Laser removal of thyroid nodes. Features of surgery on the thyroid gland
The director of the Institute of Clinical Endocrinology, vice-chairman, answers questions from readers related to this topic. Russian Association endocrinologists, academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, doctor medical sciences Galina Melnichenko.
For every fireman...
Nodes in thyroid gland are more common in women, which is explained by their reproductive function: during pregnancy and breastfeeding A woman’s thyroid gland works for two people, and therefore, the possibility of developing iodine deficiency, to which the thyroid gland reacts by increasing its size, is higher among representatives of the fair half of humanity.
Despite this, my attending physician does not consider it necessary to prescribe me a puncture of this node. In what cases is this necessary?
Gennady, Izhevsk
Puncture followed by biopsy (histological examination of the obtained biomaterial. - Ed.) all newly found nodes with a diameter of 1 cm or more are subject to treatment. If the size of the node is small and the level thyroid-stimulating hormone(TSH), secreted by the thyroid gland, and calcitonin (CT), which is produced in medullary carcinoma (another form of nodular goiter), are normal, and the ultrasound picture does not indicate the likelihood of malignancy, a puncture is not required, and the solution to this issue can be postponed for 1-1.5 years.
But modern realities Our healthcare system is such that a practical endocrinologist has so little time to examine a patient that he prefers to send him for a puncture. Sometimes with nodes of 2-3 mm.
Experts consider this approach unjustified. Even if a small node has ultrasound signs of malignancy, competent doctors try not to puncture it, but to observe it.
Cancer or not?
They found a nodule in my thyroid gland and immediately sent me for a biopsy. Does this mean I have cancer?
Antonina, Kostroma region
- Many of our patients ask this question. I hasten to reassure you: having discovered a palpable, limited formation in the area thyroid gland, in 85% of cases we are dealing with the so-called nodular colloid goiter - a benign nodular formation that will never, under any circumstances, turn into cancer. Most often, nodular goiters occur in regions of iodine deficiency, which is fraught with an increase in the size of the thyroid gland. Smoking aggravates iodine deficiency.Should not be discounted and age factor. The older the person, the more likely that he will have a nodular colloid goiter, which doctors monitor for two reasons: in 30% of cases, the goiter can increase in size and cause physical and aesthetic discomfort. In another case, the node may become hormonally active and begin to produce thyroid hormone, which can lead to thyrotoxicosis (a disease accompanied by excess production of the mentioned hormone). However, the probability of such a development is about 5%.
Approximately the same percentage falls on malignant neoplasms thyroid gland, which even in an advanced stage with properly prescribed treatment have a very favorable prognosis.
There will be no harm
I will soon have a thyroid puncture. I'm worried. Tell me, is this procedure not harmful to the gland itself?
Tatyana, Moscow region
- No, it’s not harmful. Hypothetically, there is a danger of developing purulent thyroiditis ( acute inflammation thyroid gland), which, by the way, can occur on its own, without a puncture, but in my lifetime I have only encountered four such cases. The fact is that the thyroid gland contains a lot of iodine, which is the strongest natural antiseptic. The most that can happen after a puncture is a slight hemorrhage (bruise) at the puncture site, which quickly resolves. Painful sensations during puncture, they are also minimal.Dangerous - away!
Is it necessary to remove a thyroid nodule?
Galina, Vladivostok
Necessary if a node is punctured and cancer is found. You cannot do without surgery for follicular neoplasia - an intermediate group of tumor formations of the thyroid gland, 10% of which can be malignant. Sometimes the question arises about removing a benign colloid goiter if it reaches large sizes. In this case, not only the node, but also the entire thyroid gland is removed. All operations are performed through tiny incisions. Sometimes ethanol and laser destruction of colloid goiter are used. But these methods are so specific that they are used extremely rarely.
The most common pathology of the thyroid gland is nodes. They are detected in 60% of citizens, 5% of which are malignant. In general, such formations do not pose a threat to health, but patients should be treated and monitored. constant monitoring specialists.
What are thyroid nodules?
The structure of the thyroid gland includes the parenchyma itself glandular tissue and connective tissue stroma, which is the supporting scaffold tissue. The parenchyma consists of cells of the elements of the glandular epithelium of thyrocytes. They are grouped into follicles (small vesicles), where the secretion of the hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine (protein-based substances that reside in these tiny vesicles in the form of a colloid) is secreted.
Thanks to a large number capillaries that surround the follicles, during normal functioning of the thyroid gland, active absorption of hormones occurs in blood vessels. But if the follicle is overfilled due to a disruption in the absorption process, an increase in the viscosity of the colloid, or the release of hormones exceeds normal levels, then tissue compaction occurs and nodes (nodular goiters) are formed.
Reasons these changes May be:
- lack of iodine in the diet and water;
- excess radiation;
- impaired circulatory processes;
- permanent mental stress;
- transfer of various inflammatory processes;
- injury;
- genetic predisposition.
Typology of nodes and methods for their identification
Nodes in the thyroid gland can be either single or multiple, located in only one or two lobes at once. Also, formations come in different sizes:
- small – up to 2 cm;
- medium - from 2 to 5 cm;
- large – from 5 cm.
According to the features of the structure, they differ:
- colloid goiters;
- adenomas – tumors in the gland;
- cysts - formations with a hollow internal structure;
- cancerous tumors.
The procedure for examining the patient's thyroid gland is carried out using ultrasound and scintigraphy. In case of suspicion of oncological formations, MRI and PET are additionally performed. If the parameters of the formations are more than 1 cm, the doctor performs a puncture biopsy. During the examination, the presence of malignant cells in the material is identified or refuted. IN mandatory The content of pituitary hormones – thyroid and thyroid-stimulating – is checked.
Why are nodule formations dangerous?
On initial stages small nodes up to 2 cm are only benign in nature and may not even be noticeable to the patient, but their growth can cause adverse consequences, among which:
- difficulty breathing and swallowing;
- changes in timbre and pitch of voice;
- asymmetry in the neck area, its deformation.
Probability of transition to malignant formations ranges from 1 to 3%. The provocateurs of this process can be:
- viruses;
- decline protective function body;
- injury;
- radiation rays.
If the disease begins to produce excessive hormones, the following symptoms may occur:
- weight loss;
- nervousness, frequent irritability;
- feeling constant fatigue;
- heartbeat;
- increased performance pressure;
- elevated temperature;
- increased need for fluid;
- eye symptoms(the eyes protrude, the eyelids “lag behind” the eyeball).
Prices
Name of service area
Name of service area
Name of service area
Comprehensive reception of Professor Bondarenko V.O. (examination, ultrasound of the thyroid gland, puncture of the thyroid gland (without the cost of a biopsy), conclusion based on the results of a cytological examination)
10245 rub.
Consultation with Professor Bondarenko V.O.
4110 rub.
Appointment with an endocrinologist, primary treatment and diagnostic, outpatient
1665 rub.
Repeated treatment and diagnostic appointment with an endocrinologist, outpatient
1460 rub.
Appointment with an endocrinologist based on examination results
835 rub.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland
1560 rub.
Cytological examination(planned)
1560 rub.
show all
Three years ago I noticed that my neck was slightly swollen right side. None painful sensations It wasn’t there, it just stuck out slightly. A year later it became more noticeable. I went to Olympus, where they performed an ultrasound and found a nodule about 3 cm in size. The puncture took about 15-20 minutes, I didn’t feel any pain, regular injection in the buttock - and it hurts more. I returned for the results two days later - no signs cancer cells. I thank Professor Vladimir Olegovich for his professional and high-quality work!
Expand
Indications for removal of nodules
Not every nodule that appears in the thyroid gland needs to be urgently removed. Formations of small sizes, not growing and not causing discomfort, can be treated conservatively, taking into account functional state thyroid gland.
Surgery is the only option if:
- education parameters range from 2.5 cm;
- the doctor identified “cold” nodes (in the absence of hormonal activity);
- the node is growing rapidly;
- the specialist discovered cancerous or atypical elements.
Removal of formations cannot be carried out:
- for complex pathology internal organs;
- in case of a violation of the blood clotting process;
- an elderly person.
Preparing for surgery
On preparatory stage the patient must undergo a large number of studies, including:
- ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland, including the vocal cords;
- hormonal blood status;
- laryngoscopy;
- thyroid scintigraphy;
- thyroid biopsy;
- tumor markers.
In addition, he must pass a number of standard tests before the operation:
- general analysis blood;
- coagulogram;
- hepatitis;
- syphilis
Thanks to big picture the doctor will be able to determine the exact and correct actions that will lead to a successful result.
Before surgery, you must not eat or drink for 12 hours.
Ways to remove nodes
Long-term surgical intervention carried out in cases where one or two parts of the gland must be removed. Its cause is a large goiter or multiple formations. The operation is also performed if atypical cells have been identified. The operation is performed from a mini access.
Carrying out the operation
The duration of surgery to remove thyroid nodules is approximately 1 hour. But if during this procedure it is necessary to remove nearby lymph nodes, then it can take up to 4 hours.
- The patient is given general anesthesia.
- Next, a small incision is made on his neck.
- After visually assessing the condition of the thyroid gland, the surgeon decides which part needs to be removed. He tries to preserve the healthy parts of the organ as much as possible, but in almost all cases, when removing a node, it is necessary to remove the part of the gland damaged by them. If neoplasms are located in two lobes of the organ, a procedure is required.
- The excised affected tissue is sent to histological examination. Its results should be reported during the operation. If the nodes have increased to cover the area of the entire gland, or the histologist’s findings are not reassuring, then the organ and affected lymph nodes are completely removed to stop the spread of malignant growth.
- At the final stage, the surgeon applies cosmetic stitches on the incision area, which are covered with a special adhesive that protects them from external factors.
Possible complications
- hypothyroidism is not complex disease and appears after complete removal of an organ or part of it. Recovery hormonal levels, which was lost during the operation, is carried out using the technique synthetic drug, containing hormones similar to natural ones;
- dysphonia is a consequence mechanical damage vocal cords during surgery;
- problems with respiratory organs– appear after damage recurrent nerves;
- injury parathyroid glands which produce parathyroid hormone (responsible for the balance of phosphates and calcium in the body) - causes serious problems with health.
In women, negative consequences after surgery can be expressed:
- disorder menstrual cycle;
- obesity;
- infertility.
But these pathologies are a consequence radical operations on the thyroid gland, after which patients undergo hormonal therapy.
Postoperative period
After minimally invasive interventions, the recovery process lasts 6-12 days and may be accompanied by:
- pain in the throat area;
- slight swelling of the neck;
- voice problems.
Used in our center modern methods Operating on the thyroid gland is not risky to life and health. If they are carried out on time by our specialists, and the patient follows the diet and doctors’ recommendations, then the rehabilitation process is fast and effective.
Experienced surgeons at the Olympus Medical Diagnostic Center successfully perform surgery to remove nodes in the thyroid gland using innovative medical equipment, which guarantees positive results.
Didn't find the information you are looking for? Leave a request and our specialists will contact you shortly
Thyroid disorders are associated with dysfunction endocrine system, which are characterized by dysfunction and transformation of the structure of thyroid tissue. Treatment methods are determined by the severity of the disease. The thyroid gland produces iodine-containing hormones. Iodine deficiency provokes the appearance endemic goiter(enlargement of the thyroid gland without interruption of functioning), which causes the formation of a node. Laser destruction of thyroid nodules - method radiation therapy. This technique prevents the development of diseases associated with thyroid pathology.
Features of temperature effects
Benign tumors are treated using laser destruction. Laser beams low power destroys affected tissue up to 4 centimeters in size, without leaving scars on the skin. If the size of the node exceeds 4 centimeters, the procedure is repeated. To catalyze destruction, additional quartz LEDs are introduced.
Laser procedure technology
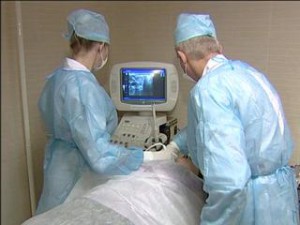
The surgeon numbs the puncture site with a local anesthetic, after which, under ultrasound control, a quartz LED is inserted through the puncture needle, through which light rays pass. The laser beam heats the assembly, destroying its structure.
The procedure for the disintegration of thyroid tumors takes 1 hour. There is no need for inpatient observation of the patient after surgery, since laser treatment painless and does not require a long recovery period.
A week after tumor removal, a control ultrasound is prescribed, through which the endocrinologist monitors the dynamics and, if necessary, adjusts the treatment. After surgery, muscle inflammation may occur cervical region, tonsillitis due to the spreading heat of light rays.
Indications
Thermal effects on nodular thyroid tumors are indicated:
- patients with solid formations(containing not liquid, but biological tissue);
- in case of a low-quality node or reappearance of an endocrine gland tumor;
- if the patient refuses surgical intervention;
- when surgery is not possible medical indications associated with the patient’s severe general condition or exacerbation of other diseases.
Laser destruction is prescribed to patients with a node on the gland that compresses the cervical organs, has a cosmetic defect, or contributes to excessive production of hormones. Only benign nodes are subject to destruction, which must be confirmed by a preliminary fine-needle biopsy.
Preparatory stage
Complex preventive measures are not required before surgery. However, it is recommended to stop eating and drinking 12 hours before laser pulses are applied to the thyroid gland.
Immediately before the procedure, the patient needs:
- take a general blood test and coagulogram;
- get tested for hepatitis groups B, C, HIV and syphilis;
- undergo and do a fine-needle biopsy of the tumor to rule out the malignancy of the origin of the tumor.
Contraindications
Surgery, one way or another, is associated with risk. Laser irradiation is not carried out:
- if the patient has an increased level of thyroid hormones in the blood;
- when there is a long-term, persistent lack of thyroid hormones, which is at an irreversible stage with;
- in case of disturbances in the functioning of the circulatory system;
- if more than two affected areas are found on the gland;
- when mental disorder sick;
- for diseases of organs and systems of the body that are in an acute or chronic state;
- when the patient suffers from inflammation of the nasal cavity, nasopharynx, oropharynx. Laser destruction of neoplasm cells safely and effectively combats thyroid diseases. The light pulse affects only the affected tissue, nearby organs are not affected. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis under ultrasound supervision. During the manipulation, the patient feels the prick of a syringe with an anesthetic, then only the heat emanating from the laser beam.
Approximately 10% of the population has thyroid nodules. Women suffer from this pathology more often than men.
In 5% of cases, the malignant nature of the nodes is revealed, and in 95% - benign. Therefore, if a nodule is detected on the thyroid gland, you need to go through everything necessary examinations and start treatment as soon as possible.
If the node is benign, small in size and grows slowly, this pathology is simply monitored. If the node is malignant, it must be removed as soon as possible.
Indications and contraindications for node removal
The main indication for removal of thyroid nodules is surgical method is inefficiency conservative treatment. In addition, nodes must be deleted:
- if their diameter exceeds 3 cm;
- if a biopsy reveals atypical cells in the nodes;
- if the nodes appeared after radiation therapy in the treatment of diseases of the scalp or neck.
Before performing surgery, the activities are examined of cardio-vascular system and the patient's blood clotting ability. The possibility of surgery depends on the vital condition important organs person. There are no specific contraindications to surgery to remove thyroid nodes.
Examination before surgery
Before surgery, it is necessary to conduct the following studies:
- determine the level of thyroid hormones in the blood;
- do an ultrasound of the thyroid gland and neck;
- perform laryngoscopy of the vocal cords;
- do a thyroid scintigraphy;
- when the nodes are located in the cervicothorax, a CT scan is performed chest and neck;
- perform a fine-needle biopsy of thyroid nodes.
Surgical removal of nodes
The question of the need for surgical intervention and all necessary examinations are carried out before the patient is hospitalized. There is no fundamental difference in what time of year it is better to have thyroid surgery. 12 hours before surgery, the patient should refrain from eating and drinking.
Removal of thyroid nodules is performed under general anesthesia. Most often, the lobe of the thyroid gland in which it is located is removed along with the detected node. This operation is called hemithyroidectomy.
If there are nodes in both parts of the thyroid gland, then a subtotal resection of the thyroid gland is performed, while the upper poles of the gland are preserved. Resection in Lately is rarely performed, since in case of resection, scars occur, which, if necessary, requires a repeat operation.
If the nodes affect the entire thyroid gland, with thyroid cancer or with diffuse toxic goiter perform a total thyroidectomy. Complete removal If cancer is detected, thyroid cancer can completely eliminate tumor recurrence.
Thyroid surgery is performed under general anesthesia. On average, the operation time is from 60 to 100 minutes. If the lymph nodes are affected, surgery may take 3-4 hours.
At surgical intervention an incision is made on the neck in a horizontal fold of skin. After this, the surgeon examines the thyroid gland and decides which part of it needs to be removed. Then the removed tissue is sent for histology, the result of which should be ready before the end of the operation. Moreover, if histology shows that the thyroid gland is affected malignant nodes, this organ is removed completely along with the adjacent ones lymph nodes(in this case further treatment held in oncology clinic). The operation is completed by applying a cosmetic suture to the wound.
Surgical intervention most often takes place without complications, since such operations have been carried out for several decades, i.e. the techniques for carrying them out have been carefully developed and verified. However, the risk of bleeding during this operation is quite high. If there are no complications after the end of the operation and the nodes are not malignant, the person is discharged on the 2nd or 3rd day.
Consequences of surgery
Complications after removal of the thyroid gland can be divided into two groups: nonspecific and specific. Nonspecific complications are those related to any surgery, these include: bleeding after surgery, wound suppuration, swelling at the surgical site.
 TO specific complications after surgery on the thyroid gland include:
TO specific complications after surgery on the thyroid gland include:
- dysphonia (hoarseness of voice) - may appear as a result of injury during surgery to the recurrent laryngeal nerve;
- respiratory failure - this complication occurs when both recurrent nerves are injured; such injury can cause complete loss of voice;
- hypothyroidism - occurs in 100% of cases when the entire gland is removed and in 30% of cases when one lobe of the thyroid gland is removed;
- damage parathyroid glands, which are small in size and located on back wall thyroid glands - these glands are responsible for the secretion of parathyroid hormone (regulating phosphate-calcium metabolism), their removal will cause huge health problems.
If the entire gland or most of it is removed, then after the operation a replacement is performed. hormone therapy. If the thyroid gland was not completely removed, then perhaps the remaining part will produce hormones in sufficient quantity For normal functioning body.
After removal of a lobe of the thyroid gland, it is necessary to monitor the blood levels of hormones produced by this gland. If hypothyroidism (persistent lack of thyroid hormones) occurs, it is necessary to compensate for them using replacement therapy. In this case, completely synthetic analogues of hormones are used. The most commonly used is thyroxine. Its correctly selected dosage does not lead to any negative consequences, unlike previously used hormones of animal origin, to which patients often experienced allergic reaction. The only thing you need to strictly adhere to is not to forget to take a hormonal drug every day.
The consequences of removing a thyroid nodule affect women more, since thyroid disease causes problems with reproductive system. The function of the thyroid gland after surgery decreases, which leads to deterioration general condition body.
Non-surgical removal of thyroid nodules is carried out by heating the gland tissue to high temperatures using a laser. This procedure is called laser hyperthermia. For non-surgical removal of thyroid nodules, it is used diode laser with a wavelength of 810 nm and a power of 5-6 W. The basic principle of this procedure is that under the influence of high temperatures the protein in the nodes is destroyed and pathological process stops. The device for non-surgical removal of thyroid nodules allows you to set heating parameters and change the time and degree of exposure.
 Non-surgical removal is carried out in the following cases:
Non-surgical removal is carried out in the following cases:
- to remove benign thyroid nodules;
- at nodular goiter and with toxic goiter;
- if the patient refuses to remove the nodes surgically;
- if conservative treatment of thyroid nodules is ineffective.
The laser hyperthermia method has the following advantages: it is minimally invasive, and after the procedure there is no need to hospitalize the patient. After non-surgical removal of thyroid nodules, a person can quickly return to to the usual way life.
Nodules with a diameter of up to 1 cm after a non-surgical treatment procedure are reduced in 80% of cases. Nodes up to 2 cm are reduced as a result of 60% of procedures performed. For nodes larger than 3 cm, surgical treatment is recommended.
When treating thyroid diseases, it is advisable to adhere to vegetarian diet With increased content Yoda. A large number of iodine is found in seaweed, root vegetables, legumes, garlic, apple seeds, persimmons, grapes, buckwheat and millet. In order not to provoke an increase in the nodes on the thyroid gland or their degeneration into a malignant tumor, you should not self-medicate.
Should you be scared when your doctor tells you that a nodule has been found in your thyroid gland? In order not to succumb to groundless panic, let's figure out what thyroid nodules are, why they occur and what threat to health they can pose. Which ones are there? indications for thyroid surgery and when can you do without surgery?
Problem out of nowhere
Usually, a message about neoplasms in the thyroid gland, and nodes are called any formations other than the main tissue of this organ, plunges the patient into shock. It seems that the problem arose suddenly and there were no prerequisites for this, because the formation of nodes is not accompanied by any pronounced symptoms, and the neoplasm itself can only be detected by ultrasound.
In fact, there is always a root cause that provoked the formation of nodes. Perhaps you were often given X-ray neck due to tonsil problems or thymus gland, and you have been exposed to excess ionizing radiation. Scientists have already identified the genes responsible for the occurrence of such formations.
But most often, nodes arise due to long-term chronic conditions in the body. It is no secret that in many regions of the country the content of this element in water and products is far from the norm. Unfortunately, this factor becomes one of the decisive ones when we're talking about about the prevalence of thyroid nodules in a particular area.
If it's cancer
The detected node can be either a benign or a malignant tumor. Don’t panic – according to statistics, only 5% of neoplasms in the thyroid gland turn out to be true cancerous tumor. However, such encouraging statistics do not mean that you can forget about the nodule in the thyroid tissue as soon as it is discovered and refuse further diagnosis.
To finally make sure that the tumor is benign, you will have to do a fine-needle aspiration biopsy(FNA), during which a tissue sample is taken from the tumor for analysis. If the analysis does not reveal malignant cells in the sample, the suspicion of oncology is removed. But even if the answer is positive, you shouldn’t give up - as a rule, it can be treated.
What are the indications for thyroid surgery?
Typically, surgery to remove the gland is prescribed if malignant tumor after confirmation of the diagnosis. If the tumor is diagnosed as benign, they are first limited to its observation. The main thing is to visit and do an ultrasound every six months to monitor changes in the size of the node. If it doesn't grow, medical intervention not required.
But in the case when nodes become the cause higher level thyroxine and triiodothyronine, treatment may be required. An excess of these hormones occurs due to the fact that they are produced by both the changed and unchanged parts of the thyroid gland. Usually the problem is solved with drug treatment, without surgical intervention.
Surgery for benign nodes is performed only in as a last resort when it grows so large that it begins to cause physical problems for the patient. Overgrown nodes can put pressure on the trachea and esophagus, causing a sensation of a lump in the throat, difficulty breathing or swallowing, and hoarseness in the voice. Usually, only large nodes whose size exceeds 3 cm lead to such consequences. But even in this case, most often only the neoplasm is removed, and not the entire gland.

