Coccygeal parietal size of the fetus. What is KTR on ultrasound during pregnancy
KTR (coccygeal-parietal size) is measured as the maximum distance from the crown of the fetus to its coccyx. This size plays important role in determining the duration of pregnancy and is the main one. The reason is that KTP almost completely depends on the gestational age, that is, on the age of the fetus. It is very weakly affected by other factors: it does not depend on race, gender and other individual characteristics.
If a woman has a violation menstrual cycle, then the obstetric gestational age can sometimes be erroneous. In this case, the term is specified based precisely on the KTP parameter. When regular cycle the doctor of ultrasound diagnostics only compares this parameter for compliance with the obstetric period.
Since the embryo grows very quickly, when calculating the gestational age using the KTP, a normal error of 3-4 days is acceptable both in one direction and in the other.
- The ideal gestational age for measuring CTE is 11 weeks. After 16 weeks, this parameter is no longer measured, but other indicators are monitored.
- Measurement of the coccygeal-parietal size is carried out with sagittal scanning of the fetus. The sagittal plane divides the body into 2 symmetrical halves and runs from front to back.
- If the baby moves, then the uzist will fix the KTR at the moment of maximum extension.
Table of fetal KTR values by week in the first trimester (weeks 7-14)
The values in the 50th percentile column are averages for the given period. The values in the 5th and 95th percentile columns are the minimum and maximum allowable normal values.
What does KTR say?
As the gestational age increases, the KTR of the fetus by weeks also gradually increases. This makes it possible to indirectly judge the course of pregnancy. If ultrasound is performed several times in the first trimester, then the dynamics of changes in CTE must be evaluated.
The rapid growth of KTP may indicate the development in the future large fruit(more than 4 kg). In this case, do not use medicines metabolic nature (actovegin, multivitamins), as they can contribute to the birth of a real “hero”.
If the KTR of the fetus by weeks strongly deviates from the norm downwards, then the following options are possible:
Incorrect obstetric term. Ovulation could be late, and therefore fertilization came later. In this case, everything is fine, but, as a rule, a second ultrasound is prescribed after 7-10 days to determine the dynamics.
Non-developing pregnancy, that is, the embryo/fetus died. It is easy to exclude by the presence of fetal heartbeats and its motor activity. This situation requires urgent medical care- curettage of the uterine cavity and removal of the fetus. Delay can cause serious violations reproductive health women, up to infertility, or even a threat to life, since bleeding, an infectious-toxic state, and even shock are possible.
Hormonal deficiency(usually a lack of progesterone) can cause spontaneous abortion. With such a suspicion, additional examinations are prescribed to determine the quality hormonal background. Upon confirmation of the diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe drugs for hormonal support(Dufaston, Utrozhestan).
 infectious factor can also cause fetal growth failure. At the same time, it is necessary to examine the woman for infections (including sexually transmitted infections), and if they are detected, rational therapy is prescribed within the allowed time frame.
infectious factor can also cause fetal growth failure. At the same time, it is necessary to examine the woman for infections (including sexually transmitted infections), and if they are detected, rational therapy is prescribed within the allowed time frame.
Genetic disorders(Down, Edwards, Patau syndromes). In this case, an additional consultation with a geneticist is necessary, delivery genetic markers, the study of the chromosomal set of the fetus. To this end, in the first trimester, along with ultrasound, on which KTR is determined, biochemical screening. If both ultrasound and biochemical indicators have deviations, then the woman is invited to make additional such diagnostic procedures: amniocentosis (analysis amniotic fluid), cordocentesis (study cord blood) or chorionic villus biopsy.
Diseases of the internal organs of a pregnant woman(diseases thyroid gland, hearts).
Violations of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity as a result of previous abortions. In this case fertilized egg does not have the ability to normally implant and develop.
Thus, the coccygeal-parietal size is the most important indicator that allows you to determine or clarify the gestational age, as well as identify the need for additional examinations, in case of suspected violation normal flow pregnancy.
In the age of highly developed medical technologies it is not difficult to calculate the exact gestational age and how the fetus develops in the womb. It is very important to do this in the 1st trimester, because right now the formation of the main organs of the child is taking place. This is done by determining the KTP - the coccyx-parietal size, and this is the most reliable way.
What is KTR. How and when is it measured
The CTE of the fetus is the length of the distance in mm from highest point the head of the unborn child to the lowest point of his back. Index possible to install when conducting. With the help of this parameter, with high accuracy, it is realistic to set the gestational age to her early stage. CTG is such a universal characteristic that it absolutely does not depend on the individual characteristics of the development of the embryo and on the sex of the unborn child.
 The measurement is carried out using ultrasound: This most safe method
examinations during pregnancy, both for the mother and for the child. KTR is determined, as a rule, for a period of 7-14 weeks (before the formation of the placenta), but it is most advisable to do the procedure for a period of 12-13 weeks.
The measurement is carried out using ultrasound: This most safe method
examinations during pregnancy, both for the mother and for the child. KTR is determined, as a rule, for a period of 7-14 weeks (before the formation of the placenta), but it is most advisable to do the procedure for a period of 12-13 weeks.
It is at this time that the characteristic will be most informative, since with the onset of the 2nd trimester, the development of the fetus is assessed by other indicators.
KTP directly depends on the duration of pregnancy, and the more weeks have passed since conception, the more value this indicator. Sex and individual characteristics do not affect the coccygeal-parietal size in any way.
Here's what you need to know about measuring CTE:
- To obtain correct results, it is necessary to carry out measurements in such a projection that the child's body can be conditionally divided into two identical parts.
- The indicator is fixed in the absence of motor activity of the fetus.
- If the child is too active at the time of the procedure, the doctor should measure at the time of full straightening.
- The figures obtained are compared with the data from the table, which shows the average statistical indicators of the compliance rate by week of pregnancy.
KTR by week
For each week there is a certain KTP value. The embryo changes and grows literally every day, and with it the KTP indicator also increases.  The KTP measurement procedure is usually carried out starting from the 11th week (before the 2nd trimester).
The KTP measurement procedure is usually carried out starting from the 11th week (before the 2nd trimester).
In this case, a deviation from the norm is allowed up to 3 days in any direction, which is due rapid growth embryo or measurement inaccuracy due to its high motor activity during the procedure.
There is a special table of average values, according to which you can find out whether the development of the fetus corresponds to the gestational age. When comparing the figures obtained with the norms, it must be remembered that every day the embryo adds 1-2 mm in growth.
Table of fetal CTE values in the first trimester (weeks 7-14)
How to decipher KTR indicators. What does KTR say?
The results of these KTR data will help in determining the gestational age (an error of 2-3 days is allowed). If the difference with table values will be more than 1 week (the measurement result is more than the standard), this indicates high probability large fruit.
- diabetes mellitus in a woman;
- Rhesus conflict;
- the appearance of neoplasms.
When the value of CTE less than that, which is shown in the table, this may indicate that:
- was late ovulation(conception, respectively, came later);
- there is a possibility of a missed pregnancy (the fetus has stopped developing, there is no heartbeat);
- some diseases of a pregnant woman (problems with the heart, thyroid gland);
- possible hormonal disorders(usually this is a lack of progesterone);
- present infectious diseases in a woman's body;
- there is a risk of genetic pathology.
For exclusion possible deviations the doctor will refer the woman for additional diagnostics. This may be a blood test, a smear test for STIs, ultrasound screening, and other tests.
Video
We hope you enjoy learning more useful information on fetal development in early pregnancy. Your attention is presented with video material about the 11th week: the norms for the development of the unborn child and necessary examinations on this period.
Determining such a parameter as the KTR of the fetus by weeks allows you to establish the correspondence of the size of the child in the womb with statistically averaged parameters, on the basis of which we can talk about its normal growth and formation. If there are deviations, doctors can detect them early, prescribe additional diagnostic tests and engage in corrective therapy so that a woman can give birth to a healthy baby.
After, carried out in the initial trimester of pregnancy, future mom receives a picture of his baby with an indication of the main indicators of his development. Among them, there is necessarily the value of the coccygeal-parietal size, which is the most reliable diagnostic indicator fetal formation. In addition, according to the KTR, it is possible to establish, since normally this indicator is little subject to fluctuations.
The coccygeal-parietal size, or KTR for short, is an indicator of the size of the embryo, which is indicated in millimeters and is determined on various terms pregnancy. Intrauterine measurement of a child is carried out at what is considered one of the most safe ways diagnosing fetal development.
In the first trimester, the embryo has a curved shape, so you can measure the length of its body, given the size of the head and body. In this case, the definition is performed between the most distant points from each other: from the crown of the head to the lower back. Therefore, the indicator is called the coccygeal-parietal.
Determination of KTP is carried out up to 12-13 weeks of pregnancy, more late diagnosis using this indicator is less informative, since starting from the doctor they look at other sizes and parameters of the fetus, which are combined by one term "fetometry".
How is the indicator measured?
KTP depends on the gestational age, while the ratio of the two values is in direct proportion, which means that the more time has passed since fertilization, the greater this indicator will be.
The following parameters do not affect the value of the coccygeal-parietal size of the fetus:
- race;
- other individual characteristics.
If a woman previously had, it is possible to establish the exact gestational age based on KTR data. With stable menstruation, the obtained parameters allow you to confirm information about the time when conception occurred.
The coccygeal-parietal size is measured from 6 weeks to 14. An earlier determination is not possible due to the too small size of the embryo. Diagnosis for a period exceeding 15 weeks does not give accurate information, in addition, other fetometric diagnostic tests can be performed, on the basis of which the development and health of the crumbs are assessed.
The main criterion limiting the conduct of KTR is education children's place(), which is why the indicator is recorded before a period of 13-14 weeks.

How is the measurement of CTE during ultrasound scanning of the fetus:
- Diagnosis is carried out in a strictly sagittal projection, when the child's body is conditionally divided into two equal halves. In this case, the measuring line runs from the parietal region to the coccyx.
- Indicators are set in the absence of fetal movements.
- When the child is too mobile during the diagnosis, the doctor needs to wait until the baby's body is as straight as possible and record the measurement.
- Received fetal KTR data are reconciled with the statistical table, which indicates the values of the indicator by weeks from conception.
Table by week
The table of values allows you to compare the results of the survey with average indicators. But you need to understand that the child grows daily and increases by 1-2 mm, so the comparison should be made strictly by day.
| Number of weeks and days | The value of the indicator, mm | Number of weeks and days | The value of the indicator, mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6.3 weeks (45 days) | 7 | 10.3 weeks (73 days) | 36 |
| 7 weeks (49 days) | 10 | 11 weeks (77 days) | 40-41 |
| 7.3 weeks (52 days) | 12 | 11.3 weeks (80 days) | 45-46 |
| 8 weeks (56 days) | 16 | 12 weeks (84 days) | 52 |
| 8.3 weeks (59 days) | 19 | 12.3 weeks (87 days) | 58 |
| 9 weeks (63 days) | 23 | 13 weeks (91 days) | 66 |
| 9.3 weeks (66 days) | 26-27 | 13.3 weeks (94 days) | 73-74 |
| 10 weeks (70 days) | 31-32 | 14 weeks (98 days) | 79-80 |
Deviations from the norm
A slight discrepancy between the indicators is considered normal, however, there are also more pronounced deviations from the tabular data, which may indicate the characteristics of the child's development.
An excess of 1 week or more indicates that the fetus is. Therefore, a pregnant woman should limit herself in food, trying not to increase the average daily calorie content of the diet, and also refuse to take metabolite drugs.

When KTR data is significantly less than the average, there are several explanations for this:
- Later than usual, so the pregnancy occurred later than was determined during registration. For clarification, it is recommended to perform a subsequent ultrasound after 1-1.5 weeks.
- when the embryo dies early. The criterion for confirming this fact is the absence of . In such a situation, an emergency uterine cavity is required.
- Hormonal imbalance resulting from insufficient production. After additional diagnostics the patient is assigned or.
- infectious process, to identify which a woman is swabbed for STIs, after which appropriate therapy is carried out.
If a genetic pathology is suspected, ultrasound screening should be performed, as well as additional diagnostics:
- amniocentesis - amniotic fluid is taken using a long thin needle for their analysis;
- chorionic villus biopsy - detection technique congenital pathology from biological material obtained from the particles preceding the placenta.
- cordocentesis - obtaining blood from umbilical vein which is carried out through abdominal wall mother.
The coccygeal-parietal size is the only reliable diagnostic indicator, on the basis of which in the first trimester of pregnancy it is possible to establish the exact term of conception, to monitor whether the fetus is developing normally, and if there are suspicions and deviations from the norm, to carry out additional examination to determine the pathology and determine the method of corrective therapy.
Useful video about ultrasound in the first trimester
I like!
Many young mothers do not know what KTP is during an ultrasound procedure during pregnancy, and doubt the expediency of the procedure.
While doctors are sure that the definition of KTR is a very important study, with the help of which the fetus is assessed.
The abbreviation KTR means coccygeal-parietal size. This terminology refers to the length of the fetus. KTP is determined by ultrasound in different dates pregnancy.
Given that ultrasound is the most reliable method for obtaining information about the development of the fetus, KTR can be regarded as an additional opportunity to assess the course of pregnancy.
The length of the fetus is measured in mm. It can serve as a guideline for determining the exact duration of pregnancy, which is especially important in its initial stage.
The fact is that in the early stages the embryo is not yet sufficiently developed to be able to make a visual assessment of it.
In the first weeks of development, the embryo consists of a torso and head, and as a whole has a curved shape.
Therefore, the determination of its length is possible only within extreme points- head and coccyx. For this reason, the procedure is called KTR.
It happens that, due to inexperience, expectant mothers confuse terminology and KTR is called "KTG". Such a misconception is unacceptable, since these are two completely different procedures.
CTG is a cardiotocography that evaluates the fetal heartbeat and the contractile potential of the uterus. Naturally, CTG has nothing to do with determining the length of the fetus.
The CTE value changes in accordance with the growth of the embryo. An increase in the length of the fetus by 1 mm per day is considered normal.
With a short gestational age, the determination of this indicator plays a special role, since during this period the potential of the body systems and internal organs of the baby is laid.
At the same time, the formation and development of the placenta begins in the mother's body. It is a natural barrier to protect the fetus. After placentation is completed, it no longer makes sense to measure CTE.
Separately, the procedure for determining the length of the fetus is not prescribed. As a rule, the determination of KTR is combined with the first planned ultrasound, which falls on the period from 6 to 14 weeks of pregnancy.

On early term when the embryo does not yet have formed organs and systems, but only has a head, body and heart, the only possible way to make a visual assessment of its development is the KTR analysis.
To do this, the results obtained during the ultrasound are compared with the normative table, which indicates the average KTP indicators.
The standard for KTP values is approved by the international medical community. Moreover, each of the indicators is tied to the gestational age by weeks.
This ratio is very convenient, as it allows the diagnostician to quickly navigate the information received and draw the right conclusions.
The correspondence of the ultrasound data to the numbers indicated in the table means that the development of the child is normal.
If the value of the coccyx-parietal size is less than the standard value, then this indicates that the development of the child is delayed.
In such a case, the doctor prescribes other studies that provide more detailed information.
Depending on the further results of the examination, the tactics of conducting pregnancy are also prescribed.
To determine the gestational age, doctors practice two methods: the first is established by the result of calculations from the moment of delay in menstruation, the second - by the results of ultrasound.
Thanks to the measurement of CTE, doctors can calculate the gestational age with an accuracy of up to three days. Accordingly, it becomes much easier to more accurately determine the date of birth.
How is an ultrasound with KTR performed?
To measure the length of the embryo, during ultrasound, two methods are used - using a transvaginal probe or using an abdominal probe.
Accordingly, transvaginal ultrasound is performed through the vagina, while abdominal ultrasound scans through the surface of the abdomen.
For transvaginal ultrasound at a gestational age of 12 weeks or more special training procedure is not required.
But if the gestational age is small, ultrasound is performed only at full bladder- this allows high-quality visualization of the uterus.
To do this, before the procedure, you need to drink enough liquids - an average of about half a liter. During ultrasound, the uterus is scanned in different planes and the maximum CTE is determined.
Normal values of the coccygeal-parietal size (KTR) depending on the gestational age (full weeks + days), data in millimeters

Due to the small significance, the size of the embryo under the age of 6 weeks is not measured.
The procedure is prescribed from the sixth week, when the CTE of the fetus can already be 7 - 9 mm.
According to the table of standard values, the length of the embryo changes every day for:
- 7 weeks - from 7 to 15 mm;
- 8 weeks - from 16 to 22 mm;
- 9 weeks - from 23 to 30 mm;
- 10 weeks - from 31 to 39 mm;
- 11 weeks - from 41 to 51 mm;
- 12 weeks - from 52 to 65 mm;
- 13 weeks - 66 to 80 mm.
The longer the gestation period, the higher the digital equivalent of the KTR. Focusing on this indicator, the doctor can judge the development of the fetus.
Minor deviations of the indicator from the norm in one direction or another are not in themselves a sign of a problem pregnancy.
This can only indicate individual characteristics fruit - large sizes or vice versa, small.
In such cases, an additional examination is prescribed to detect neoplasms or diabetes in the mother.
Much less often, the cause of the appearance of pathology at an early stage is the Rh conflict.
Also, as a therapeutic and corrective measure in case of KTR deviating upwards, doctors recommend limiting the use of metabolic drugs - Actovegin and multivitamins, which contribute to the intensive growth of the fetus.
How to decipher KTR indicators?
If the KTR indicators turned out to be significantly less than they should be, according to the parameters indicated in the table, this may mean the following reasons:
- Late ovulation often affects correct definition terms of pregnancy. The shorter the term, the shorter the length of the fetus. To find out, you need to do a second ultrasound in a week with the definition of KTR;
- Stopping the development of pregnancy. This diagnosis can be confirmed or refuted only by verifying the presence or absence of fetal heart contractions. If the development of the embryo stops, it dies, which can cause problems with reproduction in the future. Therefore, the frozen fruit in urgent order delete;
- Lack of hormones - most often progesterone - can cause spontaneous abortion. To clarify the diagnosis, the hormonal background is checked, and when it is confirmed, special preparations are prescribed;
- infection factor. Sexual infections - serious threat full development of the fetus. Timely examination and rational therapy will help improve the situation;
- Genetic disorders provoke the development of Down syndrome and other similar diseases. Therefore, it is necessary not only to consult with a geneticist, but also additional research- delivery of genetic markers, analysis of a set of chromosomes and biochemical screening.
In addition, abnormalities in the development of the fetus may indicate the presence of anomalies and pathological processes in internal organs mother.
The definition of KTP is the chance for timely diagnosis. Conscious refusal of the procedure makes the woman responsible for all possible consequences.
Ultrasound is ideal method fetal imaging during pregnancy and detection various pathologies. Women who are in position, as a rule, are assigned three ultrasounds at different times.
The first scan is carried out in the first trimester. Its main purpose is to discover developing fetus in the uterus, exclusion or confirmation of the presence of several embryos, determination of gestational age, detection of chromosomal diseases.
During the ultrasound, several important measurements are taken. Specialists determine the thickness of the collar space and the coccyx-parietal size. The second indicator is very important. What do experts learn when measuring CTE? What causes deviations from normal values?
What is KTR - a question that many pregnant women ask when receiving results ultrasound scanning carried out at an early stage. The coccygeal-parietal size is an indicator determined by ultrasound. Under the abbreviation "KTR" experts mean the maximum distance measured from the head end of the fetus to the coccyx.
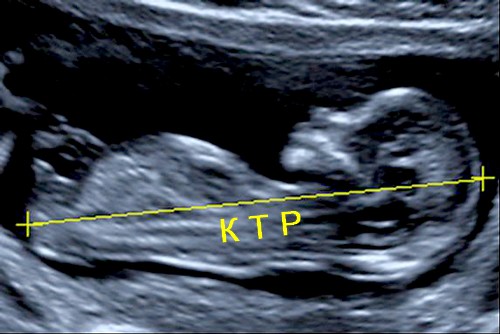
KTR is an informative indicator. It determines the gestational age. Given value is clinically important for several reasons:
- the results of some studies used in prenatal medicine depend on the exact gestational age;
- the correct definition of the term avoids the use medicines, provoking the onset of labor;
- according to the gestational age, accurately established at the beginning of pregnancy, one can judge the presence or absence of a delay prenatal development fetus.
The coccygeal-parietal size allows you to identify chromosomal diseases. According to the information obtained during the ultrasound, experts draw conclusions about whether the fetus has certain disorders:
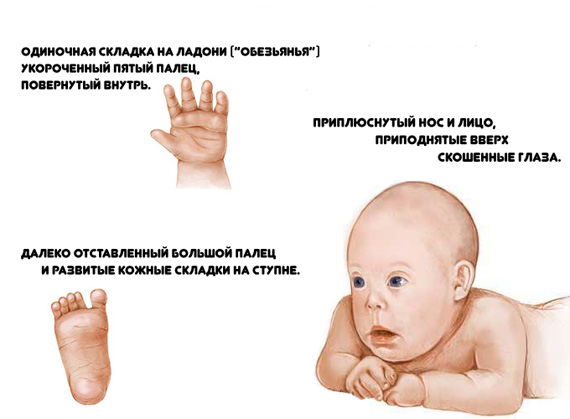
- Severe retardation of embryonic growth may indicate trisomy 18. This chromosomal disease also called Edwards syndrome and is characterized by the presence of multiple malformations.
- With a moderate growth retardation, doctors suggest that the fetus has trisomy 13. In medicine, this chromosomal pathology is usually called Patau's syndrome. Heavy birth defects characteristic of this disease.
How is CTE measured and what its values \u200b\u200bdepend on
The coccygeal-parietal size is determined during the first screening ultrasound conducted at 8-12 weeks. Specialists distinguish several main scanning planes: sagittal, coronal and axial (transverse). Measurement of CTE is carried out only with sagittal scanning in the position of maximum extension of the fetal head.
The values of the coccyx-parietal size directly depend on how much time has passed since fertilization. The longer the period, the higher the CTE of the fetus. That is why, when conducting several ultrasounds in the early stages, experts evaluate the dynamics of changes in the coccygeal-parietal size.

patau syndrome
Fetal KTR: table of values
The coccyx-parietal size in embryos is measured in millimeters. With a normal pregnancy, the fetus increases daily. Accordingly, the values of the coccygeal-parietal size also become larger.
KTR of the fetus by week: the norm at an early stage
Specialists evaluate the coccygeal-parietal size, as a rule, up to 16 weeks. In the second trimester, this indicator is no longer important. Other parameters of the fetus come to the fore. It is on them that experts begin to pay attention.
Deviations from normal values
KTR is considered the main criterion normal growth fetus in the early stages. Deviations of a couple of weeks up or down indicate a violation of the intrauterine development of the embryo.
Why deviations occur
There are quite a few reasons why the real CTE at 8-12 weeks and the norm differ significantly. Most often, the development of the fetus is delayed due to the syndrome of placental insufficiency. This complication is diagnosed in many pregnant women. It disrupts the blood supply to the placenta. The exchange between the organisms of the fetus and mother is not maintained at the proper level.
Coccyx-parietal size discrepancy normal values may be associated with a frozen pregnancy. In this condition, the development of the fetus stops. This happens due to any violations of the normal course of pregnancy.
The presence of infections is another reason why the real CTE and the norm differ significantly. pathogenic microorganisms adversely affect fetal development. To detect infections, pregnant women are prescribed necessary tests and surveys. When the presumptive diagnosis is confirmed, appropriate treatment is carried out.
The lack of dynamics of changes in the coccygeal-parietal size may be associated with hormonal deficiency. Due to the lack of progesterone, the development of the fetus stops. There is a possibility of miscarriage. To prevent this, a hormonal background is examined, and special drugs are prescribed if necessary.
Sometimes at 8-12 weeks, chromosomal pathologies (Edwards and Patau syndromes) turn out to be the cause of a slowdown in intrauterine development of the fetus. In such cases, future parents will have additional consultations with geneticists, the delivery of DNA markers.
An important role is played by the lifestyle of a pregnant woman. If the expectant mother constantly smokes and takes alcoholic drinks, this means that the fetus grows in conditions of intoxication. Naturally, there can be no talk of any normal development of it.

Deviation of KTP from the norm can be caused absolutely harmless reason. For some people, it is associated with small stature. In such cases, a small coccyx-parietal size is a completely natural phenomenon. Future parents do not require examinations and treatment.
What action to take
In order not to face intrauterine delay development of the embryo, women planning a pregnancy are advised to pay Special attention to your lifestyle. From food, physical activity, absence bad habits depends on fetal growth.

If a deviation of the coccyx-parietal size from the norm is detected during pregnancy, then it is very important to find out the specific cause. It must be eliminated, because the further course of the period of gestation depends on it. When the real CTE at 8-12 weeks and the norm differ greatly, the likelihood of a miscarriage increases. That is why during pregnancy you need to follow all the recommendations of specialists.
When appointing any tests or examinations, they must be passed. For example, if a frozen pregnancy is suspected, specialists perform an ultrasound to detect heartbeats in the fetus. If they are not found, then the woman is given emergency medical care.
When chromosomal pathologies are confirmed, experts suggest that patients have an early abortion. Women themselves decide whether to follow the recommendations of doctors or keep the pregnancy.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that the KTR of the fetus by week is very important indicator. It is he who allows doctors to determine the exact gestational age and find out if the pregnancy is proceeding normally. Deviations of KTR from the norm alarm specialists. If the values are too small or large, women are assigned additional examinations.

