Operations for atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities. Shunting of vessels of the lower extremities in gangrene
Shunt in translation from English - to bypass an obstacle. If on inner wall artery, an atherosclerotic plaque protruding into the lumen was formed and one or even several blood clots (blood clots) "sat" on it, then the passage of blood through the vessel is blocked. The tissue supplied with blood from the total vessel is at risk of necrosis (necrosis). To prevent this from happening, surgeons eliminate the obstacle that has arisen in the path of blood flow by sewing the ends of an artificial vessel - a shunt - above and below the blocked area of the vessel. The blood flow rushes along this detour, carrying oxygen to the tissues and nutrients(if it is an artery) or carrying away metabolic products (if a vein was blocked).
Select vessels for shunts, prepare a place for sewing them in - this is very thin and delicate work which requires careful preparation. The introduction of microsurgical techniques made it possible to expand the possibilities of the operation, to qualitatively change the operation itself, and thanks to this, to achieve good results.
The deposition of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of large and medium-sized arteries of the extremities leads to a narrowing of the lumen (stenosis), blockage of the lumen of the vessels and, as a result, the cessation of blood flow in them. Of course, this happens gradually, over the years. But sooner or later, due to circulatory disorders in the legs, for example, when, a person begins to quickly get tired when walking, cannot walk much, he has pain in calf muscles, and he has to stop, waiting for them. There is a so-called symptom of intermittent claudication. Against the background of ongoing bleeding, a blood clot can “sit down” on the plaque in the vessel, which will completely block the artery, and then the situation becomes acute, since necrosis, that is, gangrene of the leg, can occur. Here time runs for minutes. Happiness if the patient is on time in a specialized department vascular surgery where, with the help of ultrasound, they will find the place of blocking the blood flow and quickly perform a life-saving operation.
Removal of a thrombus and restoration of blood flow can be make directly through the incision or with special device injected through the vessel. If in this way it is not possible to eliminate the obstacle, then shunting is performed.
As shunts As a rule, synthetic prosthetic vessels of various configurations are often used. But often, in order to save an artery, a vein is sacrificed. At venous system such a feature that from one large vein several duplicating vessels may depart (for example, in the legs). Therefore, one of them can be used to replace a blocked artery. The venous insert is strong enough and holds the arterial blood flow in a small area. In addition, it is native to the body, and therefore it is used quite widely. Synthetic prostheses are mainly used when bypassing large vessels (aorta, iliac, femoral, carotid arteries), since large vessels constantly have to experience the pressure of a powerful flow of blood from a beating heart.
It happens that after suturing the injured artery, it narrows, like an isthmus in hourglass(However, this often occurs with atherosclerosis). To eliminate such a defect, autotransplantation with a fragment of a vein. In other words, a “patch” is placed on the narrowed section of the artery.
In patients with atherosclerosis, shunt operations to restore blood flow in small arteries sometimes end in thrombosis due to the hemodynamic system of the blood itself: at the periphery, where blood flows through shunts, vascular resistance is higher than when passing through shunts. But if at least one of the three arteries of the lower leg is in good condition, this will allow the development of bypass routes of blood supply. And why, then, not take the risk of having an operation that preserves a person's leg and the ability to move? After all, the technique of shunting small (peripheral) arteries lower extremities with the use of venous vessels worked out successfully.
How to behave after bypass surgery of the vessels of the lower extremities?
Periodically take blood tests, checking the number of platelets and the state of prothrombin, and evaluate two opposite processes - blood viscosity and antiviscosity. Everyone who has undergone surgery should take drugs that thin the blood and prevent blood clots. Of the simplest, this acetylsalicylic acid(thrombo-ass and aspirin), but there are more modern facilities that improve the condition vascular wall at the level of microcirculation and quality characteristics blood. The attending physician will prescribe them to the patient.
We have talked about bypassing large or small arteries without mentioning veins. The question arises: “Do veins not have to create bypasses for impaired blood flow?”
Artery- this is a powerful vessel with a thick wall; it is more convenient to operate and sew less durable walls near the vein. Nevertheless, now phlebology is actively developing - this is required by the treatment of such extremely common vein pathologies as varicose disease and thrombophlebitis (inflammation of the vein wall with the formation of blood clots). They are fraught with the danger of thromboembolism. Embolism- this is an acute blockage of the vessel by some insoluble substrate brought by the blood flow. This subgratum (embolism) may be air that has entered the vessels during intravascular injection, may be parts of a tumor or a thrombus that has come off the vessel wall.
This condition poses a threat to life, when the only way to save a person becomes emergency operation on the veins.
Vascular shunting is indicated for serious pathologies which lead to poor blood circulation. In what cases is shown surgical intervention? What rules should be followed for speedy recovery how to avoid complications?
When is shunting necessary?
Shunting of the vessels of the lower extremities is a surgical intervention that is performed in a hospital. In some cases, according to medical indications possible operation under local anesthesia, which avoids serious complications, reduces the duration of the recovery period.
Shunting is done after thorough examination, the operation is prescribed only in cases where the application medicines did not improve the patient's condition. During the procedure, a branch of the vessel is created, blood clots are removed, atherosclerotic plaques- it helps to eliminate congestion, reestablish normal movement blood. A shunt is an artificial adapter used to connect parts of a damaged vessel. They are made of synthetic materials or a piece of healthy vein, their service life is about 5 years.
Indications for shunting:
- serious pathological changes in blood vessels;
- phlebeurysm;
- atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities;
- aneurysm of peripheral vessels;
- endarteritis;
- the presence of blood clots and plaques that block the lumen of blood vessels;
- gangrene or the threat of its development.
Sometimes a metal tube can be led into the damaged vessel to expand the passages - this procedure helps to eliminate plaques. But for many patients, such manipulations are contraindicated, only shunting will help to solve the problem.
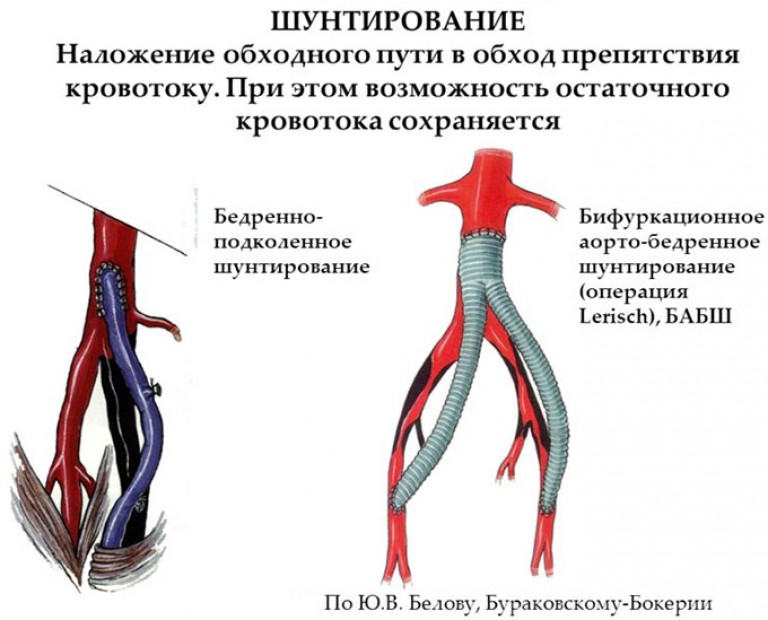
The main types of shunting
The type of shunting is selected by the attending physician, depending on the location of the damaged vessels, the results of the examination, the stage of the disease, and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
The main options for shunting:
- Femoral-aortic - the skin is cut into inguinal region or lower abdomen. A high-strength polymer shunt is attached to the walls of the vessel above the occluded area, the second end is attached to one or both femoral aortas.
- Femoral-popliteal - the prosthesis is installed through an incision in the inguinal part and the back of the knee. This method is used for damage to the arteries in the thighs.
- Tibiofemoral - as a prosthesis, a saphenous vein is used, which is attached to the affected artery. The operation is indicated for pathological changes in the vessels of the thighs or under the knee.
At total absence of arteries not affected by atherosclerosis, jumping shunts are installed - with the help of small anastomoses, healthy parts of the vessels are connected. If the arteries in the foot are affected, then microsurgical shunting is performed using autoveins.
Any type of bypass is contraindicated for hypertension that is difficult to treat, with severe forms heart failure with shortness of breath and swelling, frequent seizures angina pectoris, cardiac aneurysm, persistent violations heart rate. Your doctor may advise you to postpone surgery if high level blood sugar, the presence of infectious diseases, dermatological problems skin legs.
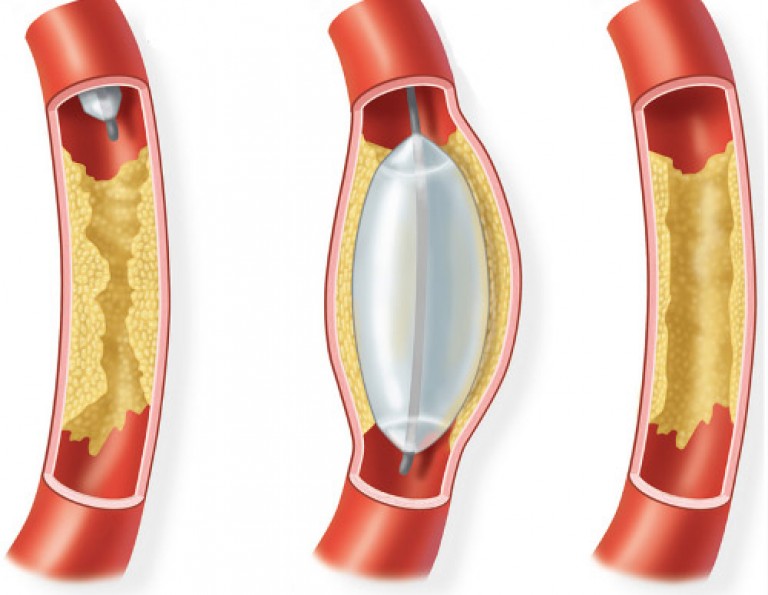
Operation steps
Bypass surgery is a serious operation that is carried out after careful medical examination. Main types preliminary diagnosis – general analysis blood, electrocardiogram, MRI, CT scan, duplex ultrasound procedure. These methods help determine the degree pathological changes in blood vessels and circulation.
A week before the operation, the patient needs to stop taking anti-inflammatory, blood-thinning drugs, start drinking antibacterial drugs. One day before surgical intervention dinner should be light, after midnight you should refuse to take water and food.
The main stages of shunt implantation in the vessels of the lower extremities:
- The surgeon makes a small incision just above the damaged vessel.
- The specialist analyzes the level of blood circulation, finds the area in which it is necessary to install the shunt.
- The second incision is made below the damaged vessel, an adapter is installed.
- The shunt is placed between the tendons, muscle fibers, it is carried out to the border of the healthy part of the vessel.
- Fixing an artificial element, checking its functional qualities.
- Before suturing, the surgeon checks the patency of the vessels using an arteriogram, duplex ultrasound.
The duration of shunting is 1-3 hours, after the end, the patient is put on an oxygen mask. Within 1-2 days the person is in the ward intensive care, with the help of a dropper, painkillers are administered to him. To reduce swelling, cold compresses are made, special socks or shoes are put on that prevent the formation of blood clots.
Shunting is a complex and expensive procedure, on average its cost is 130-160 thousand rubles. Before the operation, the patient should carefully approach the issue of choosing a clinic and a specialist - even a minor mistake by a surgeon can lead to serious complications, lethal outcome.
Possible Complications
During the operation, there are allergies to anesthesia, heart attack, drops blood pressure. Often occur severe bleeding, which leads to blockage of blood vessels with blood clots. Sometimes develop infectious pathologies This leads to the need for limb amputation.
After shunting of the arteries of the lower extremities, there may be an increase in temperature in the area of damaged vessels, inflammatory processes around the seam purulent discharge, weakness. In this case, you need additional examinations, drug therapy.
The most common complications occur in people with overweight, diabetics, hypertensive patients. Problems after shunting may be due to excessively high levels bad cholesterol, in patients with poor physical shape, obstructive pulmonary pathologies, kidney failure, coronary disease. Negatively affects the course of the operation long-term smoking, drinking alcohol.
Features of recovery after bypass surgery, prognosis for recovery
For 10-14 days after the operation, a person should be in a hospital - constant monitoring by specialists and diagnostics will help make sure that the bypass was successful. In the absence of complications, the sutures are removed after a week - by this time, blood circulation is normalized, general well-being person improves. When discharged from the hospital, the doctor gives recommendations that the patient must strictly follow - only in this case, the prognosis for full recovery will be favorable.
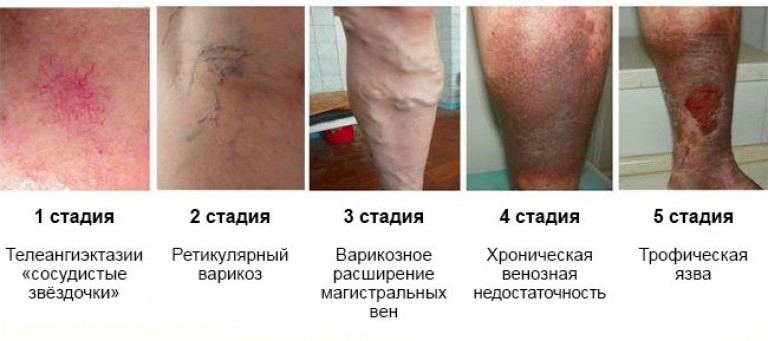
Rules of conduct in postoperative period after shunting:
- When pain syndrome, redness of the operated limb, you should immediately consult a doctor - self-medication can cause serious complications.
- Regular check-ups, exercise with a physiotherapist, walk daily, gradually increasing the distance.
- Accept medicines to normalize the work of blood vessels, prevent the appearance of new plaques and blood clots. The drugs are prescribed by the attending physician.
- Control weight, exclude harmful and high-calorie foods from the diet. Go in for sports - the load should be moderate, but regular.
- In the sitting and lying position, the limbs should always be elevated.
- Completely abandon addictions- Smoking, drinking alcohol.
- It is strictly forbidden to wet postoperative wounds, use powders.
The first 4 weeks after surgery on the vessels of the lower extremities are the most important. Need to consume more products that normalize cholesterol levels - citrus fruits, berries, vegetables with high content vitamin C. Fatty varieties should be present in the diet sea fish, all types of cabbage, bee products, you should regularly drink a decoction of rose hips. According to patients, compliance with all the rules and recommendations will speed up the recovery process, minimize the development of complications after bypass surgery.
Healthy vessels of the lower extremities are smooth inside, with atherosclerosis, plaques form on the walls, which narrow the lumen - this leads to poor blood circulation, tissue necrosis. With absence positive result, inefficiency drug therapy The patient is scheduled for a bypass complex operation, after which a long recovery awaits a person, he must strictly follow all the recommendations of the attending physician.
Shunting of the vessels of the legs is carried out in order to create a shunt bypassing a vessel clogged with blood clots or atherosclerotic plaques. This operation is performed if the patient has a severe form vascular insufficiency, and it allows you to save the limb in the development of gangrene. Treated with shunting ischemic disease heart and brain in severe form, the so-called coronary artery bypass surgery. The operation is performed in such a way that a shunt is made from the artery located above the lesion to the artery located below the affected area, thereby completely restoring blood supply.
Indications for surgery
Shunting of the vessels of the lower extremities is indicated for:
- obliterating,
- prohibition to carry out stenting or;
- endangered legs if tormented constant pain and conservative treatment turned out to be ineffective;
The patient to be bypassed must be walking. If the patient is immobilized due to another serious illness and he develops gangrene, then amputation of the leg is indicated.
Diagnostics
Before the bypass surgery of the vessels of the lower extremities, the patient must undergo general clinical examinations, magnetic resonance angiography, duplex ultrasound scan and . After all studies, the surgeon plans further actions- an artery is selected below the affected vessel, which will have to provide blood to the limb. Her final examination is the final stage of diagnosis. If it is suitable, then an operation is performed, and if the doctor considers the artery unsuitable, then continue to search or refuse bypass surgery.
The operation itself is carried out under local or general anesthesia according to doctor's instructions. For shunts, the saphenous veins of the thigh are taken, since they are not affected by atherosclerosis, and they are also quite long and large, they are easy to remove. Therefore, they are more suitable for the role of a shunt. In addition to the femoral veins, other veins or synthetic shunts may be used. Next, the surgeon makes an incision at the site of the affected artery, highlights it, and incisions are made where the shunt is supposed to be sutured. After that, the shunt is sutured to the site of the affected vessel. In general, this is the whole operation. At the end, it is necessary to do angiography and ultrasound to check the function of the shunt, the speed of blood flow in it and in lower arteries. If there is any doubt about normal operation shunt, contrast angiography is done and corrective action is taken.
After operation
Usually, blood flow is restored within a few hours, the vein in the foot fills up, and the temperature of the leg rises. The nature of the pain syndrome in the leg is changing. If before the operation you wanted to lower the affected leg down to reduce pain, then after bypass surgery, on the contrary, it is easier with the leg raised to the top. The pains are transformed into burning sensations, which completely disappear after 3-5 days. But there is one more consequence after the operation - edema, which is quite long time does not go away, but after 2 months it begins to disappear. Shunting promotes healing of gangrene on the foot.
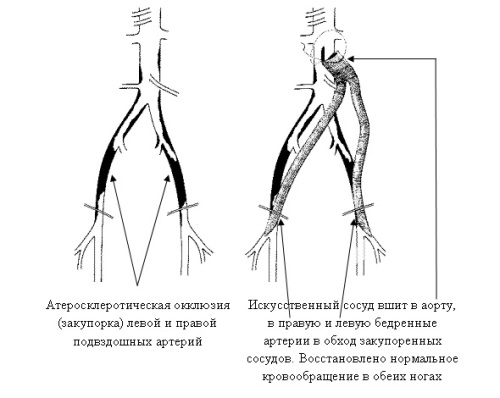
Prevention
Shunts usually function up to 5 years, but it is important to periodically do thrombosis prophylaxis and undergo examinations. Remember that when doing all postoperative recommendations, and most importantly, with a correctly performed operation, the probability of saving a gangrenous leg is 90%. It is important to know that after the operation, atherosclerosis will not go anywhere, and will still progress, and plaques can again create a problem. Therefore, doctors recommend patients:
reduce weight;
stop smoking;
raise physical activity;
limit fat and high-calorie foods in your diet;
undergo examinations in a timely manner;
take statins and anticoagulants.
Required for most patients. In some cases, if there is a risk of thrombosis in the area of the vascular suture, especially in elderly patients, anticoagulants are prescribed - heparin, 5000 IU every 4-5 hours. The introduction of anticoagulants is allowed 12-20 hours after the operation. The limb of the patient is placed between the pillows or fixed with a plaster splint and laid in bed in a horizontal position.
It is necessary that patients after operations on vessels in the first days be in special postoperative wards, where all measures would be provided in case of occurrence dangerous complications. The staff of these wards, as well as patients, should be trained in the technique of temporarily stopping bleeding (pressing the vessel over, applying a tourniquet). There must be tourniquets in these chambers; during operations on the limbs, an unstretched tourniquet is strengthened on the proximal limb.
In addition, in a sterile bix, material and sterile rubber gloves are prepared in case of pressing a bleeding vessel in the wound. In addition, the wards are equipped with sterile equipment for blood transfusion, blood substitutes and cardiac drugs.
After surgery on the vessels, warming and light distal limbs with a slight cooling of the skin, paresthesia can be recommended. Light movements are recommended to start from the 2-3rd day after the operation. On the 10-11th day, depending on the nature of the operation, the age of the patient and the postoperative course, they usually allow movement around the ward. Skin sutures removed at the usual time, on the 7th day. Throughout this period, generally recognized measures of dietary and medical nature, as in other patients undergoing complex operations.
From postoperative complications after operations on the vessels, the following should be mentioned:
- failure peripheral circulation(ischemic phenomena);
- bleeding;
- wound infection.
Peripheral circulatory insufficiency (ischemic events) are the most frequent and specific complications after operations on the vessels; they are associated with the shutdown of the arterial line by a ligature, a thrombus, or with extensive vascular spasm.
Ligature main vessels in most cases does not lead to severe ischemic disorders due to the development collateral circulation. Wherein great importance has the age of the patient, the nature of changes in the vascular bed, branching of the arteries, the method of turning off the vessel and other points. Spasm of the artery and, most importantly, of the extensive collateral network, associated with trauma to the adventitia of the artery in case of injury or ligature, undoubtedly affects the development of ischemia. This circumstance made it possible to propose methods for dissecting the artery between ligatures and arteriectomy, which were discussed above. These operations are aimed at preventing arterial spasm and the development of ischemia.
A rapidly onset thrombosis or embolism of the artery leads to an even more pronounced vasospasm, which often causes gangrene of the limb. Slow, gradually increasing, parietal thrombosis leads to less noticeable manifestations ischemia, since in this case conditions are created for the gradual expansion of the collateral bed.
In mild cases of ischemia, there is a slight cyanotic coloration of the skin of the distal limbs with separate islets. white color and crimson spots, mainly on the foot or hand. Skin temperature drops slightly slight decrease pain and tactile sensitivity, finger movements are preserved.
With more severe degrees circulatory disorders, there is a sharp constant pallor of the limb, the skin of which has a marble appearance. When squeezing the nail or skin, there is no play of capillaries. The skin temperature on this limb is reduced by 10-15° compared to the healthy side. There is a lack of sensation and movement in the limb. With thrombosis and embolism, strong pain on the periphery of the limb. In the future, with an unfavorable course, all these phenomena increase and ischemic gangrene of the limb occurs. The latter is dry or wet, depending on various conditions(infection, venous stasis). In case of blockage of the general or internal carotid artery there may be ischemic phenomena from the brain, manifested by various disorders (hemiparesis, visual impairment).
Proper organization postoperative care for patients after vascular surgery, helps to reduce these complications and mortality. If bleeding occurs, the limb above the operation site is pulled with a tourniquet. In case of bleeding from the vessels of the neck, supra- and subclavian space, pelvis, it is required that the neighbors in the bed or the patient himself press the bleeding place with his hand or squeeze the vessel along. Quickly summoned nurse should put on a sterile glove, cut and remove the bandage and close the bleeding vessel deep in the wound with your fingers. At the same time, the patient needs to establish a massive jet intravenous blood transfusion in the ward, the introduction of painkillers and cardiac drugs. After that, the patient enters the operating room and there they perform a revision of the wound, additionally suture or ligate the artery or vein.
Wound infection after vascular surgery great danger, especially with ligature main artery. In this case, there is expressed in varying degrees or ischemia peripheral departments limbs, oxygen deficiency in muscle tissue, trophic disorders. With vein ligature and venous congestion under conditions of wound contamination, thrombosis of venous collaterals and the main vein may occur, followed by infection of blood clots.
Especially often, wound infection occurs after operations for wounds of vessels in peacetime and wartime. The percentage of suppuration after surgery for gunshot wounds vessels was 23%. The most dangerous in these cases must be considered anaerobic infection, which was the cause of death after vascular surgery in 12.6% of the wounded.
The period of widespread introduction of antibiotics into practice has undoubtedly reduced the frequency of this complication. However, it is still recommended to vascular operations in especially aseptic conditions (in some cases after preliminary prophylactic administration of antibiotics). At the end of the operation on the vessels, they are used topically antiseptic solutions. After surgery on the vessels, antibiotic injections are prescribed for 3-5 days. It also requires a good wound and observation of it in order to detect infection. With the development of this complication, a wide opening and drainage of the wound is recommended.
Shunting of vessels of the lower extremities - surgery in order to restore blood supply bypassing the affected area of the vessel by creating an artificial anastomosis. The operation is performed in case of stenosis or obliteration of the vessel. Shunting is performed with obliteration coronary arteries hearts, but this operation indicated for the treatment of legs.
Vein bypass is indicated when treatment with conservative methods did not give a positive result and there is a risk of limb amputation. The operation is prescribed for:
- atherosclerosis lower vessels on foot.
- Varicose veins of the lower extremities.
- Endarteritis.
- Necrosis of the lower limb.
- Aneurysm.
- Other vascular pathologies, when tissue stenosis and ischemia are noted, etc.
Shunting is used in last resort only if stent placement or angioplasty cannot be performed for any reason. In patients with critical ischemia (malnutrition of tissues as a result of insufficient blood supply) of the lower extremities, as a rule, amputation of the leg is prescribed within six months after the onset of the disease. Bypass surgery performed in patients with critical ischemia allows 90% to save the patient's limb.
In case of severe vascular injury, life threatening patient, angioplasty of the arteries or veins of the leg is first offered. Endarteritis with gangrene of the leg - good reason for microsurgical shunting. With segmental narrowing of the veins, endovascular treatment is indicated - stenting, balloon dilatation or angioplasty. Vein bypass surgery is used to save the lower limb, in case of ineffective treatment.
In case of stenosis of a long vessel, shunting is combined with prosthetics of the affected area of the vein or artery with an alloprosthesis, thromboendarterectomy. In cases of multiple atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities, vein shunting is combined with dilatation of the course. If tissue nutrition is disrupted for a long time and there is necrosis or trophic ulcers, then after restoring blood flow, another operation is required to remove dead tissue and close trophic ulcers with a skin flap. Such an operation can be carried out on the same day as the bypass, or after a certain period of time.
If a necrotic changes affect vast areas of the soft tissues of the leg and the restoration of blood flow is impossible, then, in order to save the patient's life, amputation of the limb is indicated. Use of vein bypass or other methods surgical treatment and restoration of blood supply to the lower extremities is prescribed after a thorough study of the state of the lower vessels.
Patient preparation
Vascular bypass surgery of the lower extremities requires preoperative preparation. The doctor prescribes a hardware study of the condition circulatory system legs. It:
- Duplex scanning for examining the cavity of veins and arteries, determining the localization of blocked areas of the lower vessels and the speed of the hemoflow.
- Magnetic resonance angiography for layer-by-layer examination of the lower veins.
- Angiography - an assessment of the nature of the narrowing of the vein is carried out and a blocked area is found along the course of the vessel.
Shunting of the heart vessels is preceded by ultrasound of the organ and coronography. An increased risk of postoperative treatment complications is observed in patients with:
- High blood pressure.
- High cholesterol.
- Pathology of the heart, lungs, kidneys.
- Diabetes, etc.
In this case, vein bypass is justified only if there is a threat to the life of the patient. Conducting a thorough assessment of the condition of the saphenous veins is due to the fact that the period of operation of the shunt and the effectiveness of treatment depend on this. Shunting with an artificial prosthesis is done as a last resort, since surgeons' reviews indicate that half of the veins are clogged after 3 years.

Basic Options
Depending on the localization of the narrowing of the area along the course of the vessel of the lower limb, treatment is carried out using various options bypass:
- Femoral-tibial - during the operation, the patient's great saphenous vein is used, which is left in place. This type of leg vascular shunting is the main treatment for severe ischemia. AT initial stage gangrene, accompanied by necrosis of the toes and trophic ulcers, in 90% it is possible to save the limb. If big saphenous vein is not suitable, then a fragment of the veins of the legs or arms is taken for treatment.
- A peroneal artery bypass is performed if the blood volume is not sufficient for the shunt to function. For the success of treatment, it is necessary to accurately determine the volume of hemoflow. To reduce pressure in the artery, the imposition of collaterals with veins located along the vessel, at some distance from the anastomosis, is used.
- Multi-storey shunts - in the absence of patency of the artery on the lower leg, several anastomoses can be made to sections of the artery with preserved blood flow. To avoid overloading the shunts, a certain number of unloading fistulas are used along the course of the vessel.
Microsurgical shunting on the foot of the limb is indicated with complete closure of all arteries of the lower leg. To save the leg, the treatment is carried out with the imposition of microshunts along the vessels of the foot. Such an operation became possible with the use of an operating microscope in surgery at a 25-50-fold magnification.
Progress
How is shunting done? As a rule, shunting is performed under epidural anesthesia. This helps not only to avoid complications caused by general anesthesia but also to eliminate pain in the postoperative period. First, small incisions are made along the vessel in the groin, on the lower leg or foot of the lower limb. After assessing the condition of the artery, a shunt is prepared. A vessel is pulled out through the holes along the vein on the lower leg and thigh. Shunting of the vessels of the lower limb begins with the connection of the vein with the artery of the thigh. With the help of valvulot, the valves of the vein are removed and blood is drawn through the great saphenous vein into the lateral part of the leg.
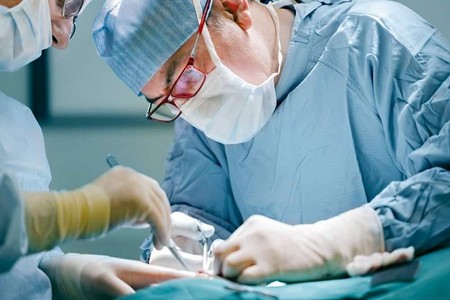
Conducting hardware research, the doctor finds places where blood flows through the shunt into the lateral branches, and through small incisions along the branches, ligates them. Then, under a microscope, a vein is sutured to an artery in the leg and foot area, blood flow is started and evaluated using ultrasound. If the blood flow in the vein is normal, then the incisions are sutured. If the result is unsatisfactory, then a repeated hardware analysis is performed and the plasticity of the vessel lateral to the shunt is performed. The duration of the operation depends on the complexity and extent of the vascular lesion.

