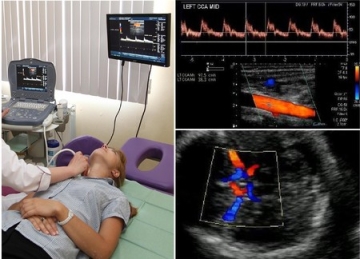
Duplex scanning of brachiocephalic arteries. Ultrasound duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries
Ultrasound duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries or BCA ultrasound for short is a modern ultrasound method for diagnosing blood vessels, including carotid and vertebral vessels that supply blood to the brain, and subclavian arteries.
First of all, a person who is assigned this study may have a question - what are the brachiocephalic arteries and where are they located.
Brachiocephalic vessels are the largest arteries and veins that are responsible for blood flow to the tissues of the head, brain and to upper limbs. They are also called main lines.
The brachiocephalic arteries include the carotid, subclavian, vertebral and their junction, which forms the brachiocephalic trunk. These vessels and some others near the base of the brain form the circle of Wellis, which is responsible for the distribution of blood flow to all parts of the brain.
What is it - duplex scanning of brachiocephalic arteries, and what is the basis of the technique?
The apparatus for examining BCA is based on the principles of echolocation. The working surface emits and then captures ultrasonic pulses. The information is converted into a digital signal. Thus, the image appears on the monitor.
The method is based on the union benefits of B-mode- visual interpretation of the state of blood vessels and adjacent tissues and Doppleroscopy - qualitative and quantitative properties of blood flow. The Doppler spectrum can also be supplemented with color mapping.
What does BCA ultrasound show?
BCA ultrasound shows:
- lumen of blood vessels;
- blood clots, plaques, detachments;
- stenosis, expansion of the walls;
- breaks, deformations.
With the help of BCA ultrasound can be diagnosed:
- vascular pathologies;
- violation of wall tone in VVD;
- arterial aneurysms;
- fistulas between vessels;
- angiopathy;
- thrombosis;
- vascular injury;
- varicose disease.
Vessels of the brain - it's difficult arranged system capable of self-regulation and maintenance cerebral blood flow. Only complex diagnostics, which includes ultrasound scanning, CT, MRI, allows you to accurately and timely choose the treatment, and then evaluate its effectiveness.
Ultrasound helps to assess the anatomy of blood vessels, determine the characteristics of blood flow, assess the condition of the walls and lumen. Thus, it is possible to diagnose early stage occurrence of atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots, tortuosity of arteries and their stratification.
Peculiarities
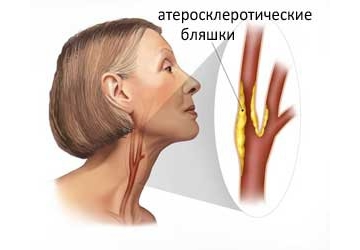
The initial sign of atherosclerosis, which can show an ultrasound study, is not even a plaque, but thickening of the wall of the carotid artery by only a fraction of a millimeter. With duplex scanning, this indicator is well defined. The thickness of the intima-media complex (the so-called KIM) is also called. IMT is taken into account to assess the effectiveness of treatment.
 An increase in IMT greater than 1 mm is most often associated with risk factors such as smoking, arterial hypertension, diabetes, etc.
An increase in IMT greater than 1 mm is most often associated with risk factors such as smoking, arterial hypertension, diabetes, etc.
As the disease progresses, plaques begin to form. Usually they are localized in the so-called. carotid bifurcation - this is the place where the common carotid artery divides into internal and external. The presence of plaque in this segment is major risk factor for stroke and myocardial infarction. Therefore, it is very important to timely detect atherosclerotic changes in the early stages.
Duplex scanning reveals the location of the plaque, as well as its shape, size, structure and degree of stenosis (narrowing of the lumen). When the lumen is already completely closed - this is occlusion.
During the study of BCA, it is often detected tortuosity of the arteries due to their lengthening. Arteries lengthen due to atherosclerosis and increased blood pressure. crimp vertebral arteries usually occurs due to defects cervical region spine. If the tortuosity leads to clamping of the lumen, then this can cause a violation of cerebral blood flow.
Ultrasound scanning is also used to examine patients with traumatic injury vessels: wall bundle or similar. The main symptom of this disease is severe headache that cannot be reduced with conventional painkillers.
The advantages of BCA ultrasound can be called:
- high information content;
- research efficiency;
- safety and the possibility of repeated holding;
- painless procedure.
During the study on the monitor an image is formed similar to a conventional ultrasound, but a vessel is clearly visible against its background where the blood flow is formed. Due to the advantages of ultrasound, BCA is considered the gold standard for diagnosing pathologies. A timely ultrasound of the vessels can save lives and prevent possible disability.
Indications for carrying out
The indications for the appointment of duplex scanning of the BCA are:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- violation of coordination of movement;
- pressure problems;
- fainting;
- elevated cholesterol levels;
- sensory disturbance (numbness) of the limbs;
- blurred vision;
- flashing flies in the eyes;
- memory impairment and decreased concentration;
- preoperative examination.
Direct indications for the study are following pathologies:
- atherosclerosis;
- hypertension;
- cardiac pathologies;
- neck injuries;
- compression of arteries and veins and other vascular injuries;
- vasculitis;
- blood diseases;
- suffered a stroke or heart attack.
Training
Preparation before the study consists in excluding from the menu products and dishes that can affect the tone and filling of blood vessels, which will distort the results of the study.
On the day of the study, you can not drink tea, coffee, energy drinks, Coca-Cola, alcohol, you should not be zealous with overly spicy and salty dishes. Right before the ultrasound of the BCA, one should not be in stuffy or smoky rooms, as this can also change the blood supply to the vessels. It is better to refrain from taking vitamins and nootropics the day before the study.
The use of the device is absolutely harmless and has no effect on the body person.
How is it carried out
The patient lies on his back on the couch near the apparatus, the doctor puts a roller under his neck. The head should be turned in the opposite direction from the device. The doctor lubricates the surface of the skin with a gel that facilitates the passage of the ultrasound signal.
 The doctor will examine the sensor segment by segment, observing the change in the signal on the monitor. He can lightly press the sensor on the vessels or ask for a short time stop breathing.
The doctor will examine the sensor segment by segment, observing the change in the signal on the monitor. He can lightly press the sensor on the vessels or ask for a short time stop breathing.
None discomfort during the study does not occur: according to the sensations, the procedure is no different from the usual, familiar to everyone ultrasound. The study lasts 20-30 minutes.
Deciphering the results of the study
The scanner will record the necessary indicators, the doctor will enter them into the scan protocol. Deciphering the Doppler spectrum, cartograms of blood flow will take no more than 10 minutes, after which you will receive a transcript.
The result of the scan is a decoding of the information received, printed out with a list of the examined vessels and a description of their size and condition. Decryption gives the ability to determine whether the vessels correspond to the anatomical norm whether there is a pathology, etc. Based on the transcript, your attending physician, if necessary, prescribes treatment.
The decoding is carried out by comparing the indicators:
- the nature of the blood flow;
- its speeds: systolic (max) and diastolic (min);
- wall thickness;
- pulsator index (so-called PI) is the ratio of the difference between max and min speeds to the average (the sum of max speed and two min divided by three);
- resistive index (so-called RI) is the ratio of the difference between max and min speeds to min;
- systole-diastolic ratio: max speed divided by min.
Based on the last 3 indices, the patency of the vessel is judged.
The blood flow is assessed in the external and internal carotid arteries, common (ECA and ICA, CCA), supratrochlear (NMA), basilar (OA), vertebral (PA) and in its segments, each of which has its own designations, for example, Vo, V1, V3 etc.
 Also in front, back, middle cerebral arteries(PMA, PCA, MCA), subclavian (RCA), anterior and posterior communicating (PSA, PCA) arteries. Changes in indicators can also be assessed with horizontal and vertical position body.
Also in front, back, middle cerebral arteries(PMA, PCA, MCA), subclavian (RCA), anterior and posterior communicating (PSA, PCA) arteries. Changes in indicators can also be assessed with horizontal and vertical position body.
It can be summarized that ultrasound of the BCA is a special type of ultrasound diagnostics of blood vessels that provide nutrition to the brain, other organs of the head, neck, girdle of the upper extremities.
This is an affordable, safe, detailed and informative study, which in ten minutes can show the state of the vessels and identify the cause of some unpleasant symptoms. An annual examination will allow 90% to predict the development of a cerebral stroke.
Among the advantages of duplex ultrasound, it is worth noting the high information content, safety and lack of pain. In addition, such a diagnosis does not require special preparation from the patient. The procedure does not side effects and complications, therefore, does not imply restrictions on the age of the patient.
Operating principle
This research method is based on the Doppler effect. Ultrasound, reflected from the vessels, changes its frequency. This allows you to determine the angle of the received signal. Doppler shift can be encoded as a stream moving with different speed. Each indicator is assigned its own characteristic color. It can be easily seen against the background of a monochrome image displayed on the monitor screen. The blood flow is collateral or main. The first is characterized by a reduced speed, the second is normal.
Indications for research
Ultrasound scanning of the arteries of the extremities examines the diameter of the vessels and the nature of the movement of blood. Often it is supplemented with functional tests. These studies help to diagnose deviations in work. vascular system, as well as the presence of general disorders in the body. In addition, such tests allow us to study the mechanisms responsible for the movement of arms and legs. So, in a healthy limb, the vessels tend to expand, which significantly increases the rate of blood flow. Violation in the mechanisms of the limbs often leads to malfunctions of the vessels. To conduct such studies, for some time the patient is subjected to a small physical activity. Then the doctor measures the speed of blood movement and compares them with those that were recorded before the procedure. The change in these data should not exceed 40%.
Sometimes tests associated with the tension of the limbs are used. In this case, the data taken before and after the study is also recorded. Specialists also sometimes prescribe a test using nitroglycerin. In this case, the property of the substance is used to relax the muscles of the vessels.
The first signs of damage to the arteries are the unevenness, thickening or discontinuity of their inner layer. These symptoms may indicate the beginning of the development of severe abnormalities in the work of the arteries. They can be detected using Doppler scanning. Using this method allows you to visualize the vessels well and give information about possible deviations from the norm in their work.
This study allows you to visually examine even those vessels that could not be detected with a standard ultrasound. So, duplex scanning of the skull is considered one of the few types of diagnostics that can detect circulatory disorders in the brain. Using it, you can accurately determine the location of the arteries and analyze their work.
AT modern medicine in the field of vascular pathologies, there are many different medical techniques. However, the treatment of any disease requires a complete and thorough examination. Diagnosis of blood vessels is effectively carried out using ultrasonic methods research, this is due to the structure and structure of the vessels. The concept of ultrasound for many is no longer new.
Ultrasound examination can be carried out by the method of Doppler ultrasound (USDG), and by the method of ultrasound duplex scanning (USDS), and by the method of color Doppler mapping (CDC).
Diagnostics by ultrasound
One of the simple and available ways study of venous and arterial patency is Doppler ultrasound. The Doppler effect is at the heart of the ultrasound scan, that is, to obtain the necessary data, changes in the reflected sound waves from moving blood cells. Ultrasound is prescribed if it is necessary to determine vascular patency, either to obtain an assessment of blood flow, or to identify pathologies of the venous valve.
When conducting a Doppler ultrasound, veins and arteries are not visible, the assessment of blood flow velocity and patency is carried out on the basis of the Doppler effect values obtained. According to the results of the ultrasound scan, headaches are successfully diagnosed, hypertonic disease, . But if the identification of impaired vascular patency is done with ease, then establishing the causes of such a pathology using Doppler ultrasound is very difficult. This is due to the fact that this diagnostic method does not allow visualization of the vascular walls and their possible curvatures that affect the speed and quality of blood flow.
Initially, the images shown by the ultrasound machine were made in a flat and thin projection of the organ under study. In modern diagnostic medicine, equipment is used that allows obtaining a three-dimensional image of organs in real time and in motion.
 Dopplerography is prescribed to determine the patency of blood vessels, to obtain characteristics of blood flow
Dopplerography is prescribed to determine the patency of blood vessels, to obtain characteristics of blood flow Diagnostics by ultrasound
Ultrasound duplex scanning - more complex diagnostic technique, is characterized by a combination of B-mode and Doppler effect. The use of the B-mode allows you to visualize the studied veins and arteries and study the condition of the surrounding tissues. The study of blood flow in the vessels is carried out using color Doppler mapping or spectral analysis techniques.
As a result of the study and subsequent computer processing of the data, it is possible to obtain readings presented in the form of a Doppler spectrum or a color blood flow cartogram. The cartogram is obtained using various color mapping technologies and, in fact, it is a “cast” of the cross section of the vessel under study. During vessels, an image of the vessel is displayed on the monitor screen, which allows you to make a visual assessment of the patency of a vein or artery and find the cause that caused the decrease in blood flow velocity. With the help of ultrasound, the following pathological vascular conditions can be detected:
- development of vascular stenosis, thickening of the vascular walls;
- the occurrence of various anomalies during the passage of blood vessels through tissues;
- cholesterol plaques and blood clots in veins and arteries;
- vascular junctions after operations.
Difference duplex study and Doppler ultrasound lies in the fact that ultrasound combines two research functions. Doppler ultrasound allows you to evaluate the speed characteristics of blood flow in the vessels, and the B-mode makes it possible to identify anatomical features the structure of a vein or artery, due to the visualization of the vessel itself on the monitor.
Advantages of the ultrasound technique
Using ultrasound, you can easily determine most pathological abnormalities in the normal course of the vessels, for example, tortuosity or deformation. In addition, this is the main method in studying changes in vascular lumens, determining the presence of cholesterol plaques and thrombi. Ultrasound of this type can provide visualization and assessment of the characteristics of the blood flow of the entire vascular system, including large trunk trunks and small subcutaneous organ vessels.
Investigating USDS large veins and arteries, it is possible to create a clear and reliable picture of the existing structural pathologies of the vessel walls at the very first stages of the development of the disease. Thus, non-stenosing atherosclerosis and diabetic angiopathy. Pathological processes accompanied by intraluminal vascular lesions, which disrupt patency or reduce the speed of blood flow, for example, blood clots and plaques, also do not cause difficulties for ultrasound diagnosis.
 duplex scanning combines two methods of research and allows you to identify most pathological processes in vessels
duplex scanning combines two methods of research and allows you to identify most pathological processes in vessels Diagnosis by color flow method
When conducting a triplex scan, the above-mentioned techniques are carried out and color visualization of the vessels and blood flow in them is added. Scanning in this way allows for a more informative examination, with high accuracy to determine the vascular patency and the degree of stenotic damage to the vessels. In other words, CFM is a combination of Doppler ultrasound diagnostics and duplex scanning, combined with additional research internal vascular lumen in color imaging mode.
Indications for diagnostics
The appearance of certain symptoms often becomes the reason for the appointment of an ultrasound examination:
- the appearance of headaches and dizziness;
- violations of the vestibular apparatus;
- feeling of heaviness in the head;
- the appearance of ear noise and flashing black dots before the eyes;
- causeless loss of consciousness;
- disease of varicose veins;
- development of edema of the upper and lower extremities;
- frequent convulsions;
- a sharp decrease in vision.
 The development of edema of the extremities is a good reason for prescribing a Doppler study or duplex scanning of blood vessels
The development of edema of the extremities is a good reason for prescribing a Doppler study or duplex scanning of blood vessels Pathological conditions human vascular system, in which without fail shown holding ultrasound diagnostics one of the ways like this:
- aneurysm of cerebral vessels;
- disease chronic nature accompanied by the development of vascular insufficiency;
- bruises of the cervical spine and head injuries;
- venous diseases;
- stroke conditions;
- reconstructive surgery on the spine;
- the state of vegetovascular dystonia;
- atherosclerotic lesions;
- cervical osteochondrosis.
In traditional ultrasound diagnostics, ultrasonic waves are used that are not perceived human ear. When interacting with internal organs, waves are reflected and captured by a special ultrasonic sensor. The intensity of the reflection of ultrasonic waves depends on the density of the organ under study and its structure. After the sensor catches the reflected ultrasonic waves, the computer processes them and converts them into a black and white two-dimensional image.
With duplex scanning, traditional ultrasound procedure complemented by dopplerography - a study based on measuring the reflection of ultrasonic waves from moving objects.
A beam of ultrasonic waves is reflected from erythrocytes moving with the blood flow and is evaluated by a special sensor, and the reflection speed depends on the speed of blood movement. Thus, the addition of Doppler scanning to conventional ultrasound makes it possible to assess not only the structure of the tissue under study, but also the direction, speed and intensity of blood flow inside it. The movement of blood is reflected on the monitor in the form of red-blue flashes, the intensity and direction of which is assessed by the diagnostician.
Ultrasound duplex scanning: indications for examination
Ultrasound examination in combination with Doppler sonography is widely used in medical practice due to its painlessness and simplicity. The disadvantage of such a study is the sufficient high cost of equipment, not all medical institutions can afford it.
The ultrasound allows you to reliably evaluate such indicators as:
- intensity and speed of vascular blood flow;
- thickness vascular wall;
- the presence of blood clots or plaques in the lumen of the vessels;
- structure of the vessel, its width, length, degree of tortuosity.
The quality of the results obtained during the study directly depends on the quality of the equipment and the qualifications of the diagnostic specialist. Ultrasound is performed to diagnose the following pathologies:
- occlusion of the carotid arteries;
- atherosclerosis of the lower extremities;
- thrombosis and thromboembolism of any localization;
- arterial aneurysms;
- diseases of the aorta;
- atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries;
- varicose disease;
- Raynaud's disease;
- cerebral circulatory disorders.
Preparation for the study of ultrasound
Ultrasound duplex scanning does not require any special preparation from the patient, the only exception is ultrasound of the abdominal vessels ( abdominal region aorta).
Ultrasound of the abdominal aorta requires additional preparation, including:
- cleansing the intestines with an enema;
- hunger for 8 hours.
Preparation measures are related physical features the passage of ultrasound waves that are not able to pass through the intestinal gases.
Ultrasound duplex scanning technique
Ultrasound is a non-invasive and painless research method that has no contraindications. For the procedure, the patient is placed on a special couch with a raised head end. The doctor applies a special gel to the ultrasound transducer, and with sliding movements begins the study of the required vascular area.
After obtaining a clear picture of the structure of the organ under study using traditional ultrasound, the diagnostician switches to Dopplerography mode, which allows assessing vascular blood flow. The monitor of the ultrasound device displays the information received from the sensor in the form black and white pictures with colored flashes, it is the colored flashes that reflect the movement of blood through the vessels.
Duplex scanning of the veins of the lower extremities
Ultrasound of the veins of the lower extremities is one of the most precise methods assessment of the state of the venous bed, allowing:
- evaluate the venous structure and patency of the veins;
- identify excessive narrowing or expansion of venous vessels;
- establish availability venous thrombosis or atherosclerotic plaques;
- measure the speed and intensity of venous blood flow;
- assess the condition of the valves in the venous bed;
- monitor the progress of treatment.
Doppler scanning of the veins of the lower extremities reveals the appearance of vascular pathology in the early stages when clinical manifestations no illness yet. Thanks to early detection blood flow disorders, treatment begins at an early stage, which minimizes adverse effects for the patient.
Regular conduct of this study is indicated for all people over 40 years of age. Necessarily ultrasound appointment veins at:
- swelling and pain in the legs;
- increased vascular pressure;
- diabetes mellitus;
- visible varicose veins veins;
- smoking;
- obesity
- non-healing ulcers and discoloration skin lower limbs.
The results of the study are evaluated by a phlebologist, surgeon or therapist.
Duplex scanning of vessels of the head and neck
Examination with duplex scanning of extracranial (neck vessels) and intracranial (head vessels) arteries and veins is used to evaluate disorders cerebral circulation. Wide use received this study to assess the state of large cerebral and carotid arteries. The method allows:
- assess the speed of vascular blood flow in the arteries and veins of the neck and head;
- determine the presence of atherosclerotic formations and the degree of their influence on the blood supply to the brain;
- assess the risk of developing vascular complications(ischemic attacks, strokes);
- identify vascular aneurysms and arterial constrictions;
- assess the hemodynamics of the brain;
- assess the reserve capacity of the blood circulation of the brain;
- identify venous outflow disorders.
An objective assessment of the condition of the arteries and veins of the brain and neck, obtained with the help of a duplex study, helps to choose the right treatment, monitor its effectiveness and make an individual recovery prognosis. Ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck is indicated in the following conditions:
- headache;
- dizziness and heaviness in the head;
- noise in ears;
- periodic loss of consciousness;
- change in gait and impaired coordination of movements;
- memory loss;
- visual impairment;
- numbness and weakness of the hands.
An examination of the vessels of the neck can be prescribed by a neurologist in case of pathology of the cervical spine, to assess the degree of impaired vascular blood flow. You can read more about methods for examining cerebral vessels.
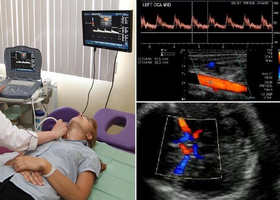
Duplex scanning of brachiocephalic arteries
The brachycephalic arteries, or BCA, are blood vessels in the neck and subclavian region that provide nutrition to the brain, namely vertebrates, sleepy, subclavian arteries. Duplex scanning of brachycephalic arteries allows assessing the intensity of blood supply to the brain, as well as identifying the presence of their atherosclerotic lesions.
Most often, duplex scanning of the BCA is used specifically for the diagnosis of atherosclerosis and an objective assessment of the size atherosclerotic plaque.
Ultrasound allows to detect atherosclerosis of brachycephalic arteries already in the early stages, at the stage of thickening of the arterial wall and long before the appearance of a full-fledged atherosclerotic plaque. The thickening of the walls of the BCA is assessed by the thickness of the intima-media complex, and or IMT. An increase in this indicator even by one millimeter above the norm is an unfavorable criterion for the development of atherosclerosis.
Duplex BCA is indicated for patients with the following symptoms:
- dizziness, headache, noise in the head;
- high blood pressure;
- deterioration in visual acuity;
- memory loss;
- goosebumps and numbness in the hands.
Ultrasonography of the brachiocephalic arteries is mandatory for patients with osteochondrosis of the spine with localization in the cervical region, as well as for patients with ischemic disease, or diabetes.
Duplex scanning of the vessels of the head and neck is a non-invasive study based on the properties ultrasonic wave, reflected from erythrocytes moving in the vessel, to form an image of this vessel. This type of diagnostics allows you to visualize each vessel against the background of the surrounding tissues.
Preparation for the study is not required, it is completely painless and safe, has no contraindications. The result is issued immediately at the end of the procedure.
Types of ultrasound diagnostics of blood vessels
Any study of vessels, both cavitary and passing under the skin, is also called Doppler after the name of its inventor.
In this case, the ultrasound not only passes through the tissues, but also, reflecting off the cells floating in the liquid part of the blood, sends an image or graph of the vessel to the screen. Based on it, the doctor judges its patency, the degree of narrowing.
There are several types of doppler:
- UZDG (ultrasound dopplerography). This is a study of the vessels of the neck, head, brain or other organs, which performs only one function: to determine the patency of the vessel. This is done on the basis of a graph obtained from the study of vessels (that is, there is no direct visualization of the vessel). In addition, the sensor with this type of diagnostics is placed “blindly”, at the approximate points of their projection.
- duplex ultrasound scan. So it is called precisely because it combines two functions: the study of the anatomy of blood vessels, and the assessment of the speed of their blood flow. In this case, the vessel is already visible on the monitor, an image of tissues is obtained around it, as in conventional ultrasound. It turns out that this method, unlike ultrasound, helps in diagnosing the cause of poor vascular patency. He helps to visualize plaques, blood clots, tortuosity of blood vessels, thickening of their walls.
- Triplex scanning is even better than duplex scanning. In this case, the monitor also shows the vessel against the background of the image of the tissues in the thickness of which it passes. Only the vessel itself is stained in different colors(mapping) depending on the speed of blood flow in it.
What information does the study provide?
Doppler in duplex scanning mode provides the following information:
- characteristics of the elasticity of the walls of the vessels of the head and neck
- condition of the inner lining of blood vessels
- violation of the integrity of the vascular wall
- the presence of formations inside the lumen of the artery or vein of the head and neck
- vascular anatomy: abnormal tortuosity, more small vessel in an abnormal place, a change in the course of an artery or vein.
What diseases can be detected by dopplerography
- congenital anomalies in the location, course or branching of blood vessels
- atherosclerosis
- injury to an artery or vein
- inflammation of the walls of arteries and capillaries (vasculitis)
- diabetic, hypertensive, toxic angiopathy
- encephalopathy
- vegetative-vascular dystonia.
And the neck helps to understand:
- causes of repeated transient ischemic attacks, strokes
- the degree of damage to these particular arteries due to metabolic or antiphospholipid syndromes
- the degree of violation of the patency of the vessels of the arterial bed due to atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, smoking.
Knowledge of the status of extra- and intracranial arteries and veins, obtained using duplex scanning, helps in prescribing proper treatment, objective control of its effectiveness, making an individual forecast.
Who needs to examine the vessels of the brain
Duplex scanning (or at least ultrasound) of intracranial arteries and veins (that is, those that are in the cranial cavity) is indicated in cases of such complaints:
- headache
- noise in the ears or head
- heaviness in the head
- dizziness
- visual impairment
- bouts of impaired consciousness such as fainting or inadequacy
- unsteadiness of gait
- incoordination
- impaired speech production or comprehension
- limb weakness
- hand numbness.
Examination is also performed when a pathology is detected during USDG of vessels neck, when detecting a pathology of the neck organs using CT, scintigraphy, MRI (for example, an increase thyroid gland). In this case, the neurologist for appointment adequate therapy it is necessary to know how all these diseases affect the brain, whether its nutrition can suffer from this.
Indications for the study of the vascular bed of the head and neck
Ultrasound duplex scanning of those arteries and veins that supply the brain, but are located in the neck (that is, extracranially - outside the cranial cavity) should be performed in the following cases:
- headache
- dizziness
- unsteadiness of gait
- memory impairment, attention
- incoordination
- when planning operations on the vessels and muscle of the heart
- when detecting a pathology of the neck organs, due to which the vessels passing there can be compressed
- visually visible contraction of the vessels of the heart.
When is Planned Doppler Ultrasound Necessary?
Doppler of both extra- and intracranial arteries and veins as a routine study (even before the appearance of any complaints) should be carried out at least once a year:
- all women over 45
- all men over 40
- those whose close relatives suffer from hypertension, diabetes mellitus, ischemic disease
- with diabetes
- smoking
- antiphospholipid syndrome
- with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
- metabolic syndrome
- arterial hypertension
- if you had a stroke or transient disorder cerebral circulation
- if a person suffers from rhythm disturbances (increased likelihood of cerebral thromboembolism followed by a stroke)
- increased levels of cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoproteins in the blood (signs of atherosclerosis)
- operations on the spinal cord or brain
- before planned operation on the heart.
How to prepare for the study
Both duplex scanning and UZDG arteries and veins of the head and neck are carried out without special preparation. On the day of the study, it is necessary to abandon the intake of those substances that affect vascular tone:
- nicotine
- energy drinks.
The question of whether medications that can distort the ultrasound picture should be discontinued ( antihypertensive drugs, "Betaserk", "Vinpocetine", "Cinnarizine", "Phezam" and others), you need to ask directly to the neurologist, who will then prescribe the treatment.
Also, before the study, you will need to remove all jewelry from the head and neck, and after the procedure, wash your hair.
How the examination is carried out
Dopplerography, whether duplex ultrasound or ultrasound, is carried out according to the general principle.
The patient lies on the couch on his back. A hard pillow or roller is placed under his head. He releases his neck for research and turns his head in the direction opposite to the sensor. The doctor applies a little gel to the skin, along which he will move the transducer, looking through each artery and vein, making measurements in them.
The vessels of the brain are examined through the bones of the skull. To do this, the doctor places the sensor in the following areas of the head:
- temporal areas on both sides
- supraorbital regions
- junction occipital bone with spine
- region of the occipital bone.
A water-soluble gel will also be applied to these places, which, by removing air from under the sensor, will allow you to get more accurate results UZDG.
In addition to a simple examination of the arteries and veins of the head and neck, the doctor performs certain functional tests(for example, asks to hold his breath) in order to assess with the help of a Doppler whether autonomic regulation is disturbed.
Interpretation of study data
According to the results of the examination, the doctor receives data on blood flow (its speed and type), defects in the filling of blood vessels.
Dopplerography of the venous bed allows you to evaluate the anatomy, tortuosity, patency, diameter, outflow rate, intraluminal formations. At the same time, there are almost no figures in the conclusion of the ultrasound of the cerebral vessels.
Doppler arterial vessels holds digital analysis, that is, the data obtained by various measurements are compared with the norms. For example, normal performance internal and general carotid artery such:
- maximum systolic rate: less than 0.9
- peak velocity in diastole: less than 0.5
- percentage of stenosis: 0%
- formations inside the lumen should not be
- artery wall thickness: 0.9-1.1.
Signs of vascular pathology
- If the Doppler detects an increase in the thickness of the vascular wall, a change in echogenicity of an uneven type, while the narrowing of the artery is less than 20%, this indicates non-stenosing atherosclerosis of this artery.
- If there are changes in the vascular wall, its echogenicity is changed, the differentiation of wall layers is impaired, this speaks in favor of vasculitis.
- Plaques in arteries that are described as "thin-rimmed hypoechoic" or those that are "decreased in echogenicity but have little echogenic content within the plaque itself" may be the cause of the patient's symptoms.
- Stenosis of any cerebral artery over 50% is an indication for mandatory treatment.

