Everything an expectant mother needs to know about fetal movement. First fetal movements during pregnancy
Most likely, the most exciting event for any woman is the first movements during her first pregnancy. Many representatives of the fair sex are interested in the question of when and how a woman can feel the movements of her child, and whether she should worry about this. In some cases, fetal movement during pregnancy does indicate the presence of an unfavorable situation, but usually there is no need to worry about this. The first fetal movements during pregnancy usually occur in the second half of the gestation period. In addition, women who have already given birth begin to feel this a little earlier than mothers who will have their first child.
This feature is due to the fact that women who have already given birth are accustomed to such sensations and are able to distinguish the movements of the baby. Those who are pregnant for the first time, due to the fact that the baby’s movements are weak, may confuse them with muscle contractions, gas formation or intestinal peristalsis. In addition, the anterior abdominal wall of women who have given birth is stretched much more, making it more sensitive. It is also worth saying that skinny girls feel this phenomenon more often and earlier than the fuller representatives of the fair sex.
Baby's first movements
Many believe that the expectant mother begins to feel the first movements of the fetus during pregnancy after twenty weeks. Mothers who are not giving birth for the first time begin to feel them after eighteen weeks. However, you should not rely entirely on these figures, as they are mostly statistical averages. In general, everything depends on individual characteristics body, as well as the woman’s sensitivity level. Thus, slender representatives of the fair sex, adherents active image life, as a rule, begins to feel movement a little earlier. In general, it should be noted that the baby begins to move between 16 and 24 weeks.
The first signs of the baby moving are felt rather weakly, which is why they are very difficult to describe. Some say it feels like a sort of “gurgling” in the stomach, while others say it feels like stroking or tickling the insides. Closer to 24 weeks, movements in the abdomen begin to appear more clearly - they resemble full-fledged tremors, and other people are also able to feel them by placing their hand on the stomach.
Child activity standards
In fact, the fetus is in almost constant motion except during sleep, when it becomes immobile.
For example, a calculation was made according to which a child makes about 200 movements during the day.

During pregnancy from 26 to 32 weeks, this figure increases from 200 to 600. However, then the activity of the fetus decreases, but there is no need to worry about this, as this is due to the growth of the child. In addition, the expectant mother does not feel most of the movements of the fetus - only the strongest tremors are felt.
The activity of a child’s movements depends on many factors, which include:
- Times of Day. Typically, the peak of fetal movements occurs in the evening or at night, but for some mothers it may also occur during the day.
- Psychological state of the expectant mother. When mommy is in stressful situation or has seizures strong fear, the child may hide and not move or, conversely, begin active, exciting movements.
- Power loads. Physical exercise mothers, as a rule, force the fetus to become motionless, while at rest the strongest and most intense tremors are felt.
- Diet of a pregnant woman. At a thrill When the mother is hungry, the child begins to stir restlessly, and movements are also noticed when eating food, especially sweets.
- Ambient acoustics. It has been observed that the fetus reacts to sudden loud sounds strong movement, and sometimes, on the contrary, by calming down.
- The position in which the mother is. If the expectant mother for a long time is in an uncomfortable position for her, the child may respond with painful movements.
As a rule, during the period when the fetus is awake, the mother can feel about 15 tremors per hour. The norm is about 4 hours of complete immobility - during this period the child sleeps.
Warning signs
The most alarming sign is a partial decrease in movement activity or its complete cessation. This sign often indicates that the fetus is susceptible to a lack of life-giving oxygen, or hypoxia. You should start to worry in a situation where the child has been motionless for more than 6 hours. If the silence is within this figure, do not panic, as the child may also be in sleep mode. If the child still does not move for more than 6 hours, an urgent visit to the obstetrician is necessary.
What measures to take
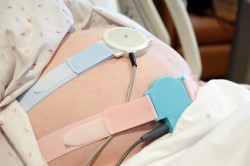 If you cannot get to the doctor yourself, you should call an ambulance. First, the obstetrician will check the baby's heartbeat using a special stethoscope. The minute rate of the fetal heartbeat is from 120 to 160 beats. But even with a normal heartbeat, another important procedure- cardiotocographic study, or CTG. This procedure will accurately show whether the fetus is suffering from hypoxia or not, and it will also determine functional state baby To the front abdominal wall A sensor is installed for the woman to conduct the study (this is where the baby’s heart is supposed to be located). The sensor installed in the lower abdomen also determines the heartbeat curve.
If you cannot get to the doctor yourself, you should call an ambulance. First, the obstetrician will check the baby's heartbeat using a special stethoscope. The minute rate of the fetal heartbeat is from 120 to 160 beats. But even with a normal heartbeat, another important procedure- cardiotocographic study, or CTG. This procedure will accurately show whether the fetus is suffering from hypoxia or not, and it will also determine functional state baby To the front abdominal wall A sensor is installed for the woman to conduct the study (this is where the baby’s heart is supposed to be located). The sensor installed in the lower abdomen also determines the heartbeat curve.
In addition, the pregnant woman is given a special button. The expectant mother must press the button every time she feels movement. Each click is marked on a special graph. Normally, every time the baby moves, his heartbeat increases. This happens due to the motor-cardiac reflex. However, this reflex appears only after 30 weeks from the start of pregnancy, so early stages this method diagnosis is practically useless.
As a rule, the time for CTG is 30 minutes. If during this period there has never been any increase in heart rate, the doctor will ask the pregnant woman to walk a little or climb the stairs. After such procedures, CTG is repeated. If accelerations do not appear, this indicates the presence of hypoxia in the fetus. In such a situation, the obstetrician will most likely prescribe a Doppler examination, which reveals the speed of blood circulation through the vessels of the umbilical cord, as well as in the vessels of the child. The indications of this procedure will accurately indicate whether hypoxia is present in the fetus.
If hypoxia is detected in the fetus, measures are selected depending on its stage. If hypoxia is at the initial stage, the pregnant woman is prescribed periodic examinations and treatment. medications aimed at improving blood circulation in the vessels and oxygen supply to the fetus. If hypoxia is in a severe stage, urgent delivery will be prescribed, since in our time there is no medications capable of dealing with this problem. Whether delivery will be performed depends on the duration of pregnancy, the condition of the pregnant woman and the readiness of the fetal tract. naturally or by caesarean section.
Every expectant mother should listen to her feelings and movements of the fetus. However, you should not worry or worry too much, as sometimes the child may be in the sleep phase and rest peacefully. Attention and accuracy are the key successful course pregnancy.
EVERY FUTURE MOTHER IS WAITING FOR THIS MOMENT WITH IMPATIENCE, AND WHEN THE BABY FINALLY MAKES HIMSELF KNOWN, THERE IS NO LIMIT TO THE JOY, EVEN IF THE FIRST PUSH IS MORE RELATED TO A TRUE HOOK. FROM HERE UP TO BIRTH, WITH THE HELP OF MOVEMENTS OF DIFFERENT STRENGTH AND DIRECTION, THE BABY WILL INFORM ABOUT ITS PASSIONS, NEEDS AND INCONVENIENCES. HOW TO DECODE THESE SIGNALS?
Women who are preparing for the birth of their first child begin to feel the baby’s movements, as a rule, from the 20-22nd week, and those who are expecting a second or third child, a little earlier - from 18 weeks, because the muscles of the uterus are more stretched. and it’s easier for them to recognize familiar sensations. Some expectant mothers claim that they registered the first “tremors” already at 15-16 weeks. There is no point in questioning their words: everything is very individual, and therefore quite probable.
There is also no unanimous opinion about what the baby’s first movements look like. For some women, they resemble “gurgling” in the stomach, for others - light tremors, for others - gentle stroking. Sometimes it happens that it is quite difficult to distinguish the work of the gastrointestinal tract from the baby’s movements. If you have strong doubts, you can consult an obstetrician-gynecologist and, if necessary, undergo additional examination. But if the child does not give obvious signals even after the 20th week, this is a reason to be wary and make a mandatory visit to the doctor.
Entertaining dynamics
At the end of the 8th week of pregnancy, the baby begins to develop nervous system, which is responsible for motor activity. At this point, the baby already has muscle And nerve fibers, through which it passes nerve impulse, giving her the command to contract. Having at its disposal everything that is needed for free movement in the intrauterine space, the child begins to perform its first exercises in the period from the 8th to the 9th week of pregnancy. But his movements are still poorly coordinated, and he himself is so small that the woman does not feel his rare touches to the walls of the uterus.
At 16 weeks, the baby begins to move in response to sounds, primarily to the mother’s voice, reacting to changes in intonation. At 17 weeks, he already knows how to squint his eyes, at 18, finger the umbilical cord, clench and unclench his fists, touch his face and even cover it with his hands, as if protecting himself from sharp, loud or unpleasant noise effects. The longer the period, the more actively the child moves, so that by the time of birth he has mastered the key skills necessary for survival and honed a full set of innate reflexes.
So, at the 20th week, according to various sources, the baby moves about 200 times per day. From the 24th week of pregnancy until birth, he moves almost the same as all newborn babies. The greatest activity (approximately 600 movements per day) is observed between the 28th and 32nd weeks: uterine size and volume amniotic fluid They still provide enough room for maneuvers. At this stage, during sleep, the baby can suck a finger and smack sweetly, and during periods of wakefulness - stretch, yawn and move its arms and legs. After 32 weeks physical activity begins to gradually decline: the child grows, and the uterus becomes cramped for him, so that he is no longer able to perform somersaults or somersaults. For this reason, by the end of the third trimester, the number of movements may decrease slightly, but their strength and intensity will only increase.
Direct dependency
The baby’s activity is influenced not only by the size of the uterus and his own temperament: emotional condition mothers are also taken into account. In moments of joy, the level of endorphins in a woman’s body rapidly increases, and under the influence of strong negative emotions or nervous overload stress hormones are released. In both cases such sharp jumps affect the functioning of not only the heart, but also blood vessels, including those located in the placenta. Thanks to this cunning mechanism, the baby perfectly reads the mother’s mood.
Sometimes the baby is forced to move by the feeling of hunger. If the mother has not eaten for a long time, the glucose level decreases in two organisms at once. To increase the flow nutrients from the umbilical cord, the baby begins to actively move, accelerating blood circulation. Thus, he sends an eloquent message to his mother: “It’s time for lunch!” As soon as this urgent request is fulfilled, the baby will calm down and become quiet.
TO active movements A child is often encouraged by affectionate speeches addressed to him, and it does not matter who speaks to him, mom or dad. Also, according to many observations, children great pleasure deliver strokes through the abdominal wall!
If the baby's movements become too sudden, most likely the mother has taken uncomfortable position: for example, lay down on your back or sat down with your legs crossed. In order for the baby to calm down, it is usually enough to turn on his side or change the position of his legs. If this does not help and painful movements continue for several hours, you should consult a doctor.
Home test
However, with the help of pushes, the baby can communicate not only that the music chosen by dad does not cause him delight, but that it would be nice to repeat mom’s fairy tale for an encore. The nature and number of movements allow us, first of all, to judge its general health, more precisely about whether he receives enough oxygen. You can evaluate the baby’s condition using these two parameters from about the 28th week. It is believed that from this moment on, within an hour, the child should remind himself of himself at least 10 times a day. You just need to take into account that he can fall asleep for 3-4 hours, and during these periods there is no need to expect a response from him. It should be borne in mind that the intensity of the baby’s movements may change throughout the day, and this is also normal.
Sometimes the movements are so delicate that the woman does not feel them. If, for her own peace of mind, the expectant mother wants to make sure that everything is okay with the baby, you can try to encourage him to be active. For this, a cup of sweet tea with cream and a small muffin, biscuits or toast with jam are usually enough. 15 minutes after eating dessert, you should lie down for a couple of hours and relax in a calm environment. If the baby does not react to the bait in any way, most likely he has quiet time. In this case, the experiment can be repeated a little later. But if, despite all the tricks, the child does not remind himself during the day, consult a doctor to rule out hypoxia (oxygen starvation).
Be wary to the expectant mother It should also be done if the baby begins to move less often than usual. At home, testing can be done in two ways. Particularly popular is the Pearson “Count to 10” test, which is carried out from the 28th week of pregnancy. From 9 a.m. to 9 p.m., you need to record the time of every tenth movement. If the score is less than 10, the child may have hypoxia. According to the Sadowski method, the baby's movements should be counted within one hour after eating, preferably in a lying position. If during this time he moved less than four times, you need to continue summing up the results during the second hour. If four movements are not achieved in two hours, there is reason to suspect hypoxia. In both cases, you must immediately consult a doctor.
Check digits
Cardiotocography will help dispel doubts. This test is done after 34 weeks of pregnancy. The woman sits or lies on her back and two sensors are attached to her stomach. One shows the tone of the uterus, the other shows the baby’s heart rate. The study lasts from 20 to 60 minutes, during which the expectant mother must note every movement of the baby by pressing a special button. Normally, at rest, the heart rate of a toddler is 120-160 beats per minute, and during movement it increases to 170-190. Deviations from these indicators indicate hypoxia. Then Doppler ultrasound will be required - additional ultrasonography, allowing you to assess the nature and speed of blood flow in the arteries of the uterus and umbilical cord and in the middle cerebral artery child. The procedure is painless and safe for both the woman and the baby, and it can be performed an unlimited number of times.
If hypoxia is confirmed, the doctor prescribes a special course of treatment, the purpose of which is to improve intercellular metabolism in the placenta and enhance blood microcirculation. Since there are many reasons leading to a lack of oxygen, tactics are selected individually. So, to regulate the blood supply to the uterus and reduce it contractility, sometimes required bed rest and reception special drugs. In some cases, it is necessary to take measures to reduce blood viscosity and increase cell permeability to oxygen. Good effect Vitamin E, ascorbic acid and glutamic acid, glucose solutions.
If after measures taken the nature of the movements will not change; intensive treatment in a hospital will be required. In this case, the doctor prescribes drugs that improve uteroplacental blood flow. Therapy is carried out under daily CTG monitoring.
Fetal movement is one of the main indicators of its normal development. For different terms Characteristic is the varying intensity of fetal movement during pregnancy. When movement begins during the first and subsequent pregnancies, what is considered normal and what to pay attention to is the topic of our conversation.
Neither positive test, nor a doctor's confirmation that you are pregnant can cause such powerful emotions like the baby's first movement. It is at this moment that you truly realize what is burning inside you. new life. During the first pregnancy, the mother begins to feel fetal movement at twenty weeks (i.e., in the middle of the term). During the second, as well as during the 3rd pregnancy, fetal movement is felt approximately two weeks earlier.
The intensity of the baby's movements depends on the period of gestation. If you try to characterize fetal movements during pregnancy week by week, you will get something like this:
- 7-8 weeks - appearance of physical activity;
- 10-11 weeks - the appearance of the swallowing reflex;
- 16-17 weeks - reaction to external stimuli (light, sound);
- 18-19 weeks - movements become conscious (touches face with hands, clenches fingers into fists, touches umbilical cord);
- 18-20 weeks - the first sensations of movement by the mother;
- 24 weeks - distinct movements, reminiscent not of movement, but of tremors (they can be felt even by those who put their hand to the pregnant woman’s belly);
- 26-32 weeks - the most high period activity (up to 600 movements per day);
- From the 33rd week, the number of felt movements decreases (this is explained by the increase in size of the fetus).
Frequent fetal movements during pregnancy
The frequency of movements of a child in the womb is influenced by many factors. The expectant mother should learn to understand by the nature and frequency of movements how comfortable the baby feels. To understand whether the movement of your fetus during pregnancy is normal or if there are abnormalities, you can conduct a special test.
You just need to count the number of movements within an hour. It is considered normal if during this time you felt at least ten and no more than fifteen movements of the child. If there are deviations from the norm in one direction or another, you must inform your doctor about this. Frequent violent movements of the fetus during pregnancy are observed when:
- mother is in a smoky or stuffy room,
- she feels dizzy
- she has an attack of nausea.
Under such circumstances, the fetus experiences insufficient oxygen supply. All a pregnant woman needs to do is take a walk fresh air, and everything returns to normal. The baby's activity also depends on glucose levels. The higher it is in the blood during pregnancy, the more active the fetal movement is. So in this way the baby asks his mother to eat.
An increased level of fetal movement activity may indicate polyhydramnios, the threat of preterm labor, or initial stages entwining the baby with the umbilical cord.
The baby can “protest” with intense movements even when the mother’s position is uncomfortable for him (for example, when lying on his back for a long time). Conversely, it calms down if you sit for hours without changing posture, are worried, or are worried for some reason. Start moving, eat something tasty, and everything will return to normal.
Starting from thirty-two weeks, the baby develops regular cycle"rest-activity". Usually from this period the waking rhythms of mother and baby coincide.
There is no need to worry too much when the child is not moving. three hours. Most likely he's just sleeping.
First fetal movements during pregnancy
In fact, during pregnancy, the first movements of the fetus occur as early as the eighth week, although, as mentioned above, the mother begins to feel its movements at 18-20 weeks. The baby is still so small that it simply “swims” in the amniotic fluid without touching the walls of the uterus.
As the fetus grows, its nervous system develops, and movements become more and more orderly. He begins to react not only to internal state, but also to external stimuli. He can no longer avoid touching the walls of the uterus. This is where the sensations of fetal movement during pregnancy come to you.
If a mother is carrying two children at once, she begins to feel their kicks much earlier than during a singleton pregnancy. Moreover, they are also felt with redoubled force, since there is not enough space for them. As practice shows, the period for the start of fetal movement during pregnancy with twins is the fifteenth or sixteenth week.
However, all the times given above are statistical averages. No one can give an unambiguous answer to the question of when the fetus will begin to move during pregnancy in a particular mother. Some expectant mothers feel movement as early as the thirteenth week. But they are episodic, appearing not just irregularly, but even once every few days.
The movement of a baby during pregnancy is one of the most wonderful processes during this wonderful period. When does the expectant mother begin to feel the fetus? What actions of the baby cause certain sensations?
When does fetal movement begin?
The baby first makes itself known at the end of the first half of pregnancy. Each woman feels the movement of her fetus differently. Someone notices light tremors, someone is gently stroked by the baby, and someone is tickled. There is an opinion that fetal movement in primiparous women begins at 20 weeks, and when repeated births movements can begin as early as the 18th week. But this opinion is erroneous, since in fact the fetus begins to show activity already from 8-9 weeks of pregnancy, but the mother begins to feel these movements a little later. If a pregnant woman says that she began to feel the baby’s movements already at the 15-16th week, then this may well be the case, since it all depends on how sensitive and receptive the woman is to irritants. Usually, slender women Fetal movements during pregnancy begin to be felt earlier than full. The sensations usually become regular after 21–22 weeks.
Due to the fact that the baby needs development and preparation for a future independent life, he is in constant movement in the stomach. Even if the baby is quiet for 3-4 hours, this is not a cause for concern. At week 20, the fetus makes about 200 movements per day. In the period between the 28th and 32nd weeks, when the volume of the uterus and amniotic fluid allow the baby to move freely, the fetus greatest number movements, which reaches a value of 600. After the 32nd week, the activity of the fetus begins to gradually decrease as it grows and the free space in the uterus decreases. Even while the baby is sleeping, he can suck a finger, even sometimes during an ultrasound this can be seen, move his lips, smack his lips. When the baby is awake, he can move his legs and arms, stretch, or give his mother some signs about how he is feeling. For example, a baby may begin to react violently to loud music or, conversely, it can hide when it hears a sharp sound. It has been noticed that the baby moves more when the mother is resting, and when she is working or physically active, the fetus becomes quiet. But this is not always the case, it may be different; this is largely determined by the character of the little man.
Methods for assessing fetal movement
1. Cardiff technique. The essence of the technique is that the woman must record all movements of the fetus, starting from 9 am. It is necessary to measure how long it takes the baby to make 10 movements. If the baby does not make this number of movements before 9 pm, then you need to notify your doctor about this, since there is a possibility that additional cardiotocography (CTG) and Doppler measurements will be necessary.
2. Sadowski method. After eating for an hour, the woman counts how many movements the fetus made. It is advisable to do this in a lying position. If four movements are not observed during the first hour, then it is necessary to continue counting the movements during the second hour. If during these two hours four movements have not been made, then you must inform the doctor.
There is an opinion that if the baby moves too violently, this indicates hypoxia ( oxygen deficiency fetus). But in practice it has been proven that this is not the case at all. It is worth paying attention to the number and intensity of fetal movements: if the movements are rare, then you should contact additional examination, as this may indicate some trouble. If after 28 weeks of pregnancy you notice that the fetus moves rarely, weakly and sluggishly, then it is recommended to urgently seek medical advice.
When the baby moves normally, these movements do not cause concern to the mother. IN rare case The baby may bother his mother a little if his heel gets under the rib. But in any case, these sensations are so pleasant and unique that sometimes women after childbirth begin to miss these periods of their lives, when they formed a single whole with the baby and communicated in a language accessible only to them.
It describes how taking a bath during pregnancy affects a woman’s body. It was considered whether it is possible to wash in shower stalls and in hot tubs. Recommendations for taking baths during pregnancy are given.
Evening primrose oil during pregnancy and healing properties this plant. Medical indications and contraindications for the use of evening primrose oil by pregnant women.
Sex during pregnancy is good because you don’t have to use protection, and semen contains useful material, which are necessary for women and which provide positive influence on the cervix, soften it, as a result, the cervix opens better

