Test for genetic abnormalities during pregnancy. genetics analysis
To prevent the occurrence of hereditary diseases in newborns, a genetic blood test is performed for pregnant women. It allows you to study hereditary traits and the state of the genes, and then make an estimated prognosis for the health of the baby.
Doctors determine the shortcomings in the development of the fetus, fix the causes of abortion. The specialist appoints a study for women who are in one of the risk groups such as:
- age over 35 years;
- effect on the fetus x-rays drugs, alcohol;
- cases of stillbirth;
- viral infection during pregnancy.
Blood is taken for genetics to determine motherhood or paternity, the child's predisposition to hereditary ailments. Genotyping helps to prescribe medicines V required doses for the treatment of an undeveloped disease.
Types of genetic blood testing
 The expectant mother is tested for the establishment of genetic thrombophilia, cytogenetic studies, the carriage of frequent mutations in hereditary pathology. A genetic study of the blood in patients with Gilbert's syndrome and the study of coagulation systems for two factors V, ii are being carried out.
The expectant mother is tested for the establishment of genetic thrombophilia, cytogenetic studies, the carriage of frequent mutations in hereditary pathology. A genetic study of the blood in patients with Gilbert's syndrome and the study of coagulation systems for two factors V, ii are being carried out.
The laboratory analyzes whole blood taken from the patient with EDTA, which determines genetic markers necessary to establish the quality of hepatitis treatment.
EDTA is a special reagent used for analysis in the form of acid, which is in a test tube with a purple cap.
Perinatal screening is carried out to identify such congenital deformities, How:
- Down syndrome;
- changes in the neural tube;
- trisomy on chromosome 18.
In a period of up to 13 weeks, indicators such as PAPP-A are studied - plasma protein A, a free B-subunit of the chorionic hormone. Processing indicators allows you to identify free estriol, L-fetoprotin.
Genetic analysis is not mandatory, but allows you to control the situation.
Genetic polymorphism established by the patient's blood
Intrapopulation phenomena are divided into such types as:
- gene polymorphism;
- chromosomal changes;
- balanced views.
When more than one allele is present in a gene, genetic polymorphism. Blood type is the most a prime example such a phenomenon.
Genetic modifications are inherent in leukocyte enzymes found in plasma. The difference in blood groups is observed by leukocyte antigens Rh, ABO, MN.
Polymorphism in blood groups is observed according to the ABO system and distinguished by the frequency of alleles. There are 4 blood groups (CA, B, AB and O) and their corresponding alleles: IA, IB and IO.
Human populations have polymorphism in the Rh, MN blood group systems. Genetic variation manifests itself in the distribution certain types diseases on the globe, in their clinical course, reactions to the treatment of the disease.
Analysis in pregnant women for chromosomal pathology
For the prevention of hereditary diseases of the unborn baby, a perinatal study of diseases at the intrauterine stage of fetal development is carried out.
Chromosomal pathology is detected by a biochemical test that determines the presence and concentration of AFP and at 15-18 weeks of gestation.
 Down syndrome and other fetal chromosomal changes are detected using the PAPP-A and P-hCG marker proteins in the first three months of pregnancy. Normally, in a future mother, the amount of PAPP-A protein is increased, and its low level indicates the formation of a hereditary pathology.
Down syndrome and other fetal chromosomal changes are detected using the PAPP-A and P-hCG marker proteins in the first three months of pregnancy. Normally, in a future mother, the amount of PAPP-A protein is increased, and its low level indicates the formation of a hereditary pathology.
At 10 weeks pregnant chorionic gonadotropin(hCG) has a maximum concentration. The maximum permissible values of the hormone indicate the presence of chromosomal pathology and the development of trisomy. The lower level is 0.5 MoM and the limit value is 2 MoM. Blood is also examined for the presence of SP1 glycoprotein. Normally, it is 1 MoM, and in a sick fetus - 1.28 MoM.
Inhibin A is studied in biochemical analysis as a marker of chromosomal pathology. In the presence of a glycoprotein parameter in the range of 1.44-1.85 MoM, a chromosomal pathology (trisomy 21) is established.
Genetic blood test for thrombophilia
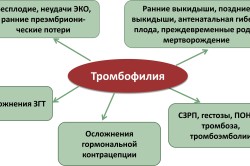 In the process of the appearance of disturbances in the hemostasis system, a increased ability to the formation of thrombi. Carriers of the gene that causes thrombophilia experience Clinical signs disease as a result of exposure to factors such as:
In the process of the appearance of disturbances in the hemostasis system, a increased ability to the formation of thrombi. Carriers of the gene that causes thrombophilia experience Clinical signs disease as a result of exposure to factors such as:
- postpartum period;
- surgical intervention;
- pregnancy;
- traumatic injuries with the imposition of a splint or plaster.
In pregnant women, the analysis is carried out if there is a history of relatives of venous thrombosis and myocardial infarction, as well as the occurrence of complications of previous pregnancies:
- preeclampsia;
- intrauterine fetal death.
The doctor determines the risk factors for the development of thrombophilia, selects prophylactic to prevent complications in the child and mother.
As a result of the study, gene mutations are found in the folate cycles MTHFR, MTRR, indicating the formation of a malformation in the form of a cleft palate, cleft lip. The genetic miscarriage factor is determined by analysis.
Venous thrombosis is caused by gene polymorphism in the amino acids of prothrombin F2, coagulation factor F5. The F2 gene has F2 polyphony 22010-6>< при риске с частотой 2-5%, проявляющийся потерей ребенка в I триместре, и гестозами, венозным тромбозом.
Fetal genetic testing
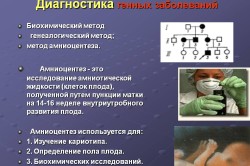 A frozen pregnancy allows you to take a genetic analysis to detect abnormalities in the chromosomes of the fetus. Research (cardocentesis) determines a number of diseases after the 18th week of pregnancy. A child's DNA analysis, or DOT test, reveals Edwards, Patau, Down syndrome.
A frozen pregnancy allows you to take a genetic analysis to detect abnormalities in the chromosomes of the fetus. Research (cardocentesis) determines a number of diseases after the 18th week of pregnancy. A child's DNA analysis, or DOT test, reveals Edwards, Patau, Down syndrome.
Biochemical markers are determined during the study, taking into account the value of the indicator for each gestational age. The doctor takes into account the age of the mother, pregnancy, her accompanying ailments, complications during childbirth.
Whole blood (EDTA) for analysis allows you to get ahead of the child's DNA and predict the risk of developing chromosomal pathology. High level homocystin disrupts blood circulation in the placenta, which causes infertility or fetal hypoxia in more late dates pregnancy.
The doctor conducts a genetic study with the help PCR method to study the polymorphic features of genes, reveals V factor and prothrombin. Blood samples are packed in individual containers, accompanied by an indication inscription. Embryonic blood cells in the mother's circulation are studied to establish the chromosomal map of the child's genes. The method completely replaces the invasive process of studying fetal anomalies.
Deciphering genetic research during pregnancy
 According to the results of the analysis, the doctor determines the degree of risk of miscarriage. The study indicates the value of F5 and F2 (Leiden factor and prothrombin).
According to the results of the analysis, the doctor determines the degree of risk of miscarriage. The study indicates the value of F5 and F2 (Leiden factor and prothrombin).
Mark fibrinogen F6B and plasmogen activator inhibitor as a standard or pathological heterozygote.
In the analysis, a coagulogram and a hemostasiogram are determined. Miscarriage is associated with polymorphism of the genes of homeostasis and fibrinolysis systems, prothrombin 620210A, gene 6667T, plasmogen inhibitor PAJ-1.
Gene polymorphism in women with abortion is associated with (FJ, LV). Deciphering the analysis for trisomy can give a result on 18/21/13, taking into account individual risks, defined as 1: 2434, 1: 16789.
Down syndrome on chromosome 21 has a birth rate of 1:900 children. If the mother is 20-24 years old, the probability of having Down's disease is 1:562, 30 years old - 1:1000, 39 -1:214. Trisomy 18 syndrome has a frequency in the population of 1: 700. Patau syndrome, or trisomy 13, is characterized by severe congenital pathology of 1: 4000. The numbers 21,18,13 indicate the risk of Down syndrome, Edwards, Patau. genetic infertility associated with a mutation of the Y chromosome in men, and in women - chromosomal abnormality(45X), Stein-Leventhal syndrome, FMR1 gene mutation, accompanied by a fragile X chromosome, trisomy 16.
Deciphering the analysis in a medical genetic consultation determines the risk of recurrence of a hereditary disease.
Genetics today plays a big role in the treatment of various diseases. Modern genetic analysis makes it possible to identify in patients the presence of various pathologies. Also, with the help of this study, it is possible to identify a person's predisposition to a particular disease. In addition, genetic information is widely used in forensics and to establish family ties between people. Today there is various methods genetic analysis, each of which has its own goals and objectives.
Why do you need a test in gynecology
Most often, a genetic blood test is recommended at the stage of pregnancy planning. This test allows you to determine in advance the risk of developing hereditary diseases in the baby and the possibility of the birth of a child with congenital defects. However, not all couples take a gene test before pregnancy. Most often, women go through it already, being in a position. In this case, there is also a chance to timely identify hereditary pathologies and take measures to ensure that the baby is born healthy. The test in early pregnancy is called the genetic deuce. It is he who allows you to identify intrauterine abnormalities in the very early stages of bearing a baby.
Today, experts insist that genetics analysis should be done by husbands and wives even before pregnancy. This will allow parents to receive a health card for the unborn child, which will display all the diseases to which the baby is predisposed. Genetic information will become a kind of guide for parents on what to pay attention to and what measures to take to keep the baby healthy.
Also, the study will help prevent the birth of a child with congenital anomalies.
Mandatory indications for a test during pregnancy are:
- The age of the pregnant woman is 35 years.
- The presence of genetic diseases in the families of parents.
- The first child was born with the presence of pathologies.
- Conception was under the influence of harmful factors.
- The presence of hereditary thrombophilia in one of the parents.
- Previously, the woman had miscarriages, miscarriages or stillborn children.
- During the gestation of the fetus, the woman was ill viral infection.
- Women who are at risk for health.
Modern methods of molecular genetic research allow doctors to identify the predisposition of the unborn child to the following diseases:
- Diabetes.
- Pathology of the thyroid gland.
- Pathologies of the digestive tract.
- Respiratory pathology.
- Heart diseases.
- Down Syndrome.
- Edwards Syndrome.
- definition of thrombophilia.
- Osteoporosis etc.
The results of molecular genetic analysis make it possible to prevent the development of these diseases in a child in a timely manner, which ensures safe gestation and birth healthy baby. Further, this information will be useful throughout the life of the child, because it will already be known to which diseases the baby's body is predisposed at the genetic level. Genetic tests can be carried out by both non-invasive and invasive methods. In the first case, the blood of the mother and father is donated for analysis, in the second case, amniotic fluid, placenta or blood from the umbilical cord can be the material for research.
Why do you need a test to determine nationality
Anyone can do a genetic analysis today. What is it for? Each person has their own goals. Someone wants to conduct a paternity test, others want to accurately determine their nationality, others want to identify their predisposition to various diseases. Determining the human karyotype today is becoming more and more popular among ordinary citizens. One of the most popular molecular genetic studies is the determination of nationality.
Genetic information contains all the secrets of the origin of each of us. It happens that in the passport we have one nationality, and the analysis shows that our ancestors were of a completely different origin. This gives us knowledge of the development of our family, which allows us to return to our roots and find out more information about our origin.
What other genetic tests are there?
Today, genetic methods for examining biological materials are used in almost all areas of science. Molecular genetic studies today can reveal a lot of diseases. They also give full information about a human.
Today medical centers can offer patients whole line analyzes for genetic diseases, among them:
- Human cytogenetic study.
- Genetic duo.
- Test for Gilbert's syndrome.
- Analysis for Down syndrome.
- Analysis for genetic thrombophilia.
- HIV/AIDS test.
- Paternity analysis.
- Analysis for celiac disease.
- Epilepsy test, etc.
The cost of analysis depends on its type. Molecular genetic research today is not yet done in public medical institutions. They are held only in private centers and are always paid. It is worth noting that if you are assigned this analysis during pregnancy, it must be done, because the health of your baby depends on it.
How the test is done
Depending on the type of research, experts choose best method research. So during pregnancy, most often the patient is taken for research venous blood. To establish paternity, an analysis of the saliva or hair of alleged relatives is carried out.
How accurate is the analysis? The advantage of molecular genetic research lies in the 100% accuracy of the analysis. Genetic information is stored in a person throughout life. It cannot change or become obsolete. For this reason, you need to pass the analysis only once in a lifetime. Based on this study, you can control your health all your life by avoiding unpleasant factors, which can provoke the development of certain diseases.
It is especially important to do an analysis if you have a bad heredity.
This applies to those people whose family has a hereditary disease, for example, thrombophilia. Why is it so important? Treatment of thrombophilia is a complex and lengthy process. Many patients do not even assume that this disease is inherited. For this reason, the definition of thrombophilia in genetic analysis gives many patients a chance to avoid the disease by taking preventive measures in a timely manner.
How much analysis is done? On average, the results of the study of biological material are ready within 10 days. But those who have already donated blood for such a study, argue that the timing directly depends on the laboratory and the workload of the center. Also, the research methods that are used in a particular case affect the speed of analysis.
How to decipher the result
Deciphering the analysis is the business of a professional. The results are deciphered by specialists called geneticists. It is they who can adequately assess all the risks of developing the disease, determine your nationality and accurately tell men whether they are the father of their child. Despite the fact that many are still frightened by the methods of genetic research, there is nothing terrible in them. On the contrary, there are times when only genetic information can shed light on a question that concerns you. Decoding takes place in the office of genetics or family planning.
Everyone knows that the disease is easier to prevent than to cure. It is for the prevention of pathologies that each person must do a genetic analysis. After all, many hereditary diseases very insidious. They can appear at any age. Remember, forewarned is forearmed. It is especially important to do a test even before pregnancy, this will completely eliminate the risks of having a sick child.
The development of genetics over time has gone beyond the boundaries of a purely scientific doctrine and moved into a branch of practice. Many modern doctors use the data of genetic analyzes in order to put correct diagnoses, foresee possible diseases and eliminate the factors that contribute to their development. To do this, the patient just needs to pass a genetic analysis, which will show a complete picture of the predisposition to diseases.
A few words about DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a complex set of nucleotides that fold into chains - genes. It is this intracellular formation that carries hereditary information received from parents and transmitted to children.
At the time of embryo formation, very rapid cell division takes place. At this stage, small failures occur, which are called gene mutations. It is they who determine the individuality can be both positive and negative.
Scientists have partially been able to decipher the human genetic code. They know which genes cause diseases and which contribute to innate resistance to certain diseases. Genetic analysis gives doctors a picture of how best to treat the patient, given his predispositions.
Monogenic diseases and polymorphism
Doctors recommend doing a genetic analysis for every person. It takes place once in a lifetime. Based on its results, a genetic passport is drawn up. It lists all possible diseases and predisposition to them. 
TO congenital diseases include monogenic mutations. They arise as a result of changing one nucleotide in a gene to another. Often such replacements are completely harmless, but sometimes they can cause serious illness. These include, for example, phenylketanuria and
Polymorphism is associated with the replacement of nucleotides in genes, but does not directly cause disease, but acts only as an indicator of predisposition to such diseases. Polymorphism is pretty frequent occurrence. It occurs in more than 1% of the individuals in the population.
The presence of polymorphism shows that under certain conditions and the influence of harmful factors, the development of a particular disease is possible. But this is not a diagnosis, but only one of the options. If you lead healthy lifestyle life, avoiding harmful factors, it is likely that the disease will never appear.
Prediction of congenital diseases
The development of modern genetics makes it possible not only to state the presence congenital diseases or predisposition to them, but also to predict the health of unborn children. For this, parents at the stage of pregnancy planning must pass a genetic analysis. This is especially important if one of the parents already has complex illnesses.
This also applies to diseases that are genetically transmitted. Among them is hemophilia, from which almost all the monarchical dynasties of Old Europe suffered, where marriages were common to strengthen political ties. 
Also, genetic analysis will show the predisposition of the unborn child to cancer, diabetes, hypertension, coronary disease hearts. This is especially important if one of the future parents in the family had such diagnoses. Predisposition genes may be in a recessive (suppressed) state, but it is likely that they will appear in the future child.
Tests during pregnancy
Such studies are necessary in order to determine the possibility of congenital diseases. These are completely unpredictable diseases that arise as a result of intrauterine mutations that cannot be foreseen in advance. Down's Syndrome is one of these diseases, when an extra chromosome appears in the fetus for some reason. Normal quantity for humans - 46 chromosomes, 23 pairs, one from father and mother. With Down Syndrome, the 47th unpaired chromosome appears. 
Also genetic mutations possible after suffering complex infectious diseases during pregnancy: syphilis, rubella. Based on the results of such an analysis, a decision to have an abortion can be made, since future child would be completely unviable.
Women at risk
Of course, the analysis intrauterine diseases it would be better for every expectant mother, but there are a number of indications for this procedure. First of all, it's age. After 30 years, the risk of developing pathologies in the fetus is always high. It also rises if there have been cases of miscarriage. To already on early stages be aware of the danger, it is worth passing tests showing that everything is in order.
Occurs in pregnant women infectious diseases, and injury. They can also influence the course of fetal development. The earlier they happened, the more risk dangerous mutations.
There is always a danger of something wrong if at the time of conception or in the early stages after it, the mother fell under the influence dangerous factors. They include alcohol, strong medicines, psychotropic substances, x-rays and other exposures.
And, of course, it is better to play it safe if the family already has one child with congenital pathologies.
Paternity test
There are situations in life when the paternity of a child cannot be established. Or, for some reason, there are doubts that the father and the child, or the mother and the child are relatives. In this case, you can conduct a genetic blood test to determine the accuracy of such a study is more than 90%.
And the procedure itself is simple. It is enough just to donate blood of the parent and the child. By several indicators, it is easy to determine whether these two people have common genes. 
The determination of paternity, as a rule, is used in forensic medicine to prove or disprove the need for alimony.
predictive medicine
Every year, doctors strive not to treat diseases, but to prevent them even before the first symptoms appear. As genetic analysis shows, this is not so difficult to do. Since by the genotype it is already possible to assume which diseases a person is most disposed to.
This direction is called predictive (predictive) medicine. Based on the genetic passport, the doctor determines the lifestyle of his patient, warning him of dangerous moments that can become a trigger for the development of a particular disease. It is much easier and cheaper than going through a long, and sometimes not very effective, therapy. 
HIV/AIDS Tests
Today, even HIV/AIDS tests are done through genetic testing. The procedure is not complicated, but it takes a long time to conduct the study. But the results of such an analysis are more accurate and revealing.
Many modern centers diagnostics do genetic analysis, the price of which is affordable for every average patient. It all depends on the goals: the cost varies from 300 rubles to tens of thousands. Therefore, there is no reason to refuse such an informative study, especially if it can save the life of you and your children.
Genetic analysis during pregnancy is a set of studies and observations necessary to determine heredity and assess likely risks. Simply put, these are tests to identify the propensity of the unborn child to various diseases. IN Lately medical statistics inexorably testifies to the increase in children born with genetic abnormalities. But, as practice shows, most hereditary diseases could have been avoided by curing them before pregnancy.
Genetic analysis when planning pregnancy
Doctors consider the ideal solution to be tested for genetic diseases not during pregnancy, but at the planning stage. Then it is possible to estimate the percentage of the probability of transmitting hereditary diseases to the child and to prevent some pathologies. To do this, you need to turn to genetics, since it is the DNA of the future mother and father that plays a major role in determining the hereditary characteristics of their child.
The doctor will analyze the state of health and select the tests that will need to be passed potential parents. Thus, it will be possible to predict the health of the unborn child, as well as to determine the likely hereditary diseases that his parents can pass on to the baby.
Another undoubted advantage of such an analysis when planning a pregnancy is that miscarriage can be prevented. According to doctors, a large percentage women resort to genetic analysis after a miscarriage to find out probable causes and not let it happen a second time.
What is genetic analysis?
Molecular genetic analysis is a laboratory research that is carried out for specific purposes:
- Analyze genetic compatibility that determines motherhood and fatherhood, as well as other blood relationships (colloquially, this analysis is called a “DNA test” or “”).
- Generate a genetic passport for the unborn child.
- Identify infectious agents.
- Analysis for genetic predisposition to certain diseases (for example, cancer). Analysis with almost 100% guarantee identifies such potential diseases:
- thrombosis;
- diabetes;
- thyroid disease;
- osteoporosis;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- myocardial infarction;
- arterial hypertension;
- Down syndrome, Edwards;
- broncho-pulmonary pathologies.
In what cases is it necessary to undergo a genetic analysis during pregnancy?
 Genetic analysis can be performed at will if the parents-to-be are serious about planning a child and want to prevent risks. But most often, women undergo such an analysis already being pregnant, and only when the gynecologist suspects fetal abnormalities.
Genetic analysis can be performed at will if the parents-to-be are serious about planning a child and want to prevent risks. But most often, women undergo such an analysis already being pregnant, and only when the gynecologist suspects fetal abnormalities.
pregnant women in without fail It is necessary to undergo a genetic analysis in such cases:
- after 35 years;
- the first child was born with malformations;
- in the families of future parents there were previously cases of genetic diseases;
- with diseases transferred during pregnancy - influenza, SARS, rubella or toxoplasmosis;
- previously had miscarriages, stillborn children;
- long-term use medicines, alcohol, nicotine or drugs;
- after exposure to radiation (radiation or x-rays).
How is genetic analysis done?
There are types and methods of genetic analysis: non-invasive (traditional) and invasive.
Non-invasive include:
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound). The first time is carried out for a period of 10-14 weeks to identify possible congenital pathologies at the fetus. main feature the presence of pathology - abnormal width of the cervical-collar space (less than 2.5 and more than 3 mm). A second ultrasound at 20–24 weeks is performed to determine fetal malformations, placental anomalies, and the amount amniotic fluid.
- Genetic (biochemical) blood test during pregnancy. Carry on initial stage to identify probable chromosomal and hereditary pathology.
If such methods of genetic analysis predispose to doubts or suspicions, then to confirm or exclude them, they resort to invasive methods:
- Amniocentesis- at 15-24 weeks of gestation, amniotic fluid is taken for analysis by puncturing the uterus with a long needle. This is done under ultrasound control and is not dangerous for the child (in 99%). The results will not be soon, because with this method specialists “sprout” cells, but with the help of this analysis, hemophilia, Down syndrome, Edwards, Patau, fibrocystic and muscle pathologies can be detected.
- Chorionic biopsy- at 9-12 weeks of gestation, the cells responsible for the formation of the placenta are examined. Their sampling is carried out by puncturing the abdominal cavity with a long needle or through the cervix. The results of the analysis are ready in 3-4 days. The risk of miscarriage is 2%. Diseases such as Down syndrome, Tay-Sachs syndrome, cystic fibrosis, thalassemia are determined.
- Cordocentesis- for a period of 20-25 weeks, a fence is taken from the uterine cavity through a puncture cord blood for genetic testing. Results will be in 5 days. Rh-conflict is reliably diagnosed and hemolytic diseases fetus.
- Placentocentesis- such a procedure is mainly carried out in the second trimester in order to identify the consequences of infectious or viral diseases. In 96-97% of cases, the analysis passes without complications, but the procedure is quite complicated and is carried out under general anesthesia. It most accurately detects Down's syndrome, since the analysis is related to the quantity and quality of chromosomes.
Almost all invasive methods of genetic analysis are prone to complications. Therefore, the procedures must be carried out under the strict supervision of specialists on day hospital and using ultrasound. In addition, after the procedures, a pregnant woman should spend some time in the hospital under the supervision of doctors. But for prevention possible complications medications are prescribed.
How much does genetic analysis cost?
 If it's not about invasive methods(ultrasound and blood test), then big money they are of course not worth it. But if it is necessary to use more complex invasive procedures then the price will increase significantly. This is due to the fact that for their implementation it is necessary to attract a complex modern medical equipment, preparations for chemical laboratory.
If it's not about invasive methods(ultrasound and blood test), then big money they are of course not worth it. But if it is necessary to use more complex invasive procedures then the price will increase significantly. This is due to the fact that for their implementation it is necessary to attract a complex modern medical equipment, preparations for chemical laboratory.
In addition, the services of competent geneticists also have a considerable cost. It is for these reasons that the price of genetic analysis significantly exceeds the cost of conventional tests. Depending on the region and clinic, a genetic study for one disease costs from 600 rubles to 40 thousand rubles.
However, do not forget that the initial investment in genetic analysis will save money in the future. In addition, it is difficult to overestimate the joy of having a healthy baby.
Where and how can genetic analysis be done?
Pass a genetic analysis, get qualified consultations and detailed explanations on family planning and pregnancy, normal conception, bearing and birth of a healthy, without deviations, child can be in the centers reproductive technologies, scientific centers molecular genetic research, modern gynecological clinics, genetic and specialized medical centers.
Only such modern centers are equipped with the necessary medical equipment and have a biochemical laboratory in the unit to carry out the necessary genetic analyzes. In addition, such complex studies cannot be carried out by an ordinary gynecologist in antenatal clinic, here you need the help of a geneticist.
Summing up all the information, we can highlight the main advantages in conducting a complete genetic analysis during pregnancy:
- detection 400 pathological diseases out of 5000 probable;
- detection of anomalies, mutations, deformities;
- with serious gene pathologies, it is possible to have an abortion in the early stages or to carry out an artificial birth.
The main thing to remember is that genetic analysis does not correct violations in the development of the fetus, but only provides the necessary information. The right of choice always remains with the parents. A responsible approach to pregnancy planning will avoid problems and ensure the birth of a healthy and full-fledged child.
Genetic analysis is a combination of various experiments, calculations and observations, the purpose of which is to determine hereditary traits and study the properties of genes. An analysis for genetic compatibility and an analysis for genetic diseases, doctors recommend that women go through at the stage of family planning. Thus, it is possible to predict the health of the unborn child in advance, identify possible hereditary diseases and find ways to solve the problem of pathology. As a rule, in practice, women carry out genetic analysis during pregnancy, which has already begun, due to which the cause of miscarriage and congenital malformations of the fetus are revealed.
Indications for genetic analysis during pregnancy
Genetic analysis during pregnancy must be carried out in the following cases:
- At the age of a woman over 35 years;
- If there were hereditary (genetic) diseases in the family of the mother and father of the unborn child;
- The previous child was born on birth defects development;
- When during the period of conception and pregnancy a woman was exposed to harmful factors(X-ray, radiation, drugs, alcohol, certain medications);
- If during pregnancy future mom had an acute viral infection (ARVI, influenza, toxoplasmosis, rubella);
- If a woman has had miscarriages or stillborn babies in the past;
- All pregnant women at risk, based on ultrasound data and a biochemical blood test.
A gynecologist supervising pregnancy will definitely prescribe a woman an analysis for genetic compatibility and an analysis for genetic diseases if she belongs to the so-called risk group. This is the age over 35 years, when the risk of developing mutations and fetal malformations increases dramatically. To avoid unpleasant consequences late pregnancy and other risk factors listed above, a woman needs to be tested for genetic compatibility and analysis for genetic diseases.
Why is genetic analysis performed?
The main directions of the laboratory research based on genetic analysis methods are the following:
 1. Analysis of genetic compatibility, which determines paternity, motherhood and other consanguinity;
1. Analysis of genetic compatibility, which determines paternity, motherhood and other consanguinity;
2. Identification of genetic predisposition to common diseases;
3. Identification infectious agents;
4. Formation of a person's genetic passport.
A genetic compatibility test is also called a DNA test or a paternity test. For its implementation medical indications are not required, and a genetic compatibility test is carried out privately, at the request of the parents. Often this type of research is used in divorces, division of property and other litigation. You can determine the degree of relationship of the child before birth, during pregnancy.
An analysis for genetic diseases gives a 100% result and can reveal a child's predisposition to the following potential problems with health:
- myocardial infarction;
- arterial hypertension;
- Thrombosis;
- Osteoporosis;
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Bronchopulmonary pathologies;
- Diabetes;
- Diseases of the thyroid gland.
Having made a genetic analysis during pregnancy in time, and by identifying violations, it is possible to influence the successful bearing of the fetus and correct the health of the unborn child.
Everyone knows that there are infections that cannot be detected using the traditional forms of diagnosis that are routinely used in the process of monitoring pregnancy. Genetic analysis methods make it possible to quickly detect the DNA of infectious pathogens in the body, classify them, control their behavior and select the correct treatment. So, having made an analysis for genetic diseases, it is possible to identify such common pathologies as Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, etc.
The conclusion of an expert geneticist forms a genetic passport of the individual using genetic analysis methods. This is a kind of combined DNA analysis, which contains data on his profile, the uniqueness of a person. This information can provide a person invaluable help throughout life, with all sorts of health problems.
Traditional (non-invasive) methods of genetic analysis are:
2. Biochemical analysis blood.
Ultrasound of the fetus, as a method of genetic analysis during pregnancy, is carried out for a period of 10 to 14 weeks. It is at this time that pathology in the baby can be detected. Blood tests (biochemistry) are starting to be done for more early term pregnancy, it helps to identify chromosomal and hereditary (genetic) pathology, if any. If there are suspicions, after a previous genetic analysis during pregnancy, later, at a period of 20-24 weeks, a second ultrasound of the fetus is done. This method of genetic analysis allows you to identify minor malformations in the development of the fetus.
If the suspicions are confirmed, the woman is prescribed invasive methods of genetic analysis:
- Amniocentesis (examination of amniotic fluid);
- Chorionic biopsy (examination of the cells that are the basis for the formation of the placenta);
- Placentocentesis (procedure to detect consequences after past infection during pregnancy);
- Cordocentesis (examination of cord blood).
Timely analysis of genetic compatibility and analysis of genetic diseases makes it possible to identify approximately 400 types of pathologies out of 5000 possible.
How is genetic analysis performed during pregnancy
The main methods of genetic analysis, using ultrasound of the fetus and a biochemical blood test, are completely safe and harmless methods for both the mother and the child. Ultrasound is performed through the belly of a pregnant woman, using a special apparatus. Much less often, transvaginal ultrasound is used (the device is inserted into the woman's vagina). Biochemical analysis is carried out using patients' blood, which is taken from a vein.
With invasive methods of genetic analysis, an introduction into the body of a woman takes place. So, during an amniocentesis, the uterus is pierced with a special needle and a fence is made from it amniotic fluid(amniotic fluid). In this case, constant monitoring is carried out using ultrasound. Chorionic biopsy is understood as a puncture in abdominal cavity women to take material containing the cells necessary for the study (the basis of the placenta). Sometimes, for this analysis, the contents of the cervix are used. Placentocentesis is usually performed in the second trimester of pregnancy, under general anesthesia, as this procedure is considered a major operation. Cordocentesis is a method of genetic analysis during pregnancy, not earlier than 18 weeks. Blood from the umbilical cord is taken by means of a puncture through the uterine cavity of a woman. At the same time, anesthesia is also given.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Reviews and comments (41):
Quote: Evgenia
Hello! My son is 3.5 years old, about a year ago he had an attack similar to an epileptic one, during the year the attacks were repeated 4 times. Examinations of the child, encephalogram, video and CT scan were carried out. None of the examinations revealed epileptic foci. Nevertheless, the epileptologist diagnosed epilepsy, and hereditary. No one in my family, neither my husband nor I had such a disease. I would like to know if it is possible to find out the cause of my son's seizures with the help of genetic analysis? Thank you.
Hello Evgeniya.
Exact reasons of childhood epilepsy have not been fully studied, but it has been established that in about 2/3 of cases this may be a mutation in one of the genes, and there are quite a few such genes. However, in this case too we are talking rather about predisposition to epilepsy, and not about the disease itself - i.e. it may develop under unfavorable circumstances, or it may not. With the help of genetic analysis, it is possible to find out whether either of the parents is a carrier of the mutated gene.
Quote: Natalia
Quote: natalia
Quote: Natalia
Hello, Doctor. My son was diagnosed as a child with Tourette's disease (generalized tics, including vocal tics). Now my son is 22 years old. The tics are gone. But the question arises: will this disease be inherited by his future children? Are there tests that can help answer this question?
Hello, Natalia! We were also diagnosed with this, you can be asked to write how you were treated. We are already desperate!
Hello. We were not helped by any sedatives and psychotropic drugs. Cured with ordinary Clonidine! Clonidine is found in different dosage. We took the biggest one. Treated by a very experienced pediatric neurologist who tried everything on my son traditional preparations both ours and imports. Nothing helped and then they tried a method that our doctors usually do not use. They gave the child ordinary clonidine (a medicine that older people drink for pressure). They gave it three times a day. First, a clonidine tablet was divided into 4 parts and given one part three times a day. And we watched how it works for two days. Improvements were noticeable literally on the second day. Then the dose was slightly increased. The tablet was divided into three equal parts and also given one part three times a day. After two days, the improvements were very significant. True, the first three or four days the child was sleepy. At this time, it is better to keep him at home. Do not take them to kindergarten or school and do not let them go out alone. Then he adapts and is no longer so sleepy, but noticeably calmer. And there are far fewer ticks. When you pick up a suitable dose on which there are almost no ticks (and the child should not sleep all the time), then they gave the medicine for two months. The tics returned after six months and then the treatment with clonidine was repeated. Thus treated twice a year at home but under the supervision of a doctor in private. They were treated for about three years. Now there are no ticks! They may appear a little only if they are very tired or very nervous. But tics are almost imperceptible. In such cases, I give Glycine a month. Try it and it will help your child. Good luck!!! Sorry for writing without commas. Time is short.
Quote: natalia
Quote: Natalia
Hello, Doctor. My son was diagnosed as a child with Tourette's disease (generalized tics, including vocal tics). Now my son is 22 years old. The tics are gone. But the question arises: will this disease be inherited by his future children? Are there tests that can help answer this question?
Hello, Natalia! We were also diagnosed with this, you can be asked to write how you were treated. We are already desperate!
Quote: Natalia
Quote: natalia
Hello, Doctor. My son was diagnosed as a child with Tourette's disease (generalized tics, including vocal tics). Now my son is 22 years old. The tics are gone. But the question arises: will this disease be inherited by his future children? Are there tests that can help answer this question?
Hello, Natalia! We were also diagnosed with this, you can be asked to write how you were treated. We are already desperate!
Hello. No sedatives and psychotropic drugs helped us. Cured with ordinary Clonidine! Clonidine comes in different dosages. We took the biggest one. We were treated by a very experienced pediatric neurologist who tried all the traditional drugs on my son, both ours and imports. Nothing helped and then they tried a method that our doctors usually do not use. They gave the child ordinary clonidine (a medicine that older people drink for pressure). They gave it three times a day. First, a clonidine tablet was divided into 4 parts and given one part three times a day. And we watched how it works for two days. Improvements were noticeable literally on the second day. Then the dose was slightly increased. The tablet was divided into three equal parts and also given one part three times a day. After two days, the improvements were very significant. True, the first three or four days the child was sleepy. At this time, it is better to keep him at home. Do not take them to kindergarten or school and do not let them go out alone. Then he adapts and is no longer so sleepy, but noticeably calmer. And there are far fewer ticks. When you pick up a suitable dose on which there are almost no ticks (and the child should not sleep all the time), then they gave the medicine for two months. The tics returned after six months and then the treatment with clonidine was repeated. Thus treated twice a year at home but under the supervision of a doctor in private. They were treated for about three years. Now there are no ticks! They may appear a little only if they are very tired or very nervous. But tics are almost imperceptible. In such cases, I give Glycine a month. Try it and it will help your child. Good luck!!! Sorry for writing without commas. Time is short.
Our doctor read the method of treatment with Clonidine in foreign medical textbooks. And I read about it on the Internet. But for some reason, our Belarusian doctors stubbornly do not use this method of treatment.
Hello!
Please tell me if the woman is sick diabetes type 1 and thyrotoxicosis, how best to proceed? When to take a genetic analysis (during pregnancy planning or already being pregnant)? And what is the probability that the unborn child will suffer autoimmune diseases?
Hello Victoria.
During the planning period of pregnancy, it is worth undergoing an examination and preparing the body. The need for genetic analysis during pregnancy will be determined by the doctor under whose supervision you will be - he decides whether there are indications for additional (that is, in addition to planned ultrasound) studies. The child is likely to be predisposed to such diseases, but they themselves are not inherited, only a tendency is transmitted, which can be realized under certain conditions.
Do you know that:
More than $500 million a year is spent on allergy medications in the US alone. Do you still believe that a way to finally defeat allergies will be found?
To say even the shortest and simple words, we use 72 muscles.
A job that a person does not like is much more harmful to his psyche than no job at all.
Human bones are four times stronger than concrete.
Many drugs were originally marketed as medicines. Heroin, for example, was originally introduced to the market as a cure for baby cough. And cocaine was recommended by doctors as an anesthetic and as a means of increasing stamina.
With regular visits to the solarium, the chance of getting skin cancer increases by 60%.
In 5% of patients, the antidepressant clomipramine causes orgasm.
Each person has not only unique fingerprints, but also a tongue.
The first vibrator was invented in the 19th century. He worked on a steam engine and was intended to treat female hysteria.
There are very interesting medical syndromes such as compulsive swallowing of objects. In the stomach of one patient suffering from this mania, 2500 foreign objects were found.
74-year-old Australian James Harrison donated blood about 1,000 times. Him rare group blood, whose antibodies help newborns with severe anemia survive. Thus, the Australian saved about two million children.
American scientists conducted experiments on mice and came to the conclusion that watermelon juice prevents the development of atherosclerosis of blood vessels. One group of mice drank plain water, and the second group drank watermelon juice. As a result, the vessels of the second group were free from cholesterol plaques.
In addition to people, only one living creature on planet Earth suffers from prostatitis - dogs. These are really our most faithful friends.
The liver is the most heavy organ in our body. Her average weight is 1.5 kg.
The weight of the human brain is about 2% of the total body weight, but it consumes about 20% of the oxygen entering the blood. This fact makes human brain extremely susceptible to damage caused by lack of oxygen.

Every time a child has a fever, a sore throat, a runny nose and a cough, parents are worried about the question - is it a common cold or the flu? In th...

