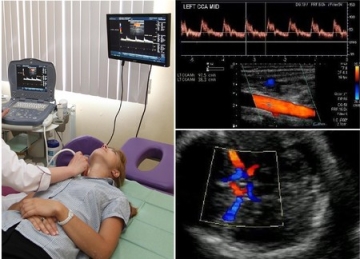
Duplex scanning of brachiocephalic arteries. Doppler ultrasound and duplex scanning
Ultrasound duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries or BCA ultrasound for short is a modern ultrasound method for diagnosing blood vessels, including carotid and vertebral vessels that supply blood to the brain, and subclavian arteries.
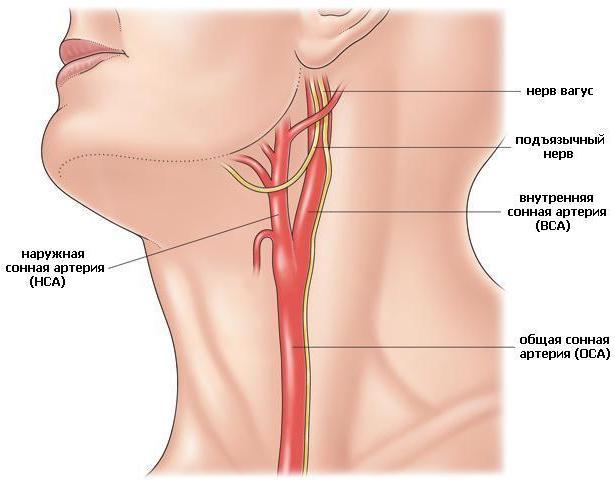
First of all, a person who is assigned this study may have a question - what are the brachiocephalic arteries and where are they located.
Brachiocephalic vessels are the largest arteries and veins that are responsible for blood flow to the tissues of the head, brain and to upper limbs. They are also called main lines.
The brachiocephalic arteries include the carotid, subclavian, vertebral and their junction, which forms the brachiocephalic trunk. These vessels and some others near the base of the brain form the circle of Wellis, which is responsible for the distribution of blood flow to all parts of the brain.
What is it - duplex scanning of brachiocephalic arteries, and what is the basis of the technique?
The apparatus for examining BCA is based on the principles of echolocation. The working surface emits and then captures ultrasonic pulses. The information is converted into a digital signal. Thus, the image appears on the monitor.
The method is based on the union benefits of B-mode- visual interpretation of the state of blood vessels and adjacent tissues and Doppleroscopy - qualitative and quantitative properties of blood flow. The Doppler spectrum can also be supplemented with color mapping.
What does BCA ultrasound show?
BCA ultrasound shows:
- lumen of blood vessels;
- blood clots, plaques, detachments;
- stenosis, expansion of the walls;
- breaks, deformations.
With the help of BCA ultrasound can be diagnosed:
- vascular pathologies;
- violation of wall tone in VVD;
- arterial aneurysms;
- fistulas between vessels;
- angiopathy;
- thrombosis;
- vascular injury;
- varicose disease.
Vessels of the brain - it's difficult arranged system capable of self-regulation and maintenance cerebral blood flow. Only complex diagnostics, which includes ultrasound scanning, CT, MRI, allows you to accurately and timely choose the treatment, and then evaluate its effectiveness.
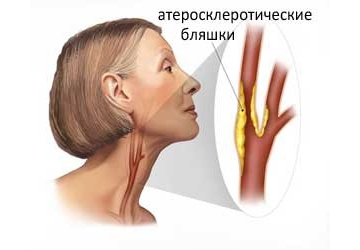
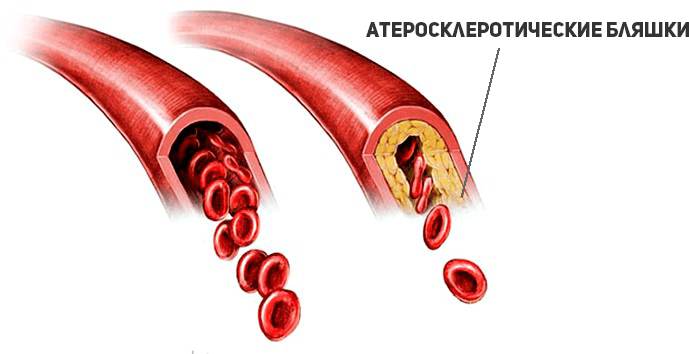
Ultrasound helps to assess the anatomy of blood vessels, determine the characteristics of blood flow, assess the condition of the walls and lumen. Thus, it is possible to diagnose early stage occurrence of atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots, tortuosity of arteries and their stratification.
Peculiarities
The initial sign of atherosclerosis, which can show an ultrasound study, is not even a plaque, but thickening of the wall of the carotid artery by only a fraction of a millimeter. With duplex scanning, this indicator is well defined. The thickness of the intima-media complex (the so-called KIM) is also called. IMT is taken into account to assess the effectiveness of treatment.
 An increase in IMT greater than 1 mm is most often associated with risk factors such as smoking, arterial hypertension, diabetes, etc.
An increase in IMT greater than 1 mm is most often associated with risk factors such as smoking, arterial hypertension, diabetes, etc.
As the disease progresses, plaques begin to form. Usually they are localized in the so-called. carotid bifurcation - this is the place where the common carotid artery divides into internal and external. The presence of plaque in this segment is major risk factor for stroke and myocardial infarction. Therefore, it is very important to timely detect atherosclerotic changes in the early stages.
Duplex scanning reveals the location of the plaque, as well as its shape, size, structure and degree of stenosis (narrowing of the lumen). When the lumen is already completely closed - this is occlusion.
During the study of BCA, it is often detected tortuosity of the arteries due to their lengthening. Arteries lengthen due to atherosclerosis and increased blood pressure. Tortuosity of the vertebral arteries is usually due to defects cervical region spine. If the tortuosity leads to clamping of the lumen, then this can cause a violation of cerebral blood flow.
Ultrasound scanning is also used for examining patients with traumatic injury vessels: wall bundle or similar. The main symptom of this disease is severe headache that cannot be reduced with conventional painkillers.
The advantages of BCA ultrasound can be called:
- high information content;
- research efficiency;
- safety and the possibility of repeated holding;
- painless procedure.
During the study on the monitor an image is formed similar to a conventional ultrasound, but a vessel is clearly visible against its background where the blood flow is formed. Due to the advantages of ultrasound, BCA is considered the gold standard for diagnosing pathologies. A timely ultrasound of the vessels can save lives and prevent possible disability.
Indications for carrying out
The indications for the appointment of duplex scanning of the BCA are:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- violation of coordination of movement;
- pressure problems;
- fainting;
- elevated cholesterol levels;
- sensory disturbance (numbness) of the limbs;
- blurred vision;
- flashing flies in the eyes;
- memory impairment and decreased concentration;
- preoperative examination.
Direct indications for the study are following pathologies:
- atherosclerosis;
- hypertension;
- cardiac pathologies;
- neck injuries;
- compression of arteries and veins and other vascular injuries;
- vasculitis;
- blood diseases;
- suffered a stroke or heart attack.
Training
Preparation before the study consists in excluding from the menu products and dishes that can affect the tone and filling of blood vessels, which will distort the results of the study.
On the day of the study, you can not drink tea, coffee, energy drinks, Coca-Cola, alcohol, you should not be zealous with overly spicy and salty dishes. Right before the ultrasound of the BCA, one should not be in stuffy or smoky rooms, as this can also change the blood supply to the vessels. It is better to refrain from taking vitamins and nootropics the day before the study.
The use of the device is absolutely harmless and has no effect on the body person.
How is it carried out
The patient lies on his back on the couch near the apparatus, the doctor puts a roller under his neck. The head should be turned in the opposite direction from the apparatus. The doctor lubricates the surface of the skin with a gel that facilitates the passage of the ultrasound signal.
 The doctor will examine the sensor segment by segment, observing the change in the signal on the monitor. He can lightly press the sensor on the vessels or ask for a short time stop breathing.
The doctor will examine the sensor segment by segment, observing the change in the signal on the monitor. He can lightly press the sensor on the vessels or ask for a short time stop breathing.
None discomfort during the study does not occur: according to the sensations, the procedure is no different from the usual, familiar to everyone ultrasound. The study lasts 20-30 minutes.
Deciphering the results of the study
The scanner will record the necessary indicators, the doctor will enter them into the scan protocol. Deciphering the Doppler spectrum, cartograms of blood flow will take no more than 10 minutes, after which you will receive a transcript.
The result of the scan is a transcript of the information received, printed out with a list of the examined vessels and a description of their size and condition. Decryption gives the ability to determine whether the vessels correspond to the anatomical norm whether there is a pathology, etc. Based on the transcript, your attending physician, if necessary, prescribes treatment.
The decoding is carried out by comparing the indicators:
- the nature of the blood flow;
- its speeds: systolic (max) and diastolic (min);
- wall thickness;
- pulsator index (so-called PI) is the ratio of the difference between max and min speeds to the average (the sum of max speed and two min divided by three);
- resistive index (so-called RI) is the ratio of the difference between max and min speeds to min;
- systolic-diastolic ratio: max speed divided by min.
Based on the last 3 indices, the patency of the vessel is judged.
The blood flow is assessed in the external and internal carotid arteries, common (ECA and ICA, CCA), supratrochlear (NMA), basilar (OA), vertebral (PA) and in its segments, each of which has its own designations, for example, Vo, V1, V3 etc.
 Also in front, back, middle cerebral arteries(PMA, PCA, MCA), subclavian (RCA), anterior and posterior communicating (PSA, PCA) arteries. Changes in indicators can also be assessed with horizontal and vertical position body.
Also in front, back, middle cerebral arteries(PMA, PCA, MCA), subclavian (RCA), anterior and posterior communicating (PSA, PCA) arteries. Changes in indicators can also be assessed with horizontal and vertical position body.
It can be summarized that ultrasound of the BCA is a special type of ultrasound diagnostics of blood vessels that provide nutrition to the brain, other organs of the head, neck, girdle of the upper extremities.
This is an affordable, safe, detailed and informative study, which in ten minutes can show the state of the vessels and identify the cause of some unpleasant symptoms. An annual examination will allow 90% to predict the development of a cerebral stroke.
The study of extracranial (neck) and intracranial (intracerebral) vessels is the most informative modern method diagnosing disorders cerebral circulation, which makes it possible to evaluate not only functional indicators blood flow, but anatomical changes vessel (patency, wall condition, bends, malformations, etc.). duplex scanning also used for peripheral circulation studies.
 The term "duplex" means a combination of two ultrasound modes: B-mode and Doppler. When examining in B-mode, the probe of the device emits ultrasound of a certain frequency, which penetrates the tissues. At the border of tissues with different densities, ultrasound is reflected and returned to the transducer. The sensor operates in the so-called pulsed mode, emitting ultrasound and capturing the reflected signal at various time intervals. The farther away from the sensor is the reflective structure (it is also called echogenic), the more time passes between the moment of emission and reception of the signal. A plurality of ultrasonic probe (sensor) crystals make it possible to emit signals at different angles with a variable time delay. Thus, modern powerful systems allow you to scan and reconstruct a two-dimensional image of the organ under study almost instantly. The Doppler mode is based on the "Doppler" effect - when it collides with a moving object, ultrasound is not only reflected, but also changes its frequency ("Doppler frequency shift"), the value of which is directly proportional to the speed of the object. In research blood vessels The “moving object” is the erythrocytes. In this way, the blood flow velocity is measured (more precisely, the velocity spectrum, since various flows in the vessel move with different speed). Modern systems also allow to build a color cartogram of the flow in the vessel of interest - where the color encodes the direction and intensity of blood flow in the veins. This method is called color doppler imaging(CDC).
The term "duplex" means a combination of two ultrasound modes: B-mode and Doppler. When examining in B-mode, the probe of the device emits ultrasound of a certain frequency, which penetrates the tissues. At the border of tissues with different densities, ultrasound is reflected and returned to the transducer. The sensor operates in the so-called pulsed mode, emitting ultrasound and capturing the reflected signal at various time intervals. The farther away from the sensor is the reflective structure (it is also called echogenic), the more time passes between the moment of emission and reception of the signal. A plurality of ultrasonic probe (sensor) crystals make it possible to emit signals at different angles with a variable time delay. Thus, modern powerful systems allow you to scan and reconstruct a two-dimensional image of the organ under study almost instantly. The Doppler mode is based on the "Doppler" effect - when it collides with a moving object, ultrasound is not only reflected, but also changes its frequency ("Doppler frequency shift"), the value of which is directly proportional to the speed of the object. In research blood vessels The “moving object” is the erythrocytes. In this way, the blood flow velocity is measured (more precisely, the velocity spectrum, since various flows in the vessel move with different speed). Modern systems also allow to build a color cartogram of the flow in the vessel of interest - where the color encodes the direction and intensity of blood flow in the veins. This method is called color doppler imaging(CDC).
The combination of the two modes allows you to get important information how to assess the anatomy of the vessels, their lumen, the state of the wall morphological changes and assess the impact of these changes on circulatory function, hemodynamics. Ultrasound duplex scanning of veins and arteries is a non-invasive way to assess the state of blood vessels, allows you to identify various pathologies, for example, stenoses, occlusions, atherosclerotic plaques, vascular malformations, etc.
 The duplex scanning technique has received wide use especially for the evaluation of veins and arteries, as well as brachiocephalic and large vessels, blood supply to the brain (in particular, carotid arteries) and peripheral vessels limbs. In the last decade, thanks to the development of technology, it was possible to introduce clinical practice and transcranial duplex scanning, all of these methods are available to people at affordable prices. Before that the only way assessment of intracranial cerebral circulation was transcranial dopplerography, which, despite the emergence of transcranial duplex, retained its importance as a method for assessing the function of cerebral circulation and monitoring hemodynamic parameters.
The duplex scanning technique has received wide use especially for the evaluation of veins and arteries, as well as brachiocephalic and large vessels, blood supply to the brain (in particular, carotid arteries) and peripheral vessels limbs. In the last decade, thanks to the development of technology, it was possible to introduce clinical practice and transcranial duplex scanning, all of these methods are available to people at affordable prices. Before that the only way assessment of intracranial cerebral circulation was transcranial dopplerography, which, despite the emergence of transcranial duplex, retained its importance as a method for assessing the function of cerebral circulation and monitoring hemodynamic parameters.
Goals of duplex scanning of cerebral vessels
- detection of early (preclinical) signs vascular pathology
- detection of stenosing and occlusive pathology of cerebral vessels
- detection of anomalies in the development of blood vessels (aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, hypoplasias, anastomoses)
- assessment of the hemodynamic significance of vascular pathology
- detection of vasospasm and venous circulation disorders
- identification of a complex of disorders associated with the presence of systemic vascular disease
- assessment of the reserve capacity of the cerebrovascular system
- evaluation of the effectiveness of the treatment
- gradebrachiocephalic vessels (BCA)
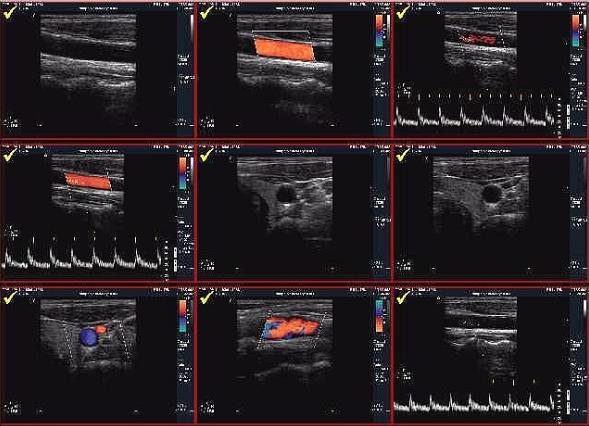
Duplex Scan System Image Gallery
If you have a question: "Where can I do a duplex scan of the veins, blood vessels, head, brain and lower extremities at affordable prices? ", the Neuro-med clinic is always at your service. Our specialists are true professionals in their field and they will be happy to help you by consulting in detail on issues of interest and conducting a scan that you need to do.
Currently, the most common methods for studying the human cardiovascular system are ultrasound (ultrasound) with Doppler techniques:
- Doppler ultrasound (USDG)
- Echocardiography (Echo-KG)
The main advantages of these methods are their absolute non-invasiveness (no trauma skin and mucous membranes), safety for the patient, high information content, sensitivity and specificity of the data obtained, the possibility of conducting studies in dynamics with the registration of both background blood flow parameters in real time and induced parameters when using a variety of functional stress tests.
What is Doppler Ultrasound?
The basis of ultrasound techniques used for vascular studies is the Doppler effect, described by Christian Doppler in 1842. Registration of blood flow at ultrasound examinations is based on a change in the frequency of an ultrasonic signal when it is reflected from moving blood particles, the bulk of which are erythrocytes, or red blood cells. Thus, they will allow obtaining objective information about the blood flow inside almost any vessel in the human body.
Where are Doppler techniques used?
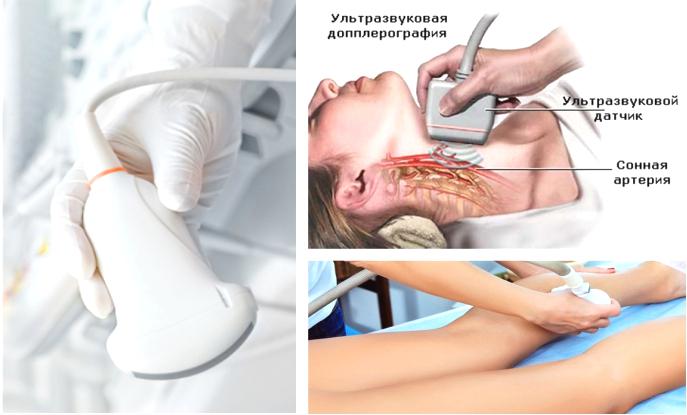
The main directions in vascular research, where Doppler techniques found the most wide application, are:
Duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries (BCA DS), also known as duplex scanning main arteries head (DS MAG). Is basic study in assessing the blood supply to the brain. At the same time, general, external, internal carotid and vertebral arteries on the neck.
The next step is the study of intracranial, i.e. intracranial sections of the same arteries and their branches - TKDS.

Duplex scanning (DS) and Doppler ultrasound (USDG) are currently used to study blood flow in the vessels.
Duplex scanning (DS) (sometimes you can find triplex scanning). Unlike ultrasound, the DS method is imaging, which significantly expands its diagnostic capabilities, since a direct assessment of the pathological process in a particular vessel of the vascular pool under study becomes real.
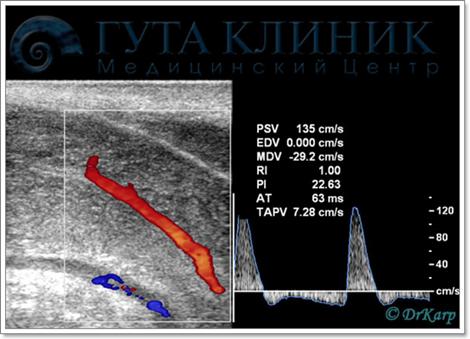
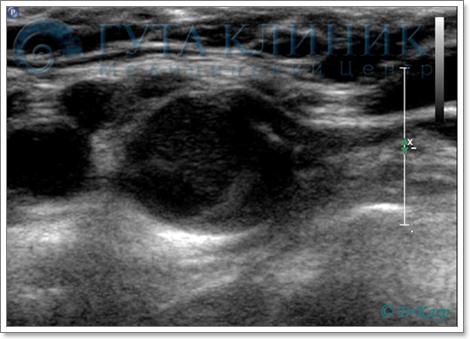 Virtually invisible atherosclerotic plaque in greyscale mode
Virtually invisible atherosclerotic plaque in greyscale mode
in the common carotid artery
The duplex scanning method combines visualization of vessels and tissues surrounding the vessel in B-mode with simultaneous study of blood flow in the lumen of the vessel using the Doppler effect using color Doppler coding (CDC) and (or) spectral Doppler analysis. At the same time, the result of computer processing can be both a Doppler spectrum and a color flow chart obtained using various color coding technologies. The color chart of the flow is a "cast" obtained from the lumen of the vessel.
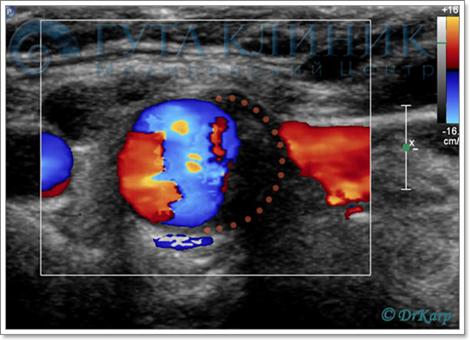 Clear visualization of the filling defect of the color flow chart
Clear visualization of the filling defect of the color flow chart
in speed color flow mode
Thus, any deviation from the normal course of the vessel (tortuosity, deformation), as well as any changes in the lumen of the vessel (plaques, blood clots, etc.) are easily determined. The Doppler spectrum characterizes the flow distribution in the lumen of the vessel, and the calculation of a number of additional indices makes it possible to clarify the nature of the pathological process. The duplex scanning method allows you to visualize and evaluate the state of blood flow in almost all departments vascular system a person, starting from large main trunks and ending with small organ and subcutaneous (subcutaneous) vessels.
In vessels of large caliber, a reliable visual assessment of all existing changes is possible. vascular wall already in the early stages vascular diseases, for example, in non-stenosing atherosclerosis, diabetic angiopathy. Moreover, it is not difficult to diagnose pathological processes in the presence of lesions characterized by various intraluminal changes (atherosclerotic plaques in stenosing atherosclerosis, blood clots) that impair the patency of the vessel.
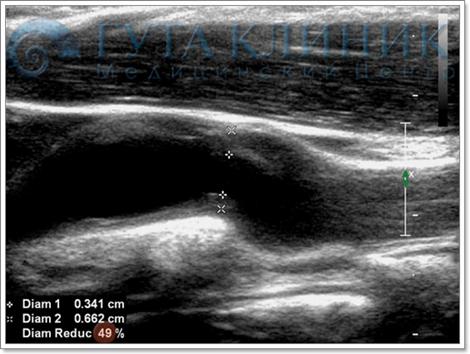 Accurate calculation of the degree of vessel stenosis
Accurate calculation of the degree of vessel stenosis
The duplex scanning method allows obtaining direct echographic signs of various vascular processes:
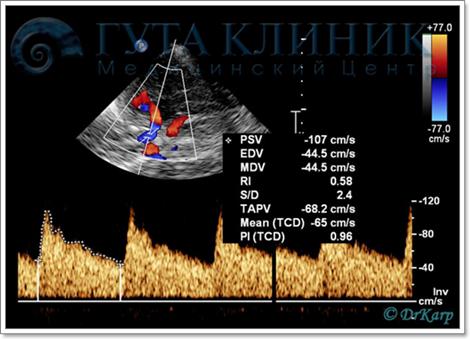
The main advantages of the duplex scanning method include: the ability to detect early preclinical signs diseases with an assessment vascular lesions, as well as changes in hemodynamics in real time with the identification of not only organic, but also functional disorders blood flow with the possibility of studying functional state vascular system.
The main limitations and disadvantages of the duplex scanning method are: the dependence of the obtained data on the experience of the operator due to the subjective nature of obtaining and interpreting the obtained ultrasound picture, as well as the resolution ultrasound scanner and from the anatomical and constitutional features of the patient.
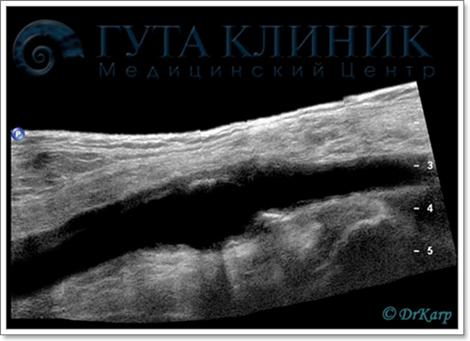
 Transcranial duplex scanning (TCDS)
Transcranial duplex scanning (TCDS)
Second ultrasonic method used to study the vascular system is Doppler ultrasound (USDG).
The Doppler ultrasound method (USDG) allows obtaining only indirect information about the state of the vessel wall and the presence of vascular pathology due to the impossibility of visualizing the vessel itself. To obtain diagnostic information using the ultrasound method, an ultrasonic sensor is installed in the anatomical projection of a certain arterial trunk, the blood flow is located, and then the display screen displays doppler spectrum of blood flow from the located vessel.
The main disadvantages of the Doppler method include:
- high probability of error in estimating blood flow velocity. This usually occurs due to the impossibility of correcting the position of the interrogation window and the angle of inclination of the ultrasonic beam to the longitudinal axis of the vessel under study;
- the impossibility in some cases (with anatomical variants of the structure and location) of the exact location of the required arterial (or venous) trunk;
- impossibility of diagnosis initial stages vascular lesions that do not lead to hemodynamic disturbances;
- the impossibility of echographic diagnosis of various vascular processes leading to the same type of hemodynamic disorders (for example, when a vessel is occluded by an atherosclerotic plaque or thrombus or embolus).
- If there are minimum vascular disorders the information content of the method is very low, which makes it diagnostically useless for patients with similar violations. Similar restrictions has a method of transcranial dopplerography used to assess blood flow in large intracranial vessels.
For these reasons this study less and less used in the clinic modern medicine. Most specialists prefer duplex scanning.
 Aneurysm popliteal artery in panoramic scan mode
Aneurysm popliteal artery in panoramic scan mode
Duplex scanning in the diagnosis of lesions of small vessels
For small vessels, including distal peripheral arteries and veins, due to Low quality visualization of the vascular wall due to its small thickness, as well as the peculiarities of the orientation of most small vessels a qualitative assessment of the presence of changes in the vascular wall and the lumen of the vessel is practically impossible. In this regard, the leading role in the study of the state of such vessels is played by the data of Doppler modes - color and spectral.
The color mode allows you to localize the vessel, thanks to the visualization of the color cartogram of the flow in its lumen, to evaluate anatomical features the location of the vessel, as well as the presence of deformations. If there are pathological overlays on the walls in the lumen of the vessel that impair its patency, a direct visual confirmation of their presence is possible by the size of the defect in filling the flow color cartogram. However, in most cases, color mode data do not allow a reliable diagnosis of intraluminal pathology. In this regard, the decisive diagnostic role is played by the data of the spectral Doppler mode, which make it possible to record all hemodynamic disorders in the affected area by the nature of changes in the qualitative and quantitative parameters of the Doppler spectrum.
The main limitation of the duplex scanning method in studying the state of small vessels is the impossibility of diagnosing processes that do not lead to significant hemodynamic disturbances in the affected area. In this way, bottom line The diagnostic resolution of the method provides for the degree of narrowing of the lumen of the vessel in diameter by more than 45-50%. According to the data of various authors. In the same range of values (from 95 to 100%) are the parameters of the positive and negative predictive value of ultrasound.
When studying changes in the microvasculature (presence of structural and functional changes vascular wall) an assessment of arterial vascular reactivity is carried out according to the nature of the reaction of blood flow in large arterial trunks in response to functional load stimuli of various directions.
 Study of erectile function
Study of erectile function
Arterial vascular reactivity is the ability of blood vessels to additional change of its diameter in response to the use of stress stimuli (in the experiment) or fluctuations in central hemodynamics to maintain a constant level of distal perfusion due to the inclusion of mechanisms for regulating vascular tone (myogenic, metabolic, neurogenic, humoral). It should be noted that vessels of the muscular type (small-caliber arteries, precapillary arterioles) are capable of a significant change in diameter. Since with an increase functional activity all changes in metabolism in the organ occur at the level of the microvasculature, which is accompanied by an increase in blood flow in it, peripheral vascular reactivity characterizes changes in this particular link of the vascular system.
 Functional load tests (FTTs) are used to assess reactivity. Depending on the nature and method of influencing the system under consideration, regulatory mechanisms will tend to either return the blood flow intensity to its original value, or change it in order to adapt to new functioning conditions.
Functional load tests (FTTs) are used to assess reactivity. Depending on the nature and method of influencing the system under consideration, regulatory mechanisms will tend to either return the blood flow intensity to its original value, or change it in order to adapt to new functioning conditions.
To obtain reliable information, it is necessary to use influences that imitate stimuli characteristic of the system of blood circulation regulation as PNT. According to the mechanism of action, stimuli can be divided into metabolic and myogenic. Stimuli can be chemical or physical in nature.
Examination of vessels by duplex scanning any region in our clinic is conducted by the leading specialist of GUTA-CLINIC, doctor the highest category, candidate medical sciences, Karpochev Maxim Viktorovich.
The introduction of the duplex scanning method into the practice of doctors made it possible to raise diagnostics by more high level. It is important that the equipment is quite affordable for urban and rural hospitals. Therefore, patients do not need to travel far for examination.
Duplex scanning of the veins of the lower extremities is widely used to study the patency of blood vessels, determine the stage of vein damage varicose disease. At the same time, not only veins are visible, but also the arterial network.
The duplex effect is a type of response to ultrasonic exposure. In this variant, ultrasound allows you to observe the flow of blood and quantify its parameters compared to normal. Different devices use black and white (B mode) or color (CFM mode) modes.
Physical basis of the method
The usual effect of reflection of ultrasound from tissues, used in ultrasound diagnostics, is not suitable for duplex scanning. Because it reflects stationary or slowly changing organs. This method will not reveal, for example, the speed of venous blood flow.
Duplex scanning uses the Doppler return wave effect. Not only the reflected part is taken into account, but also the property of the wave to coincide with the direction of the moving particle. Even if the object of study is at an angle of up to 60 degrees to the ultrasound beam, the technique allows you to fix the movement, determine its speed.
There are always in the blood shaped elements, by the reflection of the signal from these cells, it is possible to register the blood flow carrying them. The color image is obtained by special coding of the speed graph. Therefore, on the screen, the doctor sees a bright image of the vessels against the background of a black-and-white picture of the surrounding tissues.
The sensor sends ultrasonic signals and reads the response
Method capabilities
The advantages of duplex scanning are:
- the ability to examine vessels in places inaccessible to conventional ultrasound- for example, if it is necessary to diagnose blood flow through the brain, a “blind” study consists in the approximate installation of the sensor at the point of the vessel projection and registration of the reflected sound wave, although the doctor does not see the vessel itself;
- visibility small atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots in the arteries and veins of medium and small caliber;
- obtaining "online" characteristics of blood flow in the visualized vein or artery;
- detection hallmarks vascular formations with cavities and excretory ducts (for example, you can consider the vessels of the liver and gallbladder, without confusing them with small and medium bile ducts, renal arteries seen at the level of the intrarenal vessels, separate from the ureters).
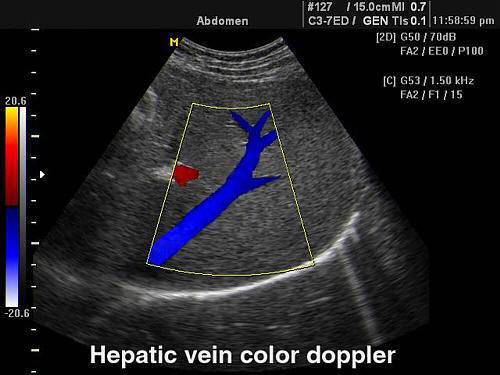
The method allows you to identify and distinguish hepatic vein from the bile ducts
In the study of blood vessels, duplex scanning is used as independent method, and if necessary exact definition shape, consistency of the organ (for example, thyroid gland) - as an addition to ultrasound, since it clarifies the blood supply to the tissue. Often the technique is used simultaneously with ultrasound as an addition and obtaining valuable information.
The principle of the method is preserved in echocardiography and allows diagnostics valvular defects, to notice the places of pathological discharge of the blood flow.
Great importance is attached early detection tumors of the uterus, prostate by the nature of the tortuosity vascular bundle, changes in the vascular pattern.
Duplex scanning of the veins of the lower extremities makes it possible to check the consistency of the valves in the superficial and deep vessels, the functioning of the perforating veins.
The duplex technique is part of a combination of triplex scanning, which first captures the "zone of interest" and then adds a spectral impulse test.
Who is eligible for Duplex Extremity Scanning?
- pain in the legs during exercise (walking) and at rest;
- feeling of heaviness, unmotivated fatigue;
- swelling in the ankle area, on the legs;
- convulsive contractions calf muscles, fingers of the upper limbs;
- inability to detect heart rate peripheral arteries limbs;
- appearance spider veins on the skin, visible bluish bands under the skin;
- darkening, pigmentation of the skin of the legs, blanching or redness;
- palpation painful seals along the veins;
- detection of non-healing trophic ulcers.
Symptoms point to vascular disease. Accurate diagnosis is essential to start treatment.
How convenient is the method in the diagnosis of venous diseases?
The duplex scanning technique is simple and fast. Its distinctive properties:
- the patient does not need special preparation;
- does not use chemicals, no side effects;
- the patient does not experience pain and discomfort;
- not associated with a violation of the skin (injections);
- has no age restrictions.
In 30-45 minutes, the doctor is able to identify following pathology veins:
- blood clots, their stage, size, condition of surrounding tissues;
- causes of recurrence of varicose veins after phlebectomy, sclerotherapy;
- dysfunction of perforating veins;
- decreased patency and sagging of valves in deep and superficial vessels;
- change in the state of the vascular wall.
How is the research done?
To make the procedure comfortable, the patient is advised to first put on clothes that will allow you to quickly open the desired area of \u200b\u200bthe body. Before examining the veins in the arms, it is better to remove all jewelry. You need to take your own sheet and a few wipes to the office to erase the gel at the end of the procedure.
The technique does not depend on the weight and age of the patient. A person is laid on a couch with his head raised. The skin of the limb is lubricated with a special gel to ensure close contact with the transducer. Without gel, signal clarity is lost.
The study is carried out in stages:
- starts from the groin area (sensor power up to 7 megahertz);
- the transducer is moved downward with a slight alternating pressure, the deep vein hips;
- below knee joint the anterior tibial vein is scanned;
- then the patient is asked to roll over on his stomach, a roller is placed under the knee, the popliteal vein is examined on the screen;
- small vessels are divided into branches of the small and large tibial veins and viewed from the source to the mouth, low-frequency sensors are used.
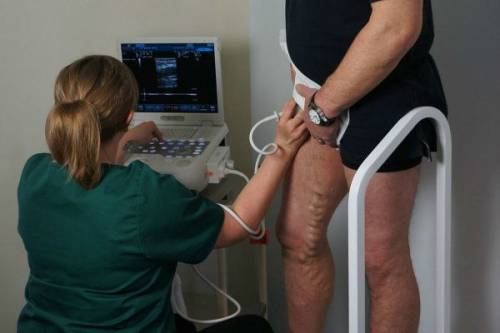
The veins of the legs are also examined in a standing position, it is enough to straighten the arm
Results in the pathology of the veins of the legs
The interpretation of the results is carried out immediately after the procedure. The result is handed over to the patient. Only a doctor can correctly assess the parameters of blood circulation. The blood flow is measured by the device according to the following criteria:
- maximum speed in systole;
- minimal - in diastole;
- vascular wall resistance;
- pulsation index;
- venous wall thickness.
The final diagnosis is made vascular surgeon or a phlebologist based on clinical manifestations and scan data.
The method allows you to identify at an early stage:
- varicose veins of superficial and deep veins;
- thrombosis and thrombophlebitis of the vessels of the legs, arms;
- atherosclerosis of the arteries of the extremities;
- obliterating endarteritis.
Is the method safe?
The Doppler effect is accompanied by the release of an energy beam. Special filters are installed in modern ultrasound machines. When using high power, there is a danger of cell damage in the retina. When examining pregnant women and children, the minimum radiation power is used.
We'll have to temporarily abandon the survey. if the patient has:
- unhealed and bleeding wounds, burns on the arms and legs;
- skin diseases in the form of a rash, sores;
- during the height of infectious diseases;
- with exacerbation of bronchial asthma.
After recovery, the study can be carried out in full.
Duplex scanning is not easy modern approach to diagnosis, but also most affordable way for the population.
Among the advantages of duplex ultrasound, it is worth noting the high information content, safety and lack of pain. In addition, such a diagnosis does not require special preparation from the patient. The procedure does not side effects and complications, therefore, does not imply restrictions on the age of the patient.
Operating principle
This research method is based on the Doppler effect. Ultrasound, reflected from the vessels, changes its frequency. This allows you to determine the angle of the received signal. Doppler shift can be encoded as a stream moving at different speeds. Each indicator is assigned its own characteristic color. It can be easily seen against the background of a monochrome image displayed on the monitor screen. The blood flow is collateral or main. The first is characterized by a reduced speed, the second is normal.
Indications for research
Ultrasound scanning of the arteries of the extremities examines the diameter of the vessels and the nature of the movement of blood. It is often supplemented functional tests. These studies help diagnose abnormalities in the functioning of the vascular system, as well as the presence of general disorders in the body. In addition, such tests allow us to study the mechanisms responsible for the movement of arms and legs. So, in a healthy limb, the vessels tend to expand, which significantly increases the rate of blood flow. Violation in the mechanisms of the limbs often leads to malfunctions of the vessels. To conduct such studies, for some time the patient is subjected to a small physical activity. Then the doctor measures the speed of blood movement and compares them with those that were recorded before the procedure. The change in these data should not exceed 40%.
Sometimes tests associated with the tension of the limbs are used. In this case, the data taken before and after the study is also recorded. Specialists also sometimes prescribe a test using nitroglycerin. In this case, the property of the substance is used to relax the muscles of the vessels.
The first signs of damage to the arteries are the unevenness, thickening or discontinuity of their inner layer. These symptoms may indicate the beginning of the development of severe abnormalities in the work of the arteries. They can be detected using Doppler scanning. Using this method allows you to visualize the vessels well and give information about possible deviations from the norm in their work.
This study allows you to visually examine even those vessels that could not be detected with a standard ultrasound. So, duplex scanning of the skull is considered one of the few types of diagnostics that can detect circulatory disorders in the brain. Using it, you can accurately determine the location of the arteries and analyze their work.

