What are focal changes in the substance of the brain. Focal formations of the liver
- Benign lesions liver
- Focal formations of a malignant nature
- Formation of lesions in children
- Methods of treatment focal lesions liver
Focal formations in the liver are the filling of a cavity or several cavities of an organ with fluid. This concept can mean several categories of diseases, during which, instead of healthy tissue, volumetric formations are obtained.
To date, there is a negative trend towards more frequent requests of patients with problems such as:
- vascular tumors;
- tumor nodes;
- formation of fluid in the cavities of the liver.
In order to assign proper treatment liver damage, doctors examine the patient with computed tomography, nuclear magnetic resonance and ultrasound. By the way, last method is the most popular, as it allows you to identify not only non-cancerous, but also malignant focal formations liver, as well as diffuse lesions.
Benign liver lesions
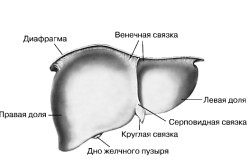 Focal lesions of a non-cancerous nature are as follows:
Focal lesions of a non-cancerous nature are as follows:
- single and multiple organ cysts, polycystosis;
- liver cystadenoma;
- hollow and capillary hemangiomas;
- nodular focal hyperplasia;
- biliary cystadenoma, hamartoma bile ducts and mesenchymal;
- wen, in which focal liver formation occurs from cells with fatty deposits.
This category of formations in most cases tends to increase. If you do not pay attention to a hypodense disease in time, then there may be consequences in the form of hemorrhages, bleeding and ruptures. When seeking help and successful treatment, it is necessary that the patient continued to monitor his condition, for which he should be re-examined every three months.
Back to index
Focal formations of a malignant nature
 This category is subdivided into groups of diseases of the primary and metastatic type. In the first case they call:
This category is subdivided into groups of diseases of the primary and metastatic type. In the first case they call:
- fibrolamellar and hepatocellular carcinoma;
- Kaposi's sarcoma;
- peripheral cholangiocarcinoma;
- hepatoblastoma;
- hemangiosarcoma;
- epithelioid hemangioendothelioma.
Focal formations of the liver of a metastatic type appear if the patient has a tumor of the ovaries, breast, gastrointestinal tract or lungs. Hypervascular volumetric education in the liver may be due to the presence of infectious disease, for example, hepatitis, tuberculosis, toxocariasis and others.
 Concerning diffuse diseases, then they can be:
Concerning diffuse diseases, then they can be:
- Hepatosis. This type It happens as a hypodense focus of education and as a malignant one. It occurs due to the fact that fat drops begin to accumulate in the cytoplasm of the cells of the organ. Hepatosis occurs when lipid metabolism is disturbed, due to alcohol abuse, if a person is a lover of tasty, fatty and junk food. Also found in patients diabetes who are on hunger strike. Such a disease can be in people taking hepatotoxic drugs. In this case, education right lobe the liver or the left gives a diffuse increase in echo signals, respectively, and the organ itself increases in size.
- Diffuse echogenicity may be increased in cases of alcoholic or chronic viral hepatitis.
- Cirrhosis of the liver is characterized by the replacement of organ tissue with neoplasms, and regeneration nodes may occur.
Whether it is a hypodense formation or some other lesion, as soon as the first signs appear, it is necessary to contact a medical institution. In this case, the patient must sequentially undergo computed tomography, ultrasound, blood tests, and tumor markers are used. If there are contentious issues, then the doctor may prescribe an additional fine-needle biopsy of the organ, angiography or laparoscopy. Identified hypodense formation is easier to cure on initial stage than to eliminate the disease later, and even treat its consequences.
Back to index
Formation of lesions in children
In order to carefully examine the child, the first push is hepatomegaly.  The reasons for going to the doctor may be the following points:
The reasons for going to the doctor may be the following points:
- Metabolic disorders in the liver. In this case, an increased size of the organ will be observed, and echogenicity will be higher than normal.
- With congestive heart failure. The level of echogenicity is higher than expected, while there is an expansion of the veins of the liver and vena cava.
- Genuine hepatitis. If you check a child who has just been born, you can see increased echogenicity liver.
- Hemangioendothelioma and hemangioma are quite common in children under the age of one year, while by the age of six months such formation can be detected. If the symptoms indicate multiple hemangiomas of small size, then most likely there are formations in the spleen. Cavernous lesions have the appearance of rough, uneven cystic neoplasms. In this case, Doppler analysis is used, which helps to identify feeding and efferent vessels and arteriovenous shunts.
- Neuroblastomas. This form occurs in half of the cases among newborns. Most of these tumors are detected during the period when metastases are in the process of separation. On echography, the liver has an enlarged size, while there are metastases. But it is possible to identify the primary focus in the adrenal glands only in half of the cases.
As for diffuse changes, they appear as a result of systemic or pathological processes. Sonography shows neoplasms in combination with jaundice and hepatomegaly. But if there is a place for cirrhosis of the liver, and the stage of the disease is already running, then the organ will not have an enlarged, but a reduced size. In such cases, hyperechogenicity is also often noted, but if there is no acute hepatitis or swelling of the body.
When diagnosing diffuse changes, the doctor determines their size, what is their surface: smooth or bumpy, as well as the edges, since they can be sharp or rounded. In parallel with this, an examination of the condition of the spleen, kidneys, lymph nodes, pancreas, liver vessels.
The liver is vital important organ in the human body. If you feel constant discomfort, and according to the results of ultrasound, dark or light areas were found - this may be signs of tumors in the liver. If a formation is found in the liver, what could it be? Consider in this article the common types of tumors and the signs by which they can be distinguished.
After conducting an ultrasound examination, many begin to panic when they hear specific terms, such as hyperechoic formations in the liver. But do not worry, as this term means characteristics diseases.
So, let's start with the concept of what is a hypoechoic formation in the liver on ultrasound (synonymous with hypodense) - this is an area with a lower density in the tissue of the organ. As a rule, on the ultrasound monitor, the hypoechoic zone looks like a dark spot. Often it looks like a cyst, or its varieties, which are a formation, the cavity of which is filled with fluid.
Click to enlarge.
dark spot on ultrasound - focus reduced density, indicating the disease and the presence of pathologies in the organ.
Hyperechoic formation in the liver (synonymous with hypervascular formation) is a formation in which echo density is increased, i.e. ability to reflect ultrasonic waves they are higher. On the ultrasound monitor, such formations are displayed as white spots. More often it benign tumors, hemangiomas (discussed below) as well as malignant tumors.
An anechoic formation is an inclusion in an organ that does not reflect ultrasound and is filled with fluid. This pathology is clearly manifested on ultrasound, has round shape. In 90% of cases, the term anechoic is applicable to the cyst. Thus, a liver cyst is clearly diagnosed.
diffuse changes tissues show structural changes in the tissue of the organ, as a result of severe lesions, impaired functioning (both minor and tangible). Diffuse changes in the liver multifaceted concept, which is not a diagnosis, but only helps to get a complete picture of the disease and choose the right treatment.
Changes can affect the entire organ. If a part of the liver is characteristically changed, they say that it is diffuse focal changes liver (focal tissue changes).
So, in the diagnosis, the detection of an abnormal focus indicates a violation normal operation organism. This is dangerous because the process of blood purification can go at a slow pace, which threatens to accumulate toxins and the development of other diseases. It is also necessary to study the characteristics of the disease.
Varieties of formations
Tumors are either benign or malignant. Vascularization is an indicator of benignness, therefore benign tumors are called hypovascular. We will consider those that are most often diagnosed by doctors.
Focal formations (or foci) of the liver are called single or multiple areas of changes in its structure, which are the most different origin both benign and malignant.
Lesions are most often found on ultrasound, but sometimes they are an incidental finding on computed tomography or MRI when the study was performed for some other reason. In this case, CT is used to clarify the size, number, location and structure of the foci. At the same time, according to the results of CT, the doctor, as a rule, must answer questions about the nature of the changes: are we dealing with a benign process (for example, a cyst or hemangioma), or a malignant process (cancer, metastases, etc.). In some cases, after performing CT, the diagnosis remains doubtful. In such cases, it is recommended to obtain a second medical opinion on the results of the study.
Sometimes a pathological formation of the liver is detected by scintigraphy or PET (the focus of radiopharmaceutical hyperfixation).
FEATURES OF PARENCHYMATOUS HEPATIC LOCATIONS
All volumetric formations of the liver, detected by computed tomography, can be divided depending on the following parameters:
1) Density- a characteristic of any tissue of the body, which is measured on computed tomograms in the so-called. Hounsfield units. Depending on the x-ray density, the foci are hypo-, hyper- and isodense with respect to the surrounding normal parenchyma. By density, it can be assumed that it is in the structure of the focus: blood, other fluid, soft tissue component. Areas of calcification – calcifications – are more reliably identified.
3) Form can be close to the ball, elongated, irregular (irregular), etc.
4) contours. Smooth or uneven, clear or fuzzy, visible all over or in a limited area.
5) Dimensions. The linear dimensions of the focus (length and diameter) are measured on the axial section, or all three dimensions (when possible, the volume is also indicated). If planned control study through certain time, the so-called. "marker" focus, the change in the size of which will be evaluated over time.
6) Location n it is necessary to indicate in the description of the CT examination: whether the pathological site is localized directly in the depth of the organ, under the capsule, next to large vessels, with bile ducts, with gallbladder etc. This may lead to thoughts about its nature: for example, biliary cysts are most often localized near the bile ducts, near the gallbladder.
7) Quantity. Solitary focus in the liver means single. The number of pathological sites (for example, metastases in cancer of the stomach or other organs of the digestive system) may vary. The detection of one metastasis already allows you to set the stage M1 according to TNM system. However, it should be borne in mind that multiple focal formations in the liver are not always metastases, and the radiologist is obliged to conduct them differential diagnosis by comparing numerous CT features.
8) Features of contrast accumulation. The less accumulation of contrast in the focus, the less it is supplied with blood. On the contrary, the faster the contrast accumulates, the more developed the vascular network. The faster the density decreases after the end of the contrast injection, the more intense the blood flow in the focus.
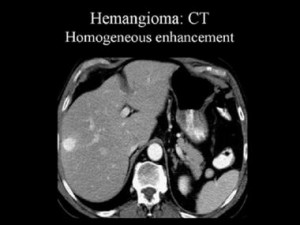
Thus, a hemangioma of the liver on CT without contrast looks like a hypodense area, the nature of which is difficult to establish. In the arterial phase of contrasting, there is a significant increase in the density characteristics of the hemangioma (due to the accumulation of contrasted blood in the vascular lacunae), but then its density decreases and gradually returns to the previous values, which makes it possible to distinguish liver hemangioma from cancer, since malignant neoplasms For example, bowel cancer with liver metastases on contrast-enhanced CT manifests itself differently: metastases are most characterized by an increase in density in the form of a “ring” (“rim”), which displays the active (vascularized) part of the tumor.
Liver hemangioma or cancer? CT abdominal cavity contrast-enhanced: typical accumulation of contrast in the form of lacunae helps to differentiate hemangioma from cancer and establish correct diagnosis: cavernous hemangioma.
HYPODENSE LOCATION OF THE LIVER
Hypodense formations have a density below the normal parenchyma (normally, its density is +50…+70 Hounsfield units - without contrasting) and represent the following morphological variants:
1) Fat formations have a density between -100 and -10 Hounsfield units. This may be a lipoma, fibrolipoma, angiolipoma, angiofibrolipoma, adenoma, liposarcoma and some other tumors from adipose tissue (and also an area with negative density may be due to a local area of fatty infiltration, or fatty hepatosis).
3) A hypodense focus with a density of +20…+40 Hounsfield units can be caused by both liquid content and soft tissue. Here much more options, when compiling differential series it is necessary to take into account the size, shape, nature of the accumulation of the contrast agent.
Capillary hemangioma of the right lobe of the liver: CT with contrast enhancement in the arterial phase reveals a hyperdense area.
HYPERDENSITY FOCUS IN THE LIVER
Hyperdense lesions have an X-ray density higher than normal parenchyma (>70 Hounsfield units) and may be due to cysts containing dense fluid (with impurities of protein or blood), or their substrate is a tumor or calcification.
1) A focus with a density of +200…+400 Hounsfield units is due to the presence of calcium in the structure. It can be a calcified cyst, fibroma, fibroadenoma (or other tumor), calcified hematoma.
2) A local area of increased density of the parenchyma is often caused by deposits of metals - aluminum salts, iron, etc.
3) Tumors can be both hyperdense and hypodense.
CYSTIC LIVER CHANGES
The cystic nature of CT scans has the following formations:
1) Simple liver cyst - what is it? A simple cyst arises as a result of embryogenesis and is a collection of fluid limited by the capsular. On CT, they have smooth edges, clear contours, usually correct form; density characteristics of the liquid +5…+20 Hounsfield units, does not contain any inclusions (blood, calcium, etc.), there are no partitions in their structure, the wall is even, without local thickening. Such cysts do not accumulate contrast. Often the question arises whether a liver cyst can develop into cancer. If the cyst has typical CT characteristics, it should not cause alarm, there is no malignancy of the cyst. But it is important to distinguish a simple cyst from an echinococcal cyst, from a cystic form of metastasis or cystic cancer.
2) Cystic liver metastases in cancer of the breast, stomach, and other organs are usually multiple, have an irregular shape, heterogeneous structure, sizes from 0.5 cm to several tens of cm. They are characterized by the accumulation of contrast in the form of a “ring”. They have infiltrative growth. MTS in the liver is often suspected on CT, in such cases a second opinion on the images may help. Nowadays, multiple metastases are often successfully treated in large cancer clinics where applied various techniques (surgical removal, chemoembolization, radiofrequency ablation, etc.).
3) Cystic form of hepatocellular cancer: the form is incorrect, it can be detected solid component(at cystic form it is minimally expressed), the tumor is single, it has a volumetric effect on adjacent vessels and bile ducts.
5) Hemangioma of the right lobe of the liver, or the left lobe. Hemangioma of the liver on CT looks like a typical hypodense focus, when contrasting in the arterial phase, it sharply increases, as a result of which vascular lacunae become visible, and then slowly loses contrast. Atypical hemangiomas on CT scan have slightly different characteristics and can be distinguished from a malignant lesion by the eye of an experienced radiologist experienced in diagnosing abdominal diseases.
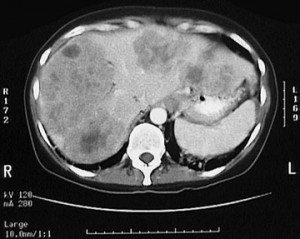
Secondary (secondary) changes in the liver on CT. Colon cancer with metastases. The prognosis is poor, given the size and number of metastases.
SOLID LIVER LESIONS
"Solid" means soft tissue, consisting of living tissue. What are solid formations?
1) Bulk formation with fat inclusions: lipoma, lipofibroma, angiolipoma, liposarcoma, etc. characteristic structure and density characteristics corresponding to adipose tissue.
2) Focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) has an irregular shape (in the form of a node), with native study- hyperdense (slightly higher than normal density), when contrasting, it is unevenly enhanced.
3) Regenerative node, a local area of fibrosis or fatty infiltration - a sign of degeneration of the liver tissue under the influence different nature intoxication or injury, a sign of cirrhosis. Looks like a local hypo-( fatty infiltration) or hyperdense (fibrosis) area.
4) Hepatocellular cancer (HCC). Looks like a volume education irregular shape, of various sizes (sometimes several tens of centimeters in diameter), its structure is heterogeneous - CT can reveal areas of necrosis, cavities (not enhanced by contrasting). Tumor tissue due to good blood supply increases the density during contrasting.
SECOND OPINION OF THE DOCTOR
Not all specialists are able to reliably determine changes in the liver detected by computed tomography. This largely depends on the experience of the radiologist, on the quality of the study. Unfortunately, when performing computed tomography and other radiation studies(especially in remote peripheral clinics), changes are sometimes missed or misinterpreted. Is it possible to confuse liver metastases? Alas, often ordinary benign hemangiomas are interpreted as metastases, or vice versa. In some cases, cystic metastases to the liver are treated as simple cysts, if, moreover, contrast is not used. In general, it should be noted that the diagnosis of "liver mts" is quite difficult in terms of differentiation from other multiple focal changes.
Volumetric formations of the liver are characterized by a number of diseases. Typically, education is different location, it can be inside or outside, and also be single or group.
- The cyst is solitary, as a rule, has a round shape.
- Multiple cysts can fill up to 30% of the liver volume.
- A false cyst may appear as a result of an organ injury, or after treatment of purulent liver lesions. The cyst contains fluid mixed with bile and blood.
- Polycystic can occupy up to 60% of the volume of the liver.
The cyst can be detected by ultrasound or MRI.
Benign liver tumors

Such formations are usually asymptomatic, located both in the epithelium and in the vessels of the liver.
Main types benign formations liver:
- Adenoma. This neoplasm is a node or their accumulation with the presence of capsules.
- . This neoplasm affects the hepatic veins. The danger lies in the squeezing of blood vessels and bile ducts, and it is also possible to degenerate into malignant tumor.
- Hyperplasia. It is a cluster of nodes, up to 4 cm in diameter.
Since benign tumors are quite difficult to detect using, the most successful diagnostic methods are ultrasound, MRI and.
Liver formations can be caused by various injuries and surgical interventions:
- An abscess is suppurative lesion liver, which occurs as a result of an infection in the blood, or an injury or an unsuccessful operation. The symptoms of an abscess are usually as follows: the presence of fever, pain in right side stomach, weakness and chills, weight loss.
- The hematoma is blood clot, which is formed as a result of damage to the vessels of the liver.
Malignant tumors of the liver
Unfortunately, malignant tumors tend to develop asymptomatically and very often cannot be treated due to late stages. This is the most dangerous view formations in the liver.
Some types malignant formations liver:
- Angiosarcoma
- Hepatoblastoma
These formations are characterized by a rather aggressive course and irreversible changes in liver tissues.As it develops, the patient may experience the following symptoms:
- Weakness.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Pain in, especially on the right.
- Loss of appetite and weight.
- With a significant increase in the tumor, it can bulge in the area.
How is the diagnosis carried out?

Each type of formation in the liver requires detailed diagnosis and research.Usually, First stage diagnosis for liver damage should include:
- Appointment with a hepatologist.
- collection.
- , or the abdominal cavity (possibly with contrast).
- Liver biopsy as indicated.
- Reception at the surgeon according to indications.
Benign tumors are also diagnosed using MRI and contrast-enhanced CT.
The same applies to malignant tumors, however, here the range of diagnostic methods is somewhat expanding. Additionally, an analysis is carried out for a liver biopsy, blood flow is measured in the affected part of the organ. In particularly severe cases, resort to diagnostic operations by laparoscopy.
Methodology of education treatment and diet

Unfortunately, the treatment of liver formations is carried out by a long drug therapy but most often surgery is required.
In order to prescribe treatment, the doctor collects an anamnesis, which should determine:
- neoplasm size
- which histological structure has an education
- how many formations were found
- where exactly is education
- which pathological processes accompany the patient
- are there any metastases
Most often, treatment requires a radical approach, and the surgeon removes the tumor focus. In the most difficult cases may require a liver transplant.If a malignant tumor is found, then surgical intervention adding chemotherapy. It is injected directly into the artery that supplies the tumor with blood.
For more information about liver cancer, see the video:
During treatment, the patient must follow a diet. Its basic rules are:
- It is necessary to consume tomatoes, since the content of lycopene has a beneficial effect on the immune system.
- Garlic has the same property.
- Predominance of fruits and vegetables in the diet important aspect treatment. Thanks to a large number fiber, the body is cleared of toxins that the liver cannot neutralize, and side effects from drug therapy do not have such a strong effect on the patient.
- It is highly desirable to consume oily fish, as Omega-3 neutralizes free radicals, and this helps to fight the formation of metastases.
There are several recipes that can help in the fight against neoplasms in the liver:
- Infusion from club moss. 4 tablespoons of dried grass must be poured with a liter of boiling water. The infusion is cooled and taken up to five glasses a day. The first glass is drunk on an empty stomach, the next after a meal. The recipe is especially effective in the early stages of liver cancer.
- Tincture of celandine. The root of the plant must be crushed and squeezed out the juice. The same amount of forty-degree alcohol is added to it and closed in a container for three weeks. The tincture starts with one drop per day, dissolved in water, and increases every day, up to 25 drops. Drops are taken on an empty stomach.
- Chaga infusion. 500 grams of the mushroom must be crushed, pour half a liter of water and insist for two days. After that, the tincture is filtered, and it is ready for use. It is taken three times a day for half a glass (before meals).
- The use of propolis 5 grams per day (one hour before meals).
- Hemlock tincture. This plant is considered poisonous, however, very effective in the fight against liver cancer. To prepare the tincture, you need a whole plant - with roots, leaves and a stem. It must be poured with two glasses of vodka and put in the refrigerator for two weeks, while shaking the tincture daily. It is taken starting with one drop, increasing every day, up to 40 drops. Then take it in reverse order.
All recipes traditional medicine must be approved by the attending physician and be part of complex therapy. Only in this case can you get positive result in the treatment of even the most unpleasant, and dangerous formations liver.
Noticed an error? Select it and click Ctrl+Enter to let us know.

