Low-density lipoprotein levels are normal. LDL cholesterol analysis: what is LDL in a biochemical blood test? LDL cholesterol analysis: what is LDL in a biochemical blood test
Most people have the dangerous misconception that cholesterol is a very unhealthy substance. Whereas in fact, our body cannot exist without cholesterol, which it produces itself. Cholesterol is involved in almost all metabolic processes, including in the synthesis of human sex hormones. Without cholesterol, the normal functioning of not a single organ or system is possible. But since cholesterol is insoluble in water, it moves throughout the body as part of special formations - lipoproteins. They have different densities. Lipoproteins high density, this is good cholesterol, which is delivered to its destination without delay. But low-density lipoproteins are harmful compounds that cling to the walls of blood vessels and form on them atherosclerotic plaques. But there are also very low density lipoproteins, or VLDL. That's what we'll talk about today.
Very low density lipoproteins are also cholesterol transporters. But in addition to it, they also contain another type of fat - triglycerides. This is the most common type contained in human body fats and one of the main sources of energy. After very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) have transferred the triglycerides they contain to their destination in the muscles and organs, they turn into low-density lipoproteins (LDL), of which they are essentially the precursors.
VLDL is normal. Explanation of the result (table)
A blood test for VLDL content, as a rule, is never performed separately, but always only as part of the overall lipid profile of the body. A blood lipidogram is prescribed in following cases:
- when visiting a doctor for men over 45 years of age and women over 55 years of age,
- when determining elevated levels of total cholesterol,
- with high blood pressure,
- after suffered a heart attack or stroke,
- if the patient has been diagnosed ischemic disease hearts,
- if the patient suffers from diabetes,
- the patient is diagnosed with obesity,
- the patient abuses alcohol,
- is a smoker
- leads sedentary lifestyle life.
Cholesterol levels should also be regularly checked for those people whose family has already had cases of atherosclerosis or related heart and vascular diseases. Increased cholesterol may well be hereditary factor, which leads to such diseases. If there have been cases in the family similar diseases already in at a young age, then it is recommended to do a lipid profile for a child starting from 2 years old.
Blood is drawn from a vein, strictly on an empty stomach, in the morning. It is recommended not to eat food 12-14 hours before the test. The concentration of very low density lipoproteins in the blood can vary and is not always an objective indicator of the true level of total cholesterol. Therefore, re-testing is recommended within three months.
In accordance with accepted international standards normal VLDL content in the blood ordinary people and pregnant women:
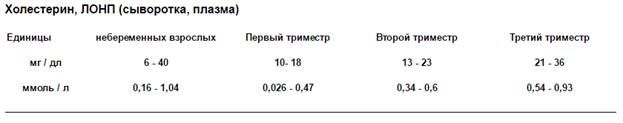
If VLDL is elevated – what does it mean?
As a rule, the content of very low density lipoproteins in the human body is lower than the content of low density lipoproteins. The increase in their concentration occurs proportionally and for the same reasons, namely:
- reduced function thyroid gland– hypothyroidism,
- cholestasis is an inflammatory process in gallbladder caused by stagnation of bile, for example due to the presence of stones or liver disease,
- chronic renal failure,
- nephrotic syndrome and chronic inflammatory process in the kidneys,
- malignant tumor pancreas,
- malignant prostate tumor.
Elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein can also be caused by obesity or excess alcohol consumption. Disorders of lipid metabolism in the body can also be hereditary.
An increase in very low density lipoprotein levels is dangerous factor talking about high risk development of atherosclerosis in the patient and concomitant diseases.
If VLDL is low – what does it mean?
A decrease in the level of very low density lipoproteins in the blood is usually not of clinical interest and is not used for diagnosis. However, it may also indicate the presence of certain diseases, namely:
- increased function thyroid gland – hypothyroidism,
- oncological diseases hematopoietic systems,
- liver diseases,
- extensive burns,
- inflammatory diseases joints,
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,
- lack of vitamin B12 in the body,
- deficit folic acid,
- presence of acute inflammatory process in organism.
A decrease in the concentration of low-density lipoproteins may be hereditary. Intensive physical exercise or the use of some medicines– statins, erythromycin, estrogens.
Unlike the level of low-density lipoproteins, the level of very low-density lipoproteins during pregnancy does not increase, but decreases.
4,75 (103 )Cholesterol- fat-like substance, vital necessary for the body. With its help education occurs cell membranes all organs and tissues of the body. Hormones are created on the basis of cholesterol, which are involved in the growth, development of the body and the implementation of the reproduction function. In addition, cholesterol is formed bile acids, which are part of bile, thanks to them, fats are absorbed in the intestines.
Cholesterol is insoluble in water, so to move around the body it is “packed” into a shell consisting of special proteins - apolipoproteins. The resulting complex (cholesterol + apolipoprotein) is called lipoprotein. Several types of lipoproteins circulate in the blood, differing in the proportions of their components:
- very low density lipoproteins (VLDL),
- low density lipoproteins (LDL),
- high density lipoproteins (HDL).
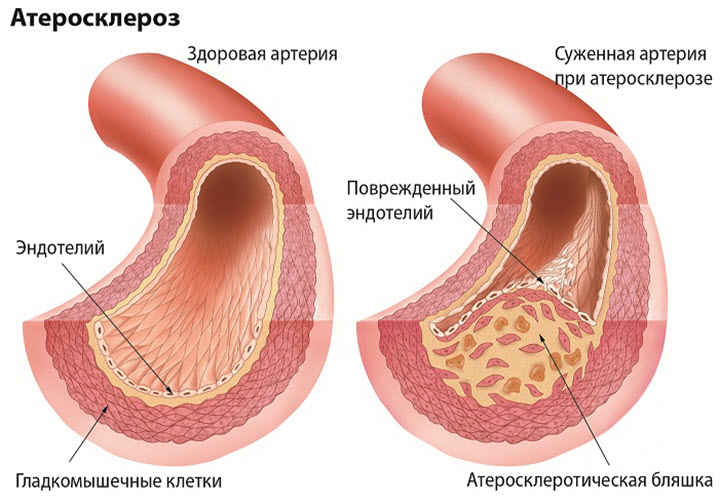
Very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol is one of the most aggressive types of cholesterol. When there is an excess of VLDL cholesterol, it is deposited on the walls of blood vessels in the form of plaques, which can restrict the movement of blood through the vessel. In addition, they make blood vessels more rigid (atherosclerosis), which significantly increases the risk of heart disease (coronary artery disease, heart attack) and stroke.
In addition, VLDL is the main carrier in the body of another type of fat - triglycerides. Elevated triglyceride levels also contribute to the development of atherosclerosis.
The liver produces enough cholesterol and triglycerides for the body's needs, but some of these fats come from food, mainly meat and dairy products. If a person has a family history of high cholesterol and triglycerides or eats too much cholesterol-containing food, cholesterol levels in the blood can rise and cause harm to the body.
What is analysis used for?
A VLDL cholesterol test, along with other tests included in the lipid profile, is necessary in order to assess the risk of developing atherosclerosis and heart problems. Atherosclerosis is the process of plaque growth inside blood vessels, which can limit blood flow through the vessel or completely block its lumen.
Besides, this study can be carried out to monitor the effectiveness of a diet with a reduced amount of animal fats and monitor blood lipid levels after the prescription of cholesterol-lowering drugs.
When is the test scheduled?
VLDL is usually included in the lipid profile, along with the determination of total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, triglycerides and atherogenicity coefficient. A lipidogram may be prescribed for planned preventive examinations or with an increase in total cholesterol, to find out due to what type of cholesterol its concentration is increased.
A lipidogram is recommended for all adults over 20 at least once every 5 years. It may be prescribed more often (several times a year) if a person is prescribed a diet limiting animal fats and/or is taking medications that lower cholesterol levels. In these cases, it is checked whether the patient has achieved the target level of lipid values and, accordingly, whether his risk of cardiovascular diseases is reduced.
Increased VLDL cholesterol levels
An increase in VLDL cholesterol concentrations may result from hereditary predisposition(familial hypercholesterolemia) or excess dietary intake of animal fats. For most people with high cholesterol, both causes are involved to some extent.
Other possible reasons increase in VLDL:
- cholestasis - stagnation of bile, which can be caused by liver disease (hepatitis, cirrhosis) or gallstones,
- chronic inflammation kidneys, leading to nephrotic syndrome,
- chronic renal failure,
- decreased thyroid function (hypothyroidism),
- poorly treated diabetes mellitus,
- alcoholism,
- obesity,
- prostate or pancreatic cancer.
Decrease in VLDL cholesterol levels
- A reduced level of LDL cholesterol has no special clinical significance, it can be observed when following states:
- hereditary hypocholesterolemia,
- serious disease liver,
- oncological diseases bone marrow,
- increased thyroid function (hyperthyroidism),
- inflammatory joint diseases,
- B12 or folate deficiency anemia,
- common burns,
- acute diseases, acute infections,
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
What can influence the result?
The amount of VLDL cholesterol can change from time to time, so a one-time measurement does not always reflect the “usual” cholesterol level. In this regard, it is sometimes necessary to re-take the test after 1-3 months.
It happens that the level of VLDL cholesterol increases or decreases over a short period of time. This phenomenon is called biological variation and reflects normal fluctuations in cholesterol metabolism in the body.
Increases VLDL cholesterol levels:
- pregnancy (lipid profile should be done at least 6 weeks after birth of a child),
- long fasting,
- change standing blood,
- anabolic steroid, androgens, corticosteroids,
- smoking,
- eating food containing animal fats.
Reduce VLDL cholesterol levels:
- being in lying down position,
- allopurinol, clofibrate, colchicine, antifungal drugs, statins, cholestyramine, erythromycin, estrogens,
- diet low in cholesterol and saturated fatty acids and, on the contrary, high content polyunsaturated fatty acids.
The following contribute to an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases:
- smoking,
- age (men over 45 years old, women over 55 years old)
- promotion blood pressure(140/90 mmHg and above),
- increased cholesterol or cardiovascular diseases in other family members (heart attack or stroke in a close male relative under 55 years of age, a female relative under 65 years of age),
- coronary heart disease, previous myocardial infarction or stroke,
- diabetes,
- overweight bodies,
- alcohol abuse,
- reception large quantity foods containing animal fats,
- low physical activity.
Preparing for the study: Do not eat 12 hours before the test, avoid physical and emotional stress and do not smoke for 30 minutes before donating blood.
Period of execution: 1 working day
Cholesterol level healthy person should be within normal limits. If the level of lipoproteins in the blood increases or decreases, it is necessary to identify the disease and begin its treatment. This is why many doctors focus Special attention LDL cholesterol analysis.
Everyone knows that increased blood cholesterol is bad. But what kind of cholesterol is it, and what types are there?
Cholesterol, which is distributed through the blood to the organs, is combined with proteins. After all, it is thanks to proteins that cholesterol is able to move in liquids. There are several types of such compounds:
- HDL is a high-density lipoprotein;
- LDL – low density lipoproteins;
- VLDL are lipoproteins with a very low density, it is from them that the liver produces the so-called bad cholesterol;
- DILP – intermediate density lipoproteins.
When the balance of bad and good cholesterol, with a shift upward in LDL, heart and vascular diseases develop or worsen.
When to Check Your LDL Level
LDL cholesterol (bad lipoprotein) levels should be checked for all people over thirty years of age at least once every 5 years. However, there are cases when an extraordinary study is indicated:
- Taking medications to help lower LDL levels.
- Liver pathology.
- Diseases of the heart muscle and blood vessels.
- Use fatty foods a lot.
- Men over 40 and women over 50.
- Patients with a history of myocardial infarction or stroke.
- Persistent hypertension with pressure values greater than 135/85 mmHg. Art.
- If a blood test has previously revealed hypercholesterolemia (increased LDL levels).
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Drinking alcoholic beverages, smoking.
- Availability excess weight bodies.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- In the presence of diabetes mellitus.

Proper preparation for a blood test
To determine the level different types cholesterol, a biochemical blood test is performed. This kind laboratory research can be done in a clinic or in any paid laboratory, at the discretion of the patient. Blood is taken from a vein.
For the results to be correct, you need to prepare for blood donation according to all the rules:
- Blood is taken for analysis in the morning on an empty stomach. You can eat 12 hours before the test.
- It is necessary to abstain for some time before the study. fatty foods and fried food.
- You should also give up alcohol and smoking for a few days. You should not smoke immediately before taking the test.
- For one or two weeks before blood sampling, avoid excessive physical activity (active and power types sports).
Lipidogram
What is a lipid profile? This is analytical data on the content of lipoproteins in blood serum. It includes the following indicators:
- total cholesterol estimated at mandatory, its level depends on the gender and age of the patients;
- HDL is an anti-atherogenic fraction (good cholesterol), it prevents the development of atherosclerotic plaques in blood vessels;
- LDL is an atherogenic fraction (bad cholesterol), an increase in its concentration is a sign of an existing or developing pathology;
- the atherogenicity coefficient is obtained as a result of the ratio of good and bad lipoprotein;
- triglycerides are involved in lipid transport.
Changes in indicators
If any indicator in the lipid profile deviates from the norm, this may indicate various pathologies or become a signal for preventive measures.
What do abnormal triglyceride levels indicate?
- When the level of this substance increases to 2.3 or more mmol/l, the presence of diseases such as coronary heart disease and atherosclerosis is indicated. various vessels. Another reason is the presence of diabetes mellitus in the patient.
- The borderline value, from 2.0 to 2.3 mmol/l, is a consequence of deteriorating health. Although atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease are not yet expressed characteristic symptoms, but their development has already begun. The period of asymptomatic course of the pathology.
- The normal triglyceride level is 1.9 mmol/l or less.
HDL can also be either low or high:
- Decline this indicator(in men up to 1.15 and less mmol/l, in women 0.8 mmol/l and below) is a clear sign the presence of pathology of the heart (coronary disease) and blood vessels (atherosclerosis).
- Borderline values: for men – from 1.15 to 1.67 mmol/l; for women – from 0.8 to 1.35 mmol/l. These values are indicators of the development of the above pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
- A high content of good lipoprotein reduces the likelihood of coronary disease and myocardial infarction.
What do LDL levels indicate?
- The presence of diseases such as ischemic heart disease and atherosclerosis is detected at levels of 4.8 mmol/l or more.
- If LDL level from 4 to 4.8 mmol/l, then, most likely, pathology of the cardiovascular system develops in the body.
- A reading below 3 mmol/l is considered normal.
Total cholesterol:
- Normal values are considered to be values from 3.1 to 5.1 mmol/l.
- If total cholesterol is above 6.2 mmol/l, then pathology of the heart and blood vessels already exists.
- If the values are in the range from 5.2 to 6.2, then the risk of pathology increases.
Signs of increased bad lipoprotein in the blood
On initial stage With hypercholesterolemia, a person may not notice any changes in their health. However, the heart and blood vessels are already beginning to suffer:
- The vascular wall loses its elasticity and firmness. The longer cholesterol does not decrease, the more the blood vessels suffer. Eventually they become brittle.
- Education takes place cholesterol plaques which impede blood flow. Due to this internal organs start to starve. As a result, atherosclerosis develops.
- Blood clots form, which can break off at any time and clog the vessel.
- The risk of myocardial necrosis, that is, myocardial infarction, increases.
If treatment is not carried out, the person begins to feel various types of ailments:
- headache;
- dyspnea;
- dizziness;
- heartbeat.
A complication of this condition can be embolism of blood vessels of vital organs:
- Blockage of cerebral vessels (CVA).
- Thromboembolism pulmonary artery(TELA).
- When blocked coronary arteries myocardial infarction occurs.
All these pathological conditions require emergency medical care and are common cause fatal outcome in patients with increased level cholesterol.
What can affect the performance?
It may happen that the cholesterol test results were incorrect. For example, the indicators are inflated, but there are no other signs of presence pathological changes in the heart and blood vessels of a person there is no. When it's possible?
- If on the eve of the study the person broke his diet and ate foods rich in lipids of animal origin.
- Cholelithiasis.
- Hypofunction of the thyroid gland.
- Cholestasis (stagnation of bile for various reasons).
- Long-term use of hormonal and antibacterial drugs.
- Kidney pathology with chronic course inflammatory process.
- Pancreatic disease (diabetes mellitus).
- Hereditary factor.
- A woman experiences an increase in LDL levels during pregnancy.
- Rescheduled severe stress or psycho-emotional stress.
- In the postoperative period.
- Recent cardiac stenting may also cause elevated rates.
In some cases, indicators may increase due to physiological characteristics patient. Therefore, if in doubt, it is indicated rerun laboratory research.
A repeat blood test is performed after 14–28 days.
Normalization of indicators
Lipid profile indicators can signal the development of pathology. In this case, it is quite possible to normalize the indicators and cope with initial stage diseases (coronary heart disease, atherosclerotic plaques) and prevent the development of such a serious pathology as myocardial infarction.
Preventive actions:
- Proper nutrition. Avoid fatty and sweet foods.
- Moderate physical activity helps raise good cholesterol and lower LDL levels.
- Get rid of bad habits, as they negatively affect the entire body.
- Avoid stressful situations.
- Follow all doctor's orders.
 How to cure hypertension forever?!
How to cure hypertension forever?!
In Russia, there are from 5 to 10 million calls to the ambulance every year medical care regarding increased blood pressure. But Russian heart surgeon Irina Chazova claims that 67% of hypertensive patients do not even suspect that they are sick!
How can you protect yourself and overcome the disease? One of the many recovered patients, Oleg Tabakov, told in his interview how to forget about hypertension forever...


