Causes of ischemic Diagnosis of coronary heart disease, classification, symptoms and treatment. Clinical signs of ischemia
– a fairly common disease among heart patients, which develops due to insufficient oxygen supply to the heart organs. This is due to the fact that the coronary arteries become clogged, the reason for this may be early development atherosclerosis, obstruction of the coronary arteries due to neoplasms in the form of blood clots and plaques. Coronary heart disease (CHD) can cause both temporary and chronic nature. And the consequences are almost irreparable - this possible development angina pectoris, persistent arrhythmia, myocardial disease and death.
Ischemic colitis can also be caused by venous occlusion. Many minor cases may not be reported. Since the most common cause is mesenteric vascular atheroma, it is mainly a disease of the elderly and is rarely seen before advanced age. Average age for diagnostics. The likelihood of the disease increases with the age of the population.
However, this condition is by no means unknown in younger age groups due to non-cardiovascular causes such as cocaine abuse. Diagnosis and restoration of the aortaAortoic reconstructionClectomy with ligation of the inferior mesenteric arteriesGynological operations.
- Thrombosis: thrombosis of the inferior mesenteric arteries.
- Mesenteric arterial embolism.
- Polyarteritis nodoses Thromboangitis obliterans Rheumatoid vasculitis.
What is IHD?
Until the beginning of the 21st century, cardiac ischemia was considered an exclusively male disease, since ischemic heart disease was extremely rarely diagnosed in the fair half of humanity. Because of wrong image life and harmful harmful factors, the disease is becoming younger and more often diagnosed in women. The risk zone for the disease includes fairly young men and women aged 40 years and older.
Proper nutrition during ischemia
Although it is relatively rare, it is a potentially life-threatening condition. Secondary clinical manifestation mesenteric ischemia occurs due to mechanical obstruction. Other reported causes include tumor compression, aortic dissection, and postangiographic thrombosis. Sometimes blunt trauma can cause isolated splitting of the upper mesenteric artery and lead to intestinal infarction.
How to treat coronary heart disease?
Symptoms are initially nonspecific before signs of peritonitis appear. While the prognosis remains grave for patients whose diagnosis is delayed until after intestinal infarction has already occurred, patients who receive appropriate treatment promptly are much more likely to recover.
It is difficult to diagnose it the first time, because the disease has a wave-like hidden nature. Acute form with a full set of symptoms and pain can suddenly give way to a chronic form. That’s why it’s so important to notice the first symptoms in time. coronary disease, pass the professional diagnostics and get full treatment from the doctor.
Tests for suspected ischemia
Treatment Options acute thrombosis aimed at surgical methods, which have changed little since the end of the 20th century. If there is no sign of improvement within 4 hours, patients should undergo testing. Because of its high mortality and difficulty of diagnosis, mesenteric ischemia poses a significant legal risk. This risk can be reduced with a high degree of clinical suspicion, early and aggressive diagnostic imaging, and early surgical consultation with clear documentation of deadlines.
Every year many people die from this disease; according to the latest statistics, this number exceeds 2 million people.
Signs of illness
The first signs are characterized by the appearance of heaviness during exertion, so many people write off similar ailments for overwork or fatigue. Any unusual sensation in the area of the heart muscle is alarm bell and a reason to consult a specialist for advice. If the patient previously suffered from another heart disease, and his symptoms have changed, then this is also a reason to go to the hospital.
Mastery of mesenteric vascular anatomy is key to understanding and treating patients with mesenteric ischemia. However, an infinite number vascular changes may make this difficult. It undergoes a course before branching into the common hepatic, splenic and left gastric arteries. Hepatic artery secretes the gastroduodenal artery, which goes further into the correct gastroarterial artery, as well as the anterior and anal pancreaticoduodenal arteries. The right gastroepiploid artery communicates with the left gastroarterial artery, which is a direct branch of the splenic artery.

Constant nagging monotonous pain, painful sensations in the heart area with severe emotional shock, regardless of the patient’s age - weight is a sign of coronary artery disease.
Causes of cardiac ischemia
is an organ that needs regular blood supply. The slightest blockage of the coronary arteries, through which blood and oxygen flows to it, leads to the development of a terrible heart disease. Therefore, the most important and primary cause its origin is education cholesterol plaques in the arteries (coronary disease).
The left gastric artery, the third important branch of the celiac axis, communicates with the right gastric artery along the posterior aspect of the lesser curvature of the stomach. The celiac artery supplies most of the blood to the lower esophagus, stomach, duodenum, liver, pancreas and spleen.
Symptoms of coronary artery disease
The inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery gives rise to corresponding anterior and inferior branches, which anastomose with their superior counterparts. This message is an important link that helps maintain intestinal perfusion during mesenteric atherosclerosis.
The first disease that occurs is angina pectoris. At first, it bothers the patient only during increased activity. The more the arteries narrow, the more often the pain bothers you, even at rest. In parallel with this, chronic heart disease may develop.
Anything can lead to this: poor nutrition, low level ecology, inactive lifestyle, availability bad habits And so on.
Tortuosity artery. The right colic artery is usually at the same level as the middle colic artery. The right and middle colic arteries are important source blood of the marginal artery of Drummond and lead to the appearance of the terminal vasa rectum, which supplies blood to the colon.
It supplies the distal transverse, descending and sigmoid colon, as well as the rectum. It was once thought that the "watershed zone" near the splenic flexure was more susceptible to ischemia secondary to poor arterial flow; however, it is now believed that poor development this area leads to an increased susceptibility to ischemia.
Symptoms of coronary artery disease
At each stage of the development of the disease, as well as in acute or chronic forms, the symptoms differ in the intensity of sensations.
TO general symptoms The following deviations can be attributed:
* Cardiopalmus;
* General malaise and weakness;
* Constant feeling compression in the area of the heart muscle;
The venous system is, for the most part, parallel arterial system. Upper mesenteric vein formed by tolerant, ileal, ileolic, right colic and middle colic veins, which drain small intestine, cecum, ascending colon and transverse colon.
The inferior mesenteric vein drains the descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum via the left colic vein, sigmoid branches, and superior rectal vein, respectively. The portal vein enters the liver. The severity of injury is inversely proportional to mesenteric blood flow and depends on the number of vessels involved, the average blood pressure system, duration of ischemia and collateral circulation. The superior mesenteric vessels are involved more often than the inferior mesenteric vessels, while the blockage of the latter is often silent due to better collateral circulation.
* Nausea;
* Spontaneous pain with sudden movements, going out into the cold, contrasting soul etc.;
* The occurrence of shortness of breath even with slow walking and other minor exertion;
* Aching pain in the area of the limbs, ribs, back, neck;
* Constant cold sweat.

Damage to the affected part of the intestine can range from reversible ischemia to transmural infarction with necrosis and perforation. Arterial insufficiency causes tissue hypoxia, leading to an initial spasm of the intestinal wall. This leads to emptying of the intestines with vomiting or diarrhea. Damage to the mucous membrane can cause bleeding into the gastrointestinal tract.
X-ray showing intestinal spasms. At this stage there is slight abdominal tenderness, creating the classic intense visceral pain, which is disproportionate to the results of the physical examination. As ischemia persists, the mucosal barrier is disrupted and bacteria, toxins, and vasoactive substances are released into the systemic circulation. This can lead to death from septic shock, heart failure, or multisystem organ failure before intestinal necrosis actually occurs.
With angina pectoris, these symptoms manifest themselves more intensely, but last a short time. At chronic illness they do not cause particular discomfort to the heart, they become a habit, but they bother you for a long time.
In addition, the disease may be accompanied by mental symptoms:
* Constant worry without any reason;
Pathological findings 2 hours after the onset of intestinal ischemia. As hypoxic damage worsens, the intestinal wall becomes swollen and cyanotic. Liquid is released into abdominal cavity; this explains the serovascular fluid sometimes recovered by diagnostic peritoneal lavage. Intestinal necrosis may occur 8-12 hours after the onset of symptoms. Transmural necrosis results in peritoneal signs and carries a much worse prognosis.
Acute mesenteric arterial embolism
Microscopic data 24 hours after the onset of ischemia. Because the vascular occlusion is sudden, patients were unable to develop a compensatory increase in side flow. Most often, emboli are located at a distance of 6-8 cm from the arterial origin, with narrowing near the appearance of the artery of medium colic.
* Sharp embrace of panic and fear;
* Low mood, apathy;
* Sudden attacks suffocation, feeling of lack of oxygen.
Any manifestations of this disease they say that you should immediately consult a doctor, because if the disease is neglected, it can result in myocardial death, stroke or death.
Acute mesenteric arterial thrombosis
Complete occlusion of the aorta with acute embolism of the superior mesenteric artery. These patients endure severe primary lesion lungs in the lungs, a condition called pulmonary lung. Symptoms usually do not develop until two of the three arteries are stenotic or completely blocked. Progressive worsening of atherosclerotic stenosis to acute occlusion allows time for the development of additional collateral circulation.
A blood clot forms during low flow, causing acute cessation of intestinal flow. Bloody stools develop as the more sensitive mucous membrane dies first. The powder gradually becomes necrotic; subsequently develops bacterial growth, and the resulting intestinal perforation causes sepsis and ultimately death.
Treatment of ischemia
Few people know that coronary heart disease is one of the most common diseases with high threshold mortality. Therefore, if there is severe narrowing of the coronary arteries and other vessels, you should act promptly.
In such cases, treatment of ischemia requires the use of the following methods:
Nonexclusive mesenteric ischemia
In inflammatory vascular diseases, more small vessels. These patients often present a history of chronic mesenteric ischemia in the form of intestinal angina before an emergency event. Many vasoactive drugs may also cause regional vasoconstriction. There are no major pathological arterial or venous occlusions observed.
Other associated causes include pancreatitis, sickle cell disease and hypercoagulation caused malignant neoplasms. The mechanism responsible for ischemia in this setting is a massive influx of fluid into the intestinal wall and lumen, resulting in systemic hypovolemia and hemoconcentration. Consistent intestinal edema and decreased blood flow secondary to venous thrombosis impede the flow of arterial blood, which leads to intestinal ischemia.
1 . Coronary artery bypass grafting – implantation of damaged vessels;
2 . Angioplasty is an artificial dilatation of a narrowed vessel;
3 . Endovascular surgery - surgery is performed directly inside the arteries, without surgical cutting and using local anesthesia.
A full range of measures aimed at treating coronary artery disease
Complex treatment of ischemia consists of the following stages:
Fluid sequestration and edema of the intestinal wall are more pronounced than with arterial occlusion. The colon is usually saved due to better collateral circulation. In a study of mortality factors in 31 patients with mesenteric venous thrombosis, Abu-Duff et al determined that 30-day mortality in these patients was strongly associated with colonic involvement of ischemia and short bowel syndrome. The anticoagulant may have been missing. The 5-year mortality rate was primarily due to short bowel syndrome, the researchers said.
Cardiac embolism - A fragment of a thrombus after myocardial infarction, an auricular thrombus associated with mitral stenosis and atrial fibrillation, or septic emboli from valvular endocarditis. Emboli from fragments of proximal aortic thrombus due to a ruptured atheromatous plaque. Atheromatous plaque dislodged by arterial catheterization or surgery. . Embolization is less commonly associated with ischemic disease than thrombosis and has better survival with optimal treatment.
1. Anesthesia before treatment and good rest in cases where the disease is at a severe stage of development. Use of epidural anesthesia as needed;
2. Thinning of blood density, whether it is necessary to do this or not is determined by taking a test for blood viscosity, blood clot formation, blood cholesterol level, etc.;
United States and international statistics
In contrast to embolic events, which typically occur in arterial branches and result in limited intestinal ischemia, thrombosis usually occurs at the source vessel, resulting in widespread intestinal involvement. Venous thrombosis occurs in approximately 001% of patients who undergo exploratory laparotomy.
Demographics related to age, sex, and race
Approximately two thirds of patients are women. Research shows that inflammatory disease intestines is another risk factor for mesenteric artery thrombosis. Men may be exposed to more high risk occlusal arterial disease because they have more high level atherosclerosis.
3 . Taking anticoagulants that prevent the development of thrombosis;
4 . Prevention of atherosclerosis;
5. Search and treatment of existing diseases of cardio-vascular system and central nervous system;
6. Taking prostaglandins – normalization of blood supply;
7 . Prescription of drugs responsible for transporting oxygen to the organs and vessels of the heart;
8 . Study of blood pressure and vascular patency using ultrasound;
9 . Testing is prescribed on an individual basis;
10 . ECG.
And these are not all the stages that a patient with chronic pain may go through. In addition, it is necessary to carry out treatment and preventive measures: adhere to proper nutrition, give up cigarettes, alcohol, normalize weight through physical activity, etc.
Preventive measures
Preventive measures include adjusting your diet. Any foods and dishes rich in cholesterol should be excluded from it: fatty pork, smoked meats
and sausages, pastries and sweets with butter creams, full fat milk And dairy products. But there are greens, an abundance of fruits, vegetable oil, seafood and fish, cereals and beans, nuts - this is a real godsend for heart-throbs.
You can also reduce body weight by increasing daily physical activity, for this it is enough to walk more often. fresh air, clean the house and do morning exercises. Giving up bad habits and eliminating the causes of stress is also good prevention illness.
At the same time, you need to understand that self-medication can lead to irreparable consequences. Therefore, a timely visit to the doctor and following his recommendations is the best preventative measure with ischemic disease.
The term "myocardial ischemia" reflects pathological consequences various diseases leading to malnutrition of the muscular layer of the heart.
The modern interpretation assumes the development in certain areas of the myocardium of a process of discrepancy in the needs and actual provision of tissues with oxygen and nutrients.
As a result, a zone is formed ischemic changes, in which normal myofibrils first experience dystrophy and are then replaced by a dysfunctional one scar tissue, the development of nonspecific inflammation is possible.
Symptoms of ischemia are not specific to one disease. They signal a “starving” myocardium and require treatment.
Reasons for development
Manifestations of a lack of substances that play the role of energy carriers form a complex of symptoms united by the diagnosis of coronary disease. She is still in the lead with violations cerebral circulation in the causes of mortality and does not allow increasing human life expectancy.
Development acute ischemia (acute heart attack myocardium) is more typical for men after 50 years of age; in women, the maximum number of cases occurs in menopause, more typical chronic forms diseases.
The main causes of ischemia:
- atherosclerotic lesion coronary vessels, narrowing of their lumen due to plaques;
- inflammatory diseases vascular bed at systemic vasculitis, syphilis, systemic diseases connective tissue, extend to the cardiac arteries.
The importance of reinforcing and provoking factors are:
- diabetes;
- hypertension;
- increased level of low-density lipoproteins in the blood;
- performing high physical activity,
- stressful situations;
- hereditary predisposition.
Mechanisms of development of ischemia
Metabolic changes during endocrine pathology cause disturbances in the composition of the blood. The fluid flowing through the coronary arteries becomes thicker. Platelets increase their ability to stick together and form clots that impede blood flow. And the fibrinolysis system is inhibited.
This is what a thrombosed coronary vessel looks like in section
With increased blood pressure the process of formation of atherosclerotic plaques is accelerated.
Physical activity and stress response are characterized by spasm of the adductor muscle. coronary artery. It is impossible to detect a short-term spasm during examination. But this mechanism has been proven when experimental studies. Arises increased need in oxygen, but the muscle does not receive it.
Serious importance is attached to the development compensatory mechanisms. The myocardium has “spare” vessels (collaterals). They begin to work when there is a problem with the patency of the main coronary arteries. The clinical picture of the disease and the degree of damage to the ischemic zone depend on how quickly the blood supply routes are replaced.
In the worst case, an acute infarction develops with the formation of necrosis of the entire myocardial wall (transmural). In the best case, collaterals will help completely restore blood supply in the ischemic area, and the fibrinolysis system will dissolve blood clots. The occurrence of foci of ischemic dystrophy can also be attributed to more favorable current ischemia.
How does subepicardial ischemia develop?
Subepicardial localization (directly under the outer layer) depends on one more specific mechanism: internal blood supply deep in the muscle fibers. Normally, small vessels run from the inside to the outside and penetrate the entire thickness of the heart muscle.
If these capillaries do not receive enough blood from central artery, they, accordingly, feed the worst extreme points, falling on the subepicardial zone. The lumen of blood vessels can be blocked by small blood clots due to increased blood clotting.
Great difficulties arise when feeding hypertrophied (thickened) muscles in hypertensive patients. Capillaries do not have time to grow through the entire layer. Therefore, subepicardial ischemia is more often detected in individuals suffering from hypertension.
Clinical signs of ischemia
Symptoms of ischemia consist of:
- a typical complex characteristic of an anginal attack (angina pectoris);
- other manifestations.
Typical pain attack characterized by:
- connection with previous physical or mental stress (manifestation at rest is an unfavorable symptom);
- localization behind the sternum or to the left of it;
- pressing, squeezing character, accompanied by a burning sensation.
The pain radiates to left shoulder, spatula, lower jaw, throat. The attack lasts from several minutes to half an hour.
Long duration and intensity indicate the development of acute myocardial infarction.
TO atypical manifestations include:
- gastralgic form (pain is localized in epigastric region, imitate a stomach ulcer or gastritis), the patient is worried about nausea, vomiting, bloating;
- asthmatic manifestations - pain syndrome poorly expressed, symptoms of acute heart failure with severe shortness of breath come first;
- painless ischemia.
When does silent ischemia occur?
Silent myocardial ischemia can be diagnosed only on the basis additional examination on the ECG. The patient himself does not feel any signs (3% of cases); sometimes he speaks of increased fatigue.
This form has its code in International classification diseases (ICD-10) I25.6. Another name is asymptomatic. It is more common among elderly patients and people with reduced general pain sensitivity.
It has been established that up to 40% of patients with stable angina They also have painless attacks. The development mechanism is no different from common reasons ischemia. Special meaning is given to a developmental anomaly nerve pathways hearts.
Diagnostics
For correct positioning ECG studies are sufficient for diagnosis. Sometimes daily monitoring is required. Holter monitoring provides significant assistance. Observation is carried out throughout the day and does not interfere with the patient.
The results are deciphered and allow you to “see” and document silent ischemia, short-term attacks, heart rhythm disturbances, the depth of damage to the heart muscle during transmural infarction, the prevalence of the ischemic zone.
Specialized clinics and departments use monitors that simultaneously record blood pressure numbers.
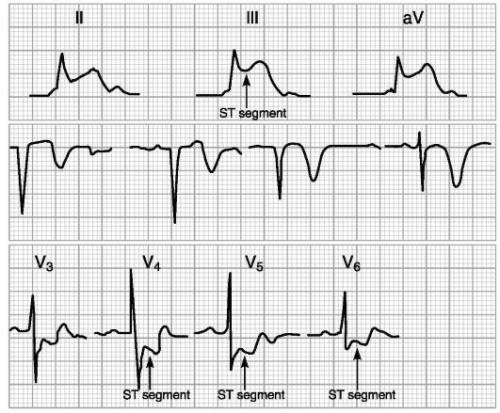
Doctors of all specialties know the signs of an acute heart attack. Other forms and specific locations of ischemic areas can be recognized by a doctor in a functional diagnostics office.
Additional lead studies are required to diagnose ischemia back wall hearts.
To identify dependence on physical activity tests are carried out with a bicycle ergometer, an ECG is taken after the administration of special medications.
Treatment
The principles of ischemia treatment are based on possible elimination all risk factors affecting the blood supply to the heart:
- you will need to quit smoking and alcohol;
- A diet with severe cholesterol restriction is called " eating behavior", it must be observed for the rest of your life;
- it is necessary to prevent stressful situations, learn to manage emotions, cope with nervous stress;
- physical activity is sharply reduced, daily exercise is required morning work-out, walks at a relaxed pace.
Medicines
Nitroglycerin under the tongue or aerosol forms (Isoket) are used to relieve attacks. With the aim of long-term use The doctor prescribes long-acting nitrates.
Drugs from the group of adrenergic blockers (Atenolol) help prevent the vasoconstrictive effects of catecholamines and improve blood flow in the vessels of the heart.
The use of aspirin compounds has made it possible, according to international cardiac monitoring, to reduce the risk of developing acute coronary pathology by 22%.
Medicines such as Ivabradine, Nicorandil, Ranolazine, Trimetazidine allow you to restore metabolism at the cellular level and cause muscle fibers to become accustomed to oxygen deficiency.
Aspirin in different drugs(Cardiasc, Cardiomagnyl), Clopidogrel is taken one tablet at a time to reduce blood clotting and the likelihood of coronary artery thrombosis.
Application of cardiac surgery
The development of cardiac surgery has shown significant success in restoring blood supply to the myocardium and eliminating sources of arrhythmia.
Surgical methods are used according to strict indications, in the absence of effect from drug therapy or impossibility of using it.
The most common operation is to install stents to widen a narrowed vessel. Choice surgical treatment remains with the cardiac surgeon. Possibilities are decided after angiography of the coronary vessels, study of the development of collaterals.
Detection of the silent form of ischemia also requires therapeutic effects. Any changes in the ECG should not go unnoticed by the patient and the attending physician.

