BPR norms by week. Biparietal fetal head size (BFS) by week
Fetal developmental disability by week (table)
In this publication, we will try to understand the essence of the method for determining fetal BPD, what it is and how much important It has this indicator. This abbreviation stands for biparietal size (BPD). This is the size of the baby's head.
He is very important indicator when monitoring the development of pregnancy, and indicates the normal development of the fetal brain.
BDP values are constantly changing over the course of pregnancy, which is why a lot of attention is paid to this indicator.
What does BPR mean and what is it for?
During each mandatory and additional ultrasound, the fetal head is examined very carefully. After all, fetal brain development most important factor correct development of the child and the course of pregnancy. After all, here is located main body, which affects the entire body. With the correct size of the baby’s head, it is possible to accurately determine how the brain and the fetus are developing as a whole.
An ultrasound specialist measures the fetal BDP. A measurement is taken from temple to temple. If the doctor takes the wrong distance and does not take into account that the line connecting the contours of the temples should be clearly above the thalamus, then he may get results that are far from correct. Next, the fronto-occipital part is measured, which is measured from the forehead to the back of the child’s head.
But the biparietal size is considered more important, because it helps to more accurately determine the gestational age. It is for this purpose that fetal birth control is established. In addition, measurement values help resolve the issue of whether independent childbirth. For example, if the baby’s head is significantly larger than birth canal, the child himself will not be able to pass them.
And then the need arises caesarean section. Although in most cases, the head is of a size that allows the baby to be born naturally.
Is there a norm for the biparietal size of the fetal head?
Having performed BPR measurements on ultrasound, the doctor compares them with normal sizes. For such comparisons, tables have been developed that record the average indicators of normal BDP for each week of pregnancy and acceptable deviations.
Any table is given from at least the twelfth week, because it is impossible to take measurements before this period. The fetus is too small for this BPD measurement.
And that’s why mistakes are common on ultrasound. Here is an example of such a table with normal indicators can be found on the Internet.
Normal indicators
BDP by week of pregnancy (table)
| BPR (BPD) |
Term on average (weeks) |
Range fluctuations (weeks) |
BPR (mm) |
Term on average (weeks) |
Range fluctuations (weeks) |
| 17 | 10,6 | 9,6-11,5 | 58 | 23,5 | 22,7-24,4 |
| 18 | 10,9 | 9,9-11,8 | 59 | 23,8 | 23,0-24,7 |
| 19 | 11,2 | 10,2-12,1 | 60 | 24,1 | 23,3-25,0 |
| 20 | 11,5 | 10,5-12,4 | 61 | 24,4 | 23,7-25,4 |
| 21 | 11,8 | 10,8-12,7 | 62 | 24,7 | 24,0-25,7 |
| 22 | 12,1 | 11,1-13,0 | 63 | 25,1 | 24,3-26,0 |
| 23 | 12,4 | 11,4-13,3 | 64 | 25,4 | 24,6-26,4 |
| 24 | 12,7 | 11,7-13,6 | 65 | 25,7 | 25,0-26,7 |
| 25 | 13,0 | 12,0-13,9 | 66 | 26,0 | 25,3-27,0 |
| 26 | 13,3 | 12,3-14,2 | 67 | 26,3 | 25,6-27,4 |
| 27 | 13,6 | 12,6-14,5 | 68 | 26,7 | 25,9-27,7 |
| 28 | 13,9 | 12,9-14,9 | 69 | 27,0 | 26,3-28,0 |
| 29 | 14,2 | 13,2-15,2 | 70 | 27,2 | 26,6-28,4 |
| 30 | 14,4 | 13,5-15,4 | 71 | 27,6 | 26,9-28,7 |
| 31 | 14,7 | 13,8-15,7 | 72 | 27,9 | 27,2-29,0 |
| 32 | 15,0 | 14,1-16,0 | 73 | 28,2 | 27,5-29,4 |
| 33 | 15,3 | 14,4-16,4 | 74 | 28,5 | 27,9-29,8 |
| 34 | 15,6 | 14,6-16,7 | 75 | 28,9 | 28,2-30,3 |
| 35 | 15,9 | 14,9-17,0 | 76 | 29,2 | 28,5-30,8 |
| 36 | 16,2 | 15,2-17,3 | 77 | 29,5 | 28,8-31,3 |
| 37 | 16,5 | 15,5-17,6 | 78 | 29,8 | 29,2-31,8 |
| 38 | 16,8 | 15,8-17,9 | 79 | 30,6 | 29,5-32,3 |
| 39 | 17,1 | 16,1-18,3 | 80 | 31,1 | 29,8-32,8 |
| 40 | 17,4 | 16,4-18,6 | 81 | 31,6 | 30,0-33,3 |
| 41 | 17,7 | 16,7-18,9 | 82 | 32,1 | 30,5-33,8 |
| 42 | 18,0 | 17,0-19,2 | 83 | 32,6 | 31,1-34,2 |
| 43 | 18,5 | 17,3-19,5 | 84 | 33,6 | 31,6-34,8 |
| 44 | 19,0 | 18,2-19,7 | 85 | 33,7 | 32,1-35,3 |
| 45 | 19,4 | 18,5-20,0 | 86 | 34,2 | 32,7-35,8 |
| 46 | 19,7 | 18,8-20,4 | 87 | 34,7 | 33,2-35,9 |
| 47 | 20,0 | 19,2-20,7 | 88 | 35,2 | 33,7-36,1 |
| 48 | 20,3 | 19,5-21,0 | 89 | 35,7 | 34,2-37,1 |
| 49 | 20,6 | 19,8-21,4 | 90 | 36,4 | 34,7-38,1 |
| 50 | 20,9 | 20,1-21,7 | 91 | 37,3 | 35,3-39,1 |
| 51 | 21,3 | 20,5-22,0 | 92 | 38,1 | 35,8-40,1 |
| 52 | 21,6 | 20,8-22,4 | 93 | 38,9 | 36,9-41,1 |
| 53 | 21,9 | 21,1-22,7 | 94 | 39,7 | 37,6-42,1 |
| 54 | 22,2 | 21,4-23,2 | 95 | 40,5 | 38,3-43,1 |
| 55 | 22,5 | 21,7-23,6 | 96 | 41,3 | 39,6-44,1 |
| 56 | 22,8 | 22,1-23,7 | 97 | 42,1 | 39,6-45,1 |
| 57 | 23,2 | 22,4-24,0 | 98 | 42,9 | 40,3-46,1 |
In order to independently establish the BPR norm, the same table that the ultrasound specialist uses will help. If you carefully study it, you can easily judge the dimensions that the doctor writes down in the conclusion. The table has three columns. The first gives the dimensions of the norm. In the second, the pregnancy dates are given, and in the third, they are discharged possible deviations from the norm. For example, at 22 weeks the size is 53 mm, deviations are possible from 21.1 m on the smaller side and up to 22.7 mm on the other side.
What to do if the BPR deviates from the norm?

BPD - Ultrasound image showing biparietal size
In case of detected deviations in the BPR, the ultrasound should be repeated a few days later with a different specialist and on a different device. If abnormalities remain, the doctor should evaluate all other fetal parameters. Maybe a very large baby will be born?!
In addition, it is necessary to take into account that the rapid growth of parameters at the beginning of pregnancy is replaced by a slowdown in recent months. And it is quite possible that the supposed first large fruit"will not take place".
It happens that the baby develops in spurts. This may be another reason for deviations from the norm. As a rule, after some time the parameters become normal. If this does not happen, and the BDP on ultrasound still shows abnormalities, then you need to consult a doctor.
Parameters with a strong deviation from the normal BPD indicate such pathologies of the fetal brain as: tumor, hernia and others. Doctors may prescribe a course of therapy, or may suggest solving the issue of terminating a pathological pregnancy.
If, for example, the doctor establishes the BPD and all other parameters of the fetus are less than prescribed normal results and all other parameters of the baby, a diagnosis is made - delay intrauterine development fetus The reasons for this phenomenon may be various infections or chronic hypoxia, which appeared against the background of placental disorders.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, the woman is admitted to a hospital and prescribed an urgent course of therapy aimed at eliminating the causes of this phenomenon. At the same time, procedures are prescribed that improve blood flow in the placenta and improve the supply of oxygen and vitality. important substances to the child. Even small BPD parameters on ultrasound may indicate microcephaly.
Incorrect parameters indicate various pathologies fetal brain. Doctors may prescribe a course of therapy or may suggest terminating the pregnancy.
In conclusion, the importance of diagnosing BPD size
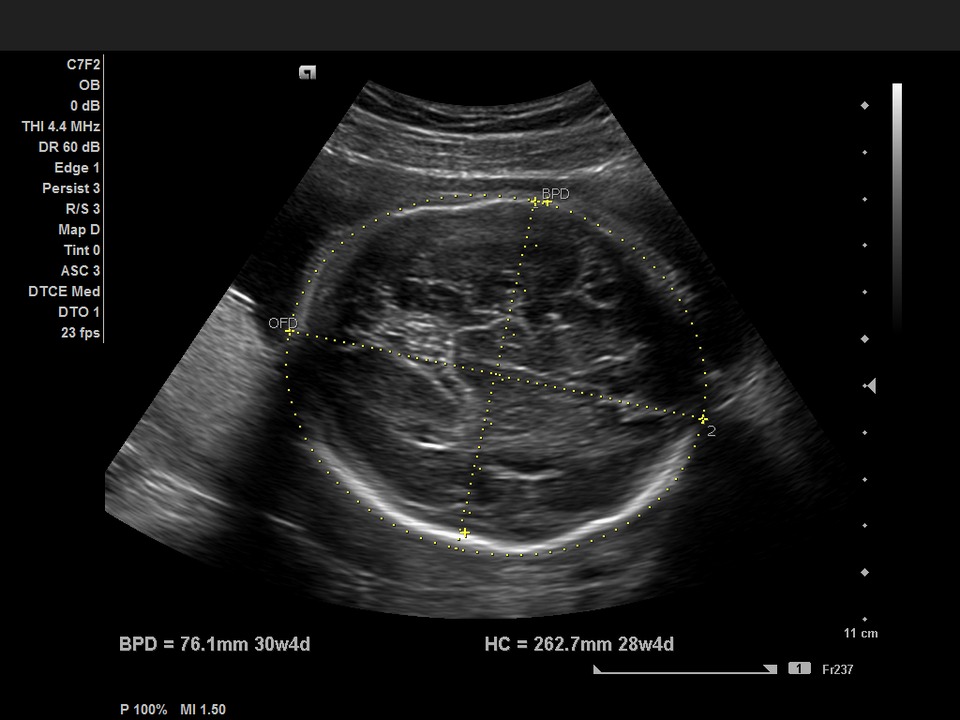
Expectant mothers are offered ultrasound examinations several times during pregnancy. After such an examination, the ultrasound specialist must give pregnant women a research protocol, which contains all the information about the baby, including the BPD.
If you undergo such an examination in time, you can get rid of many pathologies. Therefore, such examinations are strongly recommended for pregnant women. It will not cause harm, but there are many benefits from fetal ultrasound.
Today, obstetricians-gynecologists use different ways to measure the presence of various abnormalities in the fetus. In order to accurately measure the gestational age of the expectant mother down to the day, gynecologists use a special index called the biparietal size of the fetal head, which is the most accurate.
To make such a measurement, you need to conduct a special ultrasound examination, usually doctors carry it out from 12 weeks to 28. This article will help you correctly measure this index and describe in detail all the indicators, taking into account different terms maternal pregnancy and fetal development, and also tells the reader about all kinds of abnormalities.
The biparietal size of the fetal head is normal
To measure the BDP of the fetal head, you need to take the correct distance from one temple to another, but do not forget that the line that connects the contours of the parietal bones mandatory must pass strictly above the thalamus. If you arbitrarily change this long-established rule, the results of the study will be too distorted, and as a result, the gestational age will differ significantly from reality. At a certain stage of pregnancy, there are different values, which are the norm, so the longer the period, the more significant the BPR indicator changes, but do not forget that at the end of pregnancy, growth slows down significantly.
Fetal developmental disorder by week
- at week 12, is 21 mm,
- at 13 weeks approximately 24 mm,
- at 16 weeks – 34 mm
- at 24 weeks – 61 mm
- at 32 weeks - 82 mm
- at 38 weeks – 84 mm
- and at 40 weeks – 96 mm.
The doctor evaluates the BPR, also taking into account the fronto-occipital indicators; for this, all measurements must be taken at the level of the cerebral peduncles, as well as the visual thalamus. Because these data change strictly in proportion to the time of pregnancy of the expectant mother. It is worth remembering that if the fetus is at 38 weeks of development, then its head changes shape significantly, so if there is a dolichocephalic configuration of the baby’s head, then the index will be less than normal.
Ultrasound during pregnancy BPD of the fetal head, normal and pathological
![]()
Thanks to the use in today's medicine of the fetal head and other similar indicators, doctors are able to find and prevent various deviations in the baby's development in advance, for example, such as: very big child, hydrocephalus or intrauterine development. If these indicators are slightly different from the norm, then you should not despair, you just need to measure other indicators that will show the full picture. And if all parts of the body are evenly enlarged, then we can safely conclude that there will be a large baby. But if only the size of the head is increased, then you should start to worry, because the fetus is almost certainly diagnosed with hydrocephalus and was caused by an intrauterine infection.
When a gynecologist observes that the BPD is less than the norm and all other parameters of the baby are significantly less than those that correspond real time gestation, then a disappointing diagnosis is made - delayed fetal development in the womb. The reasons for such circumstances are different, for example, it could be an intrauterine infection, as well as chronic hypoxia, which arose due to fetoplacental insufficiency.
If such a diagnosis is fully confirmed, then the expectant mother is prescribed urgent treatment, which is entirely aimed at eradicating the causes harmful effects. Therefore, doctors prescribe a number of procedures that improve blood flow in the uterus and placenta, and also have a full effect on the fetus so that it receives oxygen and all the necessary nutrients, through the use of drugs such as Curantil for pregnant women, Actovegin and, of course, Pentoxifyline.
Doctors diagnose microcephaly if the fetal BPD and fronto-occipital size are significantly reduced.
During pregnancy, expectant mothers are required to undergo an ultrasound several times, after which the ultrasound specialist must give them a research protocol, where he describes in detail all the information about the development of the baby. Here in it he indicates all important information, including even the most important parameter - biparietal head size (BSD). We will now tell you why this is done.
BPR - transcript
When a doctor conducts ultrasound monitoring of a child, he first of all spends all his time on fully examining the baby’s head. The explanation for this is very simple: the brain is located in the head - the most important organ in the human body, it is it that fully influences the condition of the fetus as a whole. Therefore, if you correctly measure the size of the head, you can also assess the development of the brain, which is why the BDP exists. To put it another way, the biparietal size is the width of the fetal head, which is measured from one temple to another.
Of course, in modern medicine This is not the only parameter; there is also the fronto-occipital size (FOR), it will be measured from the forehead to the back of the head of the fetus. But still, the main one is the BDP, because it determines the development of the fetus. His doctor is trying to measure when future mom be between 12 and 28 weeks.
Doctors also operate on BPD when they consider the possibility of a woman in labor giving birth to a baby herself without surgical intervention. Otherwise, a caesarean section is prescribed.
Biparietal head size is normal
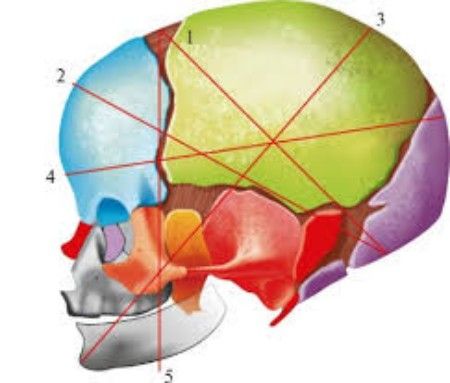
When I evaluate the BDP, I use specially designed tables that collect average data for estimating head size for a certain period using this method. In such a table, the data is indicated in percentiles, which are needed for special designation in medical statistics, that is, the average value is the 50th percentile.
When a doctor wants to use the data from this table, then, first of all, he finds its average value, and then completely determines extreme points proper development fetus Let's look at this table using an example when the fetus is 12 weeks old and its BPD for this period is 21 mm, while the norm ranges from 18 mm to 24 mm. Therefore, within the limits of such indicators, you should not worry, because the size of each baby is different and this is affected anatomical structure his body.
Fetal BPD in the table - deviations from the norm
Of course, these indicators may not always fall exactly within the boundaries. But this does not always indicate any pathology, and in order to fully convince of this, the doctor who is observing the pregnant woman must conduct further whole line various studies. If, when measuring, all elements of the body are proportional, then we can conclude that the fetus is simply large. Sometimes it is observed with such parameters that the baby grows in leaps and bounds.
But such deviations do not always mean good things; in most cases, they indicate problems with the child’s development. If the head is much larger established norm, then this may also indicate a tumor in the brain or hydrocephalus. In such circumstances to the expectant mother The doctor suggests terminating the pregnancy. If the brain is smaller than normal, then there is nothing comforting here either, because this indicates problems with the brain. In this case, the pregnancy is also terminated. If BPD is reduced in the third trimester, then this only indicates intrauterine growth retardation, which can be easily treated today.
In the transcript of the ultrasound there is a point “Fetal fetal development”, which is what it is desirable for all expectant mothers to know. When conducting ultrasound examination The doctor draws up a special protocol in which data on the development and growth of the child is recorded. One of the indicators will be the BDP. This abbreviation means biparietal head size. This is a very important indicator of fetal development.
The human brain is the most important organ along with the heart. The development of the embryo's brain in the mother's womb determines its life and health in the future. When performing an ultrasound, the doctor must pay Special attention baby's head. The doctor conducts a fetal developmental disorder study week by week. This determines the development of the embryo.
Decoding the biparietal head size is an indication of the length from one temple to the other. The distance is measured at the narrowest temporal part.
Determining biparietal size is of paramount importance during pregnancy. It is calculated quite correctly for a period of 12 to 28 weeks. Although BPR head The fetus shows the intrauterine development of the baby, and it also indicates whether physiological childbirth will be able to proceed normally.
BDP allows you to determine fetal maturation before the onset of labor activity, A Newest technologies allow ultrasound diagnostics to be carried out efficiently and safely. And in the 2nd trimester, the doctor will determine the timing of future births. If strong deviations are observed, then we may talk about delivery by cesarean section. This method will be the most correct in this situation.
BPR norms
 To make it easy to understand the values of normal and abnormal, a special table has been created. It shows the average values of the BPR norm using percentiles: top - 95 points, bottom - 5 points and average - 50 points.
To make it easy to understand the values of normal and abnormal, a special table has been created. It shows the average values of the BPR norm using percentiles: top - 95 points, bottom - 5 points and average - 50 points.
The doctor needs to find the 50th percentile, and then the specialist looks at the boundary of the extreme values. For example, the table at the 12th week shows that the BPR norm is 21 mm. This means that if the BPR indicator is 18 mm, future parents do not need to worry, the main thing is that the result does not exceed the upper norm.
Why are deviations dangerous?
If the doctor sees that the biparietal size of the fetus by week differs from permissible level, what needs to be done in this case? To begin with, the specialist evaluates other fetal data: abdominal circumference, hip length, etc.
When all values are outside the normal range, this indicates that the fetus is too large or has irregular development.
In the first case, all body sizes should increase evenly. The head, tummy and chest retain their proportions. In the second circumstance, during a repeat ultrasound in a few weeks, the indicators should level out. But if the BPR values are very far from the norm, this indicates a serious problem with the child’s health. Larger sizes occur with a brain tumor of the head and other neoplasms, hydrocephalus. When the final diagnosis is made, pregnant women are taken under special control. Treatment is most often prescribed. In particularly serious cases, a recommendation may be given to terminate the pregnancy. A brain hernia or brain tumor does not give the baby a chance to live. No less serious consequences will be very small size fetal head. Then this means an abnormality of the brain, for example the absence of some of its parts: the hemisphere, hypothalamus or cerebellum. In such cases, the pregnancy will be terminated regardless of the term.
In conclusion, it must be said that an accurate calculation of the biparietal head size will help to timely and fully assess the degree of growth and development of the fetus in the mother’s womb.
Quick page navigation
To monitor intrauterine growth and the development of the child during pregnancy, several mandatory ultrasound studies are carried out, which include fetometry - measuring the size of the fetus.
Starting from the 1st trimester (when the embryo is already visualized), one of the mandatory parameters that are determined during fetometry is the biparietal head size or BPS.
BPR - what is it in the ultrasound protocol?
BPR is the size of the head from one parietal bone to the other, measured in the transverse plane. To do this, the ultrasound specialist positions the sensor so that the fetal head is visible from above.
Usually the shape of the head is oval, closer to round. The size from the forehead to the back of the head is determined by a parameter called the fronto-occipital size or LOR. The line that is perpendicular to the LZR will be the BPR of the fetus.
- We can say that in the transverse plane the BPR shows the width of the fetal head.
BPR - what is it (photo)
The measurement is carried out in two ways: externally - externally and internally - externally. Their difference lies in the location of the points between which the measurement is made: they can be located either on the outer and inner edges, or on both outer edges of the parietal bones.
This must be taken into account when analyzing the data obtained and comparing them with those tables of norms for which measurements were carried out in a similar way.
Why do you need BPR measurement:
- In the period from the 13th (but possibly earlier) to the 22nd week, this parameter determines the gestational age with an accuracy of 5 to 10 days. After the 28th week, the reliability of this definition becomes questionable due to the different individual growth rates of the fetuses and genetic characteristics, the appearance of “mobility” of the head shape;
- Along with parameters such as abdominal circumference and length femur, BDP indicates the expected weight of the fetus at the time of the study, which is especially important before upcoming birth, since it determines the method of childbirth: independently or by caesarean section;
- A dynamic change in this size indicates fetal growth and a normal increase in brain size;
- It is a marker of disorders of intrauterine development of the fetus and birth defects development.
Fetal BDP norm by week (table)
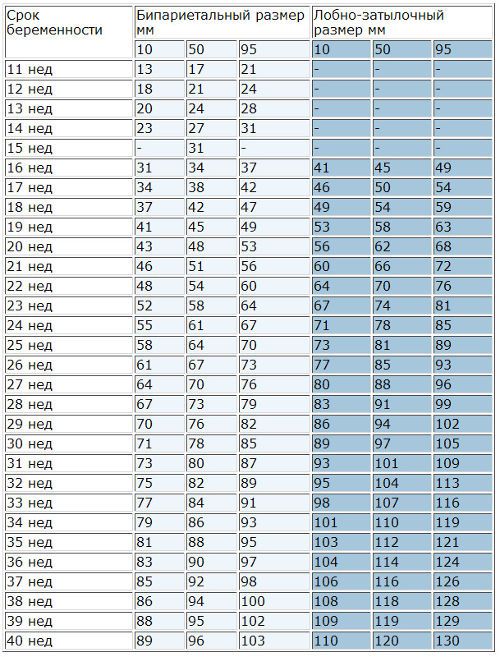
For an indicator such as fetal BPD, the norm is very variable and is never represented by one number. Nomograms (tables by which the results obtained are compared) are compiled using percentiles, that is, options that can occur during normal development.
The 90th percentile means that this indicator occurs in 90% or less of all subjects, the 50th percentile - in 50% or less, and the 10th percentile, respectively, in 10% or less.
Fluctuations within percentiles are not a pathology. Often, such nomograms are compiled for each region, even within the same country, which is associated with different ethnic and racial characteristics.
Therefore, the BPR measured in a fetus whose mother permanently lives in Moscow may differ significantly from the BPR of a fetus whose mother, for example, is from Makhachkala. To accurately determine what a parameter such as BPR provides, you need to use tables with regional standards or, if they do not exist, then based on the principle of territorial proximity.
Table - Biparietal size fetal head by week, mm(based on the internal-external measurement method, Moscow region)
| a week | percentile | ||
| 10 | 50 | 90 | |
| 13 | 21 | 24 | 28 |
| 14 | 24 | 27 | 31 |
| 15 | 29 | 31 | 34 |
| 16 | 30 | 34 | 37 |
| 17 | 35 | 38 | 42 |
| 18 | 38 | 42 | 47 |
| 19 | 40 | 45 | 49 |
| 20 | 44 | 48 | 53 |
| 21 | 47 | 51 | 56 |
| 22 | 49 | 54 | 60 |
| 23 | 53 | 58 | 64 |
| 24 | 56 | 61 | 67 |
| 25 | 59 | 64 | 70 |
| 26 | 62 | 67 | 73 |
| 27 | 65 | 70 | 76 |
| 28 | 68 | 73 | 79 |
| 29 | 71 | 76 | 82 |
| 30 | 72 | 78 | 85 |
| 31 | 74 | 80 | 87 |
| 32 | 76 | 82 | 89 |
| 33 | 78 | 84 | 91 |
| 34 | 80 | 86 | 93 |
| 35 | 82 | 88 | 95 |
| 36 | 84 | 90 | 97 |
| 37 | 86 | 92 | 98 |
| 38 | 87 | 94 | 100 |
| 39 | 89 | 95 | 102 |
| 40 | 90 | 96 | 103 |
What to do if the BPR deviates from the norm?
Deviation from the norm, which is detected once, special significance does not have, if it does not differ from normal indicator within 2-3 lines according to the table.
To suspect any developmental disorder in a child, it is necessary to record a change in the BDP several times in a row. For this purpose, ultrasound fetometry is carried out dynamically, usually at intervals of 1-2 weeks.
Increase in head size
Macrocephaly or large head
1. The reasons for a large head size may be hereditary factors. If big size head is detected in one of the parents, then no special measures are taken.
In this case, the attending physician must determine the possibility of independent vaginal birth or choose a cesarean section as a delivery method.
- If the large size of the fetal head is not associated with hereditary characteristics, then it is necessary to exclude developmental anomalies.
2. With hydrocephalus, dilation occurs internal cavities brain, which contain brain fluid - cerebrospinal fluid. The volume and pressure of the fluid increases - the size of the head increases.
The causes of hydrocephalus can be a violation of the development of the fetal brain, infection for a period of 13 to 27 weeks, tumors, injuries, hypoxia, spina bifida (non-fusion of the vertebrae, resulting in spinal cord does not have a full-fledged bone frame).
Detection of hydrocephalus before the period of fetal viability (3rd trimester) raises the question of termination of pregnancy. If the fetus is already at a viable age, then karyotyping, tests for viruses, a detailed ultrasound, and consultation with a neurosurgeon on the treatment of the child after birth are performed.
- If pressure in the ventricles increases, early delivery and further prompt elimination Problems.
3. Macrocephaly can be observed with disorders of the development of bone and cartilage tissue. This disorder is thanatoform dysplasia - congenital disorder skeletal development, which is associated with a lack of ossification.
An enlarged head, its shape in the form of a trefoil, can be detected on an ultrasound in the middle of the 2nd trimester. Another pathology is achondrogenesis, in which the production of cartilage tissue is impaired, also leading to the development of macrocephaly.
- This condition is a defect incompatible with life.

Hyperplastic development or large fetus
1. In this situation, heredity may also be the cause, and the increase in fetal size may be due to the family constitution. It is necessary to find out what body weight mom and dad were born with, as well as determine their body type.
- The large size of the fetus influences decisions on labor management tactics.
2. The second reason for a large fetal mass may be gestational diabetes, or diabetes pregnant women. It is necessary to conduct urine and blood tests for sugar. On an empty stomach, in the blood, the level of this indicator in pregnant women is lower than usual and amounts to 5.0-5.8 mmol/l.
There should be no sugar in the urine. If changes are detected in the tests, as well as for all pregnant women between 24 and 28 weeks, it is necessary to conduct an oral glucose tolerance test with 50 g. glucose. The test is carried out without preliminary preparation, Anytime. After taking the glucose solution orally, the amount of sugar in the blood is determined after 1 hour.
If this indicator is more than 7.8 mmol/l, further examination by an endocrinologist is necessary. Treatment for gestational diabetes consists of following special diet. If blood sugar continues to be elevated, insulin injections are prescribed.
- Any tablet preparations for lowering sugar during pregnancy are contraindicated.
Reducing head size
Microcephaly or small head
1. As is the case with large size heads, a small head in the fetus may be associated with small heads in the family. This feature does not require treatment.
2. Spina bifida is a developmental disorder of the spine, which can be indirectly suspected when the head shape changes to the “banana” or “lemon” type.
Refers to those defects in which termination of pregnancy is recommended if the fetus has not yet reached a viable age. In other cases, it is necessary to inform parents about possible manifestations this disorder after the birth of a child, such as impaired movement and sensitivity lower limbs, chronic pain, fecal and urinary incontinence, spinal curvature.
- If pregnancy continues, it is necessary to determine the date and method of delivery.
3. Intrauterine infection, which leads to damage to the embryo at 3-12 weeks, can lead to the formation of malformations with a decrease in the size of the head. If the infection occurs at a period of 28 weeks or more, the infection is severe and spreads, that is, it becomes generalized - fetal development is delayed and an associated decrease in head size and BPD occurs.
If you suspect infection a number of studies are carried out on the mother aimed at identifying the pathogen: PCR, detection of antibodies in the blood, microscopy of smears, bacterial cultures to nutrient media.
Treatment depends on the type of pathogen and trimester of pregnancy. From 14-16 weeks in the background general treatment carry out prevention of placental insufficiency.
- If you become ill with rubella before the 16th week and if malformations are detected, it is recommended to terminate the pregnancy.
Hypoplastic development or small fetus
1. Hereditary low weight in children in the family, asthenic type of constitution in parents. Special measures not accepted at normal course pregnancy.
2. A decrease in body size may occur with genetic diseases, such as triploidy, trisomy on the 13th pair of chromosomes - Patau syndrome, on 18 - Edwards syndrome, or on 21 - Down syndrome, which lead to early symmetrical growth retardation of the fetus: that is, both the head and the body of the fetus are mismatched with the gestational age.
In each case, the trip is individual. Children who are born alive have severe malformations of organs and their life prognosis is unfavorable - most die in the first year.
The exception is children with Down syndrome, who, when necessary treatment And social support able to have a fairly high quality of life.
Osteogenesis imperfecta - This genetic defect development, which leads to a group of diseases with impaired formation of bone and cartilage tissue. Has several types.
When performing an ultrasound, it is possible to identify only 2 types: shortened, curved bones and multiple fractures; deformation of the head occurs when the sensor presses on soft bones skulls Osteogenesis imperfecta type 2 is not compatible with life.
BDP is important when calculating the cranial index (CI, Y), which indicates the arrest of fetal development, its intrauterine death and approximate time finding a dead fetus in the uterus.
- Cranial index = BPR/LZRx100. If CHI is 83 or more, this is the norm.
After 4-5 days from the moment of death of the fetus, destruction occurs internal structures brain and a significant decrease in BDP: if CHI = 64-74, then the death of the fetus occurred less than 3 weeks ago, if CHI = 64, then the fetus is not viable for more than 3 weeks.
Change in head shape outside of pathology
Brachiocephaly or short head
The increase in the BPR in this case will not be due to a decrease in the volume of the head, but due to a decrease in the LZR, that is, a decrease in the distance between the forehead and the back of the head. The head has a more rounded or flattened shape.
- Brachiocephaly is often associated with individual characteristics. Often this head shape is observed among residents of the Caucasus and Asians.
Dolichocephaly or long head
With dolichocephaly, a decrease in the BPR is not a sign of a reduction in the head, but is caused by an increase in the LZR. The head has a more oval, elongated shape.
In the fetus common cause the formation of dolichocephaly is gluteal or breech presentation. Normally, this head structure is also genetically more characteristic of representatives of Nordic and Mediterranean peoples.
In these cases, to understand true size heads use the cephalic index: BPR/LZR, which normally ranges from 0.75 to 0.85. If extreme values of the cephalic index are detected, the gestational age is not determined using BDP.
During a normal pregnancy, a woman should have 3 scheduled ultrasounds. After each diagnostic procedure The patient is given a special protocol, which contains important data on the condition of the fetus. Among other abbreviations and special terms, which can be read there, women are often interested in what BDP is on an ultrasound during pregnancy.
BPR - indicator value
BDP, or biparietal size, is an indicator that characterizes the size of the head developing fetus. It gives a clear picture of how the nervous system is developing and whether this is consistent with the current stage of pregnancy. During an ultrasound, the semicircle of the fetal head is measured - between the temples along the minor axis - this is the width or BPR.
Timely measurement of this indicator is necessary to confirm safe passage through the birth canal for both the child and the woman in labor. Knowing the biparietal size helps to choose the optimal type of completion of labor. Artificial delivery can be carried out manually, medicinally or instrumentally.
If the fetal BPD shows a significant excess of the size of the fetal head and the woman’s birth canal, then the obstetrician and gynecologist leading the pregnancy may decide to prescribe a planned abdominal surgery, in which the baby is removed from the mother's womb through an incision in the uterus.
A uniform increase in the abdominal, chest and head indicators is not a pathology, but may indicate a large pregnancy
Features of the measurement procedure
The BDP indicator is considered the most informative if it was obtained in the 2nd trimester or at the beginning of the 3rd trimester. Such research should only be done by a trusted experienced specialist to be confident in the results. If errors were made during the measurement process, this will affect the determination of the exact gestational age and expected date of birth.
In the process of fetometry (measurement of various anatomical structures) of the fetus using ultrasound, the head is given primary attention. Along with the biparietal size, the fronto-occipital size (FOR) is measured. This is done strictly when scanning in the transverse (axial) plane.
Both of these indicators allow you to derive the cephalic index (CI). It is calculated as a percentage and is most often displayed automatically when all fetal parameters are measured on ultrasound. CI is calculated using the following formula: BPR/LZRx100%.
For more later During pregnancy, the index of BPD and LZR increases. Such prenatal measurements reveal pathological abnormalities in the development of the fetus, and also help ensure the possibility of natural childbirth.
However, all these prenatal measurements are quite subjective, since the structure of the head skeleton is different for all people. The fetal skull may be narrow and elongated from frontal bones to the occipitals. Or maybe, on the contrary, it could be round shape with a wide front part and a relatively small fronto-occipital size. This does not indicate developmental pathologies, but is associated with anatomical features.
Norm and deviations
BDP indicators are classified according to weekly standards that correspond to a certain stage of pregnancy, and special measurement tables have been created. They are standard all over the world and are already written into the device software ultrasound diagnostics. Immediately before the examination itself, the specialist selects required type data and begins the procedure, at the end of which, based on standard indicators, a conclusion is issued.
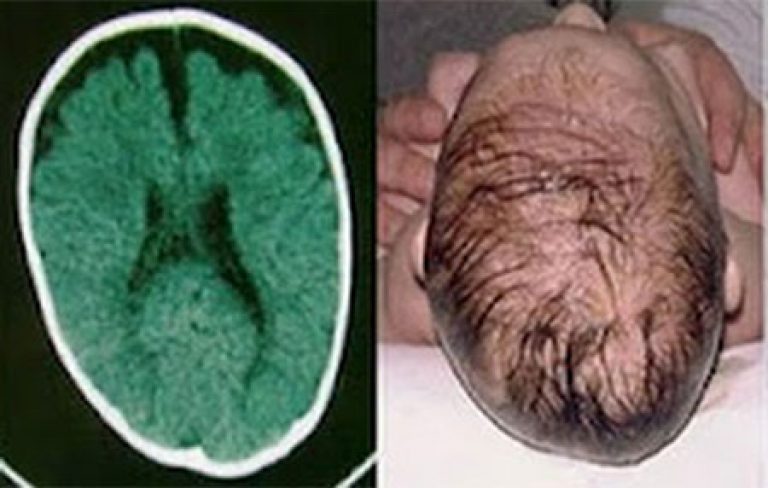
If the parameters of the fetal head in the mother’s womb are significantly deviated from the norm, then this may be a sign of the development of pathologies or conditions dangerous to the child’s health. Deviations from the norm can occur with the following pathologies:
- Intrauterine retardation physical development fetus. This diagnosis is made if the result is ultrasound examination a lower BPR value was determined than is allowed within normal limits, and all other fetometry indicators (CTE, DB, coolant, DHA) are in order. This may indicate infection of the fetus in the mother's womb or oxygen starvation.
- Hydrocephalus. Such a diagnosis can be made if the BPR and LZR are increased, and the remaining indicators are normal and fully correspond to the given period of development. Most often, the cause of this pathology is an infection that has entered the mother’s womb.
- Microcephaly. This serious pathology development of central nervous system. It is characterized by a decrease in skull circumference and a decrease in brain mass by more than 2-3 indicators of actual deviations from standard values.
- Missing parts of the brain or underdeveloped brain structure. In this case, the biparietal head size may be very small compared to the normal average at a particular stage of gestation.
In a newborn child with microcephaly, the head circumference, as a rule, does not exceed 25-27 cm, although normally it should be 35-37 cm. And the mass of the brain weighs 250 g, while normally its weight should be 400 g.
Intrauterine growth restriction
There are two main forms of intrauterine retardation: physiological development child:
- Symmetrical - the fetus is underweight and its height and head circumference suffer. All these indicators do not correspond to the gestational age.
- Asymmetrical - the fetus is light in weight, but its height and head circumference do not lag behind normal indicators.
With IUGR, it is assumed that the fetus’s nutrition is impaired, so nutrients and oxygen do not enter the child’s body during sufficient quantity. Violation of fetal trophism can be caused by the following phenomena:
- genetic metabolic disorders;
- fetal chromosomal abnormalities;
- marginal placenta previa;
- multiple pregnancy;
- late toxicosis leading to vital impairment important organs and systems;
- disturbance of blood flow in the spiral arteries of the placenta;
- abnormal structure or location of the umbilical cord;
- rubella, herpes, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus;
- pituitary dwarfism, decreased thyroid function;
- taking certain medications;
- ionizing radiation exposure;
- bad habits of the expectant mother;
- undernutrition of a pregnant woman.
However, in some cases, even if the child’s measurements are below those required for a given stage of pregnancy, you should not despair. This may indicate that the child is simply small in size. This happens especially often when the future parents themselves are short and light in weight.
Having received the survey data, you should not understand them yourself and create unnecessary stressful situation. The doctor conducting the examination only writes down all the results, and the obstetrician-gynecologist deciphers everything and explains it to the future parents.
If you detect a problem in time and immediately begin to eliminate it, you can count on a favorable prognosis. But, as a rule, one study in this case is not enough. If the indicators differ significantly from the norm, it is best to conduct a repeat ultrasound.

