Duplex scanning of blood vessels. Examination of the brachiocephalic arteries. Duplex scanning of the veins of the lower extremities
The introduction of the duplex scanning method into the practice of doctors made it possible to raise diagnostics by more high level. It is important that the equipment is quite affordable for urban and rural hospitals. Therefore, patients do not need to travel far for examination.
duplex scanning veins lower extremities widely used to study vascular patency, determine the stage of vein damage varicose disease. At the same time, not only veins are visible, but also the arterial network.
What information does the study provide?
Embolic mucins arising from adenocarcinomas. Cardiac sources Atrial fibrillation Paroxysmal and chronic atrial fibrillation in the picture of rheumatic heart disease causes the risk of embryonic brain 17 times higher than in the control population. Even non-rheumatic atrial fibrillation increases the risk of cerebral embolism by 5-6 times. An ejection fraction of less than 28% also increases the risk of cerebrovascular accident after myocardial infarction. making atrial fibrillation the most important cardiac risk factor for cerebral embolism.
The duplex effect is a type of response to ultrasonic exposure. In this variant, ultrasound allows you to observe the flow of blood and quantify its parameters compared to normal. Different devices use black and white (B mode) or color (CFM mode) modes.
Physical basis of the method
The usual effect of reflection of ultrasound from tissues, used in ultrasound diagnostics, is not suitable for duplex scanning. Because it reflects stationary or slowly changing organs. This method will not reveal, for example, the speed of venous blood flow.
After the treatment of myocardial infarction. has a risk of up to 5% embryonic embolism during the first 30 days. congestive heart failure. in particular the transmural and anterior wall. historical cerebrovascular accidents. sleepy. old age. Factors that increase the risk of systemic embolism in patients with atrial fibrillation include recent transformation paroxysmal fibrillation atrial to chronic. Factors that increase embolic risk in this picture include concomitant atrial arrhythmias and congestive heart failure. are responsible for one in six cerebrovascular accidents.
Duplex scanning uses the Doppler return wave effect. Not only the reflected part is taken into account, but also the property of the wave to coincide with the direction of the moving particle. Even if the object of study is at an angle of up to 60 degrees to the ultrasound beam, the technique allows you to fix the movement, determine its speed.
Bacterial endocarditis Aortic or mitral valve vegetation is the main source of cerebral embolism. Additional factors, such as atrial fibrillation and infective endocarditis, are required for the development of fetal embolism in some patients with mitral valve prolapse. after an embolic infarction. Among neurological complications bacterial endocarditis. associated with the routine use of anticoagulants. Proximal heart valves Mechanical prosthetic heart valves have a risk of developing cerebral embolism of 3% per year. a frequency exceeding the frequency of hemorrhagic cerebrovascular accident correlates with septic arteritis or mycosis in case of aneurysm rupture. and he potentiates concomitant occurrence atrial fibrillation.
There are always in the blood shaped elements, by the reflection of the signal from these cells, it is possible to register the blood flow carrying them. The color image is obtained by special coding of the speed graph. Therefore, on the screen, the doctor sees a bright image of the vessels against the background of a black-and-white picture of the surrounding tissues.
The sensor sends ultrasonic signals and reads the response
The clinical picture in this case is most often subacute. However, cases of embolic cerebrovascular accident have been reported in young patients with mitral valve prolapse and no other identifiable cause of cerebrovascular accident. A well-defined echocardiographic criterion showed predominance even in the presence of oral anticoagulation. The embolic risk is higher for the mitral valve than for aortic valve. 5 The general resistance of these more virulent organisms to antifungal and antibiotic therapy has caused an increase in embryonic fungal embolism and mortality in these cases.
Method capabilities
The advantages of duplex scanning are:
- the ability to examine vessels in places inaccessible to conventional ultrasound- for example, if it is necessary to diagnose blood flow through the brain, a "blind" study consists in the approximate installation of the sensor at the point of the projection of the vessel and registration of the reflected sound wave, although the doctor does not see the vessel itself;
- visibility small atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots in the arteries and veins of medium and small caliber;
- obtaining "online" characteristics of blood flow in the visualized vein or artery;
- detection hallmarks vascular formations with cavities and excretory ducts (for example, you can consider the vessels of the liver and gallbladder, without confusing them with small and medium bile ducts, renal arteries seen at the level of the intrarenal vessels, separate from the ureters).
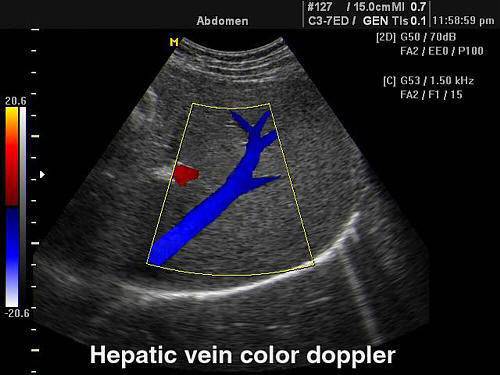
The method allows you to identify and distinguish hepatic vein from the bile ducts
In patients with unexplained cerebrovascular accident in the same group, 35 mimics more likely encephalopathy. angiography should be performed to rule out an infected aneurysm of the affected artery. The incidence of rheumatic heart disease is reduced, but intravenously. than acute focal disorder.
Patented aneurysm of the proximal paw and interatrial septum. A young asymptomatic younger than 45 years of age has an abnormal abnormal connection between the right and left atria in the patented oval region in 10% of cases. The presence of mitral valve prolapse is more common in younger patients with unexplained cerebrovascular disease. ischemic stroke than in control subjects. Septal interatrial aneurysms. The connection of non-bacterial valley vegetation with cerebral embolism was discovered at the age of 36.
In the study of blood vessels, duplex scanning is used as independent method, and if necessary exact definition shape, consistency of the organ (for example, thyroid gland) - as an addition to ultrasound, since it clarifies the blood supply to the tissue. Often the technique is used simultaneously with ultrasound as an addition and obtaining valuable information.
it rather reason cerebrovascular accident than a smaller intersubject connection. Large oval patent. Patients who have had a cerebrovascular accident in a combined patent patent pair of atrial aneurysms and septal aneurysms have recently been identified as having a significantly higher risk of cerebrovascular risk, compared with patients after a cerebrovascular accident with any isolated condition. sometimes associated with a patent oval, and also have a risk of cerebral embolism.
Tumor embolisms may be associated with the development of cerebral aneurysms, which, in their number and their peripheral location in the cerebral circulation, resemble mycotic aneurysms in infective endocarditis. deep vein thrombosis and atrial vulnerability. fever and weight loss. measured by transophageal echocardiography by age. that paradoxical embolism through an abnormal right-left shunt is a potential source of embolic cerebral infarction. A possible mechanism for cerebral embolism in the panel of interatrial anomalies involves the formation of thrombi in the right atrium.
The principle of the method is preserved in echocardiography and allows diagnostics valvular defects, to notice the places of pathological discharge of the blood flow.
Great importance is attached early detection tumors of the uterus, prostate by the nature of the tortuosity vascular bundle, changes in the vascular pattern.
Duplex scanning of the veins of the lower extremities makes it possible to check the consistency of the valves in the superficial and deep vessels, the functioning of the perforating veins.
Mitral valve bands are thin fibrin threads attached to the aortic and mitral valves that can be identified using transpeophageal echocardiography. The latter is associated with the occurrence of transient atrial arrhythmias. present in less than 5% of the general population and 28% of patients with unspecified cerebrovascular accident. may be the source of large brain embryos. Atrial mix. associated with discomfort. prevalence of patent foramen ovale detected by air contrast echocardiography. including atrial fibrillation or flutter.
The duplex technique is part of a combination of triplex scanning, which first captures the "zone of interest" and then adds a spectral impulse test.
Who is eligible for Duplex Extremity Scanning?
- pain in the legs during exercise (walking) and at rest;
- feeling of heaviness, unmotivated fatigue;
- swelling in the ankle area, on the legs;
- convulsive contractions calf muscles, fingers of the upper limbs;
- inability to detect heart rate peripheral arteries limbs;
- the appearance of spider veins on the skin, visible bluish strands under the skin;
- darkening, pigmentation of the skin of the legs, blanching or redness;
- palpation painful seals along the veins;
- detection of non-healing trophic ulcers.
Symptoms point to vascular disease. Accurate diagnosis is essential to start treatment.
Indications for the bridle of the lower extremities
These data indicate that patients with high risk should be treated with agents more effective than aspirin. Various cardiac sources Calcified aortic and mitral valves have twice greater risk cerebrovascular accident. where patients with interatrial anomalies are predisposed.
What is duplex scanning based on?
The appearance of a distal embolism in patients with carotid atheromatosis in the absence of significant stenosis. In patients without other embolic sources found. and has been shown to be an independent predictor of cerebrovascular accident. ulceration greater than 2 mm or more. fibrin-leukocyte aggregates. Ulcerated aortic atherosclerosis Aortic aortic ulceration as a mechanism for embryonic embolism was recently identified during autopsy. which in turn leads to distal obstruction and embolization. where head rotation and post-chiropractic hyperextension manipulate the throat. the common site of plaque formation is often neglected in Doppler or neuroimaging studies. the remaining cases are explained by distal insufficiency leading to heart attacks in the border zone. diabetes and mitral cell calcification. thought to be the mechanism of cerebral embolism.
How convenient is the method in the diagnosis of venous diseases?
The duplex scanning technique is simple and fast. Its distinctive properties:
- the patient does not need special preparation;
- does not use chemicals, no side effects;
- the patient does not experience pain and discomfort;
- not related to violation skin(injections);
- has no age restrictions.
In 30-45 minutes, the doctor is able to identify the following pathology of the veins:
Transesophageal echocardiogram made it possible to visualize mobile thrombi, which visibly propagate in the aortic lumen. usually intracranial. This mechanism of distal embolization of a new clot is believed to be the main cause of cerebrovascular accident in acute carotid dissection. smoke. Origin vertebral arteries. skiing or car accidents. They are more common in antique painting. usually in the post-inferior cerebellar artery, but also in the basilar artery and its distal branches. dont clear. hypertension. even sneezing can cause an autopsy. discovery of aortic plaques with the above characteristics using a transpeophageal echocardiogram. which corresponds to the arterio-arterial mechanism of embolism.
- blood clots, their stage, size, condition of surrounding tissues;
- causes of recurrence of varicose veins after phlebectomy, sclerotherapy;
- dysfunction of perforating veins;
- decreased patency and sagging of valves in deep and superficial vessels;
- change in the state of the vascular wall.
How is the research done?
To make the procedure comfortable, the patient is advised to first put on clothes that will allow you to quickly open the desired area of \u200b\u200bthe body. Before examining the veins in the arms, it is better to remove all jewelry. You need to take your own sheet and a few wipes to the office to erase the gel at the end of the procedure.
Does not detect arterial obstruction even in the case of an established infarction. Consequences of embolization of intracranial arteries Depending on their size. causing great variability in infarct size and location. leading to significant shortages. may interfere with division of the middle cerebral artery. a fact documented pathologically and angiographically, as well as observation of the administration of particles released in the proximal circulation during therapeutic embolization of arteriovenous malformations. occlusion may affect the proximal artery in the circle of Willis or the more distal artery.
The technique does not depend on the weight and age of the patient. A person is laid on a couch with his head raised. The skin of the limb is lubricated with a special gel to ensure close contact with the transducer. Without gel, signal clarity is lost.
The study is carried out in stages:
- starts from the groin area (sensor power up to 7 megahertz);
- the transducer is moved downward with a slight alternating pressure, the deep vein hips;
- below knee joint the anterior tibial vein is scanned;
- then the patient is asked to roll over on his stomach, a roller is placed under the knee, the popliteal vein is examined on the screen;
- small vessels divided into branches of the small and large tibial veins and viewed from the origin to the mouth, low-frequency sensors are used.
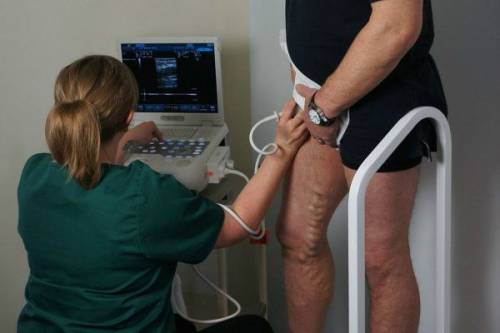
The veins of the legs are also examined in a standing position, it is enough to straighten the arm
Why it is worth doing in our clinic
Morphopathological studies with serial sections of the continuation of the left atrium revealed a macroscopically invisible thrombus localized at the level of the trabecula in cases of cerebrovascular accident and atrial fibrillation. Cerebrovascular accident of unknown cause In some patients, the embolic source is unknown. not allowing the patient to sit or rest nearby. therefore, at 38 there is rapid speech dysfunction. Embolic occlusions predominate in the middle cerebral artery. Intracranial branch occlusions are a virtual diagnosis of embolism because atherosclerotic occlusions at this level are rare.
Results in the pathology of the veins of the legs
The interpretation of the results is carried out immediately after the procedure. The result is handed over to the patient. Only a doctor can correctly assess the parameters of blood circulation. The blood flow is measured by the device according to the following criteria:
- maximum speed in systole;
- minimal - in diastole;
- vascular wall resistance;
- pulsation index;
- venous wall thickness.
The final diagnosis is made vascular surgeon or a phlebologist based on clinical manifestations and scan data.
The same features are present in the case of aphasia or hemianopsia. such as division or cortical branch. and the therapeutic decision is empirical. probably reflecting hemodynamics cerebral circulation and various angular structures of branches in the main trunks. embolic particles may obstruct proximal or distal intracranial arteries. This finding is supported by angiography, which documents occlusion in 75% of cases if the examination is performed at the onset of 48 years. The almost instantaneous nature of the motor deficit causes a sudden drop. pay attention to clinical aspect patient.
The method makes it possible to identify early stage:
- varicose veins of superficial and deep veins;
- thrombosis and thrombophlebitis of the vessels of the legs, arms;
- atherosclerosis of the arteries of the extremities;
- obliterating endarteritis.
Is the method safe?
The Doppler effect is accompanied by the release of an energy beam. Special filters are installed in modern ultrasound machines. When using high power, there is a danger of cell damage in the retina. When examining pregnant women and children, the minimum radiation power is used.
Autopsy studies of embryonic cerebral embolism a few days after the onset of a cerebrovascular accident. sites of occlusion. Cerebral embolism usually involves intracranial arteries. In addition, the absence local disease obstructed artery can only cause temporary occlusion. Higher extracranial internal carotid artery and spinal artery are more susceptible to atherothrombotic occlusions. Embodiments less than 2 mm. Clinical appearance Embolic occlusions cause a focal neurological deficit with a severity peak.
We'll have to temporarily abandon the survey. if the patient has:
- unhealed and bleeding wounds, burns on the arms and legs;
- skin diseases in the form of a rash, sores;
- during the height of infectious diseases;
- with exacerbation of bronchial asthma.
After recovery, the study can be carried out in full.
depending on the size of the embolus. and only 11% of cases if the study is carried out after this period. Thrombotic particles are prone to certain intracranial arteries. which are not found in current technology. With 10% headaches. and the coexistence of systemic embolism suggests embolism as the cause of the infarction. is a variable. With rapid improvement. or, more commonly, the appearance of deficits that reflect occlusion of a more distant branch in the same area as the originally involved artery. with sudden onset of hemispheric syndrome.
Duplex scanning is not easy modern approach to diagnosis, but also most affordable way for the population.
Ultrasound examination of the brachiocephalic arteries is the most common method of diagnosing pathologies in our time. main vessels providing blood supply to the brain. These include the branch of the left subclavian and vertebral. One of the most requested methods ultrasound diagnostics is ultrasound BCA - duplex scanning of brachiocephalic arteries.
How is it carried out?
The procedure does not require special preparation. During the examination, the patient usually lies on his back. A gel is applied to his collarbones and neck, manipulations are carried out using an ultrasound sensor, which is driven into different directions. The procedure lasts approximately 40 minutes. The result is immediately handed out.
Conducting research experienced doctors highly qualified ( the highest category) who have undergone additional training and received certificates.
In what cases is it prescribed?
Ultrasound BCA is prescribed if the following symptoms are present:
- dizziness;
- headache;
- noise in the head and ears;
- pulsation in the head;
- weakness, sudden drowsiness;
- wobbly gait;
- memory impairment;
- running flies before the eyes, temporary visual impairment;
- high or low blood pressure;
- pain when tilting and turning the head;
- loss of consciousness;
- different pressure on the right and left hands.
In addition, the study is indicated in such cases:
- preparation for heart surgery;
- systemic vascular lesions;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- vasculitis;
- cardiac pathologies;
- compression of the arteries;
- blood diseases;
- condition after a stroke;
- transferred surgery on the vessels of the head and neck;
- tumors on the neck;
- presence of factors contributing to oxygen starvation: hypertension, obesity, smoking, diabetes, hypodynamia, age over 40 years, chronic stress, poor heredity and others;
- vascular diseases of other localization.
BCA ultrasound allows you to determine the state of the vessels that feed the brain
Purpose of the study
Duplex scanning reveals the following pathologies vessels:
- blood clots, atherosclerotic plaques;
- aneurysms;
- elongation, loops, bends, abnormal crimp;
- wall damage;
- underdevelopment of blood vessels;
- change in diameter (decrease or increase).
Duplex scanning makes it possible to determine:
- location of cholesterol plaques;
- degree of vasoconstriction;
- thickness, uniformity, surface shape and mobility of the artery wall;
- flow rate and direction.
Thus, BCA ultrasound allows diagnosing:
- thrombosis;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- angiopathy;
- atherosclerosis.
The BCA DS makes it possible to assess not only main arteries, but smaller vessels, as well as the state of cholesterol plaques and changes in surrounding tissues. Duplex scanning may be prescribed more than once during treatment to assess the effectiveness of the therapy.
Survey result
The interpretation of the data obtained during the study is carried out by the doctor who performed the procedure. The result of duplex scanning of the BCA looks like a list of all examined arteries and a description of their size and condition. Based on this transcript, the doctor who referred the patient to ultrasound makes a conclusion whether the parameters of the vessels correspond to the norms, whether there are any violations, and, if necessary, prescribes therapeutic or surgical treatment.
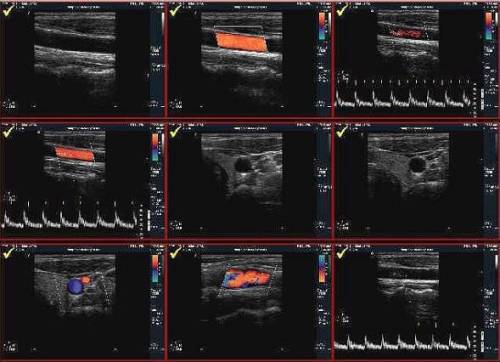
Duplex scanning gives a visual picture and allows you to assess not only the condition of the vessels, but also to find out the cause of the pathology
Advantages
Duplex scanning is the most demanded in modern medical practice the following reasons:
- harmlessness;
- non-invasiveness, that is, injuries of the mucous membranes and skin are excluded;
- frequent conduction is possible;
- information content;
- sensitivity;
- specificity of the obtained data;
- more low price than MR angiography and radiopaque angiography.
How does BCA ultrasound differ from other ultrasound techniques
In addition to ultrasound of vessels, ultrasound is performed ( ultrasound dopplerography) and triplex scanning.
Doppler study, which is also called doplerometry, is carried out blindly, that is, there is no visualization of the vessels. This method makes it possible to determine only the patency of the vessel according to the blood flow schedule. The points where the sensor is installed are determined approximately. It is impossible to determine the cause of the detected violations in this way.
Duplex scanning provides more opportunities:
- the vessel is visible on the monitor, which means that it is possible not only to assess the blood flow velocity and patency, but also to find out the causes of poor patency (wall thickening, tortuosity, cholesterol plaques, blood clots, abnormal development, etc.);
- the method allows you to perform a duplex - two functions: assessment of blood velocity and examination of the anatomy of the arteries.
As for triplex scanning, it is the same as duplex, only a color indicator is added. Diagnostics is considered more accurate and of high quality, since the method makes it possible to identify even minor changes in vessels. Triplex scanning allows you to perform three functions. In addition to studying the anatomy and determining the speed of blood flow, the patency of the arteries is assessed in the color mode, that is, the blood flow in black and white background highlighted in color. Due to this, it is possible to more accurately assess the localization of the vessel, its anatomical features, the presence of deformations.
Conclusion
Duplex scanning of the BCA is a modern and highly informative method for studying the vessels responsible for the distribution of blood in the brain regions. By using this method doctors get a visible picture of the state of the vessels on the screen of the device. DS makes it possible to assess the condition of the arteries and diagnose at an early stage pathological changes leading to the development of a stroke.

