Blood flow in the uterine arteries is impaired at 38 weeks. Causes and treatment of impaired uteroplacental blood flow. What are the consequences of impaired blood flow during pregnancy: consequences
During the period of bearing a baby, a woman may encounter such a problem as uterine dysfunction. placental blood flow 1a degree. In this case, the function of the placenta is preserved and pathological changes insignificant. However, if left untreated, hemodynamic disorders can be dangerous to the health of mother and child.
Etiology of placental insufficiency
The causes of hemodynamic disorders can be divided into two groups. Endogenous factors are associated with abnormal villous maturation and placentation disorders. This leads to the development of an enzymatic-vascular type of deficiency. Exogenous causes include many factors that lead to placental and uterine form circulatory disorders.
Preeclampsia sometimes develops without any symptoms. High blood pressure may develop slowly, or it may come on suddenly. Monitoring your blood pressure is an important part of prenatal care because the first sign of preeclampsia is usually elevated blood pressure.
Other signs and symptoms of preeclampsia may include. Excess protein in urine or additional signs kidney problems Severe headaches Vision changes, including temporary vision loss, blurred vision, or light sensitivity. Impaired liver function. Shortness of breath caused by fluid in the lungs.
- Upper pain in the abdomen, usually under the ribs on the right.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Decreased urine volume.
- Decreased platelet levels. in your blood.
Impaired blood flow during pregnancy can be caused by:
- genetic factors;
- defective ovarian function;
- viral or bacterial infection.
These factors lead to anatomical pathologies of the placenta, namely pathologies of its structure, location and attachment. In this case, primary placental insufficiency develops. It is mainly observed in women diagnosed with infertility. Secondary failure caused by complications during pregnancy or the presence of gynecological diseases.
But they are also found in many normal pregnancies, so they are not considered reliable indicators of preeclampsia. Make sure you attend prenatal visits so your doctor can monitor your blood pressure. Contact your doctor or emergency department immediately emergency care if you have severe headaches, blurred vision or other vision problems, strong pain in the stomach or severe shortness of breath.
Because headaches, nausea, aches and pains are common complaints of pregnancy, it is difficult to know when new symptoms are simply part of pregnancy and when they may indicate serious problem, especially if this is your first pregnancy. If you are concerned about your symptoms, contact your doctor.
Social conditions can provoke the development of uteroplacental insufficiency, for example, poor nutrition, physical and psycho-emotional stress during pregnancy, smoking, drinking alcohol, early or, conversely, late pregnancy.
Pregnant women with extragenital and obstetric diseases are at risk. The cause of the development of fetal-placental blood flow disorders can be diseases such as gestosis, uterine fibroids, and alloimmune cytopenia. External provoking factors include the intake of certain medicines, ionizing radiation and exposure caused by chemicals or poisons.
The exact cause of preeclampsia is related to several factors. Experts believe it begins in the placenta, the organ that nourishes the fetus throughout pregnancy. Early in pregnancy, new blood vessels develop and develop to efficiently send blood to the placenta.
In women with preeclampsia, these blood vessels do not seem to develop or function properly. They are narrower than normal blood vessels and respond differently to hormonal signaling, which limits the amount of blood that can flow through them.
During pregnancy, hemodynamic disturbances can be caused by anemia. In this case, the level of hemoglobin decreases and blood circulation accelerates in all vessels and arteries, including in the uteroplacental system.
Infections are especially dangerous during pregnancy. Pathogenic microbes can destroy placental tissue. The speed and volume of blood flow in the uteroplacental system can be negatively affected by unstable heart pressure women. One of possible reasons development of insufficiency is one artery in the umbilical cord.
Other high blood pressure disorders during pregnancy
Reasons for this abnormal development may include. Insufficient blood flow to the uterus Damage blood vessels A problem with immune system Certain genes. Preeclampsia is classified as one of four high blood pressure disorders that can occur during pregnancy.
Women with gestational hypertension have high blood pressure but do not have excess protein in their urine or other signs of organ damage. Some women with gestational hypertension eventually develop preeclampsia. Chronic hypertension is high blood pressure that occurs before pregnancy or that occurs before 20 weeks of pregnancy. But because high blood pressure usually has no symptoms, it can be difficult to determine when it started. Chronic hypertension with superimposed preeclampsia. This condition occurs in women who are diagnosed with chronic high blood pressure before pregnancy but then develop worsening blood pressure and protein in the urine or other health complications during pregnancy.
- Gestational hypertension.
- Chronic hypertension.
Impaired blood flow during pregnancy can lead to irreversible consequences for the child. Delay intrauterine development, hypoxia, defects incompatible with life and even fetal death - this is an approximate list of complications that can arise as a result of a malfunction in the well-functioning “mother-placenta-child” system. Therefore, knowing the dangers of impaired blood flow during pregnancy, doctors carefully monitor the condition of the placenta and try to take everything into account possible factors risk even at the beginning of pregnancy.
If you already have chronic hypertension, you have more high risk development of preeclampsia. The risk of developing preeclampsia is high during your first pregnancy. New fatherhood. Each pregnancy with a new partner increases the risk of preeclampsia more than a second or third pregnancy with the same partner. Age. The risk of preeclampsia is higher in very young pregnant women, as well as in older pregnant women who are obese. The risk of preeclampsia is higher if you are obese. Multiple pregnancy. Preeclampsia is more common in women who have twins, triplets, or other multiples. Interval between pregnancies. Having infants less than two years old or more than 10 years old leads to a higher risk of preeclampsia. History of certain conditions. Having certain conditions before conception—such as chronic high blood pressure, migraines, type 1 or type 2 diabetes, kidney disease, a tendency to form blood clots, or lupus—increases your risk of preeclampsia.
- History of preeclampsia.
- A personal or family history of preeclampsia significantly increases the risk of preeclampsia.
- First pregnancy.
Causes of blood flow disorders during pregnancy
Everyone knows that the placenta is a special temporary organ that combines two circulatory systems: fetus and mother. The immediate purpose of the placenta is to provide nutrients and protect the baby. In addition, the organ removes waste products of the small organism. The placenta interacts with vascular system mother and her baby, hence two types of blood flow: uteroplacental and fetoplacental. If one of them is violated, the entire system suffers, and, as a result, the baby.
Which doctors should I contact if there is a violation of fetal blood flow?
Preeclampsia may require induced labor and delivery. Delivery via caesarean section may be required if there are clinical or obstetric conditions requiring fast delivery. Your obstetrician provider will help you decide which type of delivery is appropriate for your condition.
Intimate gymnastics during pregnancy and after childbirth
Complications of preeclampsia may include. If the placenta doesn't have enough blood, your baby may receive inadequate blood and oxygen and fewer nutrients, which can lead to slow growth known as fetal growth restriction. low weight at birth or premature birth. If you have severe preeclampsia, you may need to be taken to early stage to save the life of you and your child. Prematurity can cause breathing and other problems for your baby. Your supplier medical services will help you understand when it is perfect time for your delivery. Preeclampsia increases the risk of placental abruption, a condition in which the placenta separates from the inner wall uterus before birth. Sometimes it can develop suddenly, even before high blood pressure is detected, or it can develop without any symptoms in Eclampsia. When preeclampsia is not controlled, eclampsia can develop, which is essentially preeclampsia plus seizures. It is very difficult to predict which patients will have preeclampsia that is severe enough to lead to eclampsia. There are often no symptoms or warning signs to predict eclampsia. Since eclampsia may have serious consequences For both mother and baby, delivery becomes essential no matter how far into the pregnancy. Other organ damage. Preeclampsia can cause kidney, liver, lung, heart or eye problems and can cause stroke or other brain damage. The amount of injury to other organs depends on the severity of preeclampsia. Cardiovascular diseases. Having preeclampsia may increase your risk of developing heart and blood vessel disease. The risk is even greater if you have had preeclampsia more than once, or have had preterm labor. To minimize this risk, try to keep your ideal weight, eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, exercise regularly and don't smoke.
- Restriction of fetal growth.
- Preeclampsia affects the arteries that carry blood to the placenta.
- Premature birth.
The reasons for this pathological condition some. According to scientists, genetic makeup plays an important role in the formation of a normal placenta. However, other factors also influence this process. In particular, the risk group includes women who:
- began to be sexually active early;
- had several sexual partners;
- took drugs, abused alcohol and smoked;
- have chronic diseases;
- have a history of frozen pregnancies and.
There are several types of placental insufficiency, each of which has its own characteristics and risks:
Eating less salt, changing your activities, limiting calories or eating garlic or fish oil do not reduce risk. Increasing intake of vitamins C and E was not beneficial. In some cases, however, you can reduce your risk of preeclampsia.
If you have certain risk factors, including a history of severe preeclampsia, preeclampsia that results in premature birth, chronic hypertension, or a history of kidney disease, your doctor may recommend daily aspirin with a low dose—60 to 81 milligrams—starting at the end of your first trimester. In some populations, women who are calcium deficient before pregnancy and who do not receive sufficient quantity calcium during pregnancy through their diets, may benefit from calcium supplements to prevent preeclampsia. However, it is unlikely that women in the United States or other developed countries will be calcium deficient to the extent that they would benefit from calcium supplements.
- Low dose aspirin.
- Calcium supplements.
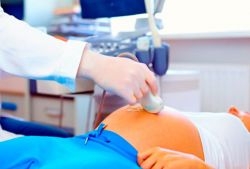
To avoid irreversible consequences and the death of the child, blood flow disturbances during pregnancy should be detected in a timely manner. For this purpose, expectant mothers undergo an ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound. Today this is the only one, but very effective method diagnostics
Before you become pregnant, especially if you have previously had preeclampsia, good idea be as healthy as you are. Lose weight if you need to, and make sure other conditions, such as diabetes, are well managed. When you're pregnant, take care of yourself and your baby through early and regular prenatal care. If preeclampsia is caught early, you and your doctor can work together to prevent complications and improve the best choice for you and your child.
Preeclampsia; short-term and long-term consequences for mother and newborn. Bed linen with or without hospitalization for hypertension during pregnancy.
- Retrieved December 23, Hofmeyr R. et al.
- Best practice and research clinical anesthesiology.
- Accessed 23 December, Meher S et al.

