How to identify intrauterine fetal hypoxia. The consequences of fetal hypoxia for the development of the child. Intrauterine fetal hypoxia: treatment and prevention
Greetings, dear readers! Intrauterine development child plays an important role in later life, because it largely determines his health. However, there are many factors and conditions that can harm the fetus during pregnancy. One of them is fetal hypoxia, the consequences for the child of which can be very sad. Let's talk about how to avoid hypoxia and recognize it in time.
Therefore, its prevention should be considered in advance. Phenotic hypoxia - insufficient oxygenation of tissues and organs of the fetus or incomplete absorption of oxygen. This term, proposed World Organization health care, but not the only one: there are also the terms "fetus" and asphyxia.
Influence oxygen deficiency in the body of the fetus different time pregnancy is different. On early stages when it is the formation of organs and systems, severe hypoxia may be accompanied by slower growth of the embryo and the appearance of malformations. To the lack of oxygen on late stages pregnancy can lead to slower growth of the fetus, the central nervous system of the fetus and newborn, impaired adaptation of the child after birth; V rare cases this can lead to stillbirth or death of newborns.
Before we talk about hypoxia in detail, let's define what it means. In medicine, this is called oxygen starvation, when nutrients and oxygen for a number of reasons do not come to the child. This condition is quite common, occurring in 10% of pregnant women.
Hyporia is not separate disease, but develops due to various pathological processes in the body of a pregnant woman. There are 2 forms of state:
Reasons for the development of pathology
Depending on the duration of the flow, chronic and acute fetal hypoxia are distinguished. Chronic hypoxia develops when there is insufficient oxygen for the fetus for a long period due to existing maternal disorders. internal organs. Difficult pregnancy. Chronic hypoxia can also result from smoking, alcohol, and drugs during pregnancy.
Acute hypoxia usually occurs during work. Less acute hypoxia occurs during pregnancy when life-threatening maternal conditions occur. Sometimes there is a combination of acute and chronic hypoxia fetus. What is the effect of hypoxia on the fetus. Not every pregnancy is against the background of the above diseases and conditions complicated by intrauterine fetal hypoxia.
- acute hypoxia (occurs unexpectedly, most often during childbirth);
- chronic (develops over several months, complicating the course of pregnancy).
Intrauterine hypoxia only with easy course does not affect the health of the child. Statistics show that only in 4% of cases, severe hypoxia does not affect the health of the child.
The point is that there are physiological features fetal development, which prevent the occurrence of this disease. The blood of the fetus "drives" more oxygen molecules than the blood of an adult; fetal heart jumping more blood per minute than the heart of an adult; in the fetal blood a large number of special, required by fetal hemoglobin, which is easier to attach oxygen to itself and there are faster tissues and cells, since high speed blood flow to the fetus; The protective factor against the development of hypoxia also refers to the structure of cardio-vascular system fetus.
Causes of hypoxia
Causes oxygen starvation most often associated with internal diseases pregnant:
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- anemia;
- diabetes;
- kidney pathology, respiratory system;
- oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios;
Another reason is disturbances in the uteroplacental blood flow due to:
Under the influence of hypoxia in the early stages of hypoxia, the function of the adrenal glands of the fetus is activated, therefore, the production of substances that increase the heart rate and increase blood pressure fetus. However, in order to receive organic damage, it must be severe asphyxiation or affect previously perfect problem. Blood from the superior vena cava, which reaches the right atrium, enters the right ventricle - pulmonary artery- arteriovenous descending aorta in 60% cardiac output. It supports circulation in the vital important organs, such as the brain, heart, kidneys and liver, decreasing in the limbs and the spleen area. Progression of hypoxia Management of fetal growth restriction.
- Only 3 shunts: ductal arteriosis, oval concha, venous canal.
- Distribution of the fetal circulation and "centralization of circulation".
- birth anomalies;
- overwearing;
- diseases of the umbilical cord, placenta;
- pregnancy complications.
Oxygen starvation is also caused by fetal diseases:
Symptoms
Symptoms that every expectant mother should pay attention to will help to recognize hypoxia in time:
- From about 4 months, the baby begins to move. A woman should pay attention to how many times a day there were episodes of stirring. One episode is considered to be the presentation of signs of life within 2 minutes. Too frequent or rare movements are considered by physicians as negative signs.
- The main symptom that a doctor may look for is infrequent or fluctuating heartbeats. Normally, the beat should occur at a frequency of 120-16 beats per minute. The number of beats of about 90-100 per minute is a dangerous sign.
During childbirth, hypoxia is determined by the following signs:
Stimulation: epidemiological characteristics. Faculty medical sciences. Correspondence Author: Maria J. Fetal death is the death of a fetus before its expulsion or complete separation from the mother's body, regardless of the duration of the pregnancy. IN a large percentage its causes are unknown, although the literature has established intrauterine hypoxia and congenital malformations as risk factors. A retrospective descriptive study was conducted to determine, through a review, clinical histories, epidemiological characteristics of fetal mortality in motherhood.
- the child is pale or bluish skin;
- weak muscle tone;
- weakened manifestation of reflexes or their complete absence;
- the baby cries badly, crying may be absent;
- breathing is difficult;
- the color of the amniotic fluid is green or brown.
Diagnostic procedures will help confirm the diagnosis:
Most of the fetal deaths mentioned occurred below 37 weeks, with male predominance. In addition, the most common medical factors such as anemic syndrome, obstetric factors such as fetal malformations and hemorrhagic complications have been found in cases of fetal death. Another important finding of the study was that the weight of dead fetuses was less than the weight of live births of the same gestational age.
Why does fetal oxygen starvation occur?
Keywords Key words: fetal death, abortion, intrauterine death. Neuroses - the death of the fetus before their expulsion or complete separation from the mother's body, regardless of the duration of pregnancy. A high percentage of its causes is unknown, although risk factors for intrauterine hypoxia and birth defects. A retrospective descriptive study was conducted to determine, through a review, medical records, epidemiological characteristics of stillbirths in the maternity hospital. Most of these stillbirths were below 37 weeks with a male predominance.
- Cardiotocography. This ultrasonography, using sensors attached to the abdomen, which determines the frequency and quality of the child's heartbeats.
- Doppler. Another ultrasound study aimed at analyzing blood flow in the placenta and uterus.
- ultrasound. The method allows you to see big picture child development.
- Biochemical analysis pregnant blood.
Based on the tests, the doctor makes a conclusion about the child's condition and the degree of danger for him of oxygen starvation.
Medical factors such as anemic syndrome, obstetric factors such as fetal malformations, and hemorrhagic disorders are most common in cases of stillbirth. Key words: stillbirth, abortion, intrauterine death. This is why intrauterine fetal death is a devastating event for the parents and, in a sense, it can mean the failure of the obstetrician and perinatologist who cared for this pregnancy.
Fetal death is the death of the product of conception before its expulsion or complete separation from the mother's body, regardless of the duration of the pregnancy. Of these rates, late fetal mortality is what was reported in most of the studies reviewed.
Consequences of hypoxia
WITH mild degree Acute or chronic hypoxia is born every third child, so a condition that does not affect the development of the fetus is not considered dangerous. Severe oxygen starvation adversely affects the formation of the fetus. Every expectant mother must know why hypoxia is dangerous:
Following an epidemiological study of fetal mortality, this pathology was included in the United Nations data collection systems. Despite this, the causes are not known for the high percentage of fetal deaths. However, in those cases where the cause was determined, intrauterine hypoxia was most common, followed by congenital anomalies. Maternal disease, which caused higher mortality from intrauterine hypoxia, resulted in placental abruption 24.4% followed by umbilical cord contraction 18.5% and placental insufficiency 10.7%.
- developmental delay;
- damage to the central nervous system;
- reduced adaptation to conditions external environment;
- change metabolic processes;
- ischemia;
- cell death in various bodies that have irreversible consequences.
Treatment pathological conditions child is long and not always effective. Treatment of hypoxia
Acute and chronic fetal hypoxia
In 22.9% of cases, not a single bound state mother. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and antiphospholipid syndrome can cause placental infarction and, as a result, intrauterine fetal death. The authors consulted taking into account intermediate and late fetal mortality, but for comparison between international data, which they used at the end. These studies have shown that pregnant women with low socioeconomic status are most affected, as 98% of cases occur in countries with low and medium socioeconomic status.
Since acute hypoxia occurs mainly during childbirth, emergency therapy is required. The drugs are administered intravenously depending on the indications:

With well-designed treatment, hypoxia does not significantly affect the health of the child. future mommy you need to be careful and take your feelings seriously. At the first suspicion of oxygen starvation of a child, consult a doctor.
More than half of the cases are at work. The main causes of complications of fetal death during childbirth were maternal infections during pregnancy, maternal diseases such as hypertension and diabetes, fetal growth restriction, and congenital anomalies.
Causes of intrauterine fetal hypoxia
In 49% of cases, the presence of pathologies associated with pregnancy was observed, mainly pregnancy hypertension, diabetes and immune pathology, the presence in them of the main antiphospholipid antibodies. In 21.7% pathology of ovular applications was observed, 12.8% intrauterine hypoxia, 6.5% birth defects development, in 4.2% of maternal pathology not associated with pregnancy, in 3.7%, the causes were not indicated and in 2.4% chromosomal abnormalities.
If the article was useful to you, leave comments in the social. networks. The information is given for reference. Until new discussions, dear friends!
The content of the article:The consequences of fetal hypoxia are mainly reflected in the brain of the newborn, which needs oxygen the most. In the future, this may lead to serious violations in work nervous system child, which require mandatory diagnosis, treatment and correction.
In the same order of ideas, Rivas and Vazquez identified placental pathology as the main cause of fetal death in 25% of cases. This study highlights a personal history of hypertension, with most cases having pregnancies of less than 36 weeks and male fetuses predominating. The most common direct factor in death was placental insufficiency caused by hypertension.
Diagnosis of intrauterine fetal hypoxia
The design of the study was retrospective, descriptive and observational. Sampling was not required because the entire population was taken for study. Although the entire population was used, which would make the use of inferential statistics unnecessary, when subsets of the population are compared, these statistical methods could be used.
Hypoxia in the fetus - what is it
Hypoxia in the fetus is an insufficient supply of oxygen to the blood of the fetus, a pathology that is often observed in newborn babies. Already after birth, the consequences of oxygen deficiency make themselves felt and are dangerous. Hypoxia in the fetus occurs during prenatal period, as well as in birth process.
The data was obtained by reviewing medical records, rather than collecting information that would allow patients to be identified to maintain medical secrecy. Demographic variables such as the age of the pregnant woman and geographic origin. Obstetric history as number of births, number of births, previous caesarean section, ectopic pregnancy, abortions, stillbirths, previous deaths. Variables associated with the current pregnancy, such as gestational age in weeks, number of fetuses, sex of the product of conception, fetal weight, fetal height and pregnancy control, obstetric and medical pathologies, are risk factors reported in the literature for fetal death.
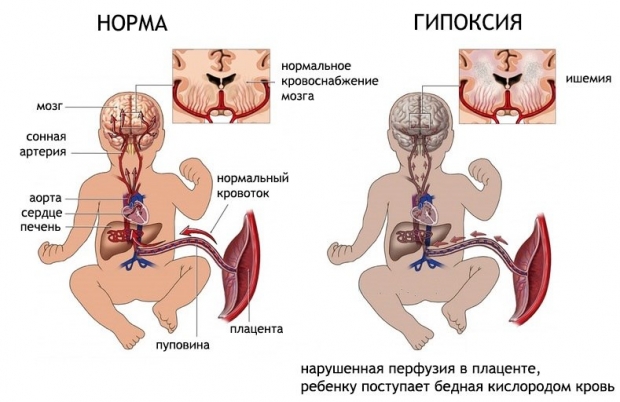
Chronic intrauterine hypoxia
The causes of this pathology are:
Risk of miscarriage;
Diabetes;
Bleeding;
Smoking;
Addiction;
multiple pregnancy;
Infection;
Diseases in the first half of pregnancy;
Diagnosis of oxygen deficiency in the fetus is quite difficult. Indirectly, the pathology is evidenced by such signs as rapid fetal movements, which then stop, tachycardia ( rapid pulse) and developmental delay (according to ultrasound, less weeks than it should be). Hypoxia is also characterized by prolapse of the uterine fundus and oligohydramnios.
This was done in order to establish comparisons with previous studies in a population similar to those covering them in the same way. The same was done with obstetric variables such as placental abruption, uterine rupture, and placenta previa, which are included as hemorrhagic complications. This grouped all dystocia, fetal malformations, funicular pathology and obstetric infections in order not to have a long list of pathologies whose prevalence was very low and to show their impact as a whole.
To detect violations in circulatory system unborn child, a woman needs to undergo an additional examination:
Fetal electrocardiogram;
Blood tests;
Cardiotocography;
NST test;
Doppler;
Determine the fetal biophysical profile (BFP).
If hypoxia is detected, the doctor prescribes therapy that improves blood flow and oxygen supply to the child developing in the uterus.
With regard to variables associated with the care of a pregnant woman, the form of termination of pregnancy, obstetric surgical intervention and hospital stay in days. We also determined its Pearson and Kurtos skewness coefficient. In addition, the arithmetic mean, median, and percentile distribution were determined.
Methods for the treatment of fetal hypoxia
When statistical or dichotomous variables presented as prevalence were compared, odds ratios and Fisher's exact test, setting a p value of 0.05, were used to determine significant differences. Out of 396 fetal deaths, they completed the abortion.
Acute hypoxia during childbirth
Intranatal hypoxia occurs during childbirth. As a rule, it does not depend on the mother herself and arises due to unqualified assistance from obstetricians and gynecologists. Any woman in labor should know exactly what kind of help doctors should give her. Their responsibility is to provide normal process delivery. (For details on who delivers and what the duties of a doctor and midwife are, read the article on our website.) A woman should not allow herself to be experimented with during childbirth. Wrong health care may be fraught serious complications both for the mother and the baby.
During the existence Soviet Union doctors actively practiced obstetrics with the use of labor-stimulating drugs, even with normal flow childbirth. Medicines stimulated contractions, pierced amniotic sac. Similar Methods quite dangerous and can threaten the health of the mother and child. Quick delivery are not natural, since the body of the fetus and the mother herself should normally prepare for the upcoming process. Incorrect intervention can complicate childbirth and lead to various injuries and acute hypoxia of the newborn.
The causes of fetal hypoxia during childbirth can also be:
Entanglement of the neck with the umbilical cord;
Weak birth process;
polyhydramnios;
Multiple pregnancy.
Prediction of the consequences of hypoxia in the fetus
Oxygen deficiency in a newborn varies in degree. The consequences for the baby can be very different. The condition of the newborn is assessed immediately after birth using the Apgar scale. If it is determined by doctors at 4-6 points, and after five minutes of life the indicator reaches 8-10, then the consequences are of moderate severity. Low grade the state of the child on the Apgar scale is fraught with very serious complications. The newborn may experience:
neurological disorder;
mental retardation;
Lagging behind in height and weight;
Speech pathology;
Mental illnesses.
Admission not enough oxygen, first of all, affects the brain. It is the brain centers that correct the work of all organs in the body. Severe hypoxia, acute and chronic, has various manifestations. After the cessation of oxygen supply, the brain centers are switched off after fifteen seconds. Neurons die massively, because oxygen is not supplied with blood. Respiratory arrest occurs.
When the umbilical cord of the child is infringed and breathing stops, then the blood stops flowing into the baby's body. In this case arterial pressure decreases, and venous increases. The child's brain can be severely damaged. Arise:
Hemorrhage;
Ischemia;
Irreversible damage to the brain centers;
Children's cerebral paralysis - most grave consequence hypoxia. IN Lately more frequent diagnosis this disease among children, which is due to the use of various labor-stimulating drugs.
A sure sign of the presence of a lack of oxygen molecules in the fetus is a reduced or increased heartbeat during childbirth. Lack of fetal activity may indicate oxygen deficiency. Signs of hypoxia include:
Bradycardia (slow heartbeat);
Tachycardia (rapid heartbeat).
If hypoxia was revealed in a baby after birth, then from the very first hours of life, a neuropathologist should take care of the child. The fight against the consequences of oxygen starvation should begin even in the hospital with oxygen inhalation. Doctors should then prescribe medications that improve brain function and sedatives. Physical education is also assigned therapeutic exercises and a special massage. In the future, parents may need classes with a speech therapist or child psychologist. The child must be registered with a neurologist in the clinic.
From the very beginning of her pregnancy, the expectant mother should carefully monitor her health. It is necessary to make long hiking, which ensures a sufficient supply of oxygen to the developing body of the child. It is very important to be observed by a gynecologist in a timely manner and undergo all the prescribed examinations that will reveal various abnormalities during pregnancy. A woman in labor should choose a qualified doctor for childbirth and a good maternity hospital.
What to do with hypoxia in the fetus?
Caring for the health of the unborn baby during pregnancy should be accompanied by the inner harmony of the woman's state of mind. No stress psychological condition pregnant should be stable. The development of any stress must be minimized. This will prevent the occurrence of phobias, which primarily affect the child.
Even serious illness women can not always cause hypoxia. Nature itself tried to ensure that the fetus was reliably protected in the woman's body from various negative factors. In the body of a pregnant woman, various physiological processes and changes that include defense mechanisms. It is they who prevent the development of many complications during pregnancy and ensure the correct development of the fetus in the prenatal period. Physiological protection prevents the development of hypoxia and normalizes the blood supply to the fetus.
The blood of an unborn child contains a large number of oxygen molecules. Much more than the average adult. The fetal heart pumps blood many times more often than the organ of adults. The hemoglobin of a baby developing in the womb has differences in structure, its molecules attach faster and perfectly split off oxygen. The work of the entire cardiovascular system of the unborn child is aimed at preventing a lack of oxygen.
You should know that as soon as various signals about the oxygen deficiency of the fetus begin in the body, immediately:
The work of the adrenal glands is activated;
The production of the necessary hormones increases;
Increased heart rate;
Increases blood pressure;
There is a redistribution of blood flow. Blood is activated primarily in the brain, then in the heart, kidneys, placenta and internal organs.
Thus, the important vital organs of the fetus receive a large volume of blood. A slight degree of hypoxia has practically no effect on the condition of the unborn child and its development.
Only when serious problems may arise dangerous complications. Poor blood supply to the fetus affects the functioning of the intestines, therefore, in amniotic fluid penetrates the original feces. During the birth process normal color amniotic fluid - transparent. The appearance of a green tint indicates the presence of chronic hypoxia. Green waters are a sign of oxygen starvation medium degree. Too cloudy amniotic fluid speaks of severe form hypoxia and possible infection of the fetus. In such cases, appropriate therapy, including antibacterial therapy, should be immediately prescribed. Treatment of a newborn with hypoxia should begin immediately. In any case, a woman in labor should not set herself up for poor delivery results. Most pregnancies end in happy outcome and birth healthy baby. Take care of your own health and visit the gynecologist regularly during pregnancy.

