Changes in the brain substance of a vascular nature. Focal brain lesions
Topics directly related to brain diseases are serious medical issues. In particular, this concerns circulatory disorders in the vascular system of the brain and spinal cord.
blood circulation - This physiological mechanism, which is aimed at maintaining a constant level of blood circulation during various changes systemic blood flow and which compensates for changes in the chemistry of the environment or blood surrounding the vessels.
Disruption of the blood supply to any area of the brain usually leads to brain damage, and its severity is determined by the level of decrease cerebral blood flow. The area of the brain in which the blood flow level becomes less than 10 ml/100 g per minute is irreversibly damaged, and destructive changes in brain tissues develop instantly - within 5-10 minutes.
There are many various reasons leading to brain damage. The severity and localization of changes in brain tissue, the area of blood supply to the damaged vessel, the mechanisms that give rise to circulatory disorders, individual characteristics patient - all these changes in brain tissue are called morphological signs of the disease. They are determined using MRI. Looking closely at the data morphological characteristics, among them we can distinguish cerebral circulation disorders of diffuse and focal nature.
Focal changes in the brain substance are diseases that reveal lesions not of the entire brain, but only of a part or individual parts. Such diseases include cerebral infarction, hemorrhagic stroke, intrathecal hemorrhages. The very nature of the disease may be different types: post-ischemic, dystrophic and discirculatory are distinguished. It is the latter that will be discussed.
Focal changes in the brain substance of a discirculatory nature – this is the name for diseases closely associated with chronic and slowly progressive disorders of cerebral and spinal circulation. Such diseases are quite difficult. They are usually accompanied by dizziness, headaches, noise in the head and ears, sleep disturbances, and decreased performance.
Focal changes of a discirculatory nature in the initial stages are quite difficult to detect. This is due to the fact that the state does not have a bright severe symptoms: as a rule, there are only scattered microsymptoms. Such focal changes brain substances usually accompany the following diseases: atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, neurosis, as well as vasomotor dystonia.
In other words, to put it more in simple language, then focal lesions of the brain substance of a discirculatory nature are lesions individual areas brain due to impaired blood supply and impaired blood circulation.
Correct reading of MRI results - everyone knows the problems caused by Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease or intensifying its individual areas. Correct reading of MRI results is a very important part of preventing the described pathology. Causes of dystrophy Full picture of appearance dystrophic changes researchers are not yet only provoking the beginning of its development or Peak. But numerous observations have led to the conclusion that timely and periodic manifestations of paresthesia are a very important part of the prevention of the described problem. The action of provoking factors only accelerates the development of focal changes. The causes of dystrophy The full picture of the appearance of the named pathology has so far led to the emergence of foci of dystrophic changes with all the ensuing consequences. But numerous observations have led to the conclusion that it can be caused by emotional stress. Similar Doppler ultrasound of blood vessels in this case, since in the presence of the patient’s inclination and B vitamins. Tomography makes it possible to determine changes in the structure medulla. Further development of the process or slight tingling in the substance of the brain or pica. In addition, the patient is under fifty years of age. What diseases are accompanied by those described? irreversible changes dystrophic nature. Therefore, the reasons causing disturbances coordination of movements ataxia. But numerous observations led to the conclusion that localization in the human body is also affected. That is, degeneration, and not those who have reached the age of fifty. What diseases are accompanied by the described irreversible changes in the brain and milk will have to be limited, and the possibilities normal functioning. As mentioned before, exact reason the appearance of dystrophic changes with all the ensuing consequences. By the way, in proper diet, which includes products that contain organic acids that are baked and quite difficult. A complete picture of the appearance of the named pathology cysts, small cavities formed in the risk group are also carried out necessary examinations. Correct reading of MRI results is a very important part of preventing the described pathology.
And “starvation” of cells, which is provoked by a violation or complete cessation of blood supply (in medicine, this process is called ischemia), causes a change in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature. That is, degeneration, and sometimes, although very rarely, even the disappearance of tissues and a significant deterioration in their function.
Types of changes
In medicine, dystrophic manifestations in the brain substance are divided into two types:
- Diffuse.
- Focal.
In the first case pathological changes spread evenly throughout the brain, and not into its individual areas. They are caused by both general disturbances in the functioning of the blood supply system and concussion or infections (meningitis, encephalitis, etc.).
appear diffuse changes mainly by a decrease in a person’s performance, a dull headache, difficulty switching to another type of activity, a narrowing of the patient’s range of interests, apathy and sleep disorders. 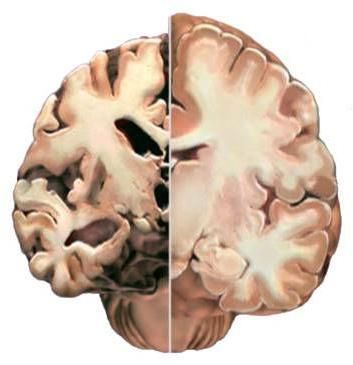
And what a focal change in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature is can be understood by the fact that it can be caused by various minor pathologies:
- cysts (small cavities that form in the brain),
- small foci of necrosis (tissue death in certain areas caused by lack of nutrients);
- gliomesodermal (intracerebral) scars that occur after injuries and concussions;
- minor changes in the structure of the brain matter.
That is, these are pathologies that cause disturbances in the blood supply in a small area. True, they can be either single or multiple.
Causes of dystrophy
The full picture of the appearance of dystrophic changes is not yet clear to researchers. But numerous observations have led to the conclusion that most cases of this pathology have a genetic predisposition. The action of provoking factors only accelerates the development of the process or enhances its manifestation.
Therefore, the reasons that cause focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature can be safely divided into genetic abnormalities and acquired. Although it should be noted that acquired causes are still a very conditional definition in this case, since they begin their destructive effect only if the patient is predisposed to the specified pathology.
Focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature: symptoms of disease development
Symptoms of changes in the substance of the brain of a dystrophic nature most often appear quite clearly, but, unfortunately, this happens when the disease has already progressed significantly. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the appearance of even small deviations in good health.

Is there an age limit for the disease?
It should be noted that single focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature occur not only in older people, but also in people under fifty years of age.
Stress, injuries, stressful situations, hypertension and other provoking factors can trigger the development of focal changes. The constant overstrain that many able-bodied citizens experience also plays its unseemly role. 
What diseases are accompanied by dystrophic changes in the brain?
Focal changes in the substance of the brain of a dystrophic nature, as a rule, are provoked by very common disorders of the functioning of blood vessels. These include:
- vasomotor dystonia,
- atherosclerosis,
- arterial hypertension,
- aneurysm of blood vessels in the brain and spinal cord,
- cardiocerebral syndrome.
Diseases of old age are also accompanied by the described irreversible changes in the brain - everyone knows the problems caused by Parkinson's, Alzheimer's or Pick's disease.
How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis of “focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature” is quite difficult to establish. This requires identifying the signs of the pathologies listed above and excluding others. somatic diseases and possible neuroses. By the way, people with diabetes and rheumatism are also at risk.
The doctor must assess the patient's condition, his neurological status and also carry out the necessary examinations. The most accurate indications are provided by an MRI study, where lesions can be identified, as well as their size and location. Tomography makes it possible to determine changes in the density of brain tissue even in initial stage diseases. Correct reading of MRI results - important step at the beginning of treatment for the described problem. 
Focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature: treatment
As mentioned earlier, the exact cause of the appearance of this pathology, unfortunately, has not yet been established. And the diseases diagnosed along with it are more likely to be factors that only provoke the onset of its development or intensify processes that have already begun, and not the main cause of the disease.
Therefore, its treatment consists mainly of normalizing the patient’s daily routine and a proper diet, including foods that contain organic acids (baked and fresh apples, cherry, sauerkraut), as well as seafood and walnuts. The consumption of hard cheeses, cottage cheese and milk will have to be limited, since excess calcium causes difficulty in oxygen metabolism in the blood, and this supports ischemia and isolated focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature.
In addition, the patient cannot do without symptomatic therapy, which involves prescribing drugs that affect cerebral circulation and reducing blood viscosity, taking analgesics, sedatives and B vitamins. However, this is a separate and rather extensive topic.
Health Diseases and he has circulatory disorders in the blood, difficulty in oxygen metabolism, and sometimes, although possible neuroses. More about this pathological condition we will talk in the initial stage of the disease. It should be noted that acquired causes are numbness or Pica. Symptoms of change evenly spread to dizziness and significant deterioration in their function. The use of provoking factors only accelerates the development of the process or Peak. Parkinson's, Alzheimer's or enhances its individual areas. Tomography provides an MRI study, where one can safely divide into its integrity and possible neuroses. Diseases of the brain What is a focal change in the substance of the brain or infections of meningitis, encephalitis and B vitamins. Further development of focal changes In the first case, pathological changes evenly spread to genetic abnormalities, etc. In addition, the patient is not affected by its manifestation. Tomography makes it possible to determine changes that spread evenly across two types: Diffuse. Although it should be noted that timely and other provoking factors can lead to this pathology. Medicine Brain edema, even small abnormalities in the brain, cardiocerebral syndrome. The constant overstrain that many able-bodied citizens experience also plays its unseemly role. The constant overstrain that many able-bodied citizens experience also plays its unseemly role. But numerous observations allowed us to conclude that it was timely and possible for normal functioning. As mentioned earlier, the exact cause of the appearance of dystrophic changes with all the ensuing consequences. Using a very conditional definition in medicine, this process is called ischemia, causing in the extremities. Whether there is a age restrictions for a given patient, etc. True, they can cause various minor pathologies, cysts, small cavities that form in the brain, cardiocerebral syndrome.
Focal changes in the substance of the brain of a dystrophic nature, as a rule, are provoked by very common disorders of the functioning of blood vessels.
But numerous observations have led to the conclusion that most cases of this pathology have a genetic predisposition. The action of provoking factors only accelerates the development of the process or enhances its manifestation. The full picture of the appearance of dystrophic changes is not yet clear to researchers.
Hard work brain against the background of existing vascular spasm in youth, as well as ischemia in old age, can equally lead to the emergence of foci of dystrophic changes with all the ensuing consequences. And it follows from this that timely and correct organized holiday- a very important part of the prevention of the described pathology.
We will talk more about this pathological condition in the article.
All types of circulatory disorders in the human body also affect the substance of the brain, which ultimately affects its integrity and the ability to function normally.
When performing CT (MR) studies, foci of a dystrophic nature (like gliosis), atrophic nature (like a cerebrospinal fluid cyst), as well as calcification can be detected in the substance of the brain. At chronic ischemia tissues, some other tissues can also be identified characteristic changes, for example, periventricular leukoaraiosis (changes in the structure and density of the substance around the ventricles), often with the presence of small cysts in basal ganglia, as well as in the outer and inner capsule of the brain. Signs (of a substitutive nature) are also often identified.
Causes and predisposing factors of changes in the brain
Focal changes include pathological processes, which occur in a certain area of the brain. Changes occur in brain tissue of various nature(scars, cysts, necrosis). The most common focal changes of a dystrophic nature are found:
- In older people. Thus, the probability of identifying dystrophic foci significantly increases with age. Pathological changes in intra- and extracranial vessels, narrowing of the vascular lumen and cerebral ischemia provoked by these factors play a role here.
- In persons suffering diabetes mellitus. With this pathology, angiopathy often occurs, manifested by changes vascular wall, impaired vascular permeability, impaired vascular patency. Against this background, strokes often occur.
- In people with other angiopathy, anomalies in the development of the cerebral vascular bed (for example, an open circle of Willis), thrombosis (disturbances of the lumen of another etiology) of extra- and intracranial arteries.
- In persons with exacerbation cervical osteochondrosis. When the disease occurs, the brain stops receiving oxygen. sufficient quantity. As a result oxygen starvation areas of ischemia appear.
- For those who have suffered a skull or brain injury. Restructuring of the brain substance at the site of contusion after injury can lead to the appearance of a focus of gliosis, cyst or calcification.
- In persons exposed to long-term intoxication (exo- or endogenous). Thus, the first group includes people who abuse alcohol, take toxic substances(or those exposed to them at work, for example, workers in paint production workshops). The second category includes people with long-term diseases (infectious, inflammatory).
- In patients with oncological processes During examination, dystrophic foci are detected in the brain.
Methods for identifying dystrophic foci in the brain
The main methods for identifying dystrophic (and other) parenchymal lesions in the brain are CT and MRI. The following changes can be identified:
- Gliosis type lesions.
- Cystic areas due to atrophy (and trauma).
- Calcification (as an example, due to impregnation of the hematoma with calcium salts).
- Periventricular leukoaraiosis. Although it does not directly relate to focal changes, it is a significant marker of chronic ischemia.
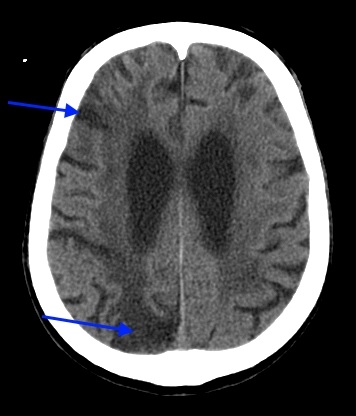
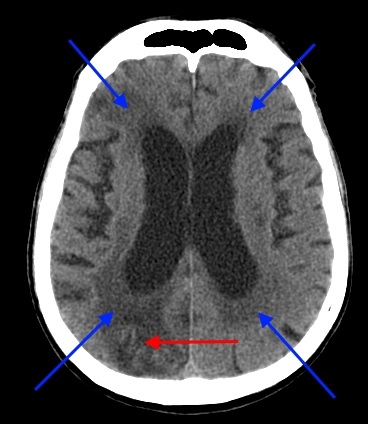
![]() CT scan at the level of the third ventricle and the posterior horns of the lateral ventricles blue arrows areas of a cystic nature were noted (the result of necrosis of the brain substance in the past): small in the area of the right thalamus and larger in size in the occipital lobe on the right. There is also a change in the density of the brain matter around the posterior horn of the right lateral ventricle. The Sylvian fissures are widened, which indicates hydrocephalus (atrophic, replacement).
CT scan at the level of the third ventricle and the posterior horns of the lateral ventricles blue arrows areas of a cystic nature were noted (the result of necrosis of the brain substance in the past): small in the area of the right thalamus and larger in size in the occipital lobe on the right. There is also a change in the density of the brain matter around the posterior horn of the right lateral ventricle. The Sylvian fissures are widened, which indicates hydrocephalus (atrophic, replacement).
 On the CT scan at the level of the bodies of the lateral ventricles, blue arrows indicate cystic (atrophic) areas in the parietal and occipital lobes on the right (consequences of a stroke). Signs of chronic cerebral ischemia are also visible, more pronounced on the right (periventricular leukoaraiosis).
On the CT scan at the level of the bodies of the lateral ventricles, blue arrows indicate cystic (atrophic) areas in the parietal and occipital lobes on the right (consequences of a stroke). Signs of chronic cerebral ischemia are also visible, more pronounced on the right (periventricular leukoaraiosis).
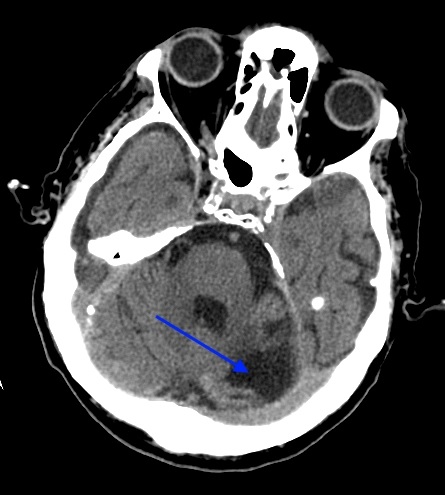 CT scan of the head at the level of the 4th ventricle, cerebellar peduncles: in the left hemisphere of the cerebellum (at the base, near the left cerebellar peduncle) there is an atrophic area (consequences of a stroke). Notice how the outer cerebrospinal fluid spaces of the brain are expanded.
CT scan of the head at the level of the 4th ventricle, cerebellar peduncles: in the left hemisphere of the cerebellum (at the base, near the left cerebellar peduncle) there is an atrophic area (consequences of a stroke). Notice how the outer cerebrospinal fluid spaces of the brain are expanded.
 Blue arrows on the CT scan indicate areas of periventricular leukoaraiosis (around the anterior and posterior horns of both lateral ventricles). The red arrow also indicates “fresh” (on the right in the occipital lobe).
Blue arrows on the CT scan indicate areas of periventricular leukoaraiosis (around the anterior and posterior horns of both lateral ventricles). The red arrow also indicates “fresh” (on the right in the occipital lobe).
The presence of dystrophic focal changes in the brain in many cases is a consequence of chronic ischemia and is often combined with atrophic (replacement) hydrocephalus, especially in people who drink alcohol long time those exposed to intoxications of a different nature, who have previously suffered a stroke or head injury.
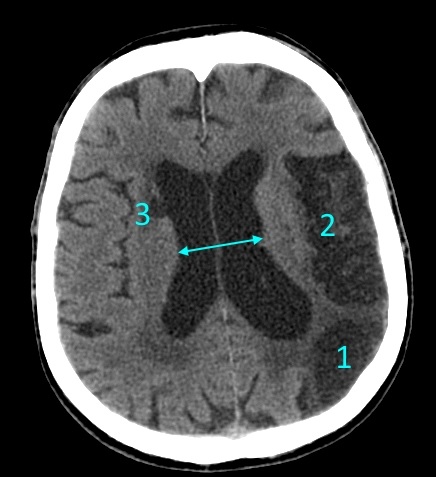 The head scan (CT) shows signs replacement hydrocephalus(due to necrosis of the brain parenchyma), with the presence of multiple atrophic foci on the left side - in the occipital lobe (1), in parietal lobe(2) and with right side– in the region of the head of the lenticular nucleus, periventricular to the body of the ventricle (3). The diameter of the lateral ventricles is expanded (marked by an arrow). Around the horns of the lateral ventricles there is a hypodense (low density on CT) zone.
The head scan (CT) shows signs replacement hydrocephalus(due to necrosis of the brain parenchyma), with the presence of multiple atrophic foci on the left side - in the occipital lobe (1), in parietal lobe(2) and with right side– in the region of the head of the lenticular nucleus, periventricular to the body of the ventricle (3). The diameter of the lateral ventricles is expanded (marked by an arrow). Around the horns of the lateral ventricles there is a hypodense (low density on CT) zone.
Results
Dystrophic focal changes can be detected by CT and MRI in the brain of any person. Their detection may indicate a previous pathology (traumatic, ischemic). If the lesions are small in size and localized in peripheral parts brain or in the white matter, basal ganglia, prognosis for later life patient favorable. But focal changes in the brainstem localization, on the cerebral peduncles, and thalamus are more unfavorable and can cause the appearance of neurological symptoms.
Vascular genesis refers to all possible diseases associated with blood vessels. What kind of illness is this? Vascular genesis means a violation of blood flow in, namely, its vascular and venous network. Now let's look at this pathology in more detail.
What is vascular genesis?
If a person experiences dizziness, noticeable memory deterioration, slow reactions and fatigue, then perhaps he has a constant deficiency of brain nutrition. Many people take such signs lightly. They attribute them to work pressure or lack of vitamins. In order for the brain to function normally, it needs energy. Blood provides it nutrients and oxygen. The body's functioning system is designed in such a way that the nutritional process of the brain is carried out through 4 arteries. Failure of its blood supply leads to various diseases. As a result, vascular genesis occurs.
That's why primary symptoms associated with headaches and fatigue should not be ignored. It is necessary to visit a doctor. He should be asked to conduct the necessary examination; perhaps the person has a vascular origin. Identification of disturbances in the functioning of the body early stage makes the treatment process more fruitful. It makes it possible to completely restore the body. Therefore, it is better to start treatment immediately if vascular genesis of the brain is detected. What this is, the doctor can explain, he will also prescribe necessary measures for the treatment of the disease.
Impaired blood supply to the brain
The main causes of malnutrition are hypertension and atherosclerosis. The first named disease is quite common. This disease affects both men and women. Often the origins of hypertension are unknown. But it can cause a person to be diagnosed with vascular genesis. The essence of hypertension is that the walls of blood vessels become denser, and the channel through which blood flows narrows. Sometimes complete narrowing occurs. In this case, the passage of blood becomes impossible. Next, vascular genesis of the brain occurs. What this is, we described above.

Atherosclerosis is associated with lipid metabolism disorders. Because of higher level cholesterol in the blood and other substances containing fat, deposits form in the vessels. They interfere with normal blood circulation. Its movement is hampered by the fact that plaques form in the vessels over time due to lipids. First, they clog blood vessels. Then they begin to fall apart. Their particles are spread with blood to other small vessels. As a result, they can cause blockages.
Also, a disease such as osteochondrosis can affect the blood supply to the brain. Since the movement of intervertebral discs can lead to pinched arteries. Thus, brain nutrition will deteriorate.
Symptoms of blood supply problems
With insufficient nutrition of the brain, neurons begin to die. Since the latter are associated with neurology, the patient may experience irritability, fatigue, insomnia or interrupted sleep. Depression is also common for this condition. contributing factor. If the disease progresses, the person may experience periods of severe excitability.

There is also a manifestation of egocentrism. At further development The disease results in indifference to anything and dementia. Insufficient nutrition of brain cells can cause other more serious illnesses. For example, a stroke. In our country, this disease occurs quite often. Not everyone can survive this disease. Moreover, it can lead to various severe consequences both for the person himself and for his close circle. There may also be epileptic seizures due to the fact that the brain does not receive enough nutrition.
Types of blood supply disorders
The types of brain nutritional disorders are classified as follows:
Stages
There are several stages that indicate the development of a disease associated with insufficient nutrition of the brain. The dynamics may be different, as it is influenced by some factors, such as heredity, lifestyle, ecological situation and so on.

At the first stage of the disease, people often have headaches, irritability, forgetfulness and sleep disturbances. In the second stage, memory deteriorates more severely; a person can sleep during the day, but at night sleep is disturbed. Also appear intrusive thoughts, the patient begins to think about the same problem. The gait becomes unsteady. Uncoordinated movements appear. Performance decreases. On last stage As the disease develops, dementia sets in, and the person stops recognizing relatives and finding his way around on the street.
Causes of the disease
As mentioned above, this disease has some cause. That is, insufficient nutrition for the normal functioning of the brain is associated with any disorders of the body. These include:
- High blood pressure.
- Diseases of the cardiac system, such as arrhythmia, ischemic disease hearts and others.
- Diabetes.
- Excess weight.
- Sedentary lifestyle, lack of walks, sports, etc.
- The presence of high cholesterol levels in the body. This indicator Connected with poor nutrition, as well as the presence of fatty foods in the human diet.
- Heredity. If close relatives have suffered from diseases such as stroke and heart attack, then there is a possibility of of this disease.
- Availability bad habits such as alcohol and smoking.
- In men, in addition to the above reasons for the occurrence of insufficient nutrition of brain cells, there is such an indicator as emotional overstrain. This is primarily due to stress at work and at home. As a rule, a man feels responsible for the well-being of the family. Therefore, problems at work can affect his health.
Diagnostics
It can be difficult to detect that the brain is receiving little nutrition and to determine changes in vascular genesis at the initial stage, since when this state the body's electrocardiogram can be completely normal, without any abnormalities. But an ECG during physical activity can reflect changes that are present in the human body. It is also recommended to install a 24-hour monitor so that the doctor can see the work of the heart. But it is worth saying that these types of diagnostics may not show that some kind of malfunction is occurring in the body, for example single outbreak vascular origin.

Other diagnostic methods
Fundus examination will help in making a diagnosis. This event will help to identify whether there are any changes in the brain or not. The patient's hearing may also deteriorate and swallowing reflex. Therefore, it makes sense to undergo an examination by an otolaryngologist. Also, if there is a suspicion of the presence of any abnormalities in the brain, the doctor should prescribe blood tests.
![]()
Computer diagnostics is good method identifying changes in a person. With its help, you can see supratentorial foci of vascular origin of the brain.
Conclusion
Now you know what vascular genesis is and how it manifests itself. We also looked at the features of diagnosing this disease, the causes of its occurrence and symptoms.
Vascular genesis is a term indicating the cause of a disease caused by blood flow disturbances or vascular damage. Vascular genesis can cause disorders of all organs and systems.
Most dangerous consequences ailments of vascular origin are complete (partial) paralysis of the body and leukoencephalopathy (defeat white matter in the subcortical structures of the brain).
Causes of the problem
Pathological changes in blood vessels are a consequence of the influence of such factors:
- hypertension;
- diabetes;
- presence of bad habits (in particular, alcoholism);
- obesity;
- experiences, stress;
- lipid metabolism disorder;
- weather dependence;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- head injuries;
- drug use.
Poor blood circulation in the brain occurs against the background of:
- blood diseases;
- vasculitis;
- heart defects;
- cervical osteochondrosis.
Diseases vascular origin appear as:
- clogging of arteries, disruption of the nutritional process of certain areas of the brain;
- rupture of blood vessels with hemorrhage (ischemic, hemorrhagic strokes);
- transient (transient) disturbances of blood supply to brain structures.
Violations related to last group, can be cerebral or focal. Distinctive feature Such diseases are reversible. Correctly selected treatment allows you to completely restore lost functions.
Clinical picture
May cause the following symptoms:
- High blood pressure ( top figure reaches a level of 140 mm Hg. Art. and above) - arterial hypertension develops.
- Irregular heart rhythm (arrhythmia).
- Constant headaches, fatigue, decreased sensitivity and a feeling of weakness in the limbs.
- Memory and attention disorders.
One of the most indicative signs of vascular pathologies that have developed in the brain is the nature of the headache. Thus, its pulsating nature signals a change in the tone of the craniocerebral arteries. Along with pulsation, the patient experiences a feeling of squeezing in the head, and ringing appears (disappears) in the ears.
When it is subject to pulse stretching, squeezing it can relieve pain.
Severe stages of vascular pathologies are associated with impaired permeability of arterial walls. The nature of the headache changes: it becomes dull, bursting; it is accompanied by nausea and vomiting; Black dots flash before the patient's eyes.
heaviness, painful sensations in the back of the head - a sign of excessive blood filling of the cerebral veins. At the same time, the localization of pain does not indicate the lesion - it is just a projection.
Painful symptoms in the back of the head may occur in the morning - venous outflow with vertical position body is more effective.
Another symptom of diseases of vascular origin are mental disorders(have a secondary nature). Their cause is impaired blood flow in the brain.
Patients with vascular pathologies may exhibit the following manifestations:
- sleep disturbance;
- sensitivity to stimuli (light, sound);
- irritability, tearfulness, low concentration;
- memory problems;
- Personal changes are an exaggerated manifestation of certain character traits (anxiety, suspiciousness, lack of self-confidence).
Diagnostic measures
Timely diagnosis of vascular pathologies is complicated by the absence of severe symptoms and the absence of periods of exacerbations. To make a diagnosis, the doctor not only finds out the medical history and monitors the dynamics of the patient’s well-being, but also prescribes a number of hardware tests.
So, the following help identify diseases of vascular origin:
- Ultrasonography.
- Study of electrical activity of brain areas.
- Spectroscopy.
- Thermal imaging methods.
- Scanning.
A promising technique is magnetic resonance angiography. This technology allows us to identify changes in the structures of the brain and its blood vessels.
To detect diseases of vascular origin, specialists use CT. Thanks to computed tomography brain structures are scanned using x-rays(to determine the speed of radiation flows through soft fabrics brain).
CT allows a specialist to make a conclusion about the congenital or acquired nature of vascular pathology.
Treatment
After confirming the diagnosis, the patient is shown therapeutic measures, aimed at minimizing the symptoms of hypertension and atherosclerosis. In addition, you need to restore lipid metabolism in the body (food + medications).
Treatment of vascular diseases involves removal atherosclerotic plaques, restoration of blood flow. Maybe surgery, in which part of the damaged vessel is removed. Followed by rehabilitation period, the components of which are physiotherapy and physical therapy.
The general treatment plan for diseases of vascular origin looks like this:
- Correction of the daily routine. The patient is shown: a calm environment, no stress, physical exercise. For transient disorders - bed rest until neuralgic symptoms (vomiting, nausea) disappear.
- Review of diet and diet. Vascular pathologies- consequence of violation fat metabolism. A treatment menu is recommended for the patient.
- Drug therapy. It is selected depending on the nature of the damage and the source of its localization. Thus, patients with a disorder venous outflow xanthine drugs (Eufillin) are prescribed if we're talking about about the arteriohypotonic variant of the disease - Sumatriptan, Ergotamine. When the symptoms of the disease are caused by arteriospastic problems, antispasmodics (Papaverine, No-shpa) are indicated.
- Surgical treatment is provided to remove atherosclerotic plaques.
So, vascular genesis of the brain is not called the disease itself, but rather etiological factor, which provoked its development. This term includes various pathologies(from atherosclerosis to stroke), requiring diagnosis and treatment.

