So fp. Causes and treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
Article publication date: 11/13/2016
Date of article update: 06.12.2018
Atrial fibrillation (abbreviated as AF) is the most common type of arrhythmia among all heart rhythm disorders.
For correct and effective work heart rhythm is set by the sinus node. This is the area from where the signal to the heart normally comes out to contract (that is, an impulse occurs). In atrial fibrillation, contractions (not impulses) are chaotic and come from different parts of the atrium. The frequency of these contractions can reach several hundred per minute. The normal frequency of contractions is 70 to 85 beats per minute. When impulses pass to the ventricles of the heart, the frequency of their contraction also increases, which causes a sharp deterioration in the condition.
Pulse conduction scheme

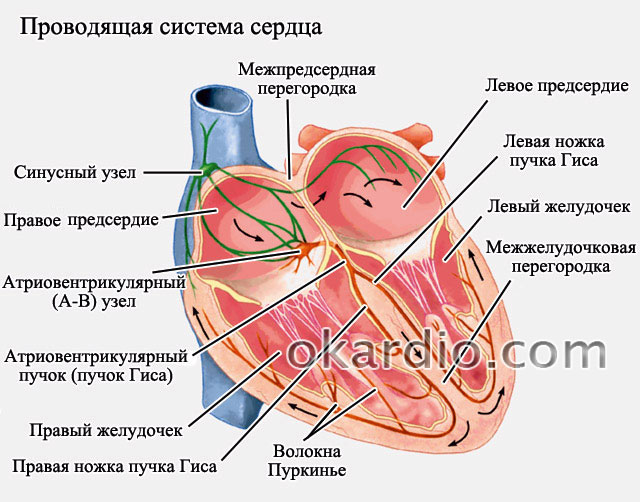
When the heart rate is high (above 85 beats per minute), then they talk about the tachysystolic form of atrial fibrillation. If the frequency is low (below 65 - 70 beats per minute), then they speak of a bradysystolic form. Normally, the heart rate should be 70–85 beats per minute - in this situation, they speak of a normosystolic form of fibrillation.
Men get sick more often than women. The risk of developing AF increases with age. At the age of 60, this problem is found in 0.5% of all people who go to the doctor, and after the age of 75, arrhythmia is detected in every tenth person.
This disease is dealt with by a cardiologist, cardiac surgeon or arrhythmologist.
According to the official data presented in the Recommendations Russian Cardiologists from 2012, atrial fibrillation and atrial fibrillation are identical concepts.
Why is fibrillation dangerous?
When the contractions are chaotic, the blood lingers in the atria longer. This leads to the formation of blood clots.
Big things come out of the heart blood vessels, which carry blood to the brain, lungs and all internal organs.
- Formed blood clots in the right atrium on a large pulmonary trunk enter the lungs and lead to pulmonary embolism.
- If blood clots have formed in the left atrium, then with the blood flow through the vessels of the aortic arch they enter the brain. This leads to the development of a stroke.
- In patients with atrial fibrillation, the risk of developing a cerebral stroke ( acute violation cerebral circulation) is 6 times higher than without rhythm disturbances.
 Thrombus formation in the left atrium leads to a stroke
Thrombus formation in the left atrium leads to a stroke Causes of pathology
The reasons are usually divided into two large groups:
Cardiac.
Non-hearted.
Rarely, with a genetic predisposition and anomalies in the development of the conduction system of the heart, this pathology can be independent disease. In 99% of cases, atrial fibrillation is not an independent disease or symptom, but occurs against the background of the underlying pathology.
1. Cardiac causes
The table shows how often heart disease occurs in patients with AF:
Among all defects, atrial fibrillation is more often detected with mitral or multivalvular heart defects. The mitral valve is the valve that connects the left atrium and the left ventricle. Multivalvular defects are the defeat of several valves: mitral and (or) aortic and (or) tricuspid.
 Mitral defect hearts
Mitral defect hearts Combinations of diseases can also be the cause. For example, heart defects can be associated with ischemic disease hearts ( coronary disease, angina) and arterial hypertension(high blood pressure).
Condition after cardiac surgery can cause atrial fibrillation, because after surgery, the following may occur:
Change intracardiac hemodynamics(for example, there was a bad valve - a good one was implanted, which began to work correctly).
Electrolyte imbalance (potassium, magnesium, sodium, calcium). electrolyte balance provides electrical stability to heart cells
Inflammation (due to stitches on the heart).
2. Non-cardiac causes
Alcohol consumption may affect the risk of atrial fibrillation. In a study conducted by American scientists in 2004, it was shown that with an increase in the dose of alcohol over 36 grams per day, the risk of developing atrial fibrillation increases by 34%. It is also interesting that alcohol doses below this figure do not affect the development of AF.
Vegetovascular dystonia is a complex functional disorders nervous system. This disease is often paroxysmal arrhythmia(description of types of arrhythmia - in the next block).
Classification and symptoms of AF
There are many principles for classifying FP. The most convenient and generally accepted is the classification based on the duration of atrial fibrillation.
* Paroxysms are seizures that can occur and stop spontaneously (that is, independently). The frequency of attacks is individual.
Characteristic symptoms
All types of fibrillation have similar symptoms. When atrial fibrillation occurs against the background of the underlying disease, most often patients present with the following complaints:
- Palpitations (frequent rhythm, but with a bradysystolic form, the heart rate, on the contrary, is low - less than 60 beats per minute).
- Interruptions ("fading" of the heart and then follows the rhythm, which may be frequent or rare). Frequent rhythm - more than 80 beats per minute, rare - less than 65 beats per minute).
- Shortness of breath (rapid and difficult breathing).
- Dizziness.
- Weakness.
If atrial fibrillation exists long time, then edema develops on the legs, by the evening.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of atrial fibrillation is not difficult. The diagnosis is established on the basis of an ECG. To clarify the frequency of seizures and combination with other rhythm disturbances, a special one is carried out (ECG monitoring during the day).
 Heartbeat on electrocardiogram. Click on photo to enlarge
Heartbeat on electrocardiogram. Click on photo to enlarge  ECG is used to diagnose atrial fibrillation
ECG is used to diagnose atrial fibrillation Treatment of atrial fibrillation
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause and/or preventing complications. In some cases it is possible to recover sinus rhythm, that is, to cure fibrillation, but it also happens that the rhythm cannot be restored - in this case, it is important to normalize and maintain the work of the heart, to prevent the development of complications.
To successfully treat AF, you need to: eliminate the cause that caused rhythm disturbances, know the size of the heart and the duration of the flicker.
When choosing one or another method of treatment, the goal is first determined (depending on the specific condition of the patient). This is very important, since tactics and a set of measures will depend on it.
Initially, doctors prescribe medication, in case of ineffectiveness - electrical impulse therapy.
When it doesn't help drug therapy, electropulse, then doctors recommend ( special treatment using radio waves).
Medical treatment
If the rhythm can be restored, then doctors will make every effort to do so.
Drugs that are used to treat AF are presented in the table. These recommendations are generally accepted for the relief of atrial fibrillation.
Electropulse therapy
Sometimes treatment with drugs (intravenous or tablets) becomes ineffective, and the rhythm cannot be restored. In such a situation, electropulse therapy is carried out - this is a method of influencing the heart muscle with a discharge of electric current.
 Electropulse therapy
Electropulse therapy There are external and internal methods:
External is carried out through the skin and chest. This method is sometimes called cardioversion. Atrial fibrillation stops in 90% of cases if treatment is started in a timely manner. In cardiac surgery hospitals, cardioversion is very effective and is often used for paroxysmal arrhythmias.
Internal. into the cavity of the heart through large veins a thin tube (catheter) is inserted into the neck or in the collarbone area. An electrode is passed through this tube (similar to wiring). The procedure takes place in the operating room, where, under the control of radiography, the doctor can visually assess on the monitors how to properly orient and install the electrode.
Then, with the help of special equipment shown in the figure, a discharge is applied and they look at the screen. On the screen, the doctor can determine the nature of the rhythm (sinus rhythm recovered or not). Persistent atrial fibrillation is the most common occurrence when physicians use this technique.
RF ablation
When all methods are ineffective, and atrial fibrillation significantly worsens the life of the patient, it is recommended to eliminate the focus (which sets wrong rhythm heart) which is responsible for the increased frequency of contractions - radio frequency ablation (RFA) - treatment using radio waves.
 RF ablation
RF ablation After elimination of the focus, the rhythm may be rare. Therefore, RFA can be combined with the implantation of an artificial pacemaker - a pacemaker (a small electrode into the heart cavity). The rhythm of the heart through the electrode will be set by a pacemaker, which is installed under the skin in the area of the collarbone.
How effective is this method? If RFA was performed on a patient with paroxysmal AF, then sinus rhythm is maintained in 64–86% of patients during the year (2012 data). If there was a persistent form, then atrial fibrillation returns in half of the cases.
Why is it not always possible to restore sinus rhythm?
The main reason for not being able to restore sinus rhythm is the size of the heart and left atrium.
If, according to the ultrasound of the heart, the size of the left atrium is up to 5.2 cm, then in 95% the restoration of sinus rhythm is possible. This is reported by arrhythmologists and cardiologists in their publications.
When the size of the left atrium is greater than 6 cm, the restoration of sinus rhythm is impossible.
 Ultrasound of the heart shows that the size of the left atrium is more than 6 cm
Ultrasound of the heart shows that the size of the left atrium is more than 6 cm Why is this happening? When this section of the heart is stretched, some irreversible changes: fibrosis, degeneration of myocardial fibers. Such a myocardium muscle layer heart) is not only unable to maintain sinus rhythm for seconds, but, according to cardiologists, should not do it.
Forecast
If AF is diagnosed in a timely manner, and the patient complies with all the doctor's recommendations, then the chances of restoring sinus rhythm are high - more than 95%. We are talking about situations where the size of the left atrium is not more than 5.2 cm, and the patient has a newly diagnosed arrhythmia or paroxysm of atrial fibrillation.
Sinus rhythm, which can be restored after RFA in patients with a persistent form, persists for a year in 50% of cases (of all patients who underwent surgery).
If the arrhythmia has existed for several years, for example, more than 5 years, and the heart has a “large” size, then the recommendations of doctors are drug treatment that will help the work of such a heart. Rhythm cannot be restored.
The quality of life of patients with AF can be improved if the recommended treatment is followed.
If the cause is alcohol and smoking, then it is enough to eliminate these factors so that the rhythm returns to normal.
Paroxysmal form Atrial fibrillation (AFFP) is one of the most common heart diseases. Every first of two hundred people on earth is subject to it. Probably all medical reference books describe this disease in their content.
As you know, the heart is the “motor” of our entire body. And when the motor fails, there are many unforeseen situations. Atrial fibrillation, also known as atrial fibrillation, is a dangerous phenomenon that modern medicine pays great attention.
Concept and forms
Normally, the heart beats about 70 times per minute. It's due to attachment this body to the sinus node. With fibrillation, other cells in the atria begin to respond to the contraction. They bring the frequency of the applied pulses from 300 to 800 and acquire an automatic function. An excitatory wave is formed, which does not cover the entire atrium, but only individual muscle fibers. There is a very frequent contraction of the fibers.
AF has many names: atrial fibrillation, and "nonsense of the heart", and "holiday of the heart." Such names are due to its unexpected contraction and arrival in sinus rhythm.
With age, the susceptibility to AF increases significantly. For example, people over the age of 60 are more likely to this species diseases, at the age of 80 - even stronger.
Some experts separate the concepts of fibrillation and atrial flutter due to the frequency of contractions. Atrial fibrillation (AF) and atrial flutter (AF) are combined into common name: atrial fibrillation.
Depending on the duration, atrial fibrillation is divided into forms:
- Paroxysmal is a form in which against the background normal operation heart, an unexpected arrhythmia occurs. The duration of the attack ranges from several minutes to a week. How quickly it will stop depends on the help provided by the medical staff. Sometimes the rhythm can recover on its own, but in most cases it is normalized within a day.
- Persistent - a form of AF, which is characterized by a longer attack period. It can last from a week or more than six months. This form can be stopped by cardioversion or medication. With an attack lasting more than six months, treatment with cardioversion is considered inappropriate, usually resorting to surgical intervention.
- Constant - a form that is characterized by the alternation of normal heart rate and arrhythmias. In this case, the arrhythmia is delayed for a very a long period(more than a year). medical intervention this form is ineffective. The permanent form of fibrillation is often referred to as chronic.
Paroxysmal form
The word "paroxysm" itself is of ancient Greek origin and means rapidly increasing pain. Paroxysm refers to recurrent seizures. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (PFAF), also known as paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (PCA), is a common disorder. characteristic feature this violation is sudden tachycardia the right rhythm heart and increased heart rate. The attack starts suddenly and can stop just as suddenly. Its duration, as a rule, is from several minutes to a week. During an attack, the patient feels severe discomfort due to high load on the heart. Against the background of this pathology, there may be a threat of atrial thrombosis and heart failure.
PFFP is classified according to the frequency of atrial contractions:
- flickering - when the heart rate exceeds 300 times per minute;
- flutter - when the mark reaches 200 times per minute and does not grow.
PFFP is also classified according to the frequency of ventricular contractions:
- tachysystolic - contraction more than 90 times per minute;
- bradysystolic - contractions less than 60 times per minute;
- normosystolic - intermediate.
Causes
The causes of PFPP may be different. First of all, this pathology affects people suffering from cardiovascular diseases. The causes may be:
- cardiac ischemia;
- heart failure;
- congenital and acquired heart disease (most often mitral valve);
- with increased mass of the myocardium (heart muscle);
- inflammatory heart diseases (pericarditis, endocarditis, myocarditis);
- hypertrophic and (or);
- weak sinus node;
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome;
- lack of magnesium and potassium;
- violation of the endocrine system;
- diabetes;
- infectious diseases;
- condition after surgery.
In addition to diseases, the following factors can act as causes:
- overuse alcoholic beverages(alcoholism);
- frequent stressful condition;
- exhaustion of the nervous system.
Very rarely, an arrhythmia can arise "out of nowhere." Claim that we are talking about this form, only a doctor can, on the basis of thorough examination and the absence of symptoms of another disease in the patient.
An interesting fact is that an attack is possible even when exposed to the slightest factor. For some people who are predisposed to this disease, it will be enough to take an excessive dose of alcohol, coffee, food, or be exposed to a stressful condition to trigger an attack.

The risk zone for this disease includes the elderly, people with problems cardiovascular disease, With alcohol addiction, people subject to constant stress.
First symptoms
Signs that can be recognized this form fibrillation:
- sudden onset of a strong heartbeat;
- general weakness;
- suffocation;
- coldness in limbs;
- shiver;
- increased sweating;
- sometimes cyanosis (blue lips).
When severe attack symptoms such as dizziness, fainting, panic attacks, against the background of sharp deterioration states.
Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation can manifest itself in different ways. Some may not notice an attack at all, but identify it at the time of examination in the doctor's office.
At the end of the attack, as soon as the sinus rhythm returns to normal, all signs of arrhythmia disappear. When the attack ends, the patient is observed increased peristalsis intestines and profuse urination.
Diagnostics
The primary and main type of diagnosis is electrocardiography (ECG). A sign of a paroxysm of fibrillation during monitoring will be the absence of a P wave in its waves. Chaotic f-wave formation is observed. becomes visible and different duration R-R intervals.
After an attack of ACA of the ventricle, ST shift and a negative T-wave are observed. Due to the risk of a small focus of myocardial infarction, the patient should be given special attention.
To diagnose fibrillation use:
- Holter monitoring is a study of the state of the heart by continuously recording cardiac dynamics on the ECG. It is carried out using the Holter apparatus, which was named after its founder Norman Holter.
- Test with physical activity on the ECG machine. Shows the true heart rate.
- Listening with a stethoscope to the patient's heart.
- EchoCG (ultrasound of the heart). Measure the size of the atria and valve.
Complications
The main complication of PFFP can be stroke or gangrene due to possible arterial thrombosis. Many people, especially after an attack that has lasted more than 48 hours, are more likely to have thrombosis, which will trigger a stroke. Due to the chaotic contraction of the atrial walls, the blood circulates at a tremendous speed. After that, the thrombus easily sticks to the wall of the atrium. In this case, the doctor prescribes special preparations to prevent thrombus formation.
If the paroxysmal form of atrial fibrillation develops into a permanent one, then there is a possibility of developing chronic heart failure.
Treatment
If the patient has paroxysmal fibrillation, it is necessary to stop the disease as soon as possible. It is advisable to do this in the first 48 hours after the onset of the attack. If fibrillation is permanent, then necessary measure will be taking prescribed medications to prevent a stroke.
To treat PFFP, first of all, it is necessary to identify and eliminate the cause of its occurrence.
Disease prevention:
- It is necessary to find the cause of the arrhythmia and begin its treatment.
- Monitor the amount of magnesium and potassium in the body. make up for their deficiency. It is advisable to take in a complex, since magnesium helps potassium to be absorbed. In the complex they are in the preparations Panangin and Asparkam. Also great content of these elements is observed in bananas, dried apricots, raisins, watermelons, pumpkins.
- Individually selected antiarrhythmic drugs will help in the prevention of treatment.
- Avoid alcohol, caffeine, nicotine.
- Avoid stressful conditions and overload of the body.
- Engage in physical therapy.
- Do not forget about a good rest.
Medical treatment
At drug treatment prescribe drugs that can equalize the level of heart rate.
So, for example, the drug Digoxin controls heart rate, and Kordaron is good because it has the smallest amount side effects. The drug Novocainamide provokes a sharp decline pressure.
Nibentan is also used to treat PPFP. it antiarrhythmic drug. Produced in the form of a solution.

Amiodarone cannot be prescribed as a means of emergency recovery, as it begins to act after 2-6 hours. But at long-term use restores sinus rhythm within 8-12 hours.
If not serious consequences, then Propafenone can be used as an instant relief agent.
Quinidine (tablets), Ibutilide, Dofetilide, Flecainide, Magnerot (a combination of potassium and magnesium), Anaprilin, Verapamil (reduce heart rate, reduce shortness of breath) are also used for treatment.
After successful relief, it is necessary to start therapy in order to avoid relapse and observe the patient. certain time. Almost all of the above drugs are administered intravenously in a hospital or emergency department under the supervision of a doctor.
Electrocardioversion is considered very effective in 90% of cases.
Surgery
For treatment atrial fibrillation widely used surgical intervention. Medicine thinks it's pretty promising method treatment.
At surgical treatment during the operation, the atrioventricular connection is partially destroyed. Radiofrequency ablation is used. During this procedure, excitation between the ventricles and atria is blocked. In order for the ventricles to contract normally, a pacemaker implant is inserted into the heart. This is very efficient but very expensive means relief of arrhythmias.
Check with your doctor when you need to come for examinations, and do not miss them.
If an attack has begun, make sure that you act Fresh air(unbutton clothes, open window). Accept the most comfortable posture(it would be better to lie down). can be accepted depressant(Corvalol, Barboval, Valocordin). Emergency medical assistance must be called immediately.
People prone to this disease should be seen by a cardiologist. Do not self-medicate, especially if atrial fibrillation is diagnosed.
Fiscal memory (FP) is included, which is a complex of software and hardware that provides uncorrected, daily (every shift) registration and non-volatile long-term storage of final information on cash settlements with the population carried out on KKM, necessary for the correct calculation of taxes. Daily (shift) registration means the unconditional recording of the final information on cash settlements in the FP during the shift closing operation, and the duration of the shift should not exceed 24 hours. Each time when a report is removed with cancellation (closing a shift), another entry is made in the FP containing the date of the entry, serial number shift closures, total daily (shift) sales. The capacity of the FP is enough for 6 years of daily recordings. If there are less than 30 free fields left in the FP for recording the final information, then at the end of the printout of the daily report with cancellation, the following message will be printed:
It is necessary to call the wizard to replace the Fiscal memory.
Only the tax inspector has access to information in the Fiscal Memory. Working with Fiscal memory is protected by a password for access to the FP. The tax inspector has the right to change the password, enter the details of fiscalization and re-registration into the FI, and remove reports from the FI. KKM provides work in non-fiscal and fiscal modes. In non-fiscal mode (before fiscalization) all functions are supported except for registration of daily reports and receipt of a fiscal report. Fiscal mode provides registration of fiscal data in FP and ECLZ. The inclusion of the fiscal regime occurs upon completion of the fiscalization process. After fiscalization, the fiscal regime cannot be turned off. On all documents issued in the fiscal mode of KKM, a message (fiscal logo) is printed:
| KKM with FP |
informing that the machine is working with fiscal memory.
Password system
Access to work with KKM is protected by passwords. There are 9 passwords in total: 8 operator passwords and an OP access password.
The maximum length of passwords is 8 decimal places (range of allowable values: 0 .. 99999999) this mode in accordance with the settings of Table 3. To work in the mode of taking reports and closing a shift, you must enter the administrator or system administrator password. The sequence for setting passwords is described in the Operation Manual. To enter the POS printer parameters programming mode, you must enter the system administrator password. To work with fiscal memory, you must enter the password for access to the FP.

