duplex ultrasonography. Duplex scanning of brachiocephalic arteries. Duplex scanning of neck and head vessels
At present, medicine offers quite wide range instrumental diagnostic methods that allow to confirm or refute the presence of a certain diagnosis in a patient with high accuracy. One of them is duplex vascular scanning - a method of examining blood vessels, based on the application of the Doppler effect using ultrasound.
This depends on the orientation of the transducer and vessel relative to each other. A spectral trace occupying approximately two-thirds of the display is often appropriate at baseline unless a significant increase is expected. When using automatic analysis software, adjustments to the scale after data collection should be avoided as this would require recalibration. The gain of the spectral Doppler trace should be increased to a point of crispness and clarity, but not so high as to fill out the background speckle or noise.
Ultrasound is not absorbed soft tissues organism (muscles, vascular wall, internal organs), but reflected from them and with the help of digital devices is displayed on the monitor of the device in the form of a two-dimensional image. In the case of studying structures with moving liquid media (vessels in this case), ultrasound is not only reflected from moving shaped elements blood, but also changes its frequency depending on the speed of movement of the elements, which is recorded on the computer screen and gives an idea of the speed of blood flow. This is called the Doppler effect.
If the gain is too high, the specular spectral trace may be visible below the baseline. Dynamic range The spectral trace can also be reduced to improve trace contrast, i.e. make it whiter than the black background; this is important if you are using automatic edge detection software for analysis.
What diagnosis can be made
Thus, in accordance with the analytical approach used, these collective measurements allow the calculation of blood flow in rhythm, as well as potentially other relevant hemodynamic variables, for example, vascular compliance, stiffness, baroreflex sensitivity, shear rate. Therefore, a compromise must be reached in order to satisfy the principles of both methods. Beam steering overcomes this problem because the beam can be steered to reduce the angle of the vessel relative to the beam for spectral Doppler analysis.
Thus, duplex scanning of blood vessels is instrumental method diagnostics of diseases of arteries and veins, allowing to visualize almost any blood vessel in human body in real time, to assess the degree of blood flow disturbance in it, to identify the presence of changes in the blood filling of the surrounding tissues.
Diameter and speed assessment protocol
A baseline assessment period of blood diameter and velocity of at least 1 min should be obtained prior to intervention. During interventions, for example, in relation to drugs or exercise, recordings should be made for at least 10 cardiac cycles, but ideally 30 s or more. For re-evaluations, system settings should be taken into account, as well as an optimal insolation window to improve reproducibility. A photograph of the transducer in situ, or alternatively a mark on the skin, may help provide this window.
Such an image of the vessel is seen by the doctor on the monitor of the apparatus.
The advantages of the method include non-invasiveness (lack of penetration into the tissues of the body), the absence of radiation exposure, accessibility (in modern medical institutions good equipment with the necessary equipment), the ability to accurately diagnose the existing vascular pathology.
Currently, two methods of edge detection systems are used to measure changes in arterial diameter. One method involves an automated edge detection system that automatically tracks the artery wall and blood velocity, while the second approach involves sonography that manually measures these components.
Automated Edge Detection Methods
The use of edge detection software for offline analysis is recommended for simultaneous acquisition of B-mode and Doppler mode information to determine vessel diameter and blood velocity. Recording the display during data collection using screen capture software allows you to extract a video clip from the complete study that can be analyzed in more late time. Many other programs for automatic edge detection software have also been developed and described in detail in the literature.
Indications for duplex vascular scanning
This method is prescribed when the doctor suspects the presence of the following pathological conditions:
- anomalies or deformations of blood vessels that create an obstacle to the normal blood supply to organs,
- atherosclerosis of the aorta and its branches,
- obliterating atherosclerosis vessels lower extremities,
- thrombosis of veins and arteries,
- Varicose veins ,
- endarteritis and vasculitis (inflammation vascular wall),
- diabetes mellitus and its complications ( diabetic angiopathy vessels of the retina, arteries of the legs and feet - "diabetic foot syndrome"),
- arterial hypertension (in combination with impaired brain function - dyscirculatory encephalopathy),
- aortic aneurysm,
- heart defects (for example, insufficiency aortic valve leading to impaired blood flow in the vessels supplying the brain),
- pathology of cerebral vessels in newborns.
Who is eligible for Duplex Extremity Scanning?
With these custom software approaches, it is now possible to directly export changes in diameter and velocity with high temporal resolution to other data acquisition software. Therefore, it is recommended to choose when selecting software if no validation studies have been reported. If edge detection software is not available, it is recommended to collect data as often as possible depending on the experimental disturbance, such as every 3-4 s if "dynamic" changes are expected, or every 10 s if more stationary measurements are taken.
During the examination, it is possible to diagnose diseases of the following groups of vessels:
1. Assessment of blood flow in the brachiocephalic (brachiocephalic) arteries– common, external and internal carotid arteries are visualized.
An examination is necessary if the patient makes complaints of a certain nature:
- frequent headaches, migraines,
- Falls with or without loss of consciousness
- "noise" in the ears, flickering "flies" before the eyes,
- transient ischemic attacks
- frequent dizziness
2. Assessment of blood flow of transcranial (intracranial) vessels- anterior, middle and posterior cerebral arteries:
- performed in combination with scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries.
3. Diagnosis of diseases of the arteries and veins of the extremities necessary in case of symptoms such as:
- the presence of vascular "asterisks" on the legs,
- varicose veins of the lower extremities,
- severe swelling of the lower extremities, aggravated by walking,
pain, feeling of fatigue in the arms or legs,
- chilliness of the limbs,
- intermittent claudication syndrome - for example, in people who smoke a large number of cigarettes for a long period of time, a persistent vascular spasm is formed, leading to impaired blood supply to the muscles of the legs and feet,
- changes in skin color (blue, purple coloration) in combination with significant painful sensations may be indicative of acute venous or arterial thrombosis.
4. Diagnosis of diseases of the aorta and its branches:
- aneurysm of the ascending, thoracic, abdominal aorta.
5. Diagnosis of vascular diseases of the kidneys, liver, thyroid gland, prostate, eyeball
:
- tumors of the corresponding organs to assess the degree of vascularization (growth of the vascular network) in them,
- liver cirrhosis, thrombosis portal vein with an assessment of intrahepatic blood flow,
- chronic kidney failure, glomerulonephritis,
- diabetes mellitus with damage to the vessels of the fundus, leading to blindness, injury to the eyeball, etc.
With this approach, the sonator carefully manually monitors systolic and diastolic changes in diameter and velocity. The main disadvantage of this method, compared to automated approaches, is that diameter and velocity measurements often cannot be collected simultaneously and therefore cannot be aligned in time. If both modes can work simultaneously, a single cyclone loop can be recorded. In any case, manual measurements of diameter and speed are required with built-in calipers, which gives rise to another disadvantage: the subjectivity of caliper placement.
Contraindications for the study
Same as for standard ultrasound, for duplex scanning of arteries and veins absolute contraindications does not exist. Difficulties of a technical nature are quite likely when ultrasound cannot “get” to the vessel under study, for example, with a high degree of obesity in a patient when examining the vessels of the liver and kidneys, injuries, open fractures skull, eye sockets, limbs, the presence of extensive wound surfaces on the skin in the projection of the studied vessels.
The results of a duplex vein scan
The loop cycle is manually cycled and the diameter can be measured with measuring calipers in successive cardiac cycles. Measurements must be recorded manually. Subsequent cardiac cycles are then analyzed in the same way. With either method, blood flow is later calculated offline from velocity and diameter.
It should be noted that absolute measurements speed and flow cannot be determined with accuracy in the presence of complex structures flow and possible non-uniform insolation of the vessel. Averaging repeated measurements can also be beneficial in smoothing out random errors.
Preparation for the patient for duplex scanning of arteries
There is no need for special preparation. The patient can follow the usual daily routine and take the usual amount of food and water.
How is the research done?
To perform a duplex scan of the arteries, you must have ultrasound scanner with software (equipment capable of perceiving reflected ultrasonic beams, registering them in the form of graphic curves and converting them into a two-dimensional image with color blood flow mapping) and an ultrasonic sensor.
The presence of arterial calcification in the vessel wall may limit the penetration of ultrasound and may obscure the lumen and tissue deep into the calcified area due to the presence of acoustic shadowing. In these cases, move the transducer around the vessel in an attempt to identify a plane where the plaque load is less to allow sufficient penetration into the vessel; however, in some cases the acoustic shadow cannot be overcome. Objects with large populations and especially those with muscular necks can be technically challenging for optimal insonization.
The patient can be taken to the office ultrasound diagnostics on a planned or emergency basis. In a planned manner, he is sent from the clinic or the specialized department of the hospital, where he is on inpatient treatment in this moment, and by emergency indications examination of persons with suspected acute thrombosis, ischemic stroke, dissecting aortic aneurysm and with other acute vascular diseases.
Different insolation windows can improve visualization; however, in rare cases, sufficient image quality cannot be achieved to use the automatic software. Similarly, extremely mobile vessels can become a technical challenge when capturing images for use with automated software. Vascular motility is sometimes noted in young people due to highly compatible vessels or in older patients due to tortuosity of the vessels, as well as during interventions involving increased ventilation.
After the patient is brought into the office, he is laid on the couch and asked to release the part of the body to be examined from clothing. Next, the doctor applies a conductor gel to the skin for better “adhesion” to the skin of the sensor and better patency of the ultrasound beam, and proceeds to the study. In the process, access for ultrasound to different points projections of the studied vessel.
There are several complications regarding the use of Doppler technology to estimate velocity and therefore flow. Interested and more advanced users are mentioned in the above link for an in-depth discussion of these important topics which are outside the scope of this article.
Duplex scanning of renal arteries and veins
Doppler ultrasound quality assurance protocols are recommended by several professional bodies to test system accuracy and performance. Doppler system evaluation is performed by selecting several known phantom flow rate presets and using the provided chart to convert flow to velocity for comparison with the velocity accuracy of the ultrasound system.
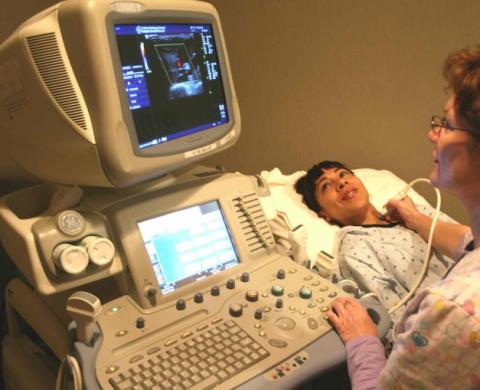
So, for example, when scanning the carotid arteries and arteries of the brain, access is made through the skin and muscles of the neck, as well as in the area of the connection of the skull with spinal column(craniovertebral articulation), over temporal bone, above occiput head, in the region of the eye socket. When scanning the aorta and its branches, renal and hepatic vessels, the doctor applies the gel and works on the skin of the chest and abdomen, while examining the vessels of the extremities - on areas of the skin of the arms and legs corresponding to the course main vessels. At latest study the patient may be asked to stand up for the scan in a standing position (this is important for assessing the patency of the perforating veins that communicate deep and superficial veins shins), as well as perform a Valsalva test (straining) to clarify changes in blood flow in the veins at the time of the test.
Conclusions and future directions
Another limitation is that ultrasound requires highly skilled and practical operators to obtain images of acceptable quality. Evaluation of extracranial blood flow combined with sensitive edge detection software is powerful tool assessment of regional cerebral blood flow. However, an accurate assessment of extracranial blood flow requires appropriate ultrasound technology and training, subject preparation, and detailed knowledge of the approach.
At this time, all information received by the scanner is processed using digital devices and displayed on the doctor's computer monitor in the form of a color image and quantitative characteristics of blood flow in the vessel, which the doctor evaluates and interprets the results.
The examination time is 20-30 minutes, after which the doctor issues his opinion to the patient for subsequent submission to the attending physician. In the case of a planned examination, the patient goes home, and in the case of an emergency examination, he is hospitalized in a specialized department for further observation and treatment.
The recommendations presented here represent the latest advances in ultrasound measurement of extracranial blood flow. These recommendations are presented in an attempt to standardize measurements across study groups and therefore ultimately improve the accuracy and reproducibility of extracranial blood flow measurements both within subjects and between groups.
From a pathophysiological perspective, there is growing evidence that cerebral hemodynamic failure is an independent cause of cognitive dysfunction in various vessels brain. Conversely, improvement cerebral blood flow with the use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or heart transplantation, increased cerebral blood flow and improved cognitive function in this population.
Deciphering the indicators of duplex scanning of blood vessels
Not every patient will be able to understand what is written in the conclusion after the scan. In principle, there is no need to try to understand this, because this information is purely medical in nature and is intended for specialists competent in this field. But still, every person has the right to know about the results of certain diagnostic methods, so we will dwell a little on the main indicators of duplex scanning of arteries and veins and try to figure out what may indicate normal condition vessels, and what about the pathology.
The consequences of changes in the diameter of the intracerebral artery with aging or the many pathologies that affect the brain are unknown. Although speculative, dilatation or narrowing of extracranial arteries may be an indicator of the condition cerebral circulation, similar to how peripheral flow-mediated expansion is an indicator of cardiovascular risk. Thus, ultrasonic measurements of extracranial blood flow can provide an effective, non-invasive, and new insight into cerebrovascular function, including the progression of cerebral hypoperfusion with various cognitive impairments.
So, in conclusion, the patient can see the following characteristics (may vary depending on the group of vessels under study):
1. Quantitative characteristics of the Doppler spectrum:
- peak systolic rate blood flow
- end diastolic blood flow velocity
- time average maximum speed blood flow
- time-averaged blood flow velocity
- resistance index
- pulsator index
Triplex ultrasound diagnostics
It is clear that the usefulness of new measures of cerebrovascular function with extracranial ultrasound is still in its infancy; however, the application of these new approaches has great potential for clinical use. From a physiological point of view, in addition to monitoring the initial blood flow, extracranial vascular ultrasound procedure can be used to provide additional information about factors such as vascular compliance, stiffness, baroreflex sensitivity, shear rate.
Of these indicators, the systolic rate is of practical importance, since it is he who indicates the presence of stenosis (narrowing) of the vessel, for example, as a result of atherosclerotic lesions of the vascular wall. The second - fourth indicators are used mainly for formulas that calculate the last two, also having practical value- for example, the higher the resistance index, the greater the resistance of the vascular wall to blood flow, as it loses its elasticity, which occurs with hypertension, diabetic angiopathy, parietal thrombi, atherosclerotic plaques. Normally, some vessels, such as the brachiocephalic trunk and subclavian arteries have high resistance.
Scanning carotid artery usually recommended by cardiologists or general practitioners if he or she thinks the patient may have carotid disease. Carotid disease is a disease in which a fatty material called plaque builds up inside the carotid arteries, causing a blockage or narrowing. Smoking High level blood fats and cholesterol High blood sugar levels due to offending diabetes resistance High blood pressure Obesity Family history of carotid disease. Symptoms of blockage or narrowing.
2. Qualitative characteristics:
- the straightness of the artery or the presence of deformities, tortuous course, aneurysms (protrusions) or other anomalies is assessed
- measurement of the diameter of the artery (using the transverse sectional plane)
- measurement of the intima-media complex (internal endothelial lining of the artery and middle muscular-elastic membrane)
These indicators show the degree of narrowing at arterial hypertension, the presence of parietal overlays (thrombi, atherosclerotic plaques). If a plaque thrombus is detected, their localization, size, echogenicity (increased, medium, decreased), structure, surface (smooth, uneven, ulcerated for plaques) are described.
- for veins, the conclusion indicates the presence or absence of expansion, varicose transformation, failure of the valves of the veins (which contributes to stagnation of blood in them and varicose veins), whether the vein is compressible during compression (when the sensor is pressed, the elasticity of the vein wall is determined), determination of retrograde (reverse) blood flow during the Valsalva test (normally, the test should be negative).
The obtained characteristics must be analyzed by the attending physician - therapist, cardiologist, neurologist, vascular surgeon in order to determine further tactics for managing the patient and choosing best method treatment.
Complications of duplex vascular scanning
There are no complications during the examination, therefore this method can rightfully be called one of the most safe methods diagnostics.
Therapist Sazykina O.Yu.
Diagnostics
Precision equipment
Modern research methods
duplex scanning vessels
Vascular ultrasound- duplex (triplex) scanning with color Doppler stream coding.
The method is safe, painless, highly informative, combines the visualization of vessels and tissues surrounding the vessel with a simultaneous study of blood flow in the lumen of the vessel to detect the presence of blood clots, atherosclerotic plaques and assessment of the degree of narrowing of the arteries, aneurysms (vasodilation), pathological tortuosity of blood vessels, violations of the blood supply to vital important organs. Allows you to reliably assess all existing changes in the vascular wall, including early stages vascular diseases.
Why it is worth doing in our clinic
In our clinic, vascular studies are carried out highly qualified specialists who inspect almost all departments vascular system having great experience in the examination of patients with vascular diseases, including those of a surgical profile, who underwent reconstructive operations on the arteries of the extremities, vessels of the head and abdominal cavity. If necessary, during the research are used additional methods, such as compression and rotation tests, Valsalva test, Allen test, test with reactive hyperemia etc. Active cooperation of specialists with doctors clinical departments will allow you to get the necessary advice on the results of the survey.
Indications
cerebrovascular disease ( headache, dizziness), osteochondrosis cervical region spine, arterial hypertension and hypercholesterolemia
Varicose disease, thrombophlebitis, phlebothrombosis, post-thrombophlebitic disease
Atherosclerosis, endarteritis and diabetic angiopathy of lower extremity arteries
Atherosclerosis visceral branches abdominal aorta(vessels supplying organs gastrointestinal tract and kidneys)
Aneurysm of the abdominal aorta and other vessels
Vascular injuries and their consequences
Vascular control before surgery
Vascular control after surgical intervention
Screening examination (a study to identify asymptomatic forms of the disease)
To determine which vessels need to be examined, a specialist will help you - a doctor - vascular surgeon(angiosurgeon), cardiologist, neurologist, therapist.
Contraindications
This research method has no contraindications.
Methods and indications:
Duplex scanning of brachiocephalic arteries, cerebral vessels
The study is carried out to identify the causes of headache, dizziness, in the presence of pathology of the spine, arterial hypertension, at elevated level blood cholesterol, to detect pathological tortuosity and variants of the structure of blood vessels supplying the brain, and also as a screening for early detection atherosclerosis. The examination begins with an examination of the vessels at the extracranial level (brachiocephalic arteries at the level of the neck), if necessary, an examination at the intracranial level (cerebral vessels).
To conduct the study, the patient needs to undress in the office from the top to the waist (down to underwear), remove jewelry from the neck and lie on the couch on his back, raising his chin. Depending on the complexity of the case, the examination can take up to 30-40 minutes.
Training
Duplex scanning of the venous system (veins of the lower extremities, veins of the upper extremities).
The study is carried out to diagnose varicose disease, thrombosis of deep and saphenous veins, identifying the causes of edema and pain in the extremities, patients who have previously undergone venous thrombosis for dynamic observation, also as preoperative preparation.
To conduct the study, the patient must undress in the office below or above the waist (up to underwear), remove socks, stockings, bandages (if any) and lie on the couch on his back. In some cases, the study is also carried out with the patient standing and lying on his stomach, at the request of the doctor, simple tests are performed (holding the breath, straining). Depending on the complexity of the case, the examination can take up to 30-40 minutes.
Training
The study does not require special preparation for the patient.
Duplex scanning of the venous system (inferior vena cava, iliac veins, renal veins)
Examination of veins at the level of the abdomen is performed in patients to determine the level of spread of thrombosis, if any, and to control the installed cava filter.
Training
Duplex scanning of the arterial system (lower limb arteries, upper limb arteries)
The study is carried out in patients to identify the causes of pain in the limbs that occur during movement and walking, to clarify the degree and extent of narrowing of the arteries in atherosclerosis, patients with diabetes, control of patients undergoing reconstructive surgery on the arteries of the extremities.
To conduct the study, the patient must undress in the office below or above the waist (up to underwear), remove socks, stockings, bandages (if any) and lie on the couch on his back. Depending on the complexity of the case, the examination can take up to 30-50 minutes.
Training
The study does not require special preparation for the patient.
Duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta, iliac arteries, visceral branches of the abdominal aorta (celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery, renal arteries)
The study is performed on patients to clarify the causes pain syndrome in the abdominal cavity, which can be caused by stenosis (narrowing) or occlusion (blockage) of the branches of the abdominal aorta (for example, the mouth of the celiac trunk) or an aneurysm (expansion) of the abdominal aorta, as well as to exclude narrowing renal arteries with arterial hypertension.
To conduct the study, the patient must undress in the office above the waist (down to underwear), lower the pants or skirt and lie on the couch on your back. Depending on the complexity of the case, the examination can take up to 30-40 minutes.
Training
The study is carried out in the morning, on an empty stomach.
1. Three days before the study, exclude gas-producing foods from the diet: vegetables, fruits, legumes, dairy products, black bread.
2. The last meal of the day before 19-00 hours.
3. If the patient has a tendency to constipation, it is recommended to perform a cleansing enema the night before.
4. On the eve of the study, take 2 capsules of espumisan after each meal (3-4 times a day
Duplex scanning of the complex: left renal vein, spermatic vein, veins of the pampiniform plexus
The study is carried out as part of an examination for infertility, in the presence of dilated veins of the scrotum (varicocele).
To conduct the study, the patient needs to undress in the office above the waist (down to underwear), lower the trousers and Underwear and lie down on the couch on your back. During the study, at the request of the doctor, simple tests are performed: holding the breath, straining. Depending on the complexity of the case, the examination can take up to 30-50 minutes.
Training
The study is carried out in the morning, on an empty stomach.
- Three days before the study, exclude gas-producing foods from the diet: vegetables, fruits, legumes, dairy products, brown bread.
- 2. The last meal of the day before 19-00 hours.
- 3. If the patient has a tendency to constipation, it is recommended to perform a cleansing enema the night before.
- 4. On the eve of the study, take 2 capsules of espumisan after each meal (3-4 times a day
Duplex scanning of vessels, rectus muscles of the eye
To conduct the study, the patient lies on the couch on his back and closes his eyes.
Training
The study does not require special preparation for the patient.
Duplex scanning of an arteriovenous fistula
The study is carried out in patients preparing for the imposition of an arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis sessions, as well as to control functioning fistulas.
To conduct the study, the patient lies on the couch on his back, freeing the arm to be examined.
Training
The study does not require special preparation for the patient.
Duplex scanning of the internal mammary arteries
The study is carried out as part of preoperative preparation for patients preparing for surgery - coronary artery bypass grafting for examining arteries as a material for shunts.
To conduct the study, the patient needs to undress from the top to the waist in the office and lie on the couch on his back.
Training
The study does not require special preparation for the patient.
- Duplex scanning of arteries upper limbs 2200
- Duplex scanning of the arteries of the upper limbs (with sample) 2750
- Duplex scanning of arteries of the lower extremities 2750
- Duplex scanning of arteriovenous fistula 2750
- Duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta 1650
- Duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta and iliac arteries 2750
- Duplex scanning of the veins of the upper extremities 2200
- Duplex scanning of the veins of the lower extremities 2500
- Duplex scanning of the complex: abdominal region aorta, renal arteries and intrarenal circulation 3850
- Duplex scanning of the complex: abdominal aorta, celiac trunk and its branches, upper mesenteric artery 3850
- Duplex scanning of the complex: left renal vein, spermatic vein, veins of the pampiniform plexus 3850
- Duplex scanning of the complex: hepatic blood flow (arterial, portal, caval) 3850
- duplex scanning main arteries head (BCA) - vessels of the neck 2600
- Duplex scanning of the inferior vena cava (assessment of the cava filter) 1650
- Duplex scanning of the inferior vena cava and iliac veins 2420
- Duplex scanning of the inferior vena cava and renal veins 2420
- Duplex scanning of the iliac arteries 1650
- Duplex scanning of iliac veins 1650
- Duplex scanning of the renal arteries 2310
- Duplex scanning of eye vessels 2420
- Duplex scanning of cerebral vessels 2420

