What is the anechoic contents of the gallbladder? Gallbladder sizes in adults and children, norms
Ultrasound of the gallbladder is performed separately or with complete ultrasound diagnostics abdominal cavity. It is scanned if gallstone disease and other pathologies are suspected. Among the main terms that will be indicated in forms with ultrasound results, you may find the definition of “anechoic contents of the gallbladder.” It must be said that an ultrasound diagnostic specialist does not make a diagnosis; he can only describe the data that he sees on the screen. The attending physician will decipher the indicators.
What is echogenicity?
In order to understand what the anechoicity of the gallbladder may indicate, you need to understand the definition and properties of ultrasound. Some facts that will help you understand the essence of ultrasonic waves:
- Ultrasound is elastic vibrations of particles of a medium that propagate in the form of a longitudinal wave.
- It can exist in liquid, gaseous or solid media, but ends up in a vacuum.
- Some animals use it as a means of communication, but it is not inaudible to the human ear.
It is used in the diagnosis of internal diseases due to its properties. Ultrasound waves are absorbed by soft tissues and reflected from inhomogeneities.
The process of obtaining an image from an ultrasound machine occurs in two stages:
- radiation of a wave into the tissue being examined;
- receiving reflected signals, on the basis of which an image is formed on the screen internal organs.
Due to the different structure and density of tissues and internal organs, they reflect differently ultrasonic waves. In addition, this property also changes in various pathologies, which makes it possible to identify many diseases, including the gallbladder. To describe the resulting image, special terminology is used, which should be familiar not only to ultrasound specialists, but also to general practitioners.
Echogenicity is the ability of a tissue or organ to reflect an ultrasound beam. Various organs look lighter or darker on the screen, and this property is determined precisely by their echogenicity.
Based on this feature, several types of fabrics can be distinguished:
- hyperechoic objects (bones, gas, collagen) are structures that reflect a large number of ultrasonic rays, appear on the screen as bright white lesions;
- hypoechoic ( soft fabrics) - partially reflect the ultrasonic beam, represent various shades gray;
- anechoic (liquid) - these are areas that do not reflect ultrasound and look like black lesions.
From this we can conclude that the anechoic contents in the gallbladder are liquid. To make a diagnosis, you need to understand how this organ should normally look on an ultrasound and what the presence of fluid in its cavity may indicate.
The accuracy of the results depends on the quality of the equipment and the sensitivity of the sensors
What does the gallbladder look like on an ultrasound scan normally?
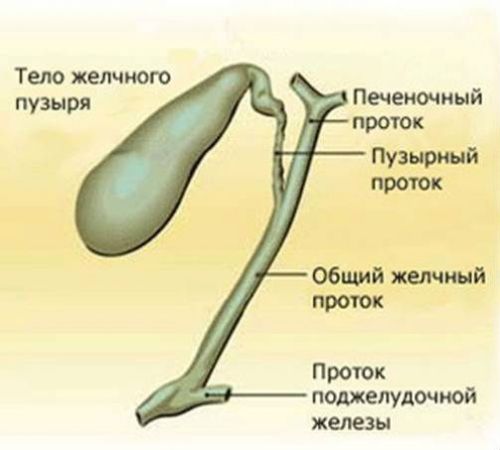
Gallbladder has a pear shape. There are 3 main elements in its structure:
- bottom - a wide edge that protrudes slightly beyond the liver;
- body - its main part;
- neck - narrowing of the bladder at its exit.
The gallbladder is hollow organ, it has a wall and a cavity where bile accumulates. Like other similar organs, it is built from muscle tissue, which is lined inside by a mucous membrane with a large number of folds and glands. On the outside, it is partially covered with a serous membrane.
The need for a reservoir for bile arose due to the fact that it does not enter the intestines constantly, but only during the digestion process. Ultrasound diagnostics are carried out on an empty stomach (even drinking water before the examination is prohibited) so that bile accumulates in the bladder and it is possible to examine its contents and walls.
Bile is produced in the liver and flows down the hepatic duct into the gallbladder. If there is an immediate need for it, it moves further along the bile duct to duodenum. If this is not necessary, the sphincters contract and do not release bile from the bladder. Until food reaches the stomach, it will accumulate in the gallbladder and stretch its walls. As soon as the digestion process begins, the muscles of the bladder walls contract, and the muscles of the sphincter and bile duct, on the contrary, relax. Therefore, during an ultrasound after eating, the bladder will be empty, and it will not be possible to accurately determine its size and the nature of the contents.
Normally, the gallbladder indicators will be as follows:
- pear-shaped;
- dimensions: 8-14 mm in length, 3-5 mm in width;
- the location is intrahepatic, only the bottom of the bladder extends beyond the liver;
- the contours are smooth and clear;
- wall thickness - up to 3 mm;
- homogeneous anechoic contents.
Any deviations from the norm indicate the presence of pathology. Thus, the walls of the bladder thicken when inflammatory processes, and the abnormal structure of the bladder will impede the outflow of bile, and it will accumulate in its cavity in large quantities. The contents are examined if gallstones and other diseases are suspected; in such cases it becomes echogenic.
The gallbladder is a kind of bag for bile, which, when filled, has the shape of a pear
Echogenicity of the gallbladder contents
The gallbladder is a reservoir for bile. Apart from this, there can normally be no liquid in the cavity of the bladder. If the contents cease to be echogenic, that is, a uniform black color, this suggests the presence of foreign objects.
According to the nature of changes in echogenicity, they can be:
- focal (helminths, stones);
- diffuse (sediment, pus or blood).
Stones play a leading role in gallbladder diseases. They may have different origins, chemical composition, shape and size and look different on ultrasound. In composition, they can be cholesterol, calcareous, pigmented and complex (of mixed origin). It is impossible to determine this with an ultrasound; tests must be carried out after the stones are removed.
Based on the results of ultrasound diagnostics, several types of stones are distinguished:
- weakly echogenic;
- medium echogenicity;
- highly echogenic;
- stones that provide general acoustic shadow.
Weakly echogenic stones have a loose structure; most often they turn out to be cholesterol. Such formations are easily destroyed special drugs, and the treatment process is monitored over time using ultrasound. Such stones must be distinguished from gall bladder polyps and cholesterol plaques, so during the procedure the patient changes his body position. If the stones remain in the cavity of the bladder and float in its contents, then the polyps attach to the walls and do not change location.
Stones of medium and high echogenicity are most often pigmented or calcareous. They look like bright light spots in the cavity of the bladder and do not pose difficulties for diagnosis. When examined with a highly sensitive sensor, you can find that they cast a shadow.
During the examination, the patient must change body position if foreign inclusions are found in the cavity of the gallbladder
A separate stage of cholelithiasis is the formation of stones that give a general acoustic shadow. This picture is observed in the presence of one large stone or many small ones that completely block the lumen of the gallbladder. The image can be confused with gases, which will also appear as light spots. For a more complete picture, you can give the patient two yolks to drink and repeat the study. When the digestion processes start, the gases will disappear, and the stones will remain in the cavity of the gallbladder.
Diffuse changes in echogenicity are rare. These include various sediments, pus or blood - substances that reflect ultrasound rays and are distributed evenly, mixing with bile. They can be recognized by the following characteristics:
- The sediment is located in the lower part of the gallbladder in an even layer, and above it there is normal anechoic bile.
- If there is pus in the cavity, it will initially look like sediment. The only difference is that when the patient changes position, it mixes with bile. For chronic purulent process it can form characteristic septa in the bladder cavity, which are visible on ultrasound.
- Blood also needs to be differentiated from sediment and other diffuse inclusions. Over time, it coagulates and forms weakly echogenic clots that resemble stones or polyps in appearance.
In the cavity of the gallbladder, echogenic inclusions may be detected, which then turn out to be neoplasms. Their difference is that they grow from the wall and do not move when the patient’s position changes. Tumors can be benign and not grow through the walls. If the patient is diagnosed malignant tumor, this means that it affects all layers of the gallbladder. Over time, the organ ceases to be detected on ultrasound due to necrosis of its wall.
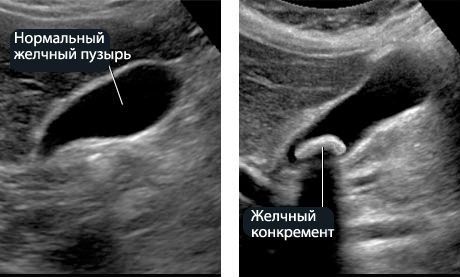
Concretions (stones) look like light-colored formations various shapes and size
Rules for performing ultrasound of the gallbladder
In order for the research results to be as reliable as possible, it is better to start preparing in advance. On initial examination The doctor will set a date for the examination and tell you how to properly prepare for it. The exception is emergency cases when there is a risk of blockage of the bile ducts with stones or urgent surgery is required.
For a routine ultrasound, the patient should adhere to a few simple rules:
- a week before the ultrasound, exclude alcohol from their diet, fatty foods and those that cause increased gas production (carbonated drinks, yeast bread, raw fruits and vegetables, legumes);
- It is recommended to start taking medications (Mezim, Espumisan and the like) 3 days in advance;
- Before the test, you should not eat for 8 hours.
If the ultrasound is scheduled for the first half of the day, you should skip breakfast and water. Dinner the day before should be no later than 19.00. If the procedure will be carried out in the evening, you can have breakfast around 7 am.
Anechoic contents in the gallbladder are normal indicator. It means that the bladder is filled with bile, in which there is no sediment or foreign substances. This important factor in the diagnosis of helminthiasis, cholelithiasis and other pathologies. Ultrasound of the gallbladder is also included in a routine examination of the abdominal cavity. In addition to this indicator, attention is paid to the size and shape of the organ, the thickness and uniformity of its walls. The indicators are written on a form and given to the attending physician, who then interprets them based on clinical signs.
Video on the topic
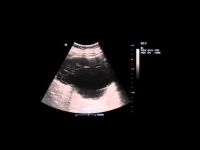
As its name suggests, the gallbladder serves as a reservoir for bile produced by the liver. It has an elongated pear-shaped shape and is filled with viscous greenish bile; there is a bubble on the lower part of the liver and, together with it, is part of the liver. The Lütkens sphincter regulates the movement of bile from the cavity of the gallbladder and back.
Bile is necessary for the digestion of fats, stimulation of intestinal motility, neutralization of hydrochloric acid, formed in the stomach and entering the intestines, as well as to suppress putrefactive processes in the gastrointestinal tract. Various pathologies gallbladder disrupt these processes. They are detected by ultrasound of the gallbladder.
Indications for ultrasound diagnostics
To prescribe treatment, timely and correct diagnosis diseases. Ultrasound is the most accurate and safe. An ultrasound of the gallbladder is prescribed to assess its condition, parameters, identify stones and developmental pathology.
They are sent for an ultrasound of the gallbladder if one of the following factors is present:
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- suspicion of acute or chronic cholecystitis;
- suspicion of developmental abnormalities;
- presence of sand or stones;
- abdominal trauma;
- jaundice;
- pancreatitis;
- presence of bitterness in the mouth, frequent nausea and vomiting mixed with bile.
 Pain in the area of the right hypochondrium may indicate serious pathological processes in the gallbladder. Therefore, in case of such complaints, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound scan of the organ and compares the result with normal values.
Pain in the area of the right hypochondrium may indicate serious pathological processes in the gallbladder. Therefore, in case of such complaints, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound scan of the organ and compares the result with normal values. Ultrasound of the gallbladder is also done to monitor the patient’s condition during or after treatment. surgical intervention. The earlier any disease is diagnosed using an ultrasound of the gallbladder, the more effective its treatment will be.
Preliminary preparation
You need to prepare for an ultrasound of the gallbladder in advance, 2-3 days before the procedure. Preparation for an ultrasound of the gallbladder is similar to that of. Special attention addresses the reduction of flatulence (gas formation and bloating). To prepare, you should:
- do not eat foods that cause bloating (cabbage, beans, brown bread, raw vegetables and fruits);
- when preparing the child, exclude any carbonated drinks;
- completely give up alcohol;
- do not eat fatty fish and meat;
- apply adsorbent, enzymatic and carminatives;
- if you have constipation, it is recommended to prepare more thoroughly and take lactulose before bed, and you can also use a glycerin suppository;
- dinner the night before should be light and nutritious;
- You should eat your last meal no later than 8 hours before the procedure;
- The ultrasound is performed strictly on an empty stomach; you cannot even drink water in the morning;
- If an ultrasound has already been performed before, you should have a transcript and pictures with you to determine the dynamics.
Of course, very young children cannot withstand this long time without eating, so infant An ultrasound is performed before the next feeding. For older children, you need to take food with you to feed after the procedure. If the presence of stones is suspected, the examination is carried out immediately, without preliminary preparation.
 Preparation for ultrasound of the gallbladder in adults and children is aimed at reducing gas formation, since excess air will interfere with a detailed examination of the organ. Must be observed special diet, and in some cases - include the use of carminatives
Preparation for ultrasound of the gallbladder in adults and children is aimed at reducing gas formation, since excess air will interfere with a detailed examination of the organ. Must be observed special diet, and in some cases - include the use of carminatives Normal gallbladder parameters
When performing an ultrasound, a diagnostic specialist evaluates the shape and size of the gallbladder, the thickness of its walls, as well as the volume of bile, and compares these parameters with normal values. In an adult This organ normally has the following basic parameters:
- length 40 - 95 mm;
- width 30 - 50 mm;
- transverse size 30 - 35 mm;
- wall thickness is about 2 mm.
Also, with an ultrasound of the gallbladder, the diameter of the common bile duct is measured, the norm of which is within 6-8 mm, and the internal diameter of the lobar bile ducts, which should be no more than 3 mm.
Parameters of normal gallbladder The child has depend on his age and fluctuate significantly. According to medical data, they should be:
| Age, years | Average length (range), mm | Average width (range), mm |
|---|---|---|
| 2 - 5 | 42 (29 - 52) | 17 (14 - 23) |
| 6 - 8 | 56 (44 - 74) | 18 (10 - 24) |
| 9 - 11 | 55 (34 - 65) | 19 (12 - 32) |
| 12 - 16 | 61 (38 - 80) | 20 (13 - 28) |
The gallbladder is considered healthy if it has normal shape, and the dimensions and thickness of the wall correspond to the norm, bile is well secreted, no stones or sand were found in the cavity.
When examining a child (if it is not being carried out for the first time), it is necessary to have a printout and transcript of past examinations with you. They need to be shown to the doctor so that he can compare the indicators and dynamics of development.
Deviations from the norm: pathology and its signs
Most often detected cholecystitis. At acute cholecystitis thickening of the wall, an increase in size, and the formation of septa in the cavity of the gallbladder are diagnosed. At chronic course The disease causes a decrease in the bladder, thickening and compaction of the wall, as well as its deformation. On the ultrasound machine monitor, the wall has fuzzy outline and a lighter shade. Small particles are projected into the cavity.
At dyskinesia Stagnation of bile is formed and the motility and tone of both the bladder itself and the bile ducts are disrupted. An ultrasound may show structural changes: bending of the neck and thickening of the bladder wall.
Cholelithiasis, or cholelithiasis, characterized by the presence of stones in the cavity and bile ducts. The screen shows light formations with dark areas behind them (the so-called acoustic shadow). When the position of the body changes, their movement in the cavity of the bladder is noticeable. The boundaries of the organ become uneven, and the wall thickens. Sonography does not show small stones, but indirect sign– expansion of the duct above the site of its blockage. The incidence of stone formation increases with age, and women are diagnosed more often than men.
Polyps they do not manifest themselves clinically on the walls, they are round formations up to 10 mm in diameter, and are usually detected during examination for other reasons. Unlike stones, polyps do not produce an acoustic shadow on an ultrasound image.
Tumors gallbladder are characterized by deformation of the contours and significant, relative to normal, thickening of the wall. On echography, tumor-like formations or polyps larger than 20 mm in size are visible in the cavity.
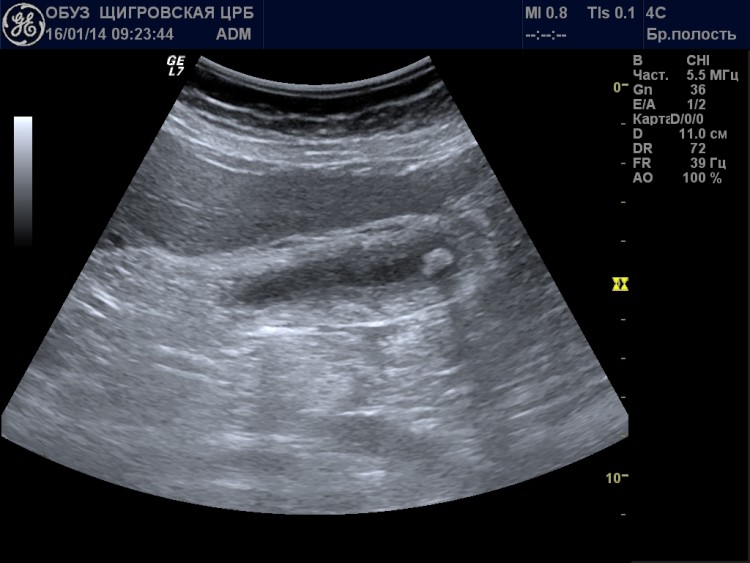 Cholecystitis on ultrasound is characterized by an increase in the size of the organ and thickening of its walls, as well as the appearance of new septa and vesicular inclusions. In the chronic course of the disease, the gallbladder can, on the contrary, become thinner and deformed.
Cholecystitis on ultrasound is characterized by an increase in the size of the organ and thickening of its walls, as well as the appearance of new septa and vesicular inclusions. In the chronic course of the disease, the gallbladder can, on the contrary, become thinner and deformed. Diagnostics with function determination
This type of diagnosis is carried out for dyskinesia (impaired wall motility with hypotonic or hypertensive type) And inflammatory diseases, which include cholecystitis (inflammation mainly in the bladder) and cholangitis (inflamed ducts), as well as cholelithiasis.
Ultrasound is performed non-invasively, it is the fastest, most informative, absolutely painless and safe method examinations. In just a few minutes, the doctor receives data on the parameters and shape of the organ being checked, the thickness of the walls, existing defects, and the presence and parameters of stones.
Ultrasound of the gallbladder to determine function is performed with a choleretic breakfast. It allows you to track the dynamics of the contractile-evacuatory function.
The doctor performing the ultrasound focuses on three main indicators: the time of the contraction period, the efficiency of bile secretion, and the tone of the sphincter of Oddi. This procedure takes approximately an hour. Decryption is carried out immediately. Initially, the examination is carried out on an empty stomach in a lying position; you cannot even drink water. After the first scan, the subject should have breakfast with two chicken yolks, or 250 ml of heavy cream or sour cream. A sorbitol solution can also be used for these purposes. An echography is done after breakfast 3 times: after 5-10 minutes, after 20 minutes and after 40-45 minutes.
Readings are taken in different positions(lying on your back, on your side, standing, sitting, etc.). The dimensions of the bladder are measured in longitudinal and cross sections, which makes it possible to assess the ducts and walls in more detail and reliably. If the bubble decreases in size by 60-70% of its original size during the examination, then it is considered that there are no violations contractile function. It should also be taken into account that with age there is a natural decrease in contractile function. Ultrasound of the gallbladder with determination of function shows the most exact information about the condition of the cavity and ducts. To obtain reliable readings, the patient only needs to accurately follow all the doctor’s instructions.
Addresses medical centers and clinics in Moscow where you can do an ultrasound of the gallbladder to determine its function.
Ultrasound of the gallbladder with determination of function - non-invasive diagnostic procedure, performed with a trial choleretic breakfast. Today, it is considered the only informative non-invasive method that allows you to study the condition of the organ, as well as determine and evaluate changes in the functions of the organ over time.
An important advantage of gallbladder ultrasound is considered to be high diagnostic accuracy and safety for the patient. Method represents dynamic observation behind the rhythm of contractions at certain time intervals.
Indications
The study reveals such a common disease as. It allows you to define 5 degrees pathological changes(including recognizing the disease by initial stage), which will allow you to choose the right treatment.
The study helps diagnose such anomalies as:
- Agenesis;
- Hypoplasia;
- Intrahepatic gallbladder;
- Vagus gallbladder;
- Bile duct atresia;
- Megalocholedochus.
Only timely diagnosis And operational assignment appropriate treatment helps prevent complications and more severe course diseases. Diseases of the gall and liver can make themselves felt with the same symptoms, which include pain in epigastric region, deterioration and complete loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting. If you experience:
- dull pain in the right hypochondrium;
- heaviness in the liver area;
- jaundice skin;
- bowel disorders;
- bloating, bitterness in the mouth, constipation;
- V biochemical analysis blood abnormalities AST, ALT, bilirubin,
This means that this study should be done to check the functioning of the gallbladder.
There are also contraindications for research. If a patient is diagnosed with cholelithiasis, and in the lumen of the gallbladder there are a large number of stones that block the bile duct, then the examination will be uninformative.
How to prepare properly
The data obtained as a result of the procedure will show the condition of the gallbladder, so you should strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions for preparing for it.
- A week before the procedure, alcoholic drinks and gas-forming products should be excluded from the menu, because if air bubbles enter the intestines, they will impede visualization. Gas-forming products include: raw whole milk, non-thermally processed vegetables and fruits, legumes, baked goods, brown bread.
- 3 days before the study you should start taking enzymes with pancreatin (Mezim, Creon). They are taken in microcapsules at a dose of at least 10,000 units per meal. The microcapsule should be taken immediately before meals or during meals with boiled water. You can consult your doctor about the dosage, he may prescribe medicine with more high content enzymes. Also at the same time, they begin to take carminative drugs - espumizan, motilium, simethicone at a standard dosage. These medications are taken after meals. For those suffering from chronic constipation, it is recommended to take lactulose - one tablespoon in the evening before bed.
- On the day before the ultrasound, dinner should be nutritious and light: for example, cereal porridge without sugar. You should eat your last meal no later than 20:00. After dinner, be sure to go to the toilet, and if problems arise, you can use a glycerin suppository.
- In the morning, on the day of the study, do not have breakfast, boil the eggs and take the yolks with you. They will be necessary for choleretic load. You can replace eggs with high-fat sour cream. You cannot eat or drink anything - not even water, otherwise the gallbladder will shrink and the results will be unreliable. If the study is carried out in the afternoon, then you need to have breakfast at 7 am. Breakfast should consist of light food. Don’t forget to take with you previous studies, test results, which you have, and a towel to wipe off the gel after the test.
Features of the procedure
Ultrasound is done in several stages. First, a study is performed at rest and the gallbladder indicators are recorded. Then the patient has breakfast with two boiled egg yolks or 250 g of sour cream (sorbitol solution can be used) and after 10 minutes the functions of the gallbladder and ducts are examined again. Then the study is carried out 2 more times - both times after 15 minutes. This concludes the study.
Unlike traditional ultrasound of the gallbladder, data is taken with the patient lying on his back, on his side, and sometimes the doctor will ask the patient to stand on his feet or on all fours. The duration of the procedure can be one to two hours.
Decoding the results
During the diagnostic process, the size of the organ in longitudinal and cross section is accurately determined. Using linear dimensions, you can accurately assess the condition of the walls and excretory ducts.
Normal indicators:
- gallbladder length - from 4 cm to 14;
- width - from 2 cm to 4 cm;
- wall width - 4 mm;
- common bile duct diameter 6-8 mm;
- the internal diameter of the lobar ducts is up to 3 mm.
- shape - pear-shaped or cylindrical, clear contours;
- bubble volume: 30 - 70 cc.
There should be no formations in the lumen. If an ultrasound has detected a shadow from tumors or stones, then the presence and composition of the stones are determined by its nature. Stones can be attached to the wall or wandering.
The doctor looks at 3 main characteristics:
- duration of the reduction period;
- biliary excretion and efficiency;
- sphincter of Oddi tone.
Diagnostics makes it possible to determine changes in gallbladder motility, the form of dyskinesia, and the consistency of the contents.
Doctor's report
Under load after 45 min. after the start of the study, the gallbladder shrinks by 60-70% of its original size. In this case, the doctor writes a conclusion that the motor function of the gallbladder is not impaired. After 45 min. restoration of organ volume begins due to bile synthesized by the liver.
Addresses of medical centers and clinics in Moscow where you can do an ultrasound of the gallbladder.
Ultrasound of the gallbladder is a highly informative and non-invasive method of examination, which makes it possible to detect functional disorders in the organ and localize pathologies. Conducted in a medical facility by a specialist in the field functional diagnostics. If necessary ultrasound scanning can be carried out at the patient's home. Despite its apparent simplicity and accessibility, preparation for this type of ultrasound takes at least 7 days.
Indications
Most often, a patient receives a referral for an ultrasound scan from a gastroenterologist, but others can also be referred for this procedure narrow specialists, for example, pediatrician, surgeon, therapist. Exists whole line reasons that are a direct indication for ultrasound. First of all, these include:
- Suspicion of cholecystitis, hepatitis, pancreatitis. Symptoms: pain under the ribs, yellowness of the skin and sclera.
- The need to monitor the dynamics of treatment, for example, inflammation and dyskinesia, the rate of dissolution of stones. Typically, several repeat scans are performed to ensure timely adjustment of the treatment regimen.
- Control examination before and after surgery to remove the gallbladder.
- Regular monitoring in the presence of chronic gastrointestinal diseases or for preventive purposes. The frequency of ultrasound is determined by the attending physician.
Preparation
To obtain diagnostically valuable results after scanning, several basic preparation rules must be followed:
- The intestinal cavity should be freed from gases, as they will interfere with adequate visualization of the organ.
- The last meal is allowed no later than 8 hours before the examination. At normal operation gallbladder and in the absence of food in the stomach, bile begins to accumulate in the bladder, which proportionally increases its size. If you start eating or drinking, bile will be excreted and the organ will shrink. This will significantly complicate the research.
- A week before the procedure, they are excluded from the patient’s diet. alcoholic drinks, fatty foods and foods that cause increased gas formation. And this is: rich pastries, bread made from rye flour, raw vegetables and fruits, legumes, milk, snacks, soda.
- Three days before the ultrasound, an appointment is recommended enzyme preparations with every meal, but not more than three times a day. Choose pancreatin products. The dosage and regimen should be checked with your doctor. The complex begins to drink and carminatives, the purpose of which is to prevent the formation of gases. Dose for an adult: 1 tablet with food.
- On the eve of the diagnosis, you can have dinner no later than 20.00. At the same time, the dishes should be satisfying, but light. And 30 minutes after dinner you need to empty your intestines by taking a laxative or doing an enema. You can use suppositories with glycerin or lactose preparations. Those who suffer from chronic constipation should start taking carminatives in advance.
- Immediately before the ultrasound, you should refrain from eating and drinking heavily.
If a scan is prescribed for a child, then enzyme agents are not prescribed, but simply adjustments are made to the diet. Children under one year old stop feeding 3 hours before the examination, up to 3 years old - 4 hours before, and from 8 years old - 6 hours before. At older ages, the same preparation rules apply as for adults, with dose correlation.
Features of the procedure
During the ultrasound, a special gel will be applied to the patient’s abdomen to ensure better adhesion of the scanning probe and the skin. After the examination, it is wiped with a napkin. These actions do not pose any danger, since the gel is hypoallergenic. This examination carried out transabdominally, that is, percutaneously, scanning along the surface of the peritoneal wall.
The patient is placed on the couch, on his back. All manipulations are painless, except when constant pain served as a referral for ultrasound and are diagnostic criterion. A functional diagnostics doctor will interpret the results immediately.
Subject to all pre-procedural recommendations Ultrasound will take place quickly and without discomfort. This will provide valuable data. There are no contraindications to this examination. If the patient has already had such an examination, then the sonologist needs to provide a past report so that he can assess the dynamics, if any. Often the gall bladder is examined not separately, but during an examination of all organs of the peritoneum; general screening is much more expensive, but provides more information and is prescribed to patients much more often.
The patient may need an ultrasound of the gallbladder with a load, when before the procedure he will specifically need to eat a choleretic breakfast. During the scanning process, the doctor will observe the function of bile secretion during the intake fatty foods. Usually, for this purpose, the patient consumes fatty dairy products or several boiled eggs. Indicators are measured linearly and several times, maintaining equal periods of time.
The standard procedure lasts 20 minutes; when using a load, the period increases depending on the volume of the study. A repeat scan can be done after 2 weeks, but for preventive purposes it should be repeated once every 12 months.
What can be revealed
Using ultrasound, the following diseases and pathologies are diagnosed:
- Cholelithiasis.
- Cholecystitis in acute and chronic form.
- Dropsy.
- Cholangitis.
- Choledocholithiasis.
Norm indicators and interpretation
First of all, the sonologist will describe the size and shape of the organ. These rates vary greatly depending on the patient's age and general condition his body. On average, these figures should not exceed the following limits:
- Length: from 4 to 14 cm.
- Width: from 2 to 4 cm.
- Wall thickness: approximately 4 mm.
In addition to the thickness of the walls, a description of the patency and width of the bile ducts is also important; the presence of stones and foci of inflammation, the location of the bile duct relative to nearby organs and fabrics. The normal bladder size in infants and children under 8 years of age is determined based on the patient’s height and weight.
When testing with functional loads– the bubble normally shrinks by no less than 70% of its original volume in 50 minutes. This indicates that the motor function of the organ is without disturbances.
Doctor's report
An extract based on the ultrasound results is issued in printed form. It reflects full information about the results of the examination and emphasis is placed on the detected pathologies. The conclusion is accompanied by a number of photographs printed in high resolution.
The gallbladder is an integral part of the liver, which is involved in many important life processes. With inflammation and disease, the patient experiences pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, and vomiting. At the first signs, you should consult a specialist for further examination.
The gallbladder is a “satellite” of the liver. It is located in anterior section right groove of the liver, somewhat reminiscent of a pear. It consists of: bottom, body, neck (continues into the duct of the bladder). Neck length – 35 mm. The common bile duct consists of the cystic and hepatic ducts. Length – 60-80 mm. The flow of bile and pancreatic juice is regulated by the smooth muscle sphincter.
The production of bile juice is carried out by liver cells. This process is constant and continuous. Bile juice enters the intestines through a system of ducts. Due to the absorption of water, bile juice in this organ increases two to three times. Composition of bile: acid and pigments, cholesterol and bilirubin (a consequence of the breakdown of hemoglobin). Partially excreted in human urine.
If a blockage occurs biliary tract, That feces become light and have putrid smell. If a person has a metabolic disorder, cholesterol can contribute to the formation of stones. Bile itself serves as a catalyst and is capable of activating enzymes, breaking down fat formations into small particles, helps fats and vitamins be absorbed faster, and enhances intestinal function.
The bile ducts facilitate the release of bile juice into the intestines. Foods such as meat, dairy products, and eggs contribute to a large secretion of bile. If there is no food in the intestines and stomach, then the flow of bile juice is insignificant. The gallbladder is considered an auxiliary container for concentrated bile.
Normal ultrasound in adults and children
 Ultrasound helps the specialist determine the presence pathological processes in the organ. This examination can be prescribed to both adults and children. Normal indicators will depend on age. The gallbladder must not be enlarged and have clear outlines. Normally, during ultrasound, the dimensions of the gallbladder in an adult should be as follows:
Ultrasound helps the specialist determine the presence pathological processes in the organ. This examination can be prescribed to both adults and children. Normal indicators will depend on age. The gallbladder must not be enlarged and have clear outlines. Normally, during ultrasound, the dimensions of the gallbladder in an adult should be as follows:
- The length of the organ is from 60 to 100 mm.
- The width of the bubble is from 30 to 50 mm.
- The normal thickness of the walls is no more than 0.3 cm.
- The internal diameter of the lobar bile ducts is normally from 2 to 3 mm.
- Inner diameter size common duct 0.6-0.8 cm are normal sizes.
- Normally, segmented and subsegmental bile ducts should not be visible on ultrasound.
As for the gallbladder indicators in normal ultrasound in children, they vary depending on age category baby. Therefore, after receiving the results of the examination, you should not engage in self-diagnosis and panic, and simply seek advice from a pediatric gastroenterologist.
The size of the gallbladder in children can vary within different limits. Most experts are of the opinion that the normal diameter should not be more than 35 mm, and the length should not be more than 75 mm. The volume in an older child is no more than 0.2 liters. Normally, the width of the common bile duct is 0.8 cm, and the size is 0.41 cm. When in good condition bladder and the absence of pathologies in the liver, intrahepatic ducts should not be visible on ultrasound. If a specialist doctor finds these ducts on an ultrasound, this indicates jaundice or cholestasis.
Dimensions of the gallbladder in children on ultrasound depending on age
If all dimensions on ultrasound are normal, then this organ is healthy, there are no pathologies regarding shape, seals and indicates normal excretion bile. An ultrasound is performed on a child only if necessary and after preliminary consultation and referral from a specialist.
Factors for enlarged gallbladder in children and adults
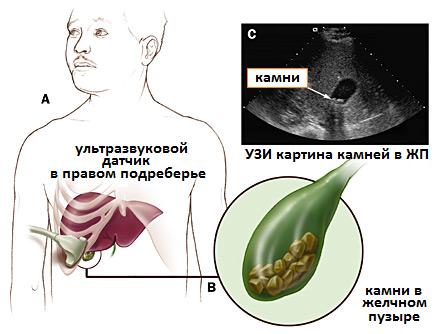 If the ultrasound showed increased sizes, this may indicate disturbances in the functioning of the liver and bladder, as well as neoplasms and pathologies in development of this body. The main reasons for the increase in size are diseases:
If the ultrasound showed increased sizes, this may indicate disturbances in the functioning of the liver and bladder, as well as neoplasms and pathologies in development of this body. The main reasons for the increase in size are diseases:
- Cholecystitis is an inflammation process accompanied by thickening of the organ wall. Signs: gag reflexes, weakened body, elevated temperature, painful sensations in the right hypochondrium.
- Cholelithiasis. Sizes of stone formations: from the smallest and insignificant to the largest. Symptoms of the disease: nausea, gag reflexes, cramping pain in the right hypochondrium. Ultrasound helps diagnose the size of stones.
- Dyskinesia - bending of the neck and increased tone of the muscles of the bladder walls
As for bladder enlargement in children, it is accompanied by diseases such as:
- Cholecystitis.
- Dyskinesia.
- Pancreatitis.
- Jaundice.
- Blockage of the biliary tract.
- Gallstones and stones.
As shown medical practice, then ultrasound of the gallbladder is recognized as the safest, most informative way to diagnose diseases in both adults and children.

