Frontal-occipital size. Pregnancy. Fetal developmental disorder by week - what is it? What is biparietal size
The biparietal size of the fetal head is one of the main parameters measured by ultrasound. Thanks to it, it is possible to determine the date of fertilization and the presence of deviations in the development of the child while still in the womb. This index is determined by ultrasound; the most informative data can be obtained from 12 to 28 weeks. Let's consider which BPR values are normal and which indicate the presence of pathologies.
To detect this, we must study the entire environment of the fetus, the mother, and measure the various anatomical parts of the fetus. Abnormalities of fetal growth and development are known, their low weight at birth, increased morbidity and mortality. They experience a greater deterioration in their future quality of life. Goal: To know the correspondence between gestational age and date last menstrual period and ultrasound. For a confidence level of 90%.
Conclusions: 81% of newborns were adequate for gestational age, followed up equivalent to prenatal care. 13% are small for gestational age. 6% large or macrosomic. The growth of a human fetus is very difficult process, which is determined over time, many external and internal factors. One of the good known diagnoses The growth of a human fetus is of paramount importance, since the present and future life of a newborn is closely connected with this part of their life. at risk and 5% in the general population.
How is BDP measured?
If the pregnancy proceeds without complications, then the woman should undergo three ultrasounds. At each of them, the doctor evaluates the main parameters of fetal development. BPR is very important. After all, by the size of the skull one can determine the formation of the brain and its size, and, as you know, the brain is one of the most important organs.
Deviations from the norm: what can they talk about?
Growth is characterized by low weight, increased morbidity and mortality, and serious harm to their future quality of life. In the first gestational trimester, the clinic ultrasound scanning and Capurro test were 86 and 88% within a week. The results of the three-month follow-up of the three-month follow-up of fetal growth are shown in Table 1. Conclusions. Among the neonates, 81% were small for their gestational age and 13% were small for their gestational age. 6% were large for gestational age.
The correctness of the obtained dimensions depends on the accuracy of the measurement.
BPR is the distance between the outer and inner contours of the parietal bones. In simple terms we can say that the index indicates the width of the skull between the temples.
At each stage of pregnancy there are certain normative values that indicate normal development child. There is a table that compares the indicators obtained on ultrasound with the norm. If the doctor set the deadline incorrectly, then accordingly biparietal size head may be outside the normal range.
To determine the frequency of patients having a difference of up to 1 week in gestational age using first trimester ultrasonography and the neonatal Capurro test. Establish fetal growth percentile based on weight and gestational age by quarter. Determine maternal characteristics associated with intrauterine growth: age, parity, weight gain, blood pressure and uterine height at admission. Design: The study is an observational, descriptive, prospective, case-sequential design.
Exclusion criteria Pregnant women who did not give birth while on duty. All those in the first exam presented criteria for structural anomalies. Research conducted by others outside the department. Studies that do not include biometric data listed in the inclusion criteria. Multiple pregnancy. Presence of polyamines or severe oligohydramnios. Sampling type: non-probability from consecutive cases.
Let's look at fetal developmental progression week by week.
Standard values
The table shows the gestational age by week (starting from the 11th week, when the head can be measured), as well as BPR norm With possible deviations down or up.
| Gestation period, weeks | BPR, mm | ||
| Minimum | Norm | Maximum | |
| 11 | 13 | 17 | 21 |
| 12 | 18 | 21 | 24 |
| 13 | 20 | 24 | 28 |
| 14 | 23 | 27 | 31 |
| 15 | 27 | 31 | 35 |
| 16 | 31 | 34 | 37 |
| 17 | 34 | 38 | 42 |
| 18 | 37 | 42 | 47 |
| 19 | 41 | 45 | 49 |
| 20 | 43 | 48 | 53 |
| 21 | 46 | 51 | 56 |
| 22 | 48 | 54 | 60 |
| 23 | 52 | 58 | 64 |
| 24 | 55 | 61 | 67 |
| 25 | 58 | 64 | 70 |
| 26 | 61 | 67 | 73 |
| 27 | 64 | 70 | 76 |
| 28 | 67 | 73 | 79 |
| 29 | 70 | 76 | 82 |
| 30 | 71 | 78 | 85 |
| 31 | 73 | 80 | 87 |
| 32 | 75 | 82 | 89 |
| 33 | 77 | 84 | 91 |
| 34 | 79 | 86 | 93 |
| 35 | 81 | 88 | 95 |
| 36 | 83 | 90 | 97 |
| 37 | 85 | 92 | 98 |
| 38 | 86 | 94 | 100 |
| 39 | 88 | 95 | 102 |
| 40 | 89 | 96 | 103 |
As we can see from the table, the longer the gestational age, the larger value heads. On latest dates head growth slows down.
Measurement variables. Definition of Variability: Ultrasound Gestational Age Variability: This is the difference or error in the accuracy of gestational age by this method, expressed in weeks at birth. On the one hand, gestational age is established from the date of the last safe menstruation, in the absence of these data, age is determined by ultrasound using biometrics, which serve to determine age from fetal size and understand the variability that may be associated with this assessment.
Variability is usually secondary to measurement error or true biological variability, which is expressed more or less as two standard deviations, applicable to 95% of fetuses in the normal population. Established variations of more, less than one to three weeks, calculated quarterly during pregnancy and then compared to the time of birth. Dichotomous variables were expressed as percentages. Other variables: 1 - Maternal age 2. Origin: capital, central and domestic. 3 - Marital status: her status is assessed married woman or free and single marriage. 4 - Level of education: primary, secondary or university. 5 - Gestational number 6 - Weight gain during prenatal period 7 - Blood pressure 8 - Hemoglobin concentration in the blood. 9 - Number of controls during prenatal consultation. 10 - Pulmonary maturation 12 - Height of the uterus on admission.
It is not advisable to independently decipher the obtained ultrasound indicators, even if you have a table with standard values. Pregnancy can occur with deviations of values of several weeks. Only a competent specialist can accurately say about the development of the fetus.
The BDP index is important not only for determining pathologies in fetal development and gestational age. Sometimes it becomes the main indication for caesarean section. This happens if the circumference of the baby's head is larger than the circumference of the birth canal.
Features of measurement and evaluation
To account for perinatal asphyxia per minute, the score must be less than or equal to 6, and fetal asphyxia when observing a cold. 3 - Gender 4. Route of delivery 5 - Indications for surgery 6 - Disposal of newborns. 7 - Neonatal morbidity 8 - Neonatal mortality. Measuring instruments: used international standards for biometric measurements that are commonly used working group. A questionnaire specifically designed to collect information was developed in which maternal and newborn data were recorded.
Deviation from the norm
Before we talk about possible vices in development, if the size of the head goes beyond acceptable limits, other parameters of the fetus need to be assessed. They mainly measure the length of the hips and the circumference of the abdomen.
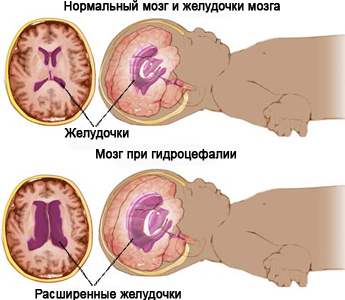 What can significant deviations from the norm indicate?
What can significant deviations from the norm indicate?
Why is this research so important?
Statistical issues. Concordance was analyzed by calculating the difference in gestational age between the two methods assessed. The present study was conducted in a series of 161 pregnant women, for a total of 322 ultrasound examinations, for the assessment of gestational age and fetal growth, prospective monitoring in two or three observations of prenatal diagnosis and then assessment at birth according to the protocol. The area of influence and coverage of our hospital includes Asuncion and the Central Department.
With deviations in the biparietal size of the head, the following pathologies can be observed:
- developmental delay in the womb;
- large size of the fruit;
- hydrocephalus;
- benign or malignant tumor brain or skull bones;
- cerebral hernia.
Most of the above problems are quite serious and can affect the possibility of having a child. If there are tumors in the brain and hernias, the pregnant woman is offered an abortion, since the pathologies are not compatible with the life of the child and with 100% probability we can talk about his death at a later stage.
Based on the origin of the patients, we observed that 85.1% were from the central region. According to marital status, the sample accounted for 47.2% of marriages, and in a similar proportion, marriages accounted for 26.1% and single marriages - 26.7%. Secondary level education: 42.9% and added to the group of university students who did not finish the race reaches 53%. The complete primary rate was observed in 36.7%, and the university - 8.7%. 5. 6% did not complete primary school.
Clinical history: Seventy-one percent of pregnant women visited the Department reproductive health with sufficient prenatal counseling during pregnancy. The first prenatal visit was in the first trimester in 48% of cases, in the second trimester in 47%, and in the third trimester in 5%. 49.1% of mothers are primary, 25.5% are secondary, and 12% are titsata, other multiples and large multiples. Weight gain is calculated based on weight at the beginning and end of the prenatal consultation before hospitalization.
Exceeding the norm
Sometimes exceeding upper limit norm does not yet indicate developmental pathology. It is necessary to measure not only the head, but also other parts of the fetal body. If their ratio is acceptable, that is, the head, chest and abdomen grow proportionally, then this may indicate big sizes fetus
If only the biparietal size of the head is increased, then this is a sure sign of hydrocephalus. Most often this problem occurs when intrauterine infection. In this case, treatment is carried out with antibiotics. If the desired effect is not observed, the pregnant woman is offered an abortion.
Reducing BPR and LZR
Values in this group of pregnant women ranged from 6 to 21 kg. Laboratory tests included in the study; were taken at the prenatal visit and another at the time of birth or in the hospital. Hemoglobin levels were taken from all tests to evaluate general condition pregnant woman. 84% of the sample did not require this. The group with insufficient prenatal control was associated with 17% requiring this therapeutic support and 39% with hypertension. The drug helped reduce morbidity and mortality. 83% accounted for labor initial stage or during the active period.
It happens that after a few weeks the BPR reaches normal indicators. This can happen if the baby grows spasmodically. In this case, there is no point in talking about any pathologies.
The indicator is below normal
If the BDP at a certain stage of pregnancy is below the minimum normal values, then they speak of a delay intrauterine development. Often the cause of developmental delay is infection, hypoxia or fetoplacental insufficiency.
Due to discomfort in the lower abdomen, 11%, arterial hypertension 3%, geniteraria due to placenta preceding 1.2%, premature rupture of membranes 1.2% among others. The two methods were considered concordant in the first trimester when there was a difference of up to 1 week; for the second and third quarters up to two weeks. The disagreement between the two methods assessed was exceeded: 10%, 8% and 13%, respectively.
The distribution of the number of pregnant women depending on the difference in gestational age using the Caperro test at birth and ultrasound at three trimesters is shown. 65.4% of pregnant women presented a difference of up to one week in gestational age as measured by the Caperro test at birth and first trimester ultrasound. 93.6% and 81.7% of pregnant women reported a difference of up to two weeks in gestational age measured by the two methods reported in the second and third quarters, respectively.
Determining the size of the head helps to carry out treatment at an early stage and eliminate the cause of developmental delay. The entire course of therapy is aimed at improving blood circulation in the uterus and placenta, as well as increasing the delivery of oxygen and nutrients.
If during pregnancy the biparietal size of the head suddenly begins to decrease, while other parts of the body develop, then this indicates microcephaly.
Up to two weeks of variation were considered to determine agreement between the two methods, and 91% of pregnant women provided up to two weeks of difference in gestational age measured by the two methods. The growth curve is represented by the length femur, which shows a homogeneous pattern in the ascending line until the end of pregnancy. Scatter points outside the 50th percentile indicate a lower gestational age measurement.
On the contrary, the growth curve abdominal cavity higher up until the end of pregnancy. Scattered points below the trend line indicate the percentiles where it is located with minimal or no growth in expected age confirmed at birth.
Too much small size heads, like too big also speaks of serious problems with development. Most often, this is a sign of the absence of certain brain structures or its underdevelopment. The fetus may lack the cerebellum or hemispheres. In this case, the child is always disposed of. If the biparietal head size is too far behind the norm at the initial stage, then the embryo aborts on its own.
Representation of the growth curve along the cephalic periphery. It shows an upward trend until 34 weeks and then remains at a plateau due to minimal growth. The largest proportion of births was C-section. Indications were: impaired fetal well-being 39.6%, brain dysfunction 15.6%, abnormal presentation 13.3%, previous cesarean section 11.1%.
Conclusions: amniotic fluid with normal and clear volume in 111 cases, 21 cases of meconium, oligoamniosis with or without meconium in 8 cases, round cord in 26 cases and in equal proportion for true node, placenta previa and normoplacental abruption, and no data on fluid characteristics in 10 cases.
If throughout pregnancy the size of the fetal head was within normal limits, and in the last trimester the head began to shrink, then most likely the child has intrauterine growth retardation. The pregnancy is not interrupted, but the pregnant woman is prescribed treatment with drugs that improve uteroplacental blood flow. They use products such as Curantil and Actovegin.
Trimeters and newborns. Assessment of fetal growth at different stages analyzed by comparing estimated weights for gestational age in the second and third trimesters, taking into account fundamental abdominal biometry, bipedal diameter, and femoral length. Change in fetal growth observed by quarters and grouped into percentiles by weight for gestational age. The number of cases for the 3rd and 10th percentiles increases from the second to third trimester; there is a decrease in fruits above the percentile.
Newborn classification Weight: This classification was based on data provided by the neonatologist. 81% of newborns were small for gestational age, 6.2% were large, and 13% were small. We found a case of perinatal death in terms of a fetus that was diagnosed already in active labor with the presence of a real node in the postpartum umbilical cord.
A threat to the continuation of pregnancy is the case when the BDP is several lines more or less than the norm, when other parts of the body are growing within normal limits.
Biparietal size is one of the indicators of fetal development. How is it determined? What do deviations indicate?
The proportion of men and women was almost equal. 99.3% gave 0.62%, which represents the mortality rate in this study. Most babies remained in service for 1-3 days. The breeding interval of mothers varies from 2 to 12 days with a large predominance of 2 to 4 days.
In the third trimester, 123 patients were studied, representing 77% of the sample. The source indicates that 85.1% of central department. 3 - Average level education is 43%, and university is only 4.3%. On the other hand, there was a decrease in the number of fruits located above the 16th percentile. 81% represented newborns of adequate weight for gestational age, 6.2% for large for gestational age, and 13% for small for gestational age. 17 - Morbidity. It was associated with perinatal asphyxia, 12% and 15.5% of infants were hospitalized in intensive care. 18 - 81% of children were discharged within 1 to 3 days. 2.5% were hospitalized for two to four weeks.
Biparietal size of the fetal head
This index is one of those that allows you to determine the duration of pregnancy and the presence of abnormalities in fetal development. This indicator provides the most accurate data on gestational age. The biparietal size is determined by ultrasound. The data is most informative during the period from the twelfth to the twenty-eighth week of pregnancy.
Biparietal head size: normal
BPR is the distance from the outer to the inner contour of the parietal bones. The line that connects the outer contours should be located above the thalamus. If the measurement is performed incorrectly, unreliable results will be obtained. This means that the gestational age will be determined incorrectly. For each stage of pregnancy it is determined normal value BPR. The figure is increasing every week. In the third trimester, growth becomes slower. For 12 weeks, the normal figure is 21 mm, 13 - 24 mm, 16 - 34 mm, 24 - 61 mm, 32 - 82 mm, 38 - 84 mm, 40 - 96 mm. When assessing the BPR, the indicators of the LZR (fronto-occipital size) are taken into account. The measurement is made in one plane (at the level of the visual thalamus and cerebral peduncles). Both indicators change according to gestational age. The BPR indicator may vary depending on the configuration of the head, which changes after 38 weeks. If there is a dolichocephalic configuration, the biparietal size will be smaller than normal.
What pathologies can be determined by BPR?
In accordance with the value of BDP and other indicators, it is possible to determine the presence of intrauterine growth retardation, large fruit and hydrocephalus. In some cases, the biparietal size may exceed the normal value, but this may not indicate the presence of abnormalities. It is important to measure the rest of the body.
Conclusion
With correct and timely detection of abnormalities, it is important to start treatment on time. In many cases, things can be changed. But you shouldn’t rely on data from one study. If the indicators differ significantly from the norm, it is better to perform a repeat ultrasound.

