Chronic hypoxia of the newborn blue child. How to avoid serious consequences of hypoxia in newborns. Treatment of hypoxia in newborns
Pregnancy is such a long-awaited and happy event in a woman's life. At the same time, this is a very important period. The health and well-being of both the mother and the unborn baby depend on how these 9 months pass.
In some cases, there is a possibility of unpleasant circumstances that can overshadow the bright feelings and the first joys of motherhood. Basically, such situations are related to the health problems of the child.
If hypoxia has progressed to permanent brain injury, with cognitive deficits, cerebral palsy, or other outcomes, then treatment focuses on a combination of medicine and long-term therapy. There is no cure for permanent traumatic brain injury caused by extended hypoxia, so treatment is mandatory for life. Lifelong costs of biological and psychological therapy are often prohibitive. Families may also need some form of psychological therapy to help cope with the emotional and financial burdens they face.
What is hypoxia
Hypoxia is one of the most common pathologies that the baby's parents can learn about even before his birth or within the walls of the maternity hospital. This state is characterized lack of oxygen during the period of gestation or directly in the process of childbirth.
fabrics, internal organs, the central nervous system and the brain, against the background of poor oxygen supply, are damaged and cannot function fully, irreversible processes occur in some cells. This situation presents serious threat For normal development fetus. Severe cases can lead to disability and even a threat to the life of the child.
Medical malpractice and legal remedies. In cases of hypoxia, injury is rapid but preventable, meaning that when right action permanent disabilities can often be avoided. Given the advances made in the detection and treatment of hypoxia over the past fifteen years, hypoxia that progresses as a result of permanent injury may be the result of medical negligence on the part of a physician or other healthcare professionals. According to this, medical workers must adhere to established standards to ensure that any distress is identified and dealt with promptly.
Causes of hypoxia
Hypoxia can occur as a result of intrauterine pathology and postpartum period, as well as directly in the process of childbirth.
Depending on the underlying cause of this condition, a distinction is made between chronic and acute form hypoxia. Chronic form develops throughout pregnancy. The main reasons for its occurrence are:
Causes of hypoxia in newborns
If a doctor fails to meet these standards and the child is continually injured as a result, the doctor may be liable for medical malpractice. Get a free legal assessment of a birth injury complaint. After a child's injury, all parents want to think about how to get help for their child. After getting the information, treatment, and support you need from your doctor, the next step may be to get the legal help you need. If you believe your child's injury may have been caused by a provider's negligence medical services you can start by getting a lawyer.
Various severe pathologies and diseases of the mother. Such as:
- Leukemia.
- Violation of the heart muscle.
- Intoxication.
- Asthma.
- Anemia.
- Infections of the genitourinary system.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
A serious risk of impaired child development occurs in women who smoke, abuse alcohol and drugs. Also at risk are expectant mothers under 18 and over 27 years old.
Treatment of hypoxia in newborns
Hypoxia is a condition where oxygen cannot get into the tissue and perinatal remedy occurs just before and after birth. While the direct translation of perinatal hypoxia means oxygen deficiency in tissues before and after birth, it is little more than that.
How does perinatal hypoxia occur?
Perinatal hypoxia is a lack of oxygen for an infant, and there may be a number of reasons why the infant does not receive required amount oxygen. The most common reasons why infants experience perinatal hypoxia include.
Pathologies of pregnancy:
- in cases of serious trophic disorders in the placenta (abstraction, presentation, premature aging and thinning)
- Preeclampsia.
- Low water / polyhydramnios.
- Rhesus conflict.
- Pathology and genetic diseases fetus.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Infection of intrauterine waters.
An acute form of hypoxia develops in the case of:
maternal smoking Traumatic injuries of the brain Magnesium anemia Hearing of asphyxia Inadequate fetal monitoring. Perinatal hypoxia can also occur when there is a problem with the umbilical cord or. All of these conditions should be diagnosed by a doctor during pregnancy as they can lead to birth complications, caesarean section emergency care etc.
What can lead to perinatal hypoxia?
Perinatal hypoxia can lead to a number of serious medical conditions such as hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy and brain injuries associated with birth asphyxia. All three of these injuries are serious brain injuries that can lead to paralysis and severe brain damage. Typically, these three lesions develop within 48 hours of perinatal hypoxia, so if the child is treated immediately, some of the serious consequences thereafter may be substantially reduced.
- Rapid childbirth.
- Prolonged childbirth.
- premature birth.
- When entangled with the umbilical cord.
- When extracting the fetus by applying forceps.
Postpartum hypoxia may occur due to:
- Anemia of the newborn.
- Congenital malformation of the lungs or heart.
- As a result of extensive blood loss.
- With an overdose of anesthesia or drugs.
- With birth trauma.
Signs and symptoms
 Most often, there is no difficulty in determining the presence or absence of hypoxia in a newborn, since given state has a clear and pronounced symptomatology.
Most often, there is no difficulty in determining the presence or absence of hypoxia in a newborn, since given state has a clear and pronounced symptomatology.
What treatment should be followed for perinatal hypoxia?
Other medical conditions associated with perinatal hypoxia include. Cerebral paralysis severe seizures Cognitive impairment Behavioral disorders. Hypothermia is medical term, which essentially means freezing to death, but is a form of treatment that has been used effectively after perinatal hypoxia. When hypothermic treatment is started within 6 hours of birth, the results show that mortality and long-term neurological disorders can be cut in half.
The main signs of hypoxia include: tachycardia, bradycardia, arrhythmia, heart murmurs, hypovolemia, blood clots, tissue hemorrhages, the presence of meconium in the analysis of amniotic fluid.
Depending on how fully the child's body functions, using the Apgar scale, experts distinguish 4 degrees of severity. oxygen starvation:
Controlled clinical neonatal therapeutic hypothermia works because during labor, the body switches into emergency mode, sometimes starting a chain of events that lead to seizures, which in turn leads to brain damage. When you cool your baby with ice blankets or a special ice cap, cellular reactions slow down, allowing more time for doctors to concentrate more oxygen on the baby. The oxygen level is then restored to natural levels.
- 8-10 points - a state without signs of impaired body functions.
- 7-6 points - 1st degree of hypoxia, mild form. In this case, recovery normal life body occurs without outside intervention within a few minutes after birth.
- 5-4 points - 2nd degree, middle form(moderate). For full recovery it will take from several days to several weeks.
- 3-0 points - 3rd degree, severe form (). To improve the condition of the child, it is necessary to resuscitate him. Subsequently, the recovery of such a baby requires full treatment and serious care.
Caring parents can determine that chronic intrauterine oxygen starvation led to the development of such a disease as encephalopathy with the naked eye.
While just before or during labor and delivery, oxygen deprivation to the fetus is called fetal hypoxia or intraoral disease hyperax. All three terms refer to a condition in which the baby's tissues receive insufficient oxygen, leading to possible serious complications including hypoxic brain injury. Neonatal asphyxia is used to describe a baby immediately after birth who does not begin to breathe or whose breathing does not provide enough oxygen to the body.
Symptoms Before birth, fetal hypoxia may be suspected if there are fetal signs. Information from these monitors is reported on a fetal monitor strip that can be used by the obstetrician, midwife nurse, or midwife nurses to see how the baby is responding to each contraction and to the overall job. low frequency fetal heart rate or unusual slowdowns heart rate baby may be a sign of the fetus. In addition, an unusual pattern of fetal heart rate variability may be a sign of traumatic brain injury or an impending brain or central nervous system injury to the infant.
In this case, the baby may experience a violation of thermoregulation. He behaves restlessly, often and (during crying, his chin trembles, it is difficult to calm him down). Arises constant weakness and sleepiness. The child shudders during sleep (). With any sound or tactile impact, the baby shudders and gets scared.
Hypoxia can lead to the development of such serious illnesses as: psychomotor retardation, hyperactivity, vegetative-vascular dystonia, epilepsy, cranial nerve damage, disorders mental development, hydroencephalopathy.
If there are signs of a fetus and labor is sufficiently developed, the middle wife's doctor or nurse can take a pH sample from the baby's head to see if there is oxygen deprivation. A baby deprived of oxygen before birth may have difficulty breathing after birth, have too much acid in bodily fluids, be present with brain damage or disorders, or have damaged organs. If oxygen deprivation has occurred during the entire delivery process, the baby may be blue at birth, not breath, not cry, mal muscle tone or low heart rate.
Treatment and recovery methods for hypoxia
In case of acute hypoxia, first of all get rid of mucus and meconium from the child's respiratory tract. Then with mask breathing or artificial ventilation lungs provide the proper level of oxygen supply to the body. After that, it is necessary to stabilize the body temperature and arterial pressure baby.
After birth, the baby may develop respiratory distress syndrome. Immediately after birth, the baby may be pink, with a good cry, good muscle tone and normal rhythm hearts. In premature newborns, this can happen because the fetal lungs have not yet matured. If this happens, the child may need supplemental oxygen through a mask or may need to be intubated with an endotracheal tube for mechanical ventilation to help the child breathe. Restoring oxygen delivery is called "resuscitation" of the baby.
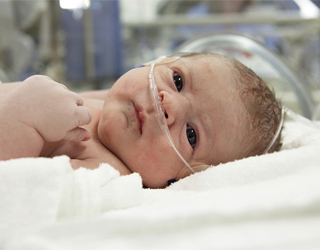 In case of blood loss, a blood or plasma transfusion procedure is performed. After all necessary procedures the child is under constant surveillance(pulse, pressure, body temperature, heart rate are monitored). If necessary, drugs are introduced to improve the condition of the newborn.
In case of blood loss, a blood or plasma transfusion procedure is performed. After all necessary procedures the child is under constant surveillance(pulse, pressure, body temperature, heart rate are monitored). If necessary, drugs are introduced to improve the condition of the newborn.
This respiratory acidosis increases the risk that the baby may develop cerebral bleeding, also known as intraventricular hemorrhage. If resuscitation does not provide enough oxygen for the child, the child may also develop metabolic acidosis, as evidenced by low pH levels in the child's blood. Low level oxygen can cause anoxic or hypoxic damage to the child's brain, leading to periventricular leukomalacia and cerebral palsy.
Symptoms of hypoxia in newborns
Whether there are signs of oxygen deprivation in utero or after birth, timely intervention and resuscitation procedures are required to ensure the baby has an adequate supply of oxygen to prevent hypoxia, brain damage, or death.
When serious violations appointed drug therapy, which may include drugs that improve the blood supply to the brain, removing from it excess liquid, vasoconstrictors, and corrective concomitant states.
Do not forget that a child whose body has suffered to some extent from oxygen starvation, requires heightened attention . To improve his condition, first of all, it is necessary to provide care. Good nutrition plays an important role.
Some risk factors for gestational fetal hypoxia include. Babies are exposed greater risk asphyxia during childbirth and childbirth when the mother is under the influence of any drug, especially anesthetics or sedatives because before the baby is born, the mother shares with the fetus whatever substances are in her bloodstream. For example, narcotic pain medication given to a woman during childbirth may have a respiratory effect on the baby at birth.
Thus, health care providers should be aware that such a medication can cause respiratory depression in a child and lack of oxygen if not corrected. Babies born prematurely may not have a fully developed respiratory system to provide them with enough oxygen. Thus, if premature birth imminent, health care providers should be aware of the need to give steroids for fetal maturity. Besides, medical staff should be aware of the possible need for PAS in preterm infants.
A positive result is given by training with specialists rehabilitation centers, regular massages and developing physical exercises.
All procedures must be performed strictly in accordance with the doctor's recommendations. The sooner the rehabilitation process begins and the more regularly classes are held, the greater the chances of full recovery and recovery of the child.
What is hypoxia in newborns?
Labor and labor that is prolonged or problematic can put the fetus at risk for conditions such as a prolapsed or compromised umbilical cord that deprive the fetus of an adequate supply of oxygen. Prolonged labors can also use oxygen stores for the baby, leaving the baby more susceptible to hypoxia at final stage childbirth.
Supplies that use obstetric instruments, such as a vacuum extractor or tongs, have more high risk injury to an infant and can lead to conditions that restrict the flow of oxygen to the brain and other organs. Postherent fetuses are more likely to pass meconium before birth and are at risk of aspiration of a sticky substance that can block the airways. Any other condition that causes a baby to be born with a "severe respiratory distress”, can lead to hypoxia if breathing is not restored quickly enough.
Hypoxia in newborns is, unfortunately, a fairly common condition, which is accompanied by a lack of oxygen in the baby's body. This dangerous violation, which, in the absence medical care may lead to the development of a number of complications or lethal outcome.
Hypoxia in newborns: causes of development and varieties.
Today, there are many factors that, as a result, lead to a lack of oxygen, which is simply necessary for normal operation human body.
This condition can be either congenital or acquired. congenital disorders develop during pregnancy, in the womb. The reason may be the condition of the mother's body. For example, it has been observed that women with diabetes have problems with endocrine system, as well as prolonged anemia, chronic diseases respiratory tract much more often babies are born in this condition.
In addition, the deficiency of this gas in the body of the fetus may be due to the Rh conflict between the mother and child. Very importance also has the lifestyle of a pregnant woman, since malnutrition, flaw fresh air And sedentary image life can lead to such consequences.
Acquired hypoxia in infants develops directly during childbirth. The cause may be trauma during passage through the birth canal, as well as the neck of the child wrapped around the umbilical cord. In addition, a mismatch in size can lead to the same result. female body and child. Hypoxia is also quite often diagnosed among, or vice versa, with too long gestation.
Hypoxia in newborns: symptoms.
In fact, it is quite simple to determine such a condition - his skin acquires a bluish tint, and the baby does not make any sounds at birth. In this case, he desperately needs medical assistance That's the only way to save his life.
Hypoxia in newborns: consequences.
It should be noted that oxygen is very important for normal functioning human body. And at not enough of this gas in the blood, first of all, the brain suffers, which regulates all other functions child's body. The longer the fetal brain is not the more severe and irreversible are the consequences.
As a rule, such children are regularly monitored by a pediatrician. Possible heart failure and vascular system as well as developmental delays, muscle weakness and trembling, and in more severe cases, convulsions.
And even if the development of the baby is normal, deviations from development in the future are very likely - this may be, for example, speech delay, lethargy, or, conversely, excessive activity.
Hypoxia in newborns: methods of treatment.
In the future, after a thorough examination, doctors prescribe certain drugs, with which you can normalize the activity nervous system and correct other violations. The treatment package also includes massage sessions, physiotherapy and methods of physiotherapy.
Hypoxia in newborns: how to avoid it?
In fact, all methods of prevention should be carried out by a woman during pregnancy. Expectant mothers need to remember proper nutrition, taking vitamins, regular visits to the doctor and taking tests that help identify the presence of certain diseases. Do not neglect outdoor walks.

