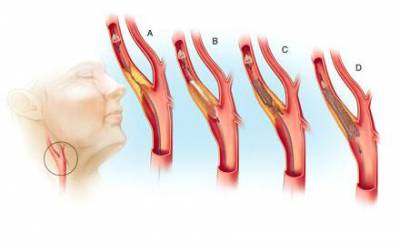
Removal of cholesterol plaques on the carotid artery reviews. Eversion carotid endarterectomy. Contraindications for surgery on the carotid arteries
The carotid arteries play a very important role in our body. important role, because they are responsible for supplying blood to most tissues and organs, as well as the brain. If this process is disturbed, the brain itself suffers, which can lead to sad consequences. Unfortunately, atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries leads to serious complications. Why does this type of atherosclerosis begin to develop?
Causes of plaque formation
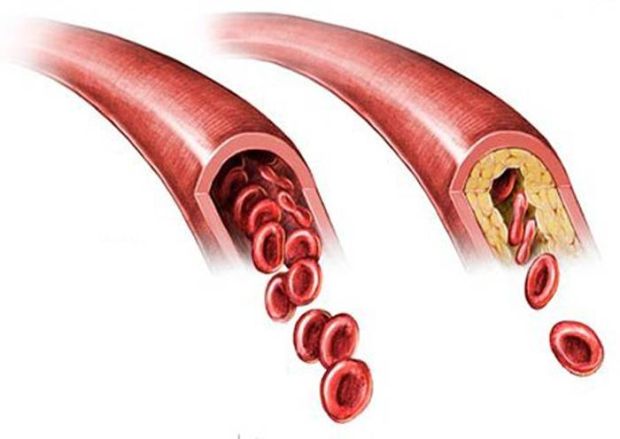
Normal and narrowed carotid artery
Most often it happens that the defeat of the carotid arteries by atherosclerosis occurs after this disease has already affected the arteries of other basins. blockage carotid artery occurs due to the fact that an atherosclerotic plaque appears in the artery. Of course, this is a deviation from the norm, since the vessel wall must be smooth, and the lumen itself must be free.
Atherosclerosis affects the carotid arteries for the same reasons as other vessels. Among the reasons are those related to lifestyle, as well as internal causes, Related certain diseases. Let's list the main ones.
- Atherosclerosis of other vessels and arteries.
- Smoking.
- Wrong nutrition.
- Excess weight.
- Diabetes.
- Hypertension.
Symptoms of the disease
Very often, this disease is asymptomatic, which further affects the complications and the treatment process. However, if you take a closer look at the state of your health, you can see certain symptoms of atherosclerosis, which will give rise to an urgent visit to the doctor.
Symptoms of the disease are different
It is important not to lose sight of transient ischemic attacks, which recur periodically. They happen just because of the fact that the brain enters an insufficient amount blood. Symptoms of such an attack usually completely cease to manifest themselves after a day, but this can happen earlier, even an hour after the onset. You should not wait for such an attack to happen again, after the first case you need to rush to the doctor to avoid complications, such as a stroke. The symptoms of an ischemic attack are as follows:
- weakness;
- a state of stupor;
- tingling and itching in the arm, leg, or one side of the body;
- inarticulate speech;
- loss of control over one limb;
- loss of vision in one eye.
All this is serious reason in order to go to the doctor and conduct a thorough diagnosis, which will help identify atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries. What does it include?
- Auscultation of the carotid arteries. Its purpose is to identify a vortex flow that indicates a narrowing of the artery.
- Measurement blood pressure.
- ultrasonic doppler study. It allows you to evaluate the blood flow and structure in the vessel.
- CT scan. The structure of the carotid arteries is determined by x-rays and radiopaque.
- Magnetic resonance angiography. It also helps to assess blood flow and structure, but with the help of magnetic field radiation.
After receiving all the results, the doctor will put accurate diagnosis and begin to prescribe effective treatment.
Treatment Methods
Carotid endarterectomy
Treatment of atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries is carried out according to the same principle as the treatment of other types of atherosclerosis. The first thing to do is to get your lifestyle in order, which includes giving up bad habits normalization of nutrition and moderate physical activity.
The doctor may prescribe drugs that lower cholesterol and normalize lipid metabolism. Blood thinners can help prevent blood clots from forming. Blood pressure medications may be prescribed.
In severe cases of the disease, surgical treatment is performed.
- Carotid endarterectomy. This method allows you to remove the plaque that blocks the flow of blood. Such an operation allows you to further prevent the risk of stroke.
- Stenting and carotid angioplasty. These surgical interventions are usually performed if carotid endarterectomy cannot be performed. A small stent is placed in place of the stenosis to prevent further narrowing of the artery.
What can happen if you do self-treatment Or give up on him altogether?
Consequences
The most serious thing that can happen with this disease is a stroke, which means a great threat to a person's life. A stroke can manifest itself in several ways.
The process of thrombus formation and stroke
Plaque rupture. A piece of plaque comes off and enters the small arteries of the brain. Their blockage occurs, which leads to a blockage of the blood supply to the part of the brain that dies.
To prevent all this from happening, you need not only to start treatment on time, but also to adhere to preventive measures to prevent atherosclerosis.
atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries. treatment
Vascular diseases.
Methods of diagnosis and treatment
Atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries. Treatment
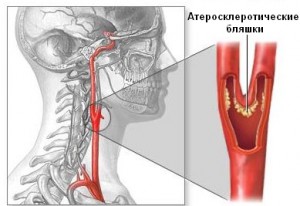
Through the carotid arteries passing through the neck, blood is supplied to the organs located in the human head, primarily the brain. With atherosclerosis, cholesterol plaques form on the walls of the arteries, the lumen of the vessel narrows, blood flow and blood supply to the brain worsens, which ultimately leads to disruption of its work, up to a stroke.
Atherosclerotic plaques in the lumen of the carotid artery are of several types, most often the surface of the plaque is uneven (loose, crumbling, like "cottage cheese", calcified, i.e. "stone", especially in diabetes mellitus).
From the moment of its formation on the vessel wall, the nature of the blood flow changes dramatically: its speed increases in the plaque area and sharply decreases after it. The so-called turbulence of the blood flow appears, and with the accompanying high blood pressure, small particles (pieces) of these plaques come off, fly into the arteries of the brain, blocking the lumen of these arteries. This is the cause of micro-strokes or "big" strokes, leading to paralysis, paresis, and, as a result, disability and even death!
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries is almost asymptomatic at first, so it is important to be very careful about your health.
On early stages the development of the disease, the patient may feel sudden weakness, tingling in the limbs of one half of the body, headaches and dizziness, sometimes with loss of consciousness. Perhaps a sudden deterioration in vision in one eye or loss of control over the movement of the limbs, speech suddenly becomes incoherent.
This condition is called a transient ischemic attack and is, in fact, a harbinger of a stroke.
If you are experiencing such sensations, then this is a clear reason for immediate appeal to the doctor.
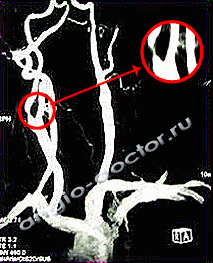
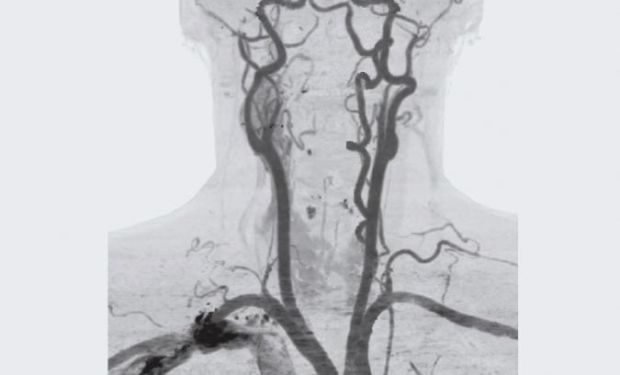
MRI and CT angiography of the carotid arteries.
Critical stenosis (narrowing of the lumen by 85%) of the internal carotid artery.
For the diagnosis of atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries is carried out:
- Auscultation of the arteries;
- Measurement of blood pressure;
- Ultrasound of the carotid arteries (duplex scanning);
- Computed tomography (CT) or CT angiography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or MRI angiography.
Usually, the Doppler ultrasound method provides enough information to diagnose the disease, in some cases, for more accurate diagnosis CT or MRI angiography of the carotid arteries is used.
The angiography method is used less frequently, only in cases where diagnostics by other methods does not give the desired result.
This is due to the fact that injury is possible with this method of examination. atherosclerotic plaque and, as a result, ischemic attack or stroke.
Prevention
To prevent atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries, you must adhere to simple rules of behavior in your daily life:
- should first be abandoned addiction smoking;
- lead active image life - doing exercise with a feasible load;
- monitor body weight;
- follow a diet;
- control cholesterol and blood sugar levels, especially in diabetes.
Methods of treatment
Treatment of atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries depends on the severity of the disease and general condition health of the whole human body.
- In the early stages of the disease, the physician vascular surgeon) can assign drug treatment diseases, including taking drugs to lower cholesterol levels in the blood, normalize lipid metabolism.
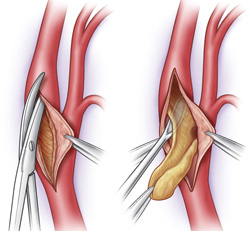
- Surgical treatment of atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries is used in cases where the removal of an atherosclerotic plaque is required - as the only way to restore the lumen of the artery and prevent a possible stroke. Removal cholesterol plaque under general anesthesia through a small incision at the site of its attachment is called a carotid endarterectomy.
Surgical treatment of atherosclerosis of the carotid artery. Operation scheme
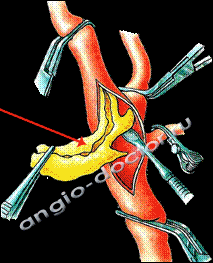
Removal of atherosclerotic plaque from the lumen of the carotid artery, yellow plaque is shown.
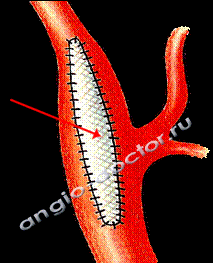
After removing the plaque, a patch is sewn in to expand the lumen of the artery and improve blood flow.
- Another method surgical treatment of this disease - balloon angioplasty and stenting.
Carotid atherosclerosis and prevention of ischemic stroke
What is ischemic stroke and transient cerebrovascular accident?
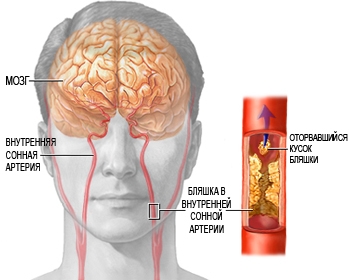
As atherosclerosis progresses, there is an increase in atherosclerotic plaque on the inner wall of the carotid artery. Accordingly, the risk of stroke increases. The progression of atherosclerotic lesions (stenosis) of the carotid arteries leads to the development chronic ischemia brain. When part of an atherosclerotic plaque is torn off, its particle (embolus), with blood flow through the carotid arteries, enters the brain, blocking the flow of blood to a certain area of the brain (embolism), as a result of which a cerebral infarction develops.
Depending on the size of the particle, and where the embolus ultimately ends up, the embolism may show no signs at all or cause a transient disturbance. cerebral circulation(transient ischemic attack), or stroke.
If the function of the damaged part of the brain is restored completely within 24 hours, the episode is called a transient cerebrovascular accident or transient ischemic attack (small stroke). If signs of brain damage do not go away after 24 hours, the condition is called a stroke.
What are the symptoms of ischemic stroke?
Harbingers of a stroke are symptoms characteristic of chronic cerebral ischemia:

- Headache.
- Dizziness.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Increased fatigue during physical and mental stress.
- Difficulty concentrating and forgetfulness.
- Noise in the ears or heaviness in the head.
It should be noted that in the absence of adequate treatment, cerebral ischemia progresses and leads to acute cerebrovascular accident (stroke) or contributes to the development vascular dementia(dementia). Since both atherosclerosis of the vessels of the brain and atherosclerosis of the vessels of the neck can lead to the above manifestations, the only way find out the reason proper treatment atherosclerosis. This means to provide reliable prevention stroke, is to conduct a modern survey.
What are the signs and symptoms of stroke and transient ischemic attacks?
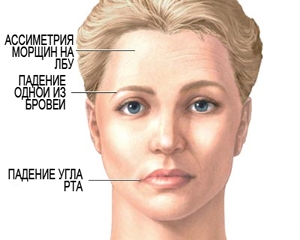
- Violations (difficulty) of speech.
- Numbness, weakness, paralysis of one side of the body or face.
- Loss of vision in one eye.
- Problems with balance or coordination.
As noted above, if these changes completely regress within a day, the patient is diagnosed with TIA, if more than 24 hours - ischemic stroke.
There is also the concept of "microstroke", which is not medical term, but is used to describe a stroke that led to an infarction of a small area of the brain and, as a result, manifested by “erased” symptoms with quick recovery. However, a microstroke can be regarded as a harbinger ischemic stroke. Approximately half of patients develop a "big" stroke over the next year.
How to detect atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels and carotid arteries?
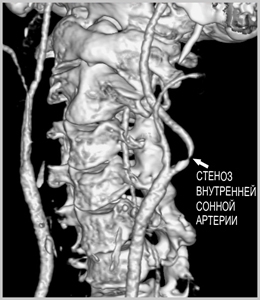
Some of the following studies can detect carotid disease before the development of a stroke, which allows timely prevention of this formidable condition.
At the level of inspection, you can identify "Carotid murmur" - this is the wrong sound ( systolic murmur) heard with a stethoscope on the neck in the projection of the carotid arteries due to narrowing of the carotid artery, or a difference in pulse between the two sides of the neck. He talks about high probability carotid artery lesions.
Treatment of atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels and carotid arteries
When a pronounced, but not manifesting atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries is detected, treatment becomes necessary. Treatment is aimed at preventing the progression of atherosclerosis and preventing stroke. The main directions of therapy in patients with atherosclerosis cerebral vessels And main vessels neck is:
- correction of organ dysfunction endocrine system(primarily diabetes)
- normalization of blood cholesterol levels (achieved by following a diet and taking medicines statins),
- normalization of blood pressure levels,
- to give up smoking.
Be sure to prescribe drugs to reduce the likelihood of the formation of a blood clot (thrombus). Most often prescribed drugs such as aspirin (thromboASS, cardiomagnyl), or Plavix.
Surgical prevention of ischemic stroke
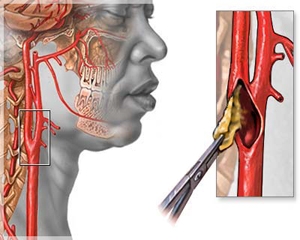
With a significant narrowing of the carotid artery by an atherosclerotic plaque, endarterectomy of the carotid artery is usually used. Surgery, which includes opening the lumen of the affected carotid artery and removing an atherosclerotic plaque from it. This procedure is well established, provides a long positive result in the form of prevention of ischemic stroke for many years. H bears minimal risk in most patients. The stay in the clinic is usually 24-48 hours.
Most patients experience little discomfort and are able to return to normal activities after treatment after a short recovery period (7-14 days).
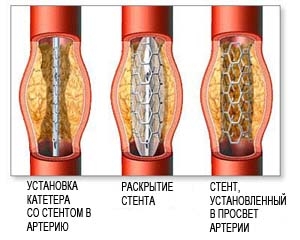 As an alternative to surgical treatment, an intravascular (endovascular) technique is used. Balloon angioplasty with stenting. Currently, international studies are evaluating the effectiveness of this technique for the treatment of carotid artery atherosclerosis. This procedure is performed in conjunction with angiography under local anesthesia through a puncture in the groin.
As an alternative to surgical treatment, an intravascular (endovascular) technique is used. Balloon angioplasty with stenting. Currently, international studies are evaluating the effectiveness of this technique for the treatment of carotid artery atherosclerosis. This procedure is performed in conjunction with angiography under local anesthesia through a puncture in the groin.
The essence of the procedure is the intravascular supply to the site of narrowing of the carotid artery with a special catheter with a balloon. When the balloon is inflated in the lumen of the carotid artery, the narrowed area is expanded. To consolidate the effect, stenting of the dilated carotid artery is performed by installing an internal stent (framework) of the vessel. The recovery period after angioplasty with stenting is also very short.
Sign up for an appointment
Vascular Center. T. Topper renders qualified assistance for all types of vascular diseases.
Medical statistics show that over 30% of strokes are caused by atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries. The danger of this disease lies in the fact that it is very difficult to identify it on initial stage development, when an atherosclerotic plaque is just being formed. The fact is that this disease can long time develop without any symptoms and pathologies, and the consequences of atherosclerosis sometimes become unforeseen and devastating (for example, disability or even death). The causes of the disease, its symptoms, diagnosis, prevention and treatment will be discussed in this article.
How does the disease develop?
The supply of blood to the brain (and therefore oxygen and beneficial substances) provide two sleepy and two vertebral arteries. IN healthy condition The walls of these vessels are smooth and elastic. inner surface. An increase in blood cholesterol levels can lead to neoplasms on inner walls vessels that grow and cause stenosis (narrowing of the lumen). An atherosclerotic plaque is most often located at the site of the branching of the carotid artery into two separate highways. At the same time, an overgrown plaque can block the internal lumen by more than 65-70%, which significantly impairs blood flow and leads to oxygen starvation brain.
Atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries is often the cause of stroke
What are the reasons?
The reasons causing such changes in the vascular system of the body can be very diverse, namely:
- aging of the body - the first atherosclerotic plaque appears after 35-40 years;
- malnutrition - consumption a large number heavy fats, fried foods, confectionery and sweets, and at the same time scarcity or complete absence on the menu fresh vegetables and fruits;
- bad habits - drinking alcohol and smoking have a very negative effect on the state of blood vessels;
- chronic diseases and heredity - these factors can cause a change in the work of a particular organ;
- obesity and lack physical activity – sedentary image life, preference for computer and TV to active walks, picnics and country trips.
All these factors invariably lead to the fact that atherosclerotic plaques clog the vessels. circulatory system in many parts of the body. This condition of the vessels can provoke thrombosis of blood vessels, including the carotid artery.
Diagnostic methods
Very often, an atherosclerotic plaque can be inside a vessel for a long time, and a person will not even guess about its existence. In other cases, the disease develops very rapidly, and this process is accompanied by tangible symptoms:
- tingling in one of the limbs - the arm or leg, as if it were numb;
- blurred vision in one eye;
- inarticulate speech;
- loss of control over one of the limbs.
When manifested similar states should immediately contact medical institution where the doctor will prescribe examination and treatment.
![]()
Angiography can detect atherosclerosis and determine the degree of narrowing of the carotid artery
To identify atherosclerosis of the carotid artery, you can use the following procedures:
- Auscultation.
- Doppler ultrasonography.
- Magnetic resonance anginography.
- CT scan.
- Measurement of pressure with a tonometer.
Atherosclerotic tissue in the vessel, detected during the diagnosis, sometimes overlaps the vessel by 3/4. This problem requires immediate surgical intervention and the resumption of normal blood flow. And for this it is very important to choose the right treatment.
Medical and surgical treatment
Treatment for atherosclerosis always depends on the results of the diagnosis. Based on this information, the attending physician makes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes conservative treatment or operation.
Drug treatment is prescribed if the atherosclerotic tissue does not cover 70% of the vessel lumen. At the same time, they assign special diet and cholesterol-lowering drugs.
If an atherosclerotic formation blocks the vessel by more than ¾, its immediate removal is required. The patient will have an operation in a specialized department, the essence of which is to make a small incision on the vessel and extract the harmful tissue.
With a severe degree of narrowing, normal blood flow can be resumed by stenting the carotid artery.
Prevention is the key to longevity
To avoid unpleasant surprises with vessels, including the brain, it is enough to follow a few simple rules:
- lead an active lifestyle (more often get out into the forest, to the river or cottage, make unhurried hiking or just walk to work)
- to eat more vegetables and fruits. They are rich in vitamins, micro and macro elements and fiber;
- avoid fatty, fried and chemical foods treated with liquid smoke or containing a lot of "yes";
- avoid alcohol and smoking (including passive) - they have a detrimental effect on the body;
- do exercises - simple exercises within 5-10 minutes in the morning will allow you to be in good shape all day;
- avoid stress - Negative influence destroys not only human life, but also his body.
It is very important in order to periodically visit a doctor and undergo examinations. After all, the sooner the formation of sclerotic plaques in the vessels is detected, the more effective the treatment will be. And while leading right image life can reduce the risk of disease and minimize it even in old age. Be healthy!
Carotid endarterectomy is surgical intervention or surgery, the purpose of which is to remove atherosclerotic plaques from the carotid arteries and is of a prophylactic nature, allowing to prevent stroke And transient disorders cerebral circulation (harbingers of a stroke).
The carotid arteries are arteries located in the neck and provide blood and oxygen to the brain. With aging, systemic atherosclerosis, various metabolic disorders, genetic predisposition in the wall of these arteries, cholesterol and fats can be deposited, which leads to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
Fig.1 Atherosclerotic plaque in the lumen of the carotid arteries
Increasing in size, plaques gradually lead to narrowing (stenosis) of these arteries, disruption of their patency and blood supply to the brain. The progressive accumulation of fat products and the constant turbulent flow resulting from constriction can lead to plaque damage and instability.
Under the influence various factors, most often it is a drop in blood pressure, plaque destruction can occur with its contents entering the lumen of the artery and the formation of a thrombus with migration into vascular system brain. This chain of events results in acute disorder cerebral circulation or stroke.
Carotid endarterectomy just allows you to interrupt this life-threatening cascade of pathological events in a timely manner, in fact being a preventive operation. That is, the implementation of carotid endarterectomy at the stage of formation of an atherosclerotic plaque significant for blood circulation can reduce the likelihood of stroke to 0%.
As shown by numerous studies in the United States, stroke is the third leading cause of death overall and the second leading cause of death for women. Among stroke patients, according to various sources, 50-75% had atherosclerotic lesions of the carotid arteries, and early carotid endarterectomy helps prevent stroke.
Conducted to date whole line prospective randomized trials comparing the efficacy and safety of carotid endarterectomy with medical therapy in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients. The data of most of them confirmed that carotid endarterectomy is characterized by better preventive measure to protect against stroke than using only drug therapy in symptomatic patients.
What are the indications for carotid endarterectomy?
As practice shows, carotid endarterectomy as a method of surgical treatment should be considered for any patient with stenosis of the internal carotid artery (less often the common carotid artery), for whom the operation will significantly improve the quality of life and is guaranteed to prevent stroke compared to medical treatment.
For symptomatic patients with low surgical risk and a predicted morbidity and mortality rate (stroke and death) of less than 6%, reliable indications for carotid endarterectomy are the following:
- one or more transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) within the last 6 months and more than 50-60% carotid stenosis
Accepted, but still debated in the scientific community, the indications are as follows:
- ipsilateral (that is, on the side of the lesion) TIA and more than 70% carotid stenosis, in combination with the need to perform (CABG)
- progressive stroke and carotid stenosis over 70%
For asymptomatic patients with low surgical risk and a predicted morbidity and mortality rate of less than 3%, a proven indication for carotid endarterectomy is stenosis of the internal carotid artery of more than 60-65%, which is hemodynamically significant and increases the risk of plaque instability.
American Association Heart Association (AHA) and the American Stroke Association (ASA) developed modern recommendations For surgical prophylaxis stroke in post-stroke or TIA patients and regarding the use of carotid endarterectomy in these patients:
- carotid angioplasty and stenting (CAS) may be used as an operation in symptomatic patients with moderate or low risk of complications associated with endovascular intervention, when the diameter of the lumen of the internal carotid artery is reduced by >70% on non-invasive imaging or >50% on angiographic imaging or non-invasive imaging with confirmation, and the expected rate of periprocedural (intraoperative) stroke or death<6% (класс IIa; уровень доказанности B)
- when choosing a treatment method between carotid endarterectomy and carotid stenting, it is advisable to take into account the age of the patient; Carotid endarterectomy in patients over 70 years of age is associated with an improved outcome compared to stenting, especially in cases where arterial anatomy unfavorable for endovascular intervention is revealed before surgery; for young patients, the results of open surgery and stenting in terms of risk of periprocedural complications and long-term risk of ipsilateral stroke are comparable (class IIa, level of evidence B)
- Carotid stenting and carotid endarterectomy in patients with symptomatic carotid atherosclerosis should be performed by surgeons with a personal risk of postoperative stroke and mortality of less than 6% (Class I; Level of Evidence B)
Are there any contraindications to performing an open intervention on the carotid arteries?
Carotid endarterectomy is contraindicated if the patient has a serious comorbidity that dramatically increases the risk of perioperative (surgery-related) complications or reduced life expectancy. It is also contraindicated in patients with an acute onset severe stroke or in patients who have already suffered a major devastating stroke with minimal recovery or significant change in the level of consciousness.
It is traditionally believed that emergency endarterectomy in case of acute occlusion of the carotid artery can transform ischemic cerebral infarction into hemorrhagic, accompanied by extremely high mortality. Therefore, most researchers tend to perform the operation in a planned manner, after the manifestations of stroke subside and optimal recovery is achieved. The minimum time for such recovery is 2 months, while assessing the state of brain tissues after a stroke, it is necessary to use any of the methods of tomographic imaging (CT or MRI). However, relatively recently there have been reports of regression of neurological deficit after early interventions in patients with acute non-hemorrhagic stroke, while the authors refer to the need for careful selection of such patients for early operations.
What features of the blood supply to the brain should be known before performing carotid endarterectomy?
A clear understanding of the anatomy of the carotid vessels and adjacent structures is critical to effectively perform carotid endarterectomy and minimize complications.
Anatomy of the internal carotid artery and vertebral arteries
The so-called brachiocephalic arteries all arise from the aortic arch and include the brachiocephalic trunk, also called the innominate artery, the left common carotid artery, and the left subclavian artery. The most common anatomy is the division of the brachiocephalic trunk into the right subclavian and common carotid arteries, and the vertebral arteries arise from the subclavian arteries.
Each common carotid artery rises up the neck and divides into the external and internal carotid arteries at the level of the submandibular region. The external carotid artery provides blood supply to the tissues and some organs of the face, thyroid gland and pharynx, dividing into the corresponding arteries. The difference of the internal carotid artery is that it has no branches at this level (the so-called extracranial or extracranial branches).
In the area where the common carotid artery or carotid sinus divides, there is a zone where numerous baroreceptors are located, and the zone is partially innervated by Hering's nerve, a branch of the IX pair of cranial nerves (glossopharyngeal nerve). They are partly responsible for the regulation of blood pressure. The bifurcation of the carotid artery contains the carotid body, which functions as a chemoreceptor, responding to changes in the level of oxygen or carbon dioxide in the blood.
An intracranial branch departs from the internal carotid artery, which is called the ophthalmic artery, and through which the system of internal and external carotid arteries communicate through the system of collateral vessels. The ophthalmic artery is a frequent site of embolism (thrombus migration) from the carotid artery, resulting in transient (transient) blindness in one eye (if the thrombus is small and subsequently dissolves) or complete blindness if the central retinal artery is blocked. Anatomically, between the systems of branches of the internal carotid artery (anterior and middle cerebral arteries) and the vertebral arteries (posterior cerebral arteries) there are collateral messages that form the so-called circle of Willis.
It is thanks to the knowledge of the anatomy of the basin of the brachiocephalic arteries and the presence of a clear anatomical and instrumental picture of the structure of the circle of Willis and other collaterals that the surgeon can build treatment tactics and make predictions regarding the results of the operation.
How is the preoperative assessment performed?
Atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries can occur both asymptomatically and with specific symptoms. Often, the clinical manifestation of atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries becomes a transient disorder of cerebral circulation or a transient ischemic attack (TIA - this condition is also called a pre-stroke or a small stroke) or immediately a stroke. In symptomatic patients, diagnosis should begin with ultrasound imaging of carotid plaques using duplex ultrasound. Ultrasound diagnostics usually allows obtaining qualitative and quantitative information about the anatomy of vascular lesions, as well as determining the degree of carotid artery stenosis with an accuracy of 90-97% and the characteristics of atherosclerotic plaque.
What complications can occur after carotid surgery?
Hypotension
One of the unpleasant effects that surgeons and anesthesiologists encounter when isolating carotid arteries is mechanical stimulation of carotid sinus baroreceptors, leading to bradycardia (slow heart rate) and a reflex drop in blood pressure (hypotension).
The elimination of this reflex influence is achieved by infiltration and chipping of the bifurcation zone and the carotid body with a solution of lidocaine. Blocking of reflex bradycardia that has already occurred is achieved by introducing atropine sulfate. In rare cases, in the postoperative period, bradycardia that occurs after removal of the carotid body may require additional vasopressor and cardiotonic support until this condition self-compensates, usually stopping within 6-24 hours.
Arterial hypertension
Carotid sinus intervention can cause postoperative blood pressure imbalance, which is also facilitated by the production of cerebral renin during carotid occlusion and the use of halogenated fluorocarbon during general anesthesia.
Adequate preoperative treatment of patients with arterial hypertension is critical to minimize its harmful effects on myocardial function, and also reduces the likelihood of developing neurological deficits and cerebral hyperperfusion in these patients. Perioperative hypertension is usually treated with sodium nitroprusside or other vasoactive agents such as .
Postoperative wound hematoma
The incidence of postoperative hematomas requiring re-intervention is less than 1%. The use of antiplatelet agents and heparin increases the risk of bleeding and the formation of subcutaneous hematomas. However, without these drugs, carotid endarterectomy is impossible, since these drugs significantly reduce the risk of thrombosis and the development of coronary or cerebrovascular complications. Very rarely, a large hematoma can lead to compression of the internal carotid artery and adjacent cranial nerves. One of the serious complications of the formation of such a hematoma is a violation of the airway, accompanied by the possibility of developing respiratory asphyxia or can become a potential focus of infection, which is why most large, intense hematomas in this area need surgical correction.
Infection and false aneurysm
Wound infection after carotid endarterectomy is extremely rare. Accession of bacterial flora is possible in cases of formation of large hematomas and aneurysms of the carotid arteries, and usually does not exceed 0.15%. Infected false aneurysms are an indication for complete removal of all infected vascular tissue and surrounding soft tissue infection. Ideally, if possible, the blood supply can be restored by using and replacing the artery with a vein.
If the infection results in damage to both the internal and external carotid arteries, reconstruction may become technically and prognostically ineffective, and even dangerous. If it is impossible to perform reconstruction, ligation and resection of vascular formations and inflamed soft tissues are performed without reconstruction. Before making a decision on the possibility of performing an operation with such lesions, a preliminary assessment is made of the tolerance of the brain to permanent ischemia, which can occur with forced ligation of the arteries. For this, angiography with balloon occlusion of the internal carotid artery is performed.
Cranial Nerve Dysfunction
The reported incidence of cranial nerve damage and dysfunction after carotid endarterectomy ranges from a few percent to 39%. Approximately 60% of these injuries are manifested by the development of characteristic symptoms, mainly in the form of dysfunction of the superior laryngeal and recurrent laryngeal nerves. Such dysfunction may be manifested by hoarseness or hoarseness of the voice. Fortunately, in most cases this is a temporary condition and the voice function is restored over time.
Damage to the vagus nerve and its branches (recurrent and superior laryngeal nerves)
Injury to the vagus nerve or recurrent laryngeal nerve can be caused by overstretching, traction, or direct trauma from forceps, forceps, or electrocoagulation. Vocal cord paralysis on the side of the operation, as a rule, leads to hoarseness and a violation of the effective cough mechanism. Unilateral damage to the vagus nerve or recurrent laryngeal nerve may be asymptomatic, but may be an obstacle when planning a carotid intervention on the other side.
For this, when planning the next stage of surgical treatment on another carotid artery, patients are advised to consult an otorhinolaryngologist before carotid endarterectomy. The superior laryngeal nerve is responsible for the quality of the voice, in particular for the high sound frequency range.
Hypoglossal nerve injury
Mobilization of the hypoglossal nerve is usually necessary when a high carotid bifurcation is detected. To prevent damage to this nerve, it is necessary to isolate the carotid artery with extreme caution in the area of origin of the external carotid artery and its branches, since the cervical branch of the hypoglossal nerve departs from the nerve in this area. Damage to this nerve can be clinically manifested by a deviation of the tongue towards the operation, but with a more severe injury, it can lead to problems with chewing, swallowing food, or impaired speech.
Glossopharyngeal nerve injury
When accessing the standard carotid bifurcation, the glossopharyngeal nerve is usually not visible. However, if a longer upward incision is made with a high carotid bifurcation or a high internal carotid lesion, injury to this nerve is possible. This nerve can be injured by improper clamping, cutting the digastric muscle, or cutting off the styloid process with high access to the carotid artery. Injury to the glossopharyngeal nerve usually causes paralysis of the middle constrictor of the pharynx, and may cause difficulty swallowing solid food.
Horner's syndrome
Horner's syndrome can occur after damage to the ascending sympathetic fibers in the region of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Damage to the branches of the facial nerve
The extreme mandibular branch of the facial nerve can be damaged when the incision is widened towards the angle of the mandible, but its most typical is its temporary dysfunction resulting from the impact of the retractor legs. Injury to this nerve results in moderate drooping of the angle of the mouth on the side of the operation. Injury to the branches of the facial nerve can be avoided by limiting the incision and moving it to this area, and by occasional alternate relaxation of the retractor.
Hyperperfusion and cerebral hemorrhage
The classic picture of hyperperfusion and cerebral hemorrhage syndrome is a unilateral headache, migraine-like attack and hemorrhage occurring on the 2nd-7th day of the postoperative period. The incidence of hyperperfusion can reach 2-3%, and progression to such a complication as cerebral hemorrhage up to 0.2-0.8% of cases. This rather serious complication can be minimized by selecting competent antihypertensive therapy and stabilizing blood pressure on the eve of surgery, as well as choosing the optimal tactics and stages of treatment for significant bicarotid bilateral stenoses.
What is the estimated cost of carotid endarterectomy?
Carotid endarterectomy is one of the most common operations performed by vascular surgeons. Currently, in most public clinics in our country, this operation is performed absolutely free of charge as part of the financing of the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund (OMI) or at the expense of the quota of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. Carotid endarterectomy is a rather complex intervention and should be performed in vascular surgery departments with extensive experience in performing such interventions, which is why it is most often performed in large medical federal centers.
Unfortunately, due to various circumstances, patients do not always manage to get into such centers and receive free treatment, so they have to turn to various commercial clinics. The range of prices for surgery in Moscow and the cost of carotid endarterectomy varies from 20 to 65 thousand rubles. But it should be noted that abroad the cost of performing an operation on the carotid artery is an order of magnitude higher and reaches 15,000 US dollars, and not in all countries such treatment is covered by standard medical insurance.
Atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries is one of the most dangerous diseases that can threaten a person not only with a deterioration in well-being, but also with disability, and even lead to death. Plaques in the carotid artery impair the blood supply to the brain and thereby deprive it of nutrition and the ability to function normally. By its composition, the plaque here is essentially the same as in other vessels, namely, the deposition of cholesterol. Together with connective tissue and other lipid fractions, the plaque in the carotid artery becomes a solid formation. When this occurs, blockage, or stenosis of the vessel. Obstruction of blood flow can even cause carotid thrombosis or cerebral stroke. If in the normal state the diameter of the carotid artery is maximum, then in the presence of deposits in the form of a plaque, the lumen can be narrowed by more than half. It is also important for the patient to know that the presence of a plaque in the carotid artery indicates that they are most likely present in other vessels, because here they appear last, which means that this disease should be treated as quickly as possible.
How does plaque form in the carotid artery?
In the cervical region of each person, 2 carotid arteries pass immediately, plus 2 vertebral arteries on the left and right sides. Through these arteries of the cervical spine, blood flows to the face and brain. Compared to the blood flow in the spine, everything happens much more intensively in the cervical region, and any deviation from the norm significantly reduces blood flow and worsens the quality of human life. That is why the importance of the carotid arteries is so high.
Of course, the process does not take place in one day and sometimes even not in one year, however, the appearance of a disease is characterized by a certain sequence of changes occurring in the human body. First, in order for such changes to occur, a person must have certain prerequisites and favorable conditions. It could be a microscopic tear in the carotid artery, where cholesterol is more likely to be deposited. Slow blood flow in a certain area is another possibility for a plaque to form in this place in the future. Finally, doctors note that very often such a problem occurs at the site of the fork of the carotid artery, where the walls of the vessels are thinner.
So, the direct prerequisites for the appearance of cholesterol growths on the walls of the carotid artery is the excessive consumption of fatty, rich in low-density lipoprotein food.
For a healthy person, an increase in calorie intake is unlikely to lead to problems in the cardiovascular system, but if overeating occurs regularly, then the body's defense mechanisms begin to fail. If usually parietal enzymes helped break down fat, then with an excess of high-calorie foods, they cannot cope with the amount of work that they have to do. And so, complex compounds of lipids, proteins and cholesterol are formed in the cavity of blood vessels and arteries. These small lumps can migrate in the vascular system and attach themselves to the weakest point, where the parietal surface is loose and edematous. It is likely that this attachment will occur in the carotid artery.
After the fat ball has joined the wall, there is an increase in fresh connective tissue. Experts call this stage liposclerosis. After some time, the build-up will already be thoroughly formed and fixed on the wall. Further, the atherosclerotic plaque will continue to increase.
Specialists divide the sclerotic plaque into two parts - the core and the tire (outer layer). The core is made up of free cholesterol with a small amount of ester to help bind. Near the nucleus, "foamy" cellular structures can be seen. These are macrophages, which are mostly composed of fats. Over time, fatty components infect macrophages and penetrate into the nucleus.
The outer layer of an atherosclerotic plaque is a fibrous sheath with elastin and collagen fibers. The percentage of collagen and elastin directly affects the ability of the tire to tear.
At the initial stages, the plaques in the carotid artery are not so strong. Their contents can be called semi-liquid, and therefore capable of dissolution. Of course, if a person knew about their existence at that moment, then the treatment would be much easier. By the way, even at this stage, atherosclerotic plaque is already a great danger. With the detachment of individual elements of the build-up, a complete closure of the vessel can occur. Such a blockage of the lumen of the carotid artery occurs if the detached part stops at another, narrower site, for example, at the fork.
Over time, the outer shell thickens. It accumulates calcium salts, which additionally give it hardness. This is how the final stage of atherosclerotic plaque formation begins - atherocalcinosis. Now this cholesterol plaque is growing slowly, it is stable and completely immobile. At this time, there is a deterioration in blood flow in this area. By the way, even a stable plaque can develop further, but this will happen over several years. The collagen contained in it helps the walls of the plaque to remain elastic and prevents its rupture.
If the plaque contains a higher percentage of lipids, then such formation is considered unstable. This means that there is a possibility of its rupture, which can lead to thrombosis.
There is also such a thing as a heterogeneous atherosclerotic plaque. In this case, the course of the disease is complicated by hemorrhages and ulcerations that regularly occur on the surface of the cholesterol plaque. The contours of such a formation are uneven, there are loose depressions on the surface.
Stages of plaque formation in the carotid artery
- Accumulation in the vessels of fatty spots that are not amenable to dissolution.
- Inflammatory cells – T-lymphocytes and monocytes – are involved in the process.
- Monocytes migrate into the arterial wall, thereby deforming the endothelium and forming foam cells.
- Platelets from the blood are attracted to the damaged area.
- As a result of damage to the endothelium, the body secretes mediators of cellular defense, and also tries to actively build up the damaged area.
- Increased production of collagen and elastin leads to their local accumulation and the appearance of a tubercle in the free lumen of the vessel.
- The growth thickens and increases in size.
Symptoms
They may not appear for a very long time, and this is a huge danger. The tangible signs can be different, and they depend on many factors - the size of the deposit, localization, and so on. Most often, with a decrease in blood flow in a certain area, it is characterized by the appearance of fatigue after physical exertion or with any acceleration of blood circulation. Many patients note mild soreness, but do not give it due attention. And of course, a symptom of the decomposition of an unstable cholesterol plaque is a heart attack or stroke.

Most often, the symptomatology goes in parallel with those signs that are observed in obese patients. So, ischemic attacks can also occur, during which it can be observed:
- Confusion of speech. Violation of the blood supply to the brain leads to multiple changes, the symptoms of which may include confusion of speech. Such oxygen starvation of the brain prevents a person from making even a simple sentence.
- Numbness. It appears suddenly and is localized only on one side of the body.
- Loss of vision in one eye. A very formidable symptom that speaks of a pre-stroke state of the body.
- Weakness. Perhaps the most insignificant, according to patients, symptom. The fact is that atherosclerotic plaque closes the blood flow, which leads to a lack of oxygen. In turn, the body switches on the "energy saving" mode. The patient feels tired constantly, chronically, and even feels low without physical work.
For each individual, the symptoms may be more pronounced or weaker. Some patients have only one sign from the list, while others describe the full clinical picture. At first, ischemic attacks can be very short, up to an hour, and subsequently can last almost a day. Over time, the periods between attacks can be reduced, and now the person becomes a patient of a cardiologist who needs immediate treatment.
Diagnostics
Before treating a patient, it is necessary to find out the whole clinical picture and outline a plan of action. Before starting the diagnosis with special devices, the doctor must necessarily conduct a consultation. Questioning the patient will help to more accurately find out exactly which symptoms prevail and when they most often appear, as well as clarify the history of the disease and find out some features of a particular medical history. Be sure to identify all risk factors, which include not only overeating, but also heredity, smoking, regular stress, physical inactivity, previous infections and age over 35 years.
Auscultation of the carotid arteries should be mandatory. This helps to detect vortex flows, which means that there is a narrowing in this section of the vessels. Then you can proceed to instrumental diagnostic methods. There are several of them:
- ultrasonic complex scanning;
- magnetic resonance therapy;
- measurement of blood pressure;
- computed tomography with angiography.
Doppler ultrasound is a very informative method. Ultrasound allows you to see the structure of the vessel and the blood flow in it. Plaques inside the carotid arteries are very well detected by this method. An experienced doctor will even be able to assess their size, as well as their composition, because the echogenicity of plaques is different depending on their composition.
Computed tomography, coupled with angiography, is a method that is used to obtain more detailed information that could not be obtained previously. To do this, it is necessary to introduce a contrast agent into the vessel, and then illuminate everything with x-rays. The doctor receives the exact location of all vessels, which allows him not only to correctly assess the extent of the damage, but also give reflection on further actions and upcoming treatment. The method is fraught with the risk of damaging the atherosclerotic plaque, which in turn can lead to the separation of part of it, and then to a stroke. That is why this instrumental method is not used so often.
Magnetic resonance therapy allows you to see the location of the vessels without the introduction of contrast and without exposing the patient to x-rays. Due to the expensive equipment that is used in this case, it is possible to find a device for MRI of blood vessels only in large clinics, and patients often have to wait for their turn, sometimes even for several days.
Finally, when measuring blood pressure in such patients, it almost always reveals its increase. For a doctor, numbers are important that indicate the degree of damage to the vascular system. Also, the pressure of the patient can affect the upcoming treatment, namely, the choice of drugs.
Medical treatment
It is usually called conservative, because it allows you to treat patients without surgery and modern medical equipment. Medicines prescribed by a cardiologist help to reduce lipids in blood vessels. Normalization of cholesterol levels is an important step in maintaining the patient's life. It will also fix the size of the atherosclerotic plaque and prevent its further growth.
With excessive blood pressure, part of the medication will be aimed at reducing this indicator. This will help the patient improve well-being and quality of life.
It is necessary to take drugs that help thin the blood. This is necessary in order to prevent the appearance of new plaques. By the way, even therapists prescribe such drugs for people over 50 today. With age, blood becomes more viscous. Against the background of weakened and damaged vessels, this becomes dangerous, because the body will perceive any damage as a call to action and will actively begin to thicken this area of blood, as well as increase the number of platelets.
All these drugs can not even be called a treatment, but a way of life for a person who is a patient of a cardiologist. It is important to take all medications regularly and not just occasionally.
Against the background of taking drugs, it is important to exclude risk factors. It is worth reviewing your diet and introducing fiber-rich foods into it. As for physical education, it is better to contact a specialist. The fact is that it is impossible for an unprepared person to start exercising intensely. Most likely, the patient is overweight, and not all types of activities will be shown to him. Over time, the amount of physical activity can be increased, but this should be done gradually and only under the supervision of an experienced trainer.
It is important to control your body during the entire period of treatment. When the situation improves, the content of individual blood components will also change. The risks of progression and severe consequences will also tend to zero.
Surgical treatment
The operation will completely and restore blood flow. The decision on which method this will be done should be taken only by the doctor. Today, two types of surgical intervention are most commonly used to treat this problem - balloon angioplasty followed by stenting and endarterectomy.
The first method is performed under local anesthesia. To do this, the doctor inserts an inflatable balloon through a catheter in the femoral artery or the radial artery in the arm. When the balloon reaches the right place in the carotid artery, it simply widens the lumen. Next, a stent is inserted into the narrowing site. This is a small metal mesh that is securely fixed at the site of the former narrowing of the carotid artery and thus allows you to restore blood flow.
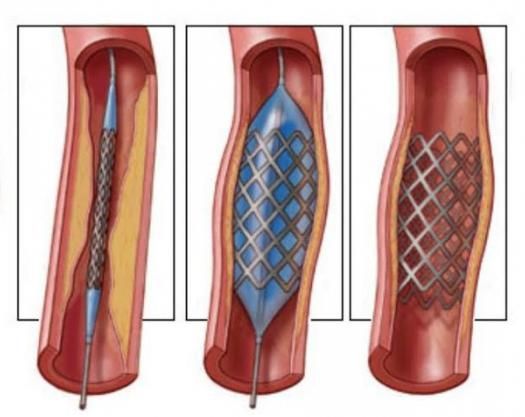
Endarterectomy is performed only under general or local anesthesia. In this case, the doctor inserts a flexible instrument that reaches the narrowing site. Now the surgeon carefully removes the plaque itself, which blocks the blood flow. Unfortunately, several cases of recurrence of the disease have been described, because the structure of the vessel wall in this place is no longer ideal, which means that the disease can return.
Laser treatment may also be used. In this case, the doctor directs the laser beam exactly at the site of plaque formation. Under the influence of this beam, the deposit literally evaporates.
Ozone therapy can be called a surgical intervention with a slight stretch. In this case, the doctor injects ozone into the patient's blood, which has the properties of an oxidizing agent and an immunomodulator. It dissolves large lipid clots in the blood, speeds up metabolism, which is simply necessary for most patients with plaques in the carotid artery.
Finally, thrombolysis can be attributed to surgical methods. Its essence lies in the fact that the doctor injects into the carotid artery a special substance that has a resolving effect. The cholesterol plaque is completely dissolved, and blood flow is restored.
Indications for surgery
First, it is the size of the plaque. As a rule, it is prescribed if the plaque in the affected carotid artery blocks more than 70% of the total lumen. Such deposits were formed for several years, and the patient felt worse all this time. The patient's insensitivity to drug treatment can also be attributed to explicit indications. In other words, if taking the drugs did not give a result, then most often the doctor decides to treat the patient with surgical methods, which can be a real salvation for the patient. Also, an indication for surgical treatment can be considered an unstable state of the plaque, its uneven shell, which at any time can come off and cause irreparable harm. If the patient already has signs of a microinfarction or stroke, then the operation should not be delayed either.
Contraindications for surgical treatment
Unfortunately, most patients with this problem have, and this makes its own adjustments to surgical intervention. At first, the cardiologist tries to equalize the pressure. The inability to bring the patient's blood pressure to a stable state is a contraindication to the start of surgical treatment. Difficulty is also a violation of the heart rhythm.
Also, the operation should not be carried out during the period of inflammatory processes occurring in the body. In this case, the body may not respond adequately to the administration of drugs administered by the anesthetist. The presence of allergic reactions to the drugs administered during the operation is an unconditional factor in the cancellation of the procedure.
Balloon angioplasty followed by stenting is usually performed if endarterectomy is impossible for some reason. Also, angioplasty is not performed in the presence of any vascular disease that prevents the use of endovascular instruments. Finally, total vascular occlusion is also a direct contraindication to angioplasty with stenting. Severe looping and tortuosity of the vessels is a complicating factor for surgical treatment, and in this case, surgical intervention is best performed by an experienced specialist.
If the patient had a history of cerebral hemorrhage in the last two months, then the operation should also be postponed. They are not carried out for patients with Alzheimer's disease.
Thrombolysis can also be dangerous. The fact is that with incorrect manipulations by an inexperienced surgeon, they can lead to hemorrhage or rupture of capillaries.
Patient life after surgery
Compliance with the rules in the postoperative period can significantly improve the results, which the surgeon has done a lot to achieve. It is mandatory to prescribe drugs that thin the blood. By the way, the simplest aspirin does an excellent job with this, and it is he who usually appears in the recipe, or prescription sheet. Statins are also prescribed, which help slow the development of atherosclerosis.
Folk remedies
They can well complement complex treatment. Hirudotherapy has the best effect. By the way, treatment with leeches is now practiced in many cardiological centers. The saliva secreted by leeches significantly thins the blood. This method allows you to quickly remove the symptoms of poor health, which was the result of the formation of plaques in the carotid artery. The effect lasts for a very long time.
Some products help to normalize blood composition and reduce cholesterol plaques in the cervical spine. So, beet juice, added in small amounts to any drink, promotes the dissolution of lipid components and prevents them from forming stable spherical shapes in vessels.
The ether contained in onions and garlic also has a similar healing effect on the walls of blood vessels. By the way, only fresh products without the slightest heat treatment have this effect.
Normalizes the chemical composition of blood and honey. In the absence of an allergy to it, a person should take two teaspoons of honey per day. Pure sugar is recommended to be excluded from the diet.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and click Ctrl+Enter and we will fix it soon!
It is known that with atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels (carotid, subclavian arteries), their lumen narrows. This disrupts the blood supply not only to the organs of the neck, but also to the brain, which can ultimately lead to a stroke. Operations on the vascular apparatus of the cervical region can be prescribed if tumors are detected. Such a formidable disease as a stroke can be caused by stenosis (narrowing of the lumen) of the carotid arteries. One of the effective methods of treating the vascular system of the cervical region is the carotid arteries, which is designed to expand the lumen of the artery and resume normal blood flow.
In what cases are operations on the vessels of the cervical region prescribed?
A disease such as atherosclerosis of the vascular apparatus of the cervical region can provoke the formation of a stroke. The cervical arteries can be prone to the formation of pathologies such as tumors, blood clots, closed and open injuries, aneurysms and other disorders that provoke serious diseases, often resulting in death.
If an aneurysm of the arteries or their open mechanical damage is detected, an operation to restore the integrity and normal operation of the vessels can be performed unconditionally. Also, operations on the vascular apparatus of the cervical region can be prescribed in the case of:
- narrowing of the vascular lumen - stenosis, in which the patency of the blood flow is impaired (in violation of the patency of the artery in the range from 40 to 80%)
- violations of the state of the internal walls of the arteries and the detection of irregularities in them
- detection of atherosclerotic plaques
- thrombosis
- complete blockage of the carotid and subclavian arteries
- observations in patients with persistent vertigo and loss of vision
- detection of malignant and benign tumors (including tumors growing inside the arteries) with their further removal
Note that the carotid and subclavian arteries with atherosclerotic changes are at high risk of complete blockage, as well as the occurrence of thrombophlebitis. Operations performed on the vascular apparatus of the cervical region effectively relieve patients of complications after most diseases and help to avoid irreparable consequences.
Operations on the cervical arteries may have some contraindications, which include:
- the presence of an acute phase of coronary disease affecting the brain
- brain bleeding detection
Operations cannot be performed if the internal carotid artery is subject to complete blockage.
Advice: with frequent headaches and a sharp deterioration in vision, it is necessary to consult a doctor for the possible detection of vascular diseases.
Methods of examination of the vascular apparatus of the neck
Various methods allow to identify the pathologies of the vessels of the neck, which allow you to make the correct diagnosis in time, perform an operation or prescribe the necessary therapeutic treatment. These include:
- Angiography and MRI of the vascular apparatus of the cervical region allow the attending specialist to accurately determine the violations of the process of blood supply to the brain and organs of the cervical region. After examining the arteries in this way, you can get a complete picture of the disease. MRI may be prescribed for suspected: atherosclerosis of the vascular apparatus; tumors of various nature (with compression of the arteries and tumors, MRI is prescribed using contrast); vascular thrombosis; vasculitis (vascular inflammation).
- Angioscanning with ultrasound. Most often, the so-called is used, in which the doctor has the opportunity to assess the state of the cervical vascular system in a two-dimensional projection, so that you can find out what condition the walls of the arteries are in. Along with duplex, triplex scanning of the vessels of the neck can be used (a similar procedure that allows you to assess the nature of the vascular system in a three-dimensional projection). After angioscanning, it is possible to assess the nature of the elasticity of arteries and veins, to detect tumors (timely removal of the tumor can get rid of undesirable consequences and significantly prolong the life of the patient) and neoplasms, as well as anomalies in the course of the bloodstream.
- Doppler examination allows you to identify vascular pathologies and a number of diseases, such as encephalopathy, angiopathy, inflammation, arterial injury and atherosclerosis.
How is cervical artery stenosis treated?
If a stenosis is found in the subclavian artery, a carotid-subclavian bypass may be prescribed. The operation consists in creating an anastomosis between the carotid and subclavian arteries through a special shunt. After such a surgical procedure, blood can enter both the subclavian artery through a sewn-in shunt, and feed the brain through the carotid artery.
The lumen can be restored with the help of endarterectomy, in which the patient is first given anesthesia, and then access to the artery is provided through a small skin incision in the cervical region. After that, the plaque is removed from the artery and the blood flow is released.
Advice: allows you to restore the work of the cardiovascular system, which significantly reduces cholesterol in the body, and also improves metabolism
Vascular atherosclerosis can be eliminated by using carotid stenting combined with angioplasty. This surgical intervention is aimed at preventing plaques from entering the brain area. First, local anesthesia is performed, and then, through a puncture in the groin area, the doctor inserts a special catheter through the femoral artery.
The catheter moves along the vascular canal up to the site of narrowing in the area of the carotid artery, where a special self-expanding stent is implanted.
Thus, the plaque is pressed against the vascular wall and securely fixed by the stent. This technique does not allow the plaque or part of it to come off and enter the brain, while restoring blood flow and significantly reducing the risk of stroke.
These techniques completely restore the functions of the main arteries of the cervical region. In addition, the risk of recurrent stroke, coronary disease, as well as oxygen starvation of the brain, which can develop due to blockage of the vascular channels, is minimized.
Attention! The information on the site is presented by specialists, but is for informational purposes only and cannot be used for self-treatment. Be sure to consult a doctor!

