Treatment of capillary circulation disorders. Symptoms of peripheral circulatory disorders. Patients whose symptoms of intermittent claudication cannot be controlled with medications.
Blood circulation in the body is a continuous process. It is necessary to provide the organs and systems of the body with oxygen and nutrients. Also, with the help of the bloodstream, substances formed as a result of metabolic processes of cellular activity are also eliminated.
Poor blood circulation in the extremities is diagnosed when the vessels are unable to provide adequate nutrition to the tissues. This can be understood if there are characteristic symptoms: tingling in the fingers, numbness, trophic changes in the skin.
The abdominal venous system is responsible for collecting nutrients, absorbed in the digestive tract. Its veins converge and form the portal vein, penetrating through the suprajepanal vein or inferior vena cava, where the blood undergoes a series of transformations before reaching the liver. In other words, the liver acts as a true filter between digestive tract and heart.
Oxidized blood follows a path through the pulmonary veins, reaching the left atrium, passing through the left ventricle and into the body through the aortic artery. The distribution of blood from the heart to the entire body is called the systemic circulation or systemic circulation. Blood cannot return from the left ventricle to the left atrium due to the presence of the mitral valve.
Circulatory disorders are divided into acute and chronic, slowly increasing. If you start treatment on time, noticing the first signs pathological changes vessels, blood supply function can be normalized.
Symptoms of peripheral circulatory disorders
On the signs poor circulation in the arms and legs the following factors indicate:
There are four pulmonary veins, superior right, inferior right, superior left and inferior left, which collect venous blood from the lungs. The pulmonary veins are an exception in the venous system as they are the only ones that carry oxygenated blood.
Sources: Lopez, Sonia and Rosso, Sergio. Strong Biloba is a relic tree based on drugs, the only representative of the Ginkgoales class is Ginkgo biloba. Components due to the formation of a plant part, the drug has noticeable nootropic activity, improves cerebral and peripheral circulation, microcirculation, toned veins and reduces permeability blood vessels, has a strong antihypoxic effect, improves blood condition and reduces the tendency of thrombosis.
- the feeling of freezing of the limbs not only in the cold season, but also in the heat;
- crawling sensation;
- periodically there is a tingling sensation in the fingers;
- numbness of the limbs occurs;
- their hair begins to fall out;
- the skin color of the extremities becomes pale to blue;
- nails peel and often break;
- erectile function disappears;
- small wounds on the skin of the extremities take a long time to heal, begin to fester, and ulcers form.
Even with constant application of cream, the skin becomes dry, cosmetics the problem cannot be solved.
The composition of ginkgo biloba is flavone glycosides, terpenolactones, organic acids and amino acids; Waxes, steroid compounds, essential oils, alkaloids, vitamins; micro - and macroelements. Pharmacological effects Biloba Forte. Under the influence of the following strong central processes, biloba are nervous system.
Stimulating the synthesis of certain neurotransmitters and inhibiting the absorption of another effect develops nootric and antidepressant; Improved memory status and increased ability to learning; stabilizes and slightly improves memory, attention and psychomotor functions, optimizes the electrical activity of the brain, slows down the development of dementia in Alzheimer's disease. When peripheral disorders blood circulation significantly influence blood flow in atherosclerotic and diabetic vascular lesions, Various types retinopathy and other forms of chronic ischemic damage fabrics.
Poor blood circulation in the extremities is caused by the following reasons:
- Damage to blood vessels due to trauma
- Violation general regime nutrition.
- Smoking.
- Chronic illnesses that interfere with work endocrine system– for example, diabetes.
- Hypertonic disease.
- Violation biochemical composition blood, especially cholesterol levels.

Release and composition form
In addition to these effects, the drug has positive influence for potency. Strong biloba is available in pink capsules containing brown powder. Ginkgo biloba leaf extract - 80 mg; Various adjuvants. . The medicine belongs to the angioprotective group made from plant material, subject to medication prescription.
Encephalopathy of various origins, which is a consequence of stroke, traumatic brain injury, age-related changes, in which memory is impaired, attention is reduced, and mental capacity; Disorders of peripheral blood flow and microcirculation; dizziness, ringing in the ears or loss and development of other diseases of the neurovascular system; Degeneration macular spot associated with age-related changes; Retinopathy arose with diabetes mellitus. Biloba Forte is contraindicated.
When initial symptoms poor blood circulation in peripheral organs, treatment must be started, otherwise the condition may cause unpleasant consequences.
Slow blood circulation increases the risk of trophic ulcers, can provoke the onset of a gangrenous state. Ulcers occur especially often in people with diabetes. Tight underwear, uncomfortable shoes– and the abrasion turns into a purulent-inflammatory process.
Hypersensitivity to the active agent or other components of the drug; Tendency to increase coagulation; as erosive gastritis; In exacerbations gastrointestinal ulcers; acute disorders cerebral circulation; Acute myocardial infarction myocardium; lactose intolerance; up to 18 years old. The dose of the drug is selected depending on the disease.
When encephalopathy receives a capsule 1-3 times a day; For violations peripheral circulation, sensory function, macular degeneration and retinopathy of the drug occurs morning and evening, capsule. Improvement is observed within a month after taking the drug. The course of treatment should be at least 3 months. If you want, repeat, you should see a doctor.
Most dangerous consequences– the occurrence of critical ischemia of the lower extremities. A symptom of the disease is swelling of the fingers, which is difficult to eliminate.
Poor circulation in the hands indicates that the blood supply is compromised of cardio-vascular system. Numbness of the hands often appears against the background of pain in the chest, tingling of the heart, and during shortness of breath.
Targeting and specific drug interactions
Gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea; Central nervous system: dizziness, headache, sleep disorders; Hypersensitivity: itching, mild tumor, redness; Blood system: decreased coagulation; possible loss hearing Development allergic reaction on medicine must be stopped; repeats during negative consequences, you need to contact a specialist; Bleeding tendency, anticoagulant or antiplatelet agents, preparation for surgical interventions, should inform your doctor about taking a strong biloba; You cannot take a drug with a tendency to dye allergies; if you have lactose intolerance and related pathologies, it is not recommended to take the drug; The drug may affect the reaction rate during operation at high concentration, caution must be exercised. Producer: Willmar Schwabe; Tanakan is an analogue of French origin. Unlike other products that have liquid dosage form, in the form of a solution for internal use with a dosing pipette.
Storage conditions
- It has the same signs and contraindications as Biloba Forte.
- Dosage active substance is 40 mg.
A blood supply disorder is diagnosed based on clinical picture and special diagnostics.
Helps identify the problem following methods research:
- Ultrasound of veins and arteries;
- UZDS;
- CT scan;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- contrast venography;
- scintigraphy.
The necessary examination methods are selected by the doctor based on the clinic and the patient’s capabilities. If the patient has a pacemaker, wave examinations are not performed.
Storage media are recommended in original packaging. Do not use after expiration date. Dietary Vascular Surgical Society. Internal medicine V clinical practice. A 76-year-old smoker and patient with hypertension asked for medical care due to discomfort in the left calf during outpatients, which began about a year ago and is relieved after rest. The patient reports worsening last weeks, limiting her daily activities, including episodes of night pain.
When was it carried out? clinical examination, the left lower extremity was found to have no impulses with slow capillary refill, hypertrophic nails and slight decrease temperature relative to the contralateral limb. Additional research using Doppler ultrasonography showed the absence of flow in the left outer iliac artery and single-phase waves with low amplitude in the femoral segment and in the arteries of the left leg. Arteriography followed by percutaneous transluminal angioplasty with stent implantation in the left external iliac artery is indicated.
Treatment of peripheral circulatory disorders
What to do if you experience symptoms of poor circulation lower limbs? Most likely, this is the beginning of varicose veins and you should contact a phlebologist.
In order to stop the development of the disease, the following drugs are prescribed:

Lower extremity ischemia can be classified as functional or critical. Functional ischemia occurs when arterial flow is insufficient during exercise and clinically presents as intermittent claudication. In critical ischemia, there is a decrease in arterial flow even at rest and is defined as the presence of pain at rest or trophic lesions lower extremities. In this latter situation, there is a risk of limb loss if adequate arterial flow is not restored by surgery or endovascular intervention.
- Venotonic drugs used orally and externally. They strengthen the venous walls and increase their tone.
- Heparin-containing drugs may also be local action and be assigned to internal use. With their help, the composition of the blood and its coagulability change.
- Venolife, a drug that combines the properties of heparin-containing and venotonic drugs, has proven to be effective. In addition, it contains vitamin B5. Venoline helps treat numbness, remove swelling and relieve external manifestations of impaired blood supply - and changes in its color. This quality of the drug is very much appreciated by women.
For treatment varicose veins massage effects and physiotherapy are included: magnetic therapy, pneumocompression. Special compression garments help reduce pain
The pathophysiological mechanism of arterial ischemia is based on the presence of stenosis, which progresses to arterial occlusion, which leads to the development to a greater or lesser extent collateral vessels. If there is a sudden imbalance between needs peripheral tissue and blood supply, in case atherosclerotic plaque, a situation of acute ischemia of thrombotic origin arises. However, due to the presence of collateral circulation, ischemia is better tolerated than acute events associated with arterial embolism.
What to do if your hands constantly swell and hurt? The best remedy to combat hand numbness - underwater massage.
Traditional medicine in the treatment of peripheral blood supply
To combat impaired peripheral blood supply in the piggy bank traditional medicine there are many recipes.
The following procedure effectively helps restore blood supply to the arms and legs:
Digital subtraction angiography with post-site occlusion of the left external iliac artery. Its prevalence has been determined in several epidemiological studies due to the occurrence of intermittent claudication as a symptomatic disease marker or abnormal index systolic pressure ankle test, the most commonly used non-invasive test.
They are more common than ischemic events in the lower extremities, both asymptomatic and symptomatic. 
Patients may describe the symptom as muscle fatigue, tenderness, or even cramps during physical exercise, usually placing the calf, but ultimately the thighs or buttocks.

- mix sugar and sunflower oil in equal quantities;
- prepare a container with hot water, 250 ml – 2 tablespoons of table salt;
- Anoint the skin with a mixture of butter and sugar, lower the limb into saline solution– its initial temperature should be about 38ºС;
- keep the limb in water for 30-45 minutes.
This medicine will help restore blood supply to the legs and arms. A quarter-liter jar is filled with crushed garlic, filled with water and placed in a dark, cool place for 2 weeks. The composition must be stirred a couple of times a day. When the product is infused, it is filtered and placed in the refrigerator. Take 3 times a day, 5 drops, diluted in a tablespoon of water. The course of treatment is 10-14 days.
The patient reports typical chronic ischemic pain at rest or presents with ischemic skin lesions, whether ulcers, necrosis plaques or gangrene. This term is usually reserved for patients with chronic disease, defined by the presence of symptoms for more than two weeks. Observational studies of patients with critical ischemia who are not candidates for revascularization indicate that at one year only 50% of these patients will be alive without amputation, 25% will be dead, and another 25% will have had an amputation1.
Such data is alarming because the forecast is similar to that of many malignant neoplasms. Acute ischemia is conceptualized as any sudden decrease in arterial circulation to one extremity with a potential risk to its viability. The clinical history should include symptoms related to the presence and severity of acute ischemia, as well as a previous history of claudication, previous percutaneous surgical or surgical interventions And concomitant diseases. The presence of paralysis is a sign of poor prognosis.
Another bath is herbal. It is made from equal parts of chamomile, nettle, oregano, and lemon balm. Pour 2 cups of herbal raw material into 3 liters of boiling water, wait until it cools down to 38ºC, and place your hands or feet in the bath.
Prevention of blood supply disorders

Muscle stiffness, swelling, or pain with passive movement is late signs developed ischemia and probable tissue necrosis. Patients with suspected acute ischemia should be assessed immediately vascular surgeon and, if indicated, revascularize as nerve and muscle damage occurs within hours.
Initial estimate includes clinical history and a physical examination, which includes assessing the feet for signs of acute or chronic ischemia, palpation of all peripheral impulses and examination of noise in femoral arteries regarding hair loss, color and trophic changes Skin. The abdomen should be assessed for evidence of murmurs or a pulsating mass. Peripheral impulses should also be assessed upper limbs, as well as the presence of murmurs in carotid arteries. Arterial pressure should be measured in both hands.
To improve the condition peripheral vessels limbs, they require dosed physical exercise. For the legs it is hiking at a moderate pace, for the arms - gymnastics. If you have to constantly type or do monotonous work, you need to stop every 45 minutes.
Must be followed special diet, bring the diet closer to dietary table according to Pevzner No. 9 and 10. Limit alcohol consumption, try to get rid of smoking.
The consequences of impaired peripheral blood supply are not only limitation of their function, pain during movement and at rest.
If a blood clot breaks off in the lower extremities, cerebral vessels may be damaged. And this is fraught with such serious illness as ischemic stroke.
Pathologies of the circulatory system, classified in pathophysiology as hemodiscirculatory processes, arise due to changes in the properties and volume of blood in vascular bed. In some pathologies of the circulatory system, blood flows outside the vessels. In addition to hyperemia, ischemia and stasis, the main types of circulatory disorders include sludge, thrombosis and embolism.
Arterial and venous circulation disorders: symptoms and causes
Pathologies such as circulatory disorders are divided into central, developing due to heart pathology, and peripheral, arising due to vascular pathology.
The main peripheral circulatory disorders are:
- hyperemia (arterial and venous) - increased blood supply to the tissue;
- ischemia - a decrease in blood supply to an organ or tissue;
- stasis - cessation of blood flow in organs and tissues.
Circulatory disorders can be of an arterial or venous nature.
Arterial hyperemia
Arterial hyperemia- this is an increase in the blood supply to an organ due to an increase in the amount of blood flowing through its dilated vessels. There are physiological hyperemia, which occurs normally with increased organ function, and also reflexively under the influence of ultraviolet rays, cold, heat, etc., and pathological hyperemia, which occurs in the following cases:
- with inflammation;
- rapid decompression of compressed vessels (for example, when emptying abdominal cavity from the accumulation of ascitic fluid);
- creating a rarefied space (vacuum hyperemia) - for example, when using medical cups;
- overload or drug blockade constricting blood vessels sympathetic nerves(neuroparalytic hyperemia).
Clinically, such a circulatory disorder as arterial hyperemia is manifested by redness of tissues and local promotion their temperatures.
Venous hyperemia
Venous (congestive) hyperemia- an increase in blood supply to a tissue area with a decrease in the amount of flowing blood.
The causes of such circulatory disorders as venous hyperemia are:
- thrombosis or compression of veins from the outside (tumor, scars, pregnant uterus, during surgical ligation of a vessel);
- stagnation and slowing of blood flow in the veins of the lower body with a decrease in the pumping function of the heart (right ventricular heart failure);
- blood stagnation in the lower extremities in people who work for a long time while standing.
Clinical symptoms of circulatory disorders (venous hyperemia) are bluish coloration of tissues, or cyanosis, and the pathology may be accompanied by edema.
Pathologies of the circulatory system: stasis and sludge
Pathologies of peripheral circulation also include disorders such as stasis and sludge.
Stasis
Stasis is a type of circulatory disorder in which local blood flow stops in the small vessels, mainly capillaries.
The cause of this circulatory disorder is a complete cessation of blood flow. Stasis can also occur due to sudden violation outflow of blood, as well as due to various diseases of an inflammatory and non-inflammatory nature (true capillary stasis), leading to intracapillary crowding (aggregation) of red blood cells and stopping capillary blood flow.
Stasis can be reversible or irreversible (in this case, blood flow is not restored, and necrosis occurs in the corresponding area of tissue). External manifestation This circulatory disorder results in a “marbled” coloration on the skin.
Sludge
Sludge (sludge syndrome)- this is a blood condition based on aggregation (crowding) of red blood cells (their extreme degree aggregation). With sludge, the boundaries between individual red blood cells become difficult to distinguish.
Main features of blood sludge: sticking to each other shaped elements and an increase in plasma viscosity, which leads to a state of blood in which it becomes difficult to flow through small-caliber vessels.
Manifestations of circulatory disorders: ischemia
 When talking about the symptoms and causes of circulatory disorders, ischemia is considered separately.
When talking about the symptoms and causes of circulatory disorders, ischemia is considered separately.
Ischemia is the reduced blood supply to any area of tissue due to the weakening or cessation of blood flow to it through the arteries.
Causes of ischemia:
- compression of the artery (tourniquet, tumor, scar, foreign body, surgical ligation of the vessel);
- blockage of an artery (thrombus, embolus, narrowing of the lumen of the artery due to vascular diseases);
- reflex ischemia (painful, visual, sound, chemical, emotional stimuli, etc.).
Clinical manifestations of ischemia depend on the location of the ischemic area. Thus, a sign of circulatory disorders, ischemia of the limbs, is their pallor, a feeling of numbness, “pins and needles”, pain, and impaired limb function. With ischemia of the heart muscle, pain occurs, and with ischemia of the brain, one or another neurological symptoms occur.
The outcomes of ischemia depend not only on the location, but also on the diameter of the switched off vessel and on the degree of development of collateral (roundabout) circulation in this area. At favorable outcome the blood supply to the ischemic area is restored; in case of an unfavorable outcome, an area of tissue necrosis occurs - a heart attack. There are: white infarction, occurring in the myocardium, kidney, brain; red infarction when the dead area of tissue becomes saturated venous blood penetrating through highly permeable vascular walls (can occur in the lung, brain, intestinal wall); white infarction with a hemorrhagic rim, in which the white zone of necrosis is surrounded by a zone of hemorrhage due to the fact that vascular spasm at the periphery of the infarction is replaced by their dilation with blood leaking through their walls.
The usefulness of collateral (roundabout) circulation depends on anatomical features blood supply to the ischemic area (main or branched type of blood supply), conditions vascular wall, cardiac conditions and nerve regulators blood circulation There are functionally absolutely sufficient and functionally insufficient (absolutely and relatively) collaterals. This, accordingly, influences the nature of the outcome of ischemia.
Circulatory system disorders: thrombosis and embolism
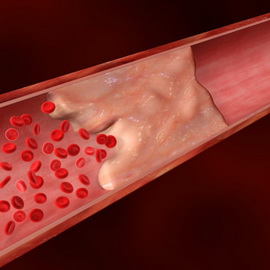 Next, circulatory disorders such as thrombosis and embolism will be considered.
Next, circulatory disorders such as thrombosis and embolism will be considered.
Thrombosis
Thrombosis is the intravital coagulation of blood or lymph in the lumen of a vessel with partial or complete blockage, leading to disruption of blood flow.
The mechanism of thrombus formation consists of a combination of three factors (Virchow’s triad):
- slowing blood flow;
- damage to the vascular wall;
- increased blood clotting.
Vein thrombosis is also called phlebothrombosis. If thrombosis is combined with inflammation of the vein wall, then they speak of thrombophlebitis. If there is a combination of thrombosis of an artery with inflammation of its wall, this is called thromboarteritis. Symptoms of a circulatory disorder called deep vein thrombosis include pain, swelling and redness of the affected area.
Embolism
An embolism is a blockage of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels particles carried by blood or lymph flow. These particles are called emboli.
Distinguish the following types embolism:
- thromboembolism - embolism by a migrated fragment of a thrombus;
- tissue and cellular embolism - embolism in tissue areas due to organ injury, tumor cells and so on.;
- fat embolism - blockage of blood vessels with drops of fat, most often due to fractures of long tubular bones;
- gas embolism (a variant of this is air embolism) - blockage of blood vessels by gas bubbles, for example, bubbles of nitrogen dissolved in the blood during decompression sickness in divers;
- bacterial embolism - blockage of blood vessels by bacterial conglomerates during various diseases(for example, in acute hematogenous osteomyelitis);
- embolism by a foreign body (for example, a bullet, a shell fragment).
If the embolus, due to gravity, falls from top to bottom against the direction of blood flow, then they speak of a retrograde embolism. If the embolus is from venous system enters the arterial through the patent septum between the left and right atrium, then this embolism is called paradoxical.
Thrombosis and embolism arterial vessels lead to ischemia of the blood supply areas of these vessels. Vein thrombosis leads to venous stagnation in the zones venous outflow of this vessel.
The fate of the blood clot may vary. The blood clot may grow over time connective tissue(organization of a blood clot), partially or completely dissolve (recanalization of a blood clot), and also undergo purulent melting.
This article has been read 1,553 times.

