Anomalies of children's development. Frequent genetic diseases of children in the Russian Federation. Deformities and their causes
As a result of a developmental defect, the fetus may die in the embryonic period or soon after birth due to its inability to exist independently, without connection with the mother’s body. For some types of malformations of organs that are not vital ( cleft lip, malformations of the uterus), occurs to varying degrees proper development child.
Fetal deformities do not always complicate the course of labor. This is most often seen in hydrocephalus and double deformities.
Hydrocephalus(hydrocephalia) - dropsy of the head. Severe hydrocephalus is rare. It occurs as a result of excessive (up to 5 l) accumulation cerebrospinal fluid in the cranial cavity, almost usually in the cerebral ventricles, extremely rarely in the subarachnoid space, and also due to its obstructed outflow. The bones of the skull, under the influence of increased intracranial pressure, diverge and sometimes become thinner to the thickness of parchment paper, their fibrous connections (fontanelles and sutures) are stretched, and the volume of the head therefore increases significantly. The brain undergoes severe atrophy from pressure.
If the fetus dies long before birth, intracranial pressure decreases, the head turns into a soft elastic bladder, which can independently pass through the birth canal during childbirth. When the fetus is alive, the large, tightly elastic head is pinched in the pelvis, resulting in overstretching of the lower segment of the uterus. If no help is provided, the uterus will rupture. At breech, more often observed with hydrocephalus, the need for surgical assistance during childbirth arises when the subsequent head is inserted into the entrance to the pelvis.
Childbirth, in addition, is often complicated by weakness of labor forces, bleeding from the uterus in the afterbirth and early postpartum periods, infection.
Hydrocephalus is recognized by its totality the following signs: big size go-. dexterity that does not fit into the pelvis, despite good labor, thinning of the bones of the skull (when you press on them with a finger, you get the sound of crunching parchment), their mobility, the presence of wide fontanelles and sutures.
In case of cephalic presentation and sufficient opening of the uterine pharynx, the skull is punctured and the fluid is released. In the future, labor is allowed to proceed independently if there are no indications for its acceleration. If the latter are present, the fetus is removed using a cranioclast.
Hydrocephalus is sometimes observed in combination with rare disease fetus - general hydrops fetalis (hydrops foetus universalis congenitalis). There is a sharp puffiness of the fetus. The swelling is sometimes so pronounced that cracks form on the skin from which fluid leaks. Such children die, if not during childbirth, then soon after. Currently, this disease is considered as erythroblastosis.
(module direct4)
Anencephaly(lanencephalia) is one of the most common fetal deformities. The fetus is missing the cranial vault and most of the brain; the facial part of the head is well developed. With anencephaly, the fetus has characteristic appearance: the small head is located directly on the shoulder girdle, the ears lie on the shoulders due to the raised face, frontal and parietal part no heads eyeballs protruded, the tongue protrudes from the half-open mouth.
Anencephalics are stillborn or die within the first hours after birth.
With this type of deformity, childbirth occurs without any difficulty. The diagnostic difficulties that arise in this case are important: an anencephale is mistaken for a fetus in a breech position. Vaginal examination without much difficulty allows us to exclude the latter.
Anencephaly is often accompanied by polyhydramnios and spina bifida.
Double deformities. Conjoined twins occur as a result of the fusion of identical twins. This pathology can occur in the absence of fertilized egg septum between twins (monoamniotic twins). In such cases, due to incomplete separation of the egg, a union may occur between the twins, as a result of which they are tied friend with a friend in some parts of the body. Double deformities can also arise as a result of incomplete splitting of the rudiment; in this case, fruits develop with doubling of entire sections of the body - two heads with a common body, two bodies with one head, doubling or tripling the number of limbs, etc.
If each of the conjoined twins is developed equally (or almost equally), they speak of symmetrical deformity. Otherwise, when one of the deformities lags significantly behind the other in its development, they speak of asymmetric deformity.
A typical example of an asymmetric deformity is a heartless freak (acardiacus): the heart of one of the twins in identical twins due to a common placental circulation also works for the heart of the second twin, which entails gradual atrophy of the heart, parts blood vessels, lungs and upper limbs the last one. Often there is also an absence of a head; the entire fruit turns into a shapeless mass covered with skin.
A heartless freak is usually born without difficulty shortly after the birth of a normally developed twin.
Incomparably greater practical significance have symmetrical deformities, often leading to severe complications childbirth requiring surgical intervention.
All double deformities (fused twins and incompletely separated twins) can be divided into two groups depending on the location of the fusion.
The first group includes twins fused at the ends of the fetal body - heads (craniopagus) or buttocks. These monsters, if they are located in one row during labor, easily pass through the birth canal and usually do not complicate the course of labor.
The second group consists of twins fused at the torso - chest (thoracopagus), as well as two-headed freaks (dicephalus), having a common torso and two heads. Ishiopagus and Thoracopagus can continue to live after birth, remaining unseparated. Such monsters included the so-called “ Siamese twins", who lived to 63 years of age. Twins can in some cases be separated surgically.
Two-headed freaks, like some other types of freaks in which the fusion is excessively intimate, present great difficulties, both diagnostic and therapeutic.
Childbirth in most cases occurs with a sharp violation biomechanism. In each individual case it is necessary to find a more gentle and Right way for delivery.
A relatively common type of deformity is cerebral hernia.
A hernia of the brain (meningocele) is usually observed in the area of the bridge of the nose if there is an opening in it, as well as in the area of the large and small fontanel. Such freaks die in the first hours or days after birth. They do not cause any difficulties during childbirth.
Spina bifida occurs due to bifurcation of the posterior vertebral arches, usually in lumbar region spine.
They protrude through the hernial opening in the form of a cyst. meninges, sometimes spinal cord, covered with thinned skin.
Children born with spina bifida often suffer later from paralysis of the limbs (mostly lower limbs), urinary incontinence and other serious illnesses.
Brain hernias do not disrupt the biomechanism of childbirth. After the baby is born, it is necessary to cover the hernial protrusion with a soft sterile cloth moistened with sterile Vaseline. Further help consists of an operation to reduce the hernia into the spinal canal and close hernial opening. You can count on the success of the operation only in mild cases of this deformity.
Brain hernias are often accompanied by other fetal deformities.
Fetal anomalies include cleft lip, cleft palate, and hernia. umbilical ring(with the entry of the omentum, liver, and intestines into the hernial sac), clubfoot, multiple toes, fusion anal opening etc. Some of these anomalies require immediate surgical treatment(fusion of the anus, hernia of the umbilical ring), in other cases the operation is performed later, when the child gets stronger (cleft lip, cleft palate), in third cases it is required orthopedic treatment(clubfoot).
It is impossible to convey in words pain, which is experienced by a mother who understands that her baby, long-awaited and beloved, was born different from everyone else. The presence of deformities and other genetic diseases in a child shocks many parents and forces them to abandon such a child. Moreover, some deformities are not at all a detriment to the lives of such children. Many of these children develop no worse than healthy ones and may well become full-fledged members of society, work, support themselves and even start families. Which genetic diseases most common in our country, what are their causes and how to prevent the development of deformities?
Hereditary and non-hereditary diseases
Diseases are divided into 2 types: hereditary and non-hereditary. The former can be passed on from generation to generation, for example, the well-known hemophilia - the inability of blood to clot. The reason for this is the presence of a certain gene. Genes are particles that are responsible for the development of all human characteristics: from eye color to heart size. Among the genes there are those that, by their presence, cause certain diseases, while they can be transmitted to children from their parents, since they are “fixed”.
Hereditary diseases are caused by the presence of spontaneous mutations- changes in gene structure. These mutations may be caused various factors: radiation, chemical compounds. Such genetic changes occur singly - only in a specific person; they are not stable and are not passed on to subsequent generations.
Congenital deformities
The most widespread is a deformity popularly called “cleft lip and cleft palate.” It looks like a hole in the sky upper jaw and in upper lip, they can occur both simultaneously and separately. Today this defect is eliminated surgically: The cleft is closed and sutures are placed on the lip to tighten the philtrum. It is imperative to eliminate such a deformity, since its presence interferes with normal breastfeeding, development of teeth and speech. However, the intelligence of children with this pathology does not suffer at all.
Another common deformity is underdevelopment to one degree or another of the upper or lower extremities, which again mental abilities has no effect. Hands, upper limbs completely, one arm or several fingers may be absent, and lower limbs in this case, they remain only in a “rudimentary” state and it is impossible to move on them. However, such people adapt and can take care of themselves even without prostheses.
In addition, there are more serious developmental defects, interfering normal function organism, among them unseparated twins, acrania - serious underdevelopment of the skull, hydrocephalus - the presence of fluid in the cranial cavity and others, although they are somewhat less common. Today all these vices can be seen in ultrasound examination, then the parents are faced with the question of maintaining such a pregnancy. However, some deformities occur after birth.
Genetic diseases characterized by developmental delays
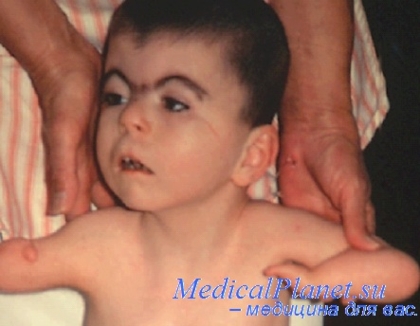
There are also a number congenital genetic diseases, accompanied by intellectual impairment and characteristic appearance. The most common and well-known is Down syndrome. Such children lag behind mental development, but in general they can develop and learn about the world, with the right approach and work with them, albeit slower than others. Usually such people are able to take care of themselves, do simple work and live normally under the supervision of relatives.
Patau syndrome- the hardest thing congenital disease, 95% of children suffering from it die in the first years of life, and those who managed to survive suffer from deep idiocy. Patau syndrome includes whole line defects - physical and mental underdevelopment, heart defects, visual impairment, cysts in thyroid gland and kidneys, disrupting their function, underdevelopment of the reproductive system.
Causes of congenital deformities
Reasons and mechanisms The occurrence of almost half of the deformities is still unknown to scientists. However, there are a number common factors, which can absolutely provoke the appearance of mutations - changes in genes.
First on the list of such factors are worth chemical compounds. Alcohol, nicotine and narcotic substances negatively affect the development of the embryo, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy.
The same can be said about medicines , the influence of many of them on fetal formation has not been fully studied. A striking example of this is the “thalidomide disaster” that occurred between 1956 and 1962. It was caused by the drug Thalidomide, which was recommended to pregnant women as a sedative and sleeping pill. The result was the birth of 12,000 “thalidomide children” around the world, suffering from underdevelopment of the upper limbs, eyes and facial muscles.
Refer to the reception vitamins it is also necessary in the strictest manner, since excess has a teratogenic effect- causes developmental abnormalities, as well as a serious lack of vitamins and microelements.
Row infectious diseases
, such as rubella, cytomegalovirus and some others, can be transmitted from mother to fetus and cause the development of deformities in it and lead to death.
Radioactive radiation negatively affects the genetic apparatus of the mother and child, causing congenital anomalies.
All eggs women are laid and formed in the ovaries during their embryonic development, they are no longer formed during life and are not renewed as male sperm. This means that all eggs are exposed negative impacts from the outside environment, wrong image life, alcohol, nicotine, poor nutrition. All this can lead to disruption of the genetic apparatus of the egg and the development of an unhealthy child from it. Remember this and protect yourself and your future children from unnecessary negative influences- it is better to prevent than to treat.
In humans, as in other animals, developmental anomalies often occur, leading to more or less serious deviations in the structure or functioning of organs. Many of these anomalies turn out to be lethal (deadly) already at early stages development.
When did sensitive methods for detecting the early stages of pregnancy appear (by detecting the hormone in the blood human chorionic gonadotropin), it turned out that more than half of human embryos die at very early stages. The percentage of spontaneous (spontaneous) abortions is also quite high. late stages which are associated with fetal non-viability. Of successfully carried babies, about 5% are born with noticeable anomalies. They can be quite harmless (for example, large birthmark), and can greatly affect physical and mental development. The reasons for these anomalies are different. A significant proportion of them are caused by hereditary diseases. These can be either mutations that are inherited (such as the hemophilia gene or the six-fingered gene), or anomalies that occur in some eggs or sperm (for example, Down syndrome). The similarity here is that the cause of the deviations is a change in the DNA of the egg.
Numerous factors can cause deformities when affecting the embryo itself. Such factors are called teratogenic. There are critical periods of development when the effect of teratogenic factors has a particularly strong effect on the embryo or on specific organs and their systems. These periods are different for different organs, but for most of them the period between the 15th and 60th days of pregnancy is critical. Deformities can be caused by mutagenic factors that affect the DNA of the embryo itself - for example, radioactive radiation. Other agents may cause disturbances in fetal development without being mutagens. These include, for example, certain types of viruses and bacteria. Some of them are able to penetrate from the mother’s body into the fetus. Thus, women who have rubella in the first third of pregnancy have a high probability of having children with visual impairment and heart disease. The causative agent of syphilis (bacterium spirochete pallidum) causes fetal death in the early stages and the birth of deaf children when exposed in later stages. Serious developmental disorders nervous system The fetus can be caused by toxoplasma - protists that are carried by cats (cats themselves do not suffer much from toxoplasmosis, but the course of pregnancy is disrupted in them too).
But perhaps the most diverse deformities and other disorders can cause chemical substances- both natural and artificial. Among them are some medications that are completely harmless for an adult. Thus, retinoic acid (a derivative of vitamin A, which was used in medical practice), when taken during a certain period of pregnancy, caused the birth of children without ears, with reduced jaws, cleft palate and other anomalies. Apparently, this substance inhibits the migration of cells from the neural crest. Its teratogenic effect was known through experiments on mice, and the label warned against using it during pregnancy. However, some women did this carelessly. An even more tragic story occurred with thalidomide, a drug that was widely used in the United States as a sedative. When tested in mice and rats, it did not have any teratogenic effects. But if women took it during a certain period of pregnancy, they had children with sharply shortened or completely absent long bones limbs (with the most severe disorders, the hands grow straight from the shoulders). Before the link between thalidomide and these abnormalities was established, more than 7,000 malformed children were born. It later turned out that thalidomide causes the same deformities in monkey embryos as in humans. These examples explain why testing each new drug is such a lengthy and expensive process.
During pregnancy, medications should be used with extreme caution, always consulting a doctor.
In addition to drugs, other substances widely used in everyday life also have a teratogenic effect. For example, alcohol (if a woman consumes 100 grams of vodka per day or more during pregnancy) in almost 100% of cases causes a noticeable delay in the mental and physical development of the child. Nicotine does not have a pronounced teratogenic effect, but in women who smoke heavily, newborns on average weigh less than normal. In addition, children of smoking mothers are more likely to die from sudden death. (Sudden neonatal death is one of the leading causes of death in children under one year of age in developed countries. Healthy child falls asleep and dies in his sleep. It is believed that death in this case occurs due to a stoppage of the respiratory center of the brain, and nicotine can disrupt its functioning if it affects the fetus).

