Tumor with leg injury treatment. Causes of injury
What to do with a leg injury Injuries happen suddenly, knock us out of the usual rhythm of life, and often we get lost in such situations.
What to do with a leg injury? - this question is often asked to a traumatologist (after all, it is traumatologists who treat bruises, sprains, fractures and other injuries).
Doctors define a bruise as soft tissue damage without breaking the integrity of the skin. Such an injury can occur when falling on a hard object or, conversely, from hitting a lower limb with a hard object.
A severe bruise is very easy to confuse with a more severe injury - a rupture of ligaments and muscles or a fracture. This is because the injuries are similar in basic features.
How does this injury manifest itself?
Here are the signs you need to be aware of:The main symptom of lower extremity impact is pain. It can be weak, and then it is enough for a person to lie down for several hours or just sit quietly, applying ice to the place of impact.
The next sign - swelling, or edema - does not appear immediately, but several hours after the bruise. This is the soft tissue response to impact.
If the blow was strong enough, small vessels burst and a hematoma (bruise) is formed. By the color of the bruise - doctors call the stages of "blooming" - you can determine the prescription of the injury.
 When the joint is hit, swelling appears after a few hours, it interferes with movement. Movement in the joint is difficult and causes severe pain.
When the joint is hit, swelling appears after a few hours, it interferes with movement. Movement in the joint is difficult and causes severe pain.
If the integrity of the skin is still broken (a blow is often accompanied by scratches and abrasions), then this can lead to the development of an infection in the wound.
A blow to the nail on the lower limb may be accompanied by a subungual hematoma (blood accumulates under the nail). After that, sometimes the nail can peel off and completely come off.
What to do if you hit the lower limb hard?
What definitely cannot be done if you hit the lower limb is rubbing it, warming the bruised area or stretching it.
You need to do the following:
- Provide rest, sit or lie down, but in no case continue to move
- Apply ice wrapped in a cloth or towel soaked in ice water. Cold helps reduce pain and prevents severe swelling from developing. However, you can not keep the ice at the site of impact for a long time, so as not to get frostbite on the tissues.
- If the impact is accompanied by a sprain, apply a tight fixing bandage.
- Take an analgesic and anti-inflammatory pill (you can use regular aspirin).
- Raise the limb so that it rests on a pillow or folded blanket.
- In case of severe pain and swelling, be sure to contact the traumatology.
Watch an interesting video about what to do with such an injury (orthopedist-traumatologist V.P. Karpinsky).
- this is a closed injury, accompanied by damage to the soft tissues of the lower limb, as a result of which blood flows from the damaged vessels into the subcutaneous tissue or into the muscles. Bruises on the surface of the skin are red, then purple, blue, green and yellow.
Most often, children suffer from bruises, as well as people who lead an active lifestyle and engage in hard physical labor. According to statistics, the fingers, foot and knee joint are most often affected.
Bruised hip
The thigh has many layers of muscles and pronounced subcutaneous tissue. Large nerves and vessels pass through this area. Therefore, with a bruise, extensive hemorrhage often occurs and a hematoma is formed.(limited cavity filled with blood). If left untreated, complications may occur:
- ossifying myositis, in which areas of ossification are formed in the place of hematomas in the muscles;
- Morel-Lavallee syndrome - detachment of subcutaneous tissue and skin due to spilled blood;
- case hypertensive syndrome - infringement of a group of muscles, as a result of which pressure arises in them, and the tissues undergo necrosis.
Symptoms
- An increase in the perimeter of the thigh, severe swelling and bruising.
- Pain on palpation. Pain can be local or diffuse, spreading over the entire surface of the thigh.
- Limited joint flexion due to severe pain. The support is preserved and lameness is observed.
- Over time, signs of inflammation and intoxication of the body may appear: an increase in lymph nodes, an increase in body temperature.
Causes
- A fall. Often during sports.
- Hit with a heavy blunt object.
- Traffic accident.
- Impacts during contact sports: wrestling, football, rugby, hockey, motorcycle racing.
Treatment
With a hip injury, it is necessary to stop leaning on the leg and give it an elevated position. Bandage the damaged area with an elastic bandage, making sure that the skin below the bandage does not turn blue. Cold should be applied to the site of injury for 10-15 minutes and in the next hour repeat this procedure 2 more times.. With severe pain, you can take an anesthetic (Bral, Ketonal, Analgin, etc.).
After providing first aid, you should consult a doctor who will conduct an examination in order to rule out a hip fracture. The specialist will feel the site of injury, bone prominences, check the pain of the axial load on the leg and the range of motion in the joint, and assess the irradiation of pain during movement. If a fracture is suspected, an x-ray is prescribed, and an MRI is indicated for a hematoma.
Treatment is conservative. Includes:
- Exclusion of any physical activity in the first 7-10 days after injury. It is recommended to walk as little as possible and keep the leg elevated (on a pillow or a bolster of a blanket). If there is swelling, then during the day a bandage of an elastic bandage is applied to the thigh, and it is removed at night.
- Taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nise, Celebrex, Movalis), which help relieve swelling and eliminate pain. The course of treatment is 5-7 days. If the pain is not intense, then it is enough to use local remedies: gels and ointments (Diklak, Febrofid, Fastum gel). They are applied 3 times a day for 10-12 days.
- Exercises. Performed 2-3 days after the injury. Prevent the development of joint stiffness and improve blood flow.
- Physiotherapy. Magnetotherapy, electrophoresis with potassium iodide and novocaine are prescribed from the 3rd day and contribute to the rapid resorption of hematomas. A week later, UHF, electromyostimulation, suction massage and warm baths are shown.
In severe hip injury, treatment is carried out in a hospital. For 2-2.5 weeks, bed rest is shown with the application of an oil-balsamic bandage, while the leg is in an elevated position on the Beler splint. Novocaine blockades are carried out according to the Vishnevsky method (every 5 days 3-4 times). You can return to physical activity after such treatment only after 2-3 months.
Surgical intervention is indicated in the presence of an extensive hematoma of the thigh with fluctuation in the damaged area. The hematoma is opened, blood clots and muscle detritus (masses resulting from tissue breakdown) are removed. Then the cavity is drained, antibiotics and painkillers are prescribed.
Shin bruise
On the lower leg, the muscles are less massive than on the thigh. Therefore, with a bruise, hematomas can form, but they are small and easily diagnosed. The faster the bruise appears, the closer it is to the surface of the skin. Hematomas in the periosteum or muscles can be detected only 2-3 days after the impact.
With a bruise, the anterior face of the tibia most often suffers due to its close location to the surface of the skin. Therefore, there is a possibility of developing periostitis - inflammation of the periosteum of the leg. In severe injuries, there is a risk of tissue detachment, in the long-term period - ossifying myositis (ossification of areas) and muscle fibrosis (replacing them with connective tissue).
Symptoms
- Pain in the injured area. It is characteristic that in the first two hours after the injury it subsides, and after 3 hours it gradually intensifies. This is due to increased swelling at the site of injury.
- Swelling, bruising on the skin.
- Restriction of movements. Limping may occur as pressure on the heel causes pain. Functional impairment occurs gradually, along with the development of hematoma and edema (unlike a fracture, in which it is impossible to step on the foot due to severe pain immediately after the injury).
- There is no shortening, bone crunch, deformity and pathological mobility, which indicates the absence of a fracture.
Causes
- A direct blow to the shin when playing sports or at home (hit on a bed, bench, etc.).
- Fall from a small height (including on ice).
Treatment
- In case of injury, it is necessary to ensure the rest of the limb (do not step on it). It is recommended to sit with a few pillows up to the leg to lift it higher. If there is a suspicion of a fracture, apply a splint and consult a doctor.
- On the first day, it is necessary to apply cold (for 20 minutes with an interval of the same duration) to stop internal bleeding.
- 3 days after the injury, thermal procedures (compresses and baths), application of an iodine mesh (0.25-0.5% solution: ordinary 5% iodine diluted with vodka or alcohol), anti-inflammatory and decongestant ointments, and Heparin are recommended on the skin. (in the absence of contraindications). If there is a bump, a massage course is shown.
In case of inflammation in the periosteum (periostitis), antibiotics are prescribed. With chronic and large hematomas, they are opened.
Hip injury
When bruised, soft tissues that are located near the greater trochanter suffer. Less often, the areas of the iliac crest, ischial tuberosity, or pubic bone branches are injured. Complications may develop:
- subcutaneous hematoma with its subsequent encapsulation or the formation of ossificates in its place (ossification areas in the muscles);
- detachments of the skin and subcutaneous adipose tissue (Morel-Lavalle syndrome);
- infringement of muscles in fascial beds (case syndrome);
- arthrosis (in the long term).
Symptoms
- Pain in soft tissues. When tapping on the greater trochanter, there is no sharp pain (unlike fractures).
- Movement is limited. Slight stiffness due to increased pain or lameness. Passive movements are possible in full (unlike fracture and dislocation). The support is maintained.
- Swelling and hemorrhage, which may sink to the thigh due to gravity. Rarely, hematomas develop gradually.
- With a bruise, unlike a fracture, there is no shortening of the leg and its forced position. By raising the leg in the supine position, the patient may lift the heel off the surface (negative sticky heel sign).
Causes
- Falling on the side or on the buttocks.
- Direct hit.
- Squeezing the pelvis with a load.
Athletes involved in contact sports are most at risk. Elderly people and ice skating enthusiasts often suffer from a bruised hip joint due to a fall when they lose their balance.
Treatment
After first aid (immobilization and cold), you should consult a doctor to clarify the diagnosis, because the symptoms of a contusion of the hip joint are similar to those of a fracture without displacement (fractures of the trochanters, impacted fractures of the femoral neck) and avulsion of bone tissue or muscle from bony prominences. To exclude such damage, MRI or radiography is performed, after which conservative treatment is prescribed:
- Ensuring rest of the limb and applying cold to the site of injury during the day. Taking painkillers (Pentalgin, Analgin, Ketorol).
- On the second day - semi-alcohol compresses in combination with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (tablets and ointments).
- After severe pain subsides, exercises should be performed to prevent joint stiffness.: slow flexion and extension of the leg in the ankle, knee and hip joints. You should lift your leg up, trying to make a "bike".
- After severe bruises, the recovery period includes physiotherapy (myostimulation, laser therapy, magnetotherapy, electrophoresis) and massage of the hip joint, lumbosacral region and the entire leg.
In case of detachment of soft tissues as a result of a severe injury, they are punctured, followed by the application of a pressure bandage. Large detachments are operated on by making a small incision, removing blood clots and draining the cavity with a rubber graduate or half-tube.
In case of encapsulation of hematomas, they are punctured with the removal of the contents. With the developed case syndrome, a dissection of the fascia is made, with ossification, the ossification sites are removed surgically.
Ankle and foot injury
Not only the soft tissues that surround the joint can be damaged, but also the periosteum, since the ankles are almost not protected by muscles and fatty tissue. Incorrect treatment tactics or its absence leads to complications:
- synovitis (fluid accumulation in the joint due to inflammation);
- hemarthrosis (blood in the joint, accumulated as a result of damage to its capsule);
- Zudek's syndrome (impaired blood flow and tissue nutrition, local osteoporosis);
- post-traumatic arthrosis, which develops months or years after a bruise with cartilage damage or as a result of repeated ankle bruises.
Symptoms
- Hemorrhage into soft tissues.
- Swelling of soft tissues is weak or moderate. Does not extend to the sole (as in a fracture).
- Perhaps numbness of the fingers and feet due to swelling.
- Walking is difficult due to the load on the distal part of the foot when rolling.
- Severe pain that occurs as a result of tissue tension due to hemorrhage into soft tissues, the subungual bed and the cavity of small joints.
- Absence of crepitus (crunchy sound), pathological mobility and pain when feeling ligaments and bones.
Causes
- Hit by a hard object or by falling.
- Falling on the foot of a heavy object.
Treatment
First aid, as with other bruises of the leg: immobilization, giving the leg an elevated position, applying a pressure bandage (starting from the toes), applying cold for 40-60 minutes. With severe pain, an anesthetic is indicated orally and intramuscularly.
Treatment is conservative. Tactics are as follows:
- On the first day after the bruise, the leg should be at rest. In the absence of severe pain, you can move short distances, after bandaging your leg with an elastic bandage. With severe bruises, the imposition of a plaster splint and immobilization of the joint for 7-10 days is indicated.
- From the second day, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ointments (Bystrum gel, Febrofid, Movaliz, Nise) are applied to the site of the bruise 3 times a day.
- On day 2-3, it is recommended to start massaging the lower leg and toes. With a decrease in pain and swelling for 5-6 days, a light joint massage should be done, combined with therapeutic exercises. In the sitting and lying position, bend and unbend the fingers and foot, make rotational movements in the ankle, slowly increasing the amplitude. These exercises are very important, as they prevent the occurrence of Zudeck's syndrome (circulatory disorders leading to joint stiffness).
- On the 5th-6th day after the bruise, thermal procedures are shown:
- foot baths (water temperature - 37 degrees) lasting 15-20 minutes;
- applying a heating pad with warm water or half-alcohol compresses for 1 hour;
- physiotherapy: UHF, potassium iodide electrophoresis, paraffin baths, magnetotherapy, etc.
In case of severe hemorrhage into the joint, to prevent the development of hemarthrosis, a puncture and removal of blood, sanitation of the joint with 0.5% or 1% novocaine solution is performed. It may be necessary to open a subungual hematoma (if any). The duration of treatment is 1-3 weeks.
Knee injury
Closed damage to the periarticular soft tissues. A knee injury can result in:
- Hemorrhage into the joint (hemarthrosis), in which its cavity and inversions are filled with blood. Occurs on the first day after injury.
- Accumulation of fluid in the capsule (synovitis). The complication appears 3-4 days after the bruise.
- The development of post-traumatic arthrosis (joint deformity) in the long term.
Symptoms
- Pain and swelling of the knee joint.
- Pain and limitation of movement. The ability to bend and unbend the knee is retained in full, but through pain.
- Bruising on the anterior and anterolateral surface of the joint.
- The support is preserved, but lameness may develop.
- Feeling the bony prominences is painless. Crunch and pathological mobility are absent.
- There may be an increase in the volume of the joint, a feeling of fullness, “balloting of the patella” (when you press on the patella, it sinks into the joint cavity until it stops against the bone). The leg is bent at the same time. All this indicates the development of complications - hemarthrosis and synovitis.
Causes
- Fall on a joint.
- Direct blow to the knee during sports or at home.
Treatment
If there is no pronounced hemorrhage, balloting of the patella, and it is possible to step on the foot, then it will be enough to follow the following recommendations:
- Limit physical activity and bandage the joint with an elastic bandage to reduce swelling. The bandage must be removed at night. It should be bandaged starting from the upper part of the lower leg and rising to the middle third of the thigh, while each subsequent round of the bandage should hide the previous one by a third.
- Raise the leg above body level and apply ice for 10-20 minutes, repeating the cold compress on the first day several times. This helps to prevent the appearance of a hematoma. A good effect is the use of NSAIDs in the form of ointments and gels.
- 2 days after the bruise, thermal procedures (half-alcohol compresses, a heating pad) are shown for 1 hour. Do it within a few days. With prolonged resorption of hemorrhage, you should consult a doctor who will prescribe phonophoresis with hydrocortisone, UHF or magnetotherapy.
The most common injury is a bruised foot. This pathology is characterized by damage to the soft tissues around the bones, without a serious violation of their functions and structure. It is quite easy to get such an injury: it is enough to get a weak blow, fall or drop something on your leg and you can get bruised.
When a bruise occurs, as a rule, damage occurs to the superficial blood and lymphatic vessels passing in the foot. In addition, muscles, ligaments or tendons can be affected. Due to the fact that the human foot is one of the most functional structures in terms of movement, it is this part of the body that is most susceptible to injury. The most common causes of soft tissue injury include:
- Hitting the foot with a hard object;
- Impact on a hard surface;
- Prolonged squeezing;
- Fall and bad landing on the foot.
Children are a special risk group: leading an active lifestyle, young people are most often faced with provoking factors. Such an injury is classified depending on where the impact occurred:
- Injury of the toes. This injury also occurs against the background of ordinary causes;
- Injury to the tissues of the dorsal side and sole of the foot.
Symptoms
Signs of this injury are typical for others:
- The appearance of pain in the damaged area. It occurs at the moment of injury and persists for a short time. Trying to move, the victim may complain that the patient is stepping on him. If you try to palpate the bruised surface, then the sensation of pain will intensify. The pain also intensifies against the background of pathological reflex muscle contraction;
- Edema formation. This symptom appears a few minutes after a blow to the foot. The skin at the site of injury becomes blue. In addition, edema has a destructive effect: increasing in volume, the swelling compresses neighboring areas, causing a destructive effect;
- Bruises of the foot are accompanied by a violation of the structure of the vessels: a bruise is formed. The volume of the hematoma depends on the degree of vascular damage;
- The injury site heats up rapidly. This is due to the strong blood flow to the site of impact;
- Restrictions in motor function;
- By damaging the passing nerve fibers, the victim may experience numbness of part or the whole foot.
How to distinguish a fracture from a bruised foot
With a fracture and bruising of the foot, there are both common and distinctive signs. Common manifestations include:
- The appearance of pain at the time of injury;
- The formation of edema at the site of injury;
- The presence of hemorrhages.
Distinctive features of these injuries:
- With a fracture, an external deformation of the bone is observed: it may be in an unnatural position for it. When bruised, the bones remain in place;
- With a fracture, there is a crunch sound directly during the violation of the integrity of the bone. The bruise is not accompanied by sounds;
- The fracture is followed by bony crepitus. This is especially heard during palpation of the affected tissues;
- It is especially easy to distinguish if the fracture is open. In this case, there is a gross violation of the skin, with visible bone fragments and severe bleeding. A bruise is a closed soft tissue injury.
It is important to remember that a closed incomplete fracture of a bone can resemble a sprain. With poor symptoms, it is difficult to find out whether it is a fracture or a bruise.
First aid
Timely implementation of a number of measures for foot injury helps to alleviate the current clinical picture and in the future will provide short-term rehabilitation. First aid actions include:
- Call an ambulance;
- Give the victim peace. The injured limb must be placed in a position in which the person will feel the least pain;
- Ice wrapped in a cloth should be applied to the injury site. If the bruise occurred at home and there is no ice, apply a bottle of cold water, a piece of frozen meat or frozen vegetables to the leg. The action of cold temperature relieves pain and stops the development of edema;
- If the child has hurt his foot, and in children the threshold of pain sensitivity is lower, he should be given an anesthetic tablet;
- The foot must be fixed. An elastic band is suitable for this. It must be remembered that the fabric must not be overtightened. Such fixation will reduce the degree of development of edema;
- In order for the inflammatory fluid not to accumulate at the site of the bruise, it is necessary to give the leg an elevated position above the heart.

Despite the distinctive differences between a bruise and a fracture, it is important to diagnose the affected foot. A closed fracture may hide under the shadow of a severe bruise. In a hospital setting, the doctor will prescribe an examination, conduct a differential diagnosis, make a diagnosis and prescribe specific therapy.
Swollen foot: what to do
If the foot is actively swollen, this is normal and should not be frightened. The development of edema accompanies any injury. However, such a phenomenon can cause discomfort and partially disrupt the structure of neighboring tissues. For the first few hours to remove the tumor, the following actions should be taken:
- Apply ice for 10-15 minutes;
- Wrap a tight bandage around the foot.
In the future, the swelling of the foot can be removed with the help of ointments and compresses. The next day, you can use warming compresses and products such as Fastum-gel or Finalgon. They also relieve pain.
Treatment at home
The use of the following folk remedies is effective:
- Mixing aloe and river sand. Proportions: 100 and 200 grams respectively. The substance is insisted during the day. It is necessary to smear 2-3 times a day;
- Vinegar. Two tablespoons of the liquid are mixed with one liter of water. In the resulting solution, the fabric is moistened and applied to the bruise;
- Warming and warming compresses from water, vodka and salt;
- Gently massage is recommended at home.

How long does it heal
The duration of the complete recovery of the injury depends on the location of the lesion, the type of injury and the extent of soft tissue damage. On average, a bruise heals in 2 weeks. With proper treatment - for a week.
User Rating: 5.00 / 5
5.00 of 5 - 1 votes
Thank you for rating this article. Published: 19 August 2017Injuries haunt a person all his life, and most often the legs suffer from blows. These are bruises, fractures, dislocations of the joints. The main characteristic of a leg injury is the absence or very slight damage to the skin. From our article, you will learn the main manifestations of this type of damage, differences from a fracture, the severity and conditions for immediate seeking medical help.
Shulepin Ivan Vladimirovich, traumatologist-orthopedist, highest qualification category
The total work experience is more than 25 years. In 1994 he graduated from the Moscow Institute of Medical and Social Rehabilitation, in 1997 he completed residency in the specialty "Traumatology and Orthopedics" at the Central Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics. N.N. Prifova.
The legs of a person are injured more often, as they experience the greatest load. The main reasons are related to everyday situations:

- Falling at home or on the street (often on ice).
- Impact on blunt objects (furniture in the interior, stairs).
- As a result of blows during sports.
- A car accident is never without bruising of the soft tissues of the legs.
Sometimes injuries occur at work., especially in people whose activities are associated with risk (builders, pilots, taxi drivers and others).
Varieties
Leg injuries are classified by location. Each type has its own flow characteristics. Consider the most common of them.
foot injury

It pursues all people leading an active lifestyle - children, athletes, outdoor enthusiasts. The tissues of the foot are often damaged when a heavy object falls, while the fingers suffer. A heel bruise is insidious in that it manifests itself in the same way as a cracked calcaneus. This is a serious injury that requires longer and more thorough treatment.
In this part, the legs are localized tendons, nerves, blood vessels and many small bones. It's always important to make sure they don't get hurt. This can only be done by seeking specialized help. A bruised foot always requires a consultation with a traumatologist.
Shin bruise
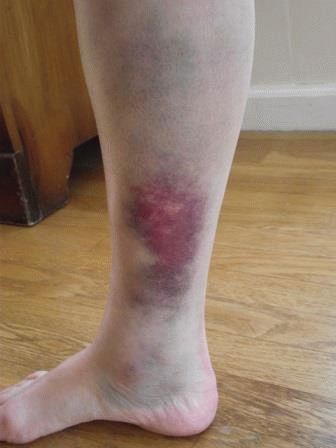
It is characterized by severe pain, as nerve fibers pass along the front surface of the lower leg. The periosteum, which has a huge number of nerve endings, is located very close to the surface, so even minor blows are very sensitive to the victim. Severe bruising of this part of the body can cause pain shock with loss of consciousness.
Such an injury should be distinguished from a fracture of the tibia, which is initially characterized by pain and swelling of greater intensity, deformity of the lower leg and complete dysfunction (a person cannot step on the injured leg at all).
Injury of the soft tissues of the leg

The leg contains some of the strongest muscles in the human body: the quadriceps femoris and the calf. Impacts lead to damage to blood vessels and hemorrhage into muscle tissue. If small vessels and capillaries are injured, the intensity of symptoms decreases rapidly, the prognosis is always favorable.
The danger is bruising of the soft tissues of the leg with a rupture of large vessels. Usually these are the strongest blows or prolonged compression, leading to necrosis of the muscle area and thrombosis of the vessels. The consequences for the patient are more serious: they require long-term treatment and often cause complications. It is not always possible to judge the severity of the condition by the size of the hematoma, since large arteries and veins are located in the deep layers, and the hemorrhage does not appear on the skin.
A bruise accompanied by swelling

Any injury is accompanied by swelling. But sometimes after a bruise, the leg swells up very much. Swelling of tissues comes to the fore and greatly worries the patient. In case of leg bruises with edema, more serious injuries are necessarily excluded: fracture and dislocation.
Manifestations of trauma
Most people have experienced symptoms of a bruised leg on themselves. Depending on the severity, they are either bright or, conversely, insignificant.
- Pain . Any injury is accompanied by pain. It is especially pronounced when hit by the front side of the lower leg. Often such injuries are combined with bruising of the bone, involvement of the periosteum and prolonged severe pain. At the first moment, this can lead to a painful shock with loss of consciousness. In the future, the intensity of the symptom decreases. This is a hallmark of a broken leg bone.
- Redness. A sign of a local inflammatory response that occurs in response to cell damage. In the first moments, the skin, on the contrary, may turn pale due to reflex vasospasm. Red color appears a little later. At the same time, the person discovers that the bruised area becomes hot.
- Hematoma. When the vessels are injured, part of the blood is poured into the tissues, forming areas of "bruises". Their appearance and gradual color change from blue to pale yellow is known to every person. Usually, small superficial hematomas do not pose a health hazard and resolve on their own. Severe bruises lead to rupture of deep vessels, hemorrhages not only in the muscles, but also in the cavity of the joints. Such hematomas may not be noticeable with a simple examination, but require serious treatment, up to surgery.
- Edema. According to the severity of this symptom, the severity of the patient's condition is assessed. It may be a slight swelling, which does not cause discomfort. Severe edema accompanies extensive tissue damage. If it captures the area of \u200b\u200bthe joints, then their mobility is completely or partially impaired. Edema compresses the surrounding tissues, increasing pain. According to the dynamics of the decrease in swelling, the effectiveness of the treatment is judged and the consequences of the injury are predicted.
- Impaired function. Depends on the severity. With light leg bruises, a person only limps a little. After severe ones, he cannot step on his foot at all.
In severe injuries, the general condition of the patient is disturbed. Weakness appears, body temperature may increase with massive crushing of soft tissues.
Diagnostics

Determining this type of injury is quite simple. This is usually done by the patient himself. The doctor needs to assess the severity of the damage and exclude bone fractures or joint dislocations that require a different treatment strategy. The clinical criteria for severity are:
- The intensity of the pain symptom.
- Severity of soft tissue edema.
- Joint involvement that always delays recovery.
- Bluish color of the skin not only at the site of injury, but also throughout the limb (it happens when crushed by a hematoma or swelling of large vessels).
- Change in skin temperature: cold, or, conversely, very hot.
The final point in the diagnosis puts x-ray examination. It is prescribed to all patients with a leg injury and shows the integrity or damage to the bones and tendons (even the slightest cracks in the periosteum or rupture of the articular ligaments are visible in the picture, which takes the injury to a completely different level of severity). In the table, we have collected criteria for distinguishing a leg injury from a fracture, which will help patients make a decision to urgently go to the emergency room.
| sign | Injury | fracture |
| Pain | Strong usually in the first hours after injury, then gradually decreases | Immediately strong, does not decrease, but increases over time |
| Edema | Small at first, builds up gradually | Severe swelling visible to the naked eye immediately forms |
| Hematoma | Dynamics similar to edema | Immediately extensive |
| Impaired function | Does not always accompany a bruise, may not intensify immediately, but as the edema increases | Complete loss immediately after injury |
| Limb deformity | No | In a displaced fracture, painful fragments protruding under the skin are found, the leg may be unnaturally twisted. On palpation, crepitus of bone fragments is felt |
| Symptom of longitudinal load (to determine it, the patient is asked to lean on the injured leg) | Soreness does not change, the patient stands independently on the injured leg | The pain increases sharply, the person cannot lean on the leg |
| X-ray changes | No | Typical for fractures |
Treatment of bruises of varying severity

The success of leg treatment largely depends on the correct actions in the first minutes after the injury. We will tell you what first aid should be provided to an injured person at home.
- injured laid in a horizontal position, the injured leg is slightly raised. This reduces tissue swelling.
- On the area of injury put on a tight bandage. It will fix the leg, which is especially important if a fracture or dislocation is suspected. To do this, use a regular or elastic bandage. The main thing is not to disrupt the microcirculation by rewinding too tightly. If, after a few minutes, the areas of the leg below the bandage turn blue, it is urgently removed and loosened.
- In case of minor damage to the skin (abrasions, scratches, shallow cuts), their treated with a disinfectant and covered with a bactericidal plaster.
- Help relieve pain and swelling, reduce hematoma cold compresses. Ice cubes, a bottle of cold water from the refrigerator are suitable for this, you can attach any cold objects that come to hand. It is important to do this in the first minutes after the injury in order to stimulate vasospasm and prevent hematoma and edema from spreading. Cold is kept on the leg for no more than 15 minutes. After two hours, repeat the procedure.
- If the patient is worried about severe pain, it is allowed to use light painkillers(analgin, paracetamol, ibuprofen). The decision to prescribe analgesic injections is made by the doctor after a complete diagnosis and exclusion of a fracture and dislocation.
Compliance with the described algorithm of actions helps to quickly cure a bruise and avoid serious consequences.
Traditional treatment for bruises
Only mild bruises, which are manifested by minor symptoms, do not require medical advice. In other cases, the victim should go to the emergency room.
Injuries in a child of any severity require the advice of a professional.
Treatment consists of the following activities:

- For the entire acute period, the patient prescribe rest- Walk less, rely on a cane. In case of severe bruises, especially on the back of the foot, a splint is applied.
- Used to treat pain and inflammation NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). With bruises of mild and moderate severity, they are applied topically in the form of ointments. In severe injuries, systemic drugs are prescribed. The most popular modern selective NSAIDs: Movalis, Celebrex, Nise, Arcoxia. They have a minimum of side effects.
- Thermal impact. Three days after injury when the risk of bleeding disappears, are prescribed thermal treatments to accelerate healing and resorption of the hematoma. Dry heat is used for bruises with swelling and extensive hematoma. Use a warm heating pad, paraffin applications, a blue lamp. The duration of the procedure is 40 minutes once a day (twice is allowed for large hematomas).
- Gymnastics is required, starting from 2-3 days after injury. Exercises are first done in a gentle mode, increasing the intensity as you recover. Gymnastics helps to avoid contractures in the joints, improves microcirculation and restores leg function after injury.
- Physiotherapy. Very effective in treating bruises. They allow you to quickly remove the swelling of soft tissues, reduce pain. The bruise is much faster and less likely to cause complications. Apply magnetotherapy, UHF, electrophoresis, laser therapy, amplipulse.
- Massage. Appointed after 7-10 days. Lymphatic drainage technique is prescribed if edema and large hematomas do not resolve on their own.
If the patient feels unpleasant symptoms (soreness, restriction of movement) or a lump persists on the leg, complications can be thought of.
Self-treatment at home
Most bruises are treated at home on their own according to the recommendations received from the doctor. Only physiotherapy and special massages require specialized assistance. Let's stop at common mistakes that patients with leg bruises make:
- Strong rubbing of the affected area. Such an effect only increases the bruise and can provoke thrombophlebitis.
- Too tight bandage, which reduces blood circulation and can lead to partial cell death.
- Rapid expansion of motor activity. It is better to take sick leave while recovering from an injury. If a person is actively stepping on the foot, it is advisable to apply a splint in order to limit the contraction of the injured muscles and movement in the joints as much as possible.
- Excessive addiction to painkillers. All of them have serious side effects that appear with the uncontrolled use of drugs.
- Active treatment with folk methods without consulting a doctor. So, many note the positive effect of alcohol compresses, which have a warming effect and quickly dissolve the hematoma. But it is important to remember about the concentration and time of continuous exposure. Otherwise, you may get skin burns.
Any folk method of treating leg bruises must first be “checked” in consultation with a traumatologist.
Treatment of induration after injury
If, after treatment of a bruise, a seal remains on the leg or a lump has formed inside the soft tissues that does not go away, you should urgently consult a doctor to identify the causes.
Most often, such residual effects are caused by complications of injury. Treatment is carried out only in a hospital, as surgical intervention and constant medical supervision are often required.
Complications of leg injuries
They occur with very severe injuries, improper treatment or concomitant diseases in humans, leading to a decrease in immunity and the ability of tissues to regenerate.
Calcification of the hematoma
This is a traumatic ossifying myositis, when, at the site of an extensive hematoma, part of the muscle tissue cells is not restored, but turns into bone cells. Then a seal is felt in the soft tissues. If it compresses the nerve endings, then this area can be very painful.
Thrombophlebitis

With a severe bruise of a vein in the leg, its elasticity is disturbed, the wall is injured, which creates the prerequisites for the formation of a blood clot. This is a very dangerous complication that can result in thromboembolism and death. The patient notes a small painful bump in the area of injury. In such cases, you need to urgently contact a traumatologist or vascular surgeon, who decides whether conservative resorption of the thrombus or surgical treatment is appropriate.
Abscess

With a decrease in immunity, large hematomas in the muscles can become infected with their own microflora, leading to the formation of abscesses. Most often they are localized on the calves or thigh. A person notes an increase in body temperature, severe pain, symptoms of intoxication. Treatment is carried out with antibiotics, surgical excision of damaged tissues with the creation of drainage, which ensures the outflow of pus.
Periostitis

Inflammation of the periosteum, which is often aseptic (without an infectious agent). Occurs on the anterior surface of the leg. It is characterized by severe pain, fever. The x-ray shows a small bump on the bone at the site of the bruise.
Long-term persistence of pain syndrome
This condition is observed when a person refuses rehabilitation measures. If a person does not step on his foot for a long time, the metabolism in all tissues (muscle, cartilage, bone) goes to a slower pace. After the resumption of loads, the cells of the legs do not cope with their function and begin to experience hypoxia. This causes pain in an already practically healthy leg. This is how chronic bruises or fractures behave. The main way to get rid of discomfort is to constantly increase the load.
The described complications with bruises are much less common than with fractures or dislocations. The prognosis of such an injury is more favorable. But this does not mean that a person can take leg bruises lightly. Non-compliance with medical recommendations, repeated trauma can lead to serious conditions and exclude a person from active life for a long time.
A set of exercises that will help you quickly recover from a leg injury
In everyday life, sometimes, there is such an annoying misfortune - traumatism. Bruises, as always, happen inopportunely, ruin our plans, spoil our nerves. But is it all that scary? Let's try to figure it out. We will give advice on how best to cope with a bruise and help the body heal itself.
Types of leg injuries
The most common leg injury is a bruise. Usually some part of the leg is injured: Thigh, Lower leg, Knee, Toe.
A bruise is a closed tissue injury (connective, muscular, nervous, vascular) without a bone fracture.
foot injury photo
As a result of an injury, you can get:
- Bruising only soft tissues;
- bruised bone;
- Joint injury.
With a bruise, the integrity of the skin is not violated, but the tissues lying under it can be significantly affected. There is a rupture of blood vessels, fatty tissue, connective fibers. This is accompanied by inflammation of a traumatic nature: pain, swelling, redness.
Stages of the post-traumatic process
- It begins with a local reaction of the body to a bruise - vasospasm, which is quickly replaced by expansion. Fluid from the bloodstream begins to seep into the interstitial space and impregnate the tissues. A bruised leg will give swelling, which will increase. Therefore, at this moment, cold is appropriate to constrict the vessels again and stop the tissue around the vessel from soaking.
- If a rupture of small and medium-sized vessels occurs, then the blood enters the surrounding tissues and stains them blue. Impregnation of nearby structures and the formation of bruising is a characteristic sign of a bruise. Blood will ooze from small vessels for 5–10 minutes, from large vessels for about a day. At first (three days) the site of the bruise with the presence of blood will be bluish-purple, then yellow blotches will appear and in a week the skin will clear up.
- If the blood only impregnates the surrounding tissues, we see a bruise, if it accumulates in them, a hematoma forms. It is dangerous by the progression of tissue stratification. This is rare because the muscles surrounding the bone are designed to withstand significant pressure and act as a shock absorber to protect the bone and periosteum.
- If the anterior surface of the lower leg is damaged, where the bone is not covered by muscle and lies immediately under the skin, severe pain is observed, and a hematoma quickly forms. Large hematomas require aspiration. For this, a puncture is used, if the blood is not extracted with a needle, then an autopsy is shown under local anesthesia. A pressure bandage is then applied.
- Also, blood can pour into the bags of the joints, forming hemarthrosis. Severe bruising of the leg can cause crushing or tissue necrosis.
Hip bruises. There is a lot of loose subcutaneous fat, so extensive hematomas can form. If the injury is strong and oblique, then the skin with fiber is torn off the fascia, cavities are formed. There is a lot of blood pouring out. In this case, the function of the limb suffers little. There is no pain at rest, it appears only when walking.
Bruises on the anterior surface of the leg very painful, especially in the area of the periosteum, up to loss of consciousness. It contains a large number of pain receptors. If the pain has taken on a constant pulsating character, this is a sure sign of a hematoma under the periosteum.
A bruised shin leg can be confused with a fracture due to severe pain, especially on palpation. It can be excluded by the absence of pain during the load along the axis (in the standing position). X-ray required.
Bruised toe. There is an opinion that this type of injury is not dangerous, and a person, despite the pain, continues his work. Bruising of the toes usually occurs in motion, sometimes at considerable speed, so the fingers receive a strong blow.
Small, fragile bones and tendons do not withstand and are damaged - this threatens to complication when walking in the future. Therefore, do not neglect a medical examination to exclude a fracture. And only then carry out the necessary course of treatment.
A bruised thumb is especially unpleasant, because it will take much longer to fully recover, which can take up to 6 weeks. The main condition is peace and time. In order not to say later: “here I hurt my toe, and problems began, now I need orthopedic shoes.”
Symptoms accompanying a leg injury

A bruise is characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain;
- swelling (edema);
- seal;
- inflammation with redness;
- movement restriction.
The first symptom of a bruise is pain. Then there is swelling. The pain usually gets worse when walking. A few days of rest and restriction of motor activity, involving the injured area, lead to a weakening of the manifestations of symptoms and the person recovers. This is if we are dealing with a slight leg injury.
The situation is more complicated when the vessels are damaged. In this case, a severe bruise of the leg is accompanied by a hematoma. Its dimensions depend on the force of impact. In this case, the terms of compliance with the rest regimen and careful attitude to the limb increase. Swelling and soreness persist for up to a month.
First aid for bruises at home
Since ordinary bruises are treated on their own, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Provide complete peace;
- Raise a limb
- The first two hours are cold;
- A day later, thermal compresses, ointments, gels;
- Painkillers (in case of severe pain);
- Seek medical attention if unable to move;
- Movements are possible only with the help of a cane and fixation with an elastic bandage (to reduce the load).
Physiotherapy helps to relieve a bruised leg. This should be taken advantage of as soon as possible. UHF and electrophoresis have not lost their significance. If pharmacies have therapeutic mud, then a weekly course will be very useful.

Thermal procedures, absorbable and anti-inflammatory drugs do well with this. Heating pads with hot water, paraffin are suitable as heat. We remove inflammation and swelling with ointments, gels, alcohol compresses.
They are applied four times a day, liberally covering the injured area. It is also important to follow a simple principle: the more puffiness, the thicker the layer of ointment.
The ointments used should be with a different mechanism of action: anti-inflammatory, decongestant (heparin-containing) and absorbable (Traumeel, Zeel T). You can combine ointments: Ketorol gel, Dolobene.
Ointment is not used if the skin is damaged. Severe tissue swelling makes it difficult for the drug to penetrate deep into. To enhance the effect, we increase the amount of the drug applied to the skin and the frequency of lubrication.
Approximate treatment regimen: "Fastum" gel, "diclofenac" ointment or "ketorol" gel is applied to intact skin, it can be wrapped with cling film and fixed, so we will increase the depth of penetration and the strength of the impact.
After 4 hours, remove the bandage, wipe the place and apply another ointment "Lioton", "Troxevasin" - to relieve swelling. So we alternate during the day. At least 4 times a day.
If the hematoma is large, then the body is fenced off from it. Creates a dense film (a bag is formed). Then you can not do without the help of a doctor. The hematoma is opened, and the contents are removed.
Possible consequences and prognosis
With bruises with or without bruising, the prognosis is favorable. Time, rest, and simple healing actions will quickly remove the consequences. This is within the power of the body. He alone can handle it. Our task is to help him reasonably in this.
The situation is more complicated when hematomas occur. The larger it is, the longer the resorption period. It compresses the nerve trunks, blood vessels, suppuration occurs due to the attachment of an infection. Time in this case does not bring relief, pain and swelling do not go away, fever joins. Need help from a surgeon.
With very severe bruises, necrosis (necrosis) of tissues may occur and emergency care will be required.
Another unpleasant complication is periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum). That is why a bruise of the lower leg in the periosteal region is not only painful, but also dangerous.
Alertness should cause bruises of the leg joint. Its complex structure predisposes to various complications: hemarthrosis, ligament rupture, damage to the joint capsule.

How to distinguish a severe leg injury from a fracture?
A severe bruise can be confused with a fracture. You can often hear that your leg has been hurt and it is swollen. What is it, isn't it a fracture? You can try to determine the signs of a fracture yourself.
It is typical for him:
- The presence of vegetative symptoms: darkening in the eyes, dizziness, tachycardia. Which indicates the involvement of the whole organism in the process with the release of stress hormones.
- Displacement of bones along the axis. The leg may be arched at an unnatural angle. Especially noticeable in the first minutes of the injury. Then there is swelling and it is difficult to see any displacement.
- Pain and swelling are increasing all the time.
- The leg cannot be moved. It is impossible to step on it, let alone move.
When bruised, a person can move the leg, although this is painful. This sign indicates the integrity of the bone.
How dangerous is an injury?
An ordinary bruise is not dangerous to health, it only causes inconvenience. Fear is caused by severe bruises, in which it is easy to miss a rupture of the ligaments, a fracture of the toes. They are fraught with partial loss of function in the future. If the knee joint is injured, arthrosis can quickly appear.
A massive hematoma and an open wound threatens with infection. In any case, if the pain during a bruise increases every day or stays at the same level, then a doctor's examination and x-rays are required.
I hurt my leg, what to smear?
If there is confidence that there is a bruise, then after a cold, the leg can be lubricated with Fastum gel, Ketoprofen, Nise gel, Diklak, Diclofenac 5% ointment, Olfen gel. All of them have a strong analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. The tumor after a leg injury will quickly subside if treated with Lyoton ointment.
It should be remembered that anesthesia allows you to load the sore leg, and this is not desirable. Therefore, after applying the ointment, the leg needs rest.

