.
Modern devices with constant-wave, pulsed-wave and color Doppler combine the information obtained from all these types of studies. In B-mode it is possible to see the structure vascular wall. Doppler shows how blood flows through the vessels and measures the speed of blood flow. Ultrasonography can also be useful in determining the diameter of a vessel, as well as the extent of stenosis (blockage) in a blood vessel.
Traditional ultrasound uses painless sound waves that are inaudible human ear that are reflected from the vessels. A duplex ultrasound can use images that are color-coded in order to show the doctor where blood flow is severely blocked, as well as the speed and direction of blood flow. Your doctor may recommend Doppler to help diagnose or investigate conditions that affect blood vessels. These states include:
- Atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries
- Thrombosis of the veins of the lower and upper extremities
- Diseases of the arteries of the legs
- Diseases of the arteries of the hands
- Aortoiliac occlusive diseases
- Varicose disease
- Aneurysms of large vessels of the abdominal cavity or extremities
Doppler duration (USDG)
Ultrasound usually lasts 20-60 minutes. Duplex ultrasound does not require the administration of special drugs and is usually associated with minimal discomfort.
How to prepare for Doppler?
 For most types of Doppler not related to abdominal cavity, no special training required. Your prescribing doctor may give specific instructions for a particular type of Doppler. For example, you will not be required to eat the night before the test. Ultrasound cannot pass through gas in the intestines and through air in the lungs.
For most types of Doppler not related to abdominal cavity, no special training required. Your prescribing doctor may give specific instructions for a particular type of Doppler. For example, you will not be required to eat the night before the test. Ultrasound cannot pass through gas in the intestines and through air in the lungs.
What happens during Doppler?
Before the examination, the doctor will ask you to lie on the table with your head slightly elevated. The gel is then applied over the study area. The gel improves the transmission of ultrasonic waves.
The doctor presses the sensor to the skin and begins to move it. The pressure from the ultrasound transducer may cause some discomfort, but most people do not find the procedure painful. The ultrasound sensor sends signals to the computer, which the computer converts into images that are displayed on a monitor that looks like a TV. You may hear a whistling sound, which is the sound the ultrasound machine uses to display the movement of blood in your body.
What to Expect After an Ultrasound (Duplex Ultrasound)?
Dopplerography of cerebral vessels
![]() Transcranial doppler (another name for ultrasound dopplerography vessels of the brain) has been used in medicine since 1983. Cerebral Doppler is used to assess blood flow (blood circulation in the vessels of the brain) - this is a complex study, the effectiveness of which depends not only on the experience and knowledge of the doctor performing Dopplerography, but also on the acoustic window (thickness and structure temporal bone through which the study is carried out). Cerebral Doppler is used to assess:
Transcranial doppler (another name for ultrasound dopplerography vessels of the brain) has been used in medicine since 1983. Cerebral Doppler is used to assess blood flow (blood circulation in the vessels of the brain) - this is a complex study, the effectiveness of which depends not only on the experience and knowledge of the doctor performing Dopplerography, but also on the acoustic window (thickness and structure temporal bone through which the study is carried out). Cerebral Doppler is used to assess:
- Risk of violations cerebral circulation– stroke
- Spasm of cerebral vessels
- After operation coronary artery bypass grafting(to assess the risk of embolism in the vessels of the brain)
- In neurosurgical patients
- Anomalies in the development of cerebral vessels
In some cases, neuropathologists prescribe transcranial Doppler for:
- Migraine
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia
- dizzy
- Headaches of unknown origin
Dopplerography of the vessels of the neck
Doppler of the vessels of the neck allows you to identify diseases of the carotid and vertebral arteries. Dopplerography is usually prescribed by a neurologist. Doppler (Doppler or Duplex Ultrasound) is indicated for the following symptoms:
- A picture of transient ischemic attacks with temporary paralysis of half of the body or arm (hemiparesis), speech impairment, etc.);
- Temporary blindness in one eye;
- Noise in the head;
- Dizziness;
- Flashing before the eyes;
- Headaches without a clear localization;
- Brief loss of consciousness;
- Falls without loss of consciousness;
- Temporary imbalances;
- Migraine or migraine-like headaches
- Detection of atherosclerotic plaques in other vessels
Dopplerography of vessels lower extremities
Doppler ( duplex scanning) vessels of the lower extremities allows you to identify diseases of the arteries and veins of the lower extremities. Doppler of the lower extremities is assigned vascular surgeon. Doppler is performed for the following symptoms and diseases:
- Diseases of the arteries of the lower extremities
- Intermittent claudication (pain in calf muscles, which appear when walking and disappear after a short rest)
- chilliness hypersensitivity feet to the cold
- Feeling of numbness in the feet
- Diseases of the veins of the lower extremities
- Heaviness in the legs
- Swelling of the legs
- Pigmentation of the skin on the legs
Examination of which vessels the patient needs is determined by the attending physician.

