Mitral valve prolapse - degrees, causes, symptoms, treatment of MVP. Mitral valve prolapse: symptoms, treatment and prognosis
Conducted since 1948, for almost three decades, the famous American study Framingham Heart Study found that mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is found in 2.5% of people.
In almost half of the cases, the pathology proceeds imperceptibly. However, sometimes the disease requires special attention and appropriate therapy.
What it is?
The valve is a double flap of connective tissue located between the chambers of the heart on the left side. Its main task is to prevent the backflow of blood into the atrium during cardiac contraction.
In order to understand what mitral valve prolapse is, it is necessary to consider the normal process and compare it with the pathological one.
During systole, the valves open and blood enters the ventricle. Then the valves close, the ventricle contracts and ejects blood into the aorta. With the development of pathology, a violation of the structure of the connective tissue is detected, which leads to the "sagging" of the valve.
Severity of valvular deformity
There are three degrees of the disease, depending on the amount of sagging of the valves in millimeters.
Mostly does not affect the patient's well-being and rarely has symptomatic manifestations. Mild prolapse (1) is a deflection of the connective tissue, not exceeding 3-5 mm. The condition has a favorable prognosis and usually does not progress.
More pronounced protrusion of the connective tissue towards the left ventricle. Its value ranges from 6 to 9 mm. PMK of the 2nd degree usually affects the condition of the person and requires observation.
3 degree
Intensive sagging of the valves, amounting to 9 mm or more. It should be noted that grade 3 mitral valve prolapse does not always reflect the severity of the disease. The main criterion for assessing the condition is the degree of violation of blood circulation.

Mitral valve prolapse
Classification by localization of prolapse
With MVP, a lesion of one of the two valves or both at once can be detected.
front sash
This part of the valve is the most developed. The level of connection of the leaflet with the annulus is about 5-6 mm below the attachment of the rear part.
Prolapse of the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve is the most common type of pathology. Due to the defeat of a significant area, it manifests itself more often than other forms.
rear sash
Pathology is expressed in the deflection of the posterior leaflet. The back of the valve is smaller, but much wider than the front. In 90% of cases, PMK of this type is not dangerous to life and health.
Regurgitation
The name of this phenomenon comes from two Latin words meaning “reverse action” and “fill”. It is the return of blood from the ventricle to the atrium during systole, caused by sagging of the valve walls. It is the assessment of the degree of regurgitation that underlies the determination of the severity of MVP.
Hemodynamically insignificant
If the sagging is less than 3 mm, the patient is diagnosed with prolapse without regurgitation. This is the most harmless form of the disease, requiring periodic monitoring. With a deflection of up to 3 mm, a diagnosis can be made: "Mitral valve prolapse is hemodynamically insignificant." This means that a violation of the structure of the connective tissue does not affect the functioning of the heart muscle and the body as a whole. Usually considered a hereditary pathology.
With a significant negative effect on blood circulation
 Mitral valve prolapse of the 3rd degree and 2nd degree of regurgitation adversely affects the work of the heart muscle.
Mitral valve prolapse of the 3rd degree and 2nd degree of regurgitation adversely affects the work of the heart muscle.
The blood flow reaches the middle of the atrial chamber, and in severe cases it touches the walls of the left atrium. This leads to stretching of the heart chamber and, as a result, to the development of heart failure. The state does not tolerate inaction, but needs to be taken as soon as possible. The patient needs a consultation with a cardiac surgeon.
Is it a heart defect or not?
Conventionally, “heart disease” means a defect in an organ or large vessels. According to this definition, the answer to the question of what is mitral valve prolapse, heart disease or not, should be positive. However, in most cases, this phenomenon is so insignificant for the patient's well-being that it is referred to as cardiac anomalies.
Some cardiologists say that "the valve is entitled to a defect," comparing a heart with a MVP to a nose that has a slight hump. Visually, the flaw is present, but the quality of life is not reflected. However, for patients with hemodynamically significant prolapse, the consequences may be quite different.
Pronounced forms of MVP, which have a serious impact on the work of the heart, are valve disease (mitral insufficiency).
ICD code 10
In 1997, the International Classification of Diseases of the 10th revision was introduced throughout the country. Mitral valve prolapse also received its place in the classification. ICD-10 includes pathology in class I under the number 34.1 (I34.1).
Symptoms
The clinical picture of the course of the pathology depends on the degree of regurgitation, the state of health, age and lifestyle of the patient.
Table 1. Symptoms and manifestations of mitral valve prolapse
| Pain in the chest | They can be piercing, cutting, pulling. Mostly found after exercise or stress |
|---|---|
| Sinus Rhythm Disorders | Tachycardia and extrasystole can be provoked by a cup of coffee, emotional outburst and physical activity. Prolapse can be manifested by a feeling of "fading" of the organ, sharp jolts, "interruptions" |
| Autonomic dysfunction | Perhaps a feeling of nausea, a foreign body in the throat, rapid loss of working capacity, sleep disturbances. Sometimes the patient complains of panic attacks |
| Change in body temperature | The appearance of a small subfebrile temperature |
| Respiratory disorders | The appearance of a sudden need for oxygen, rapid breathing, shortness of breath |
| Loss of consciousness | May be triggered by stuffiness, high fever, stress, or occur without apparent cause |
A competent specialist already during the anamnesis will suspect mitral valve prolapse. Symptoms tend to be more common in women and children than in men.
In the vast majority of cases, the pathology proceeds without symptoms.
Does the heart hurt?
 Some patients believe that any heart disease is accompanied by the appearance of discomfort.
Some patients believe that any heart disease is accompanied by the appearance of discomfort.
Does prolapse hurt? As a rule, the patient does not complain of any sensations in the chest. Single tingling is possible, but in a calm state they are practically not detected. The exception is severe mitral valve prolapse with grade 2-3 regurgitation, in which pain occurs more frequently.
Features in different groups of patients
Pathology can proceed in different ways, depending on the category of patients. In addition, for some categories of patients, PMK is more dangerous.
In children
Pathology is found in babies of any age. Mitral valve prolapse is least often diagnosed in children who have just been born. As a rule, the disease is combined with other connective tissue pathologies, which leads to the appearance of characteristic signs of MVP.
Table 2. Secondary signs of prolapse in a child
| Appearance Features | Arachnodactyly, high stature, asthenic physique, elongated torso and shortened limbs, etc. |
|---|---|
| Head | Long-headed, high "Gothic" sky, ears set lower than usual, etc. |
| Eyes | Myopia, bluish whites |
| Breast | Concavity, elongation, scoliosis |
| Skin | Pale, thin, vulnerable skin, prone to bruising and abrasions |
| Vessels | Possibly varicose veins |
| joints | Extremely mobile and flexible |
According to available statistics, the diagnosis proceeds in parallel with other disorders in 89% of cases. In half of the children, pathology causes disharmonious development.
Teenagers
 The greatest number of complaints about the manifestation of MVP occurs in adolescents over 12 years old, while the majority of patients are girls.
The greatest number of complaints about the manifestation of MVP occurs in adolescents over 12 years old, while the majority of patients are girls.
The appearance of symptoms is associated with changes in the hormonal background that have arisen due to the onset of adolescence. Often, young people have psycho-emotional disorders and depressive states. Often, prolapse in adolescents requires the supervision of not only a cardiologist, but also a neurologist and a psychotherapist.
Among women
Another risk group is young girls. Although often the diagnosis is found in middle age. In the fair sex, PMK is in some cases associated with asthenic syndrome, autonomic dysfunction.
In pregnant women
The pathology of the initial stage is found infrequently. However, in most cases this is not due to pregnancy, but to the identification of this valvular feature during the examination. Mitral valve prolapse and pregnancy require monitoring the health of the expectant mother by an obstetrician-gynecologist together with a cardiologist. With MVP of stage 2-3, complicated by regurgitation, a woman is given personal recommendations. Usually such patients are observed in specialized institutions.
How does it affect the ECG?
Electrocardiography does not always allow to detect pathology, mainly echocardiography and ultrasound of the heart are recommended for diagnosis. Prolapse on the ECG can manifest itself as follows:
- scattered negative T-waves without displacement of the ST segment;
- negative T-waves in the leads from the arms, legs and left side of the chest against the background of a slight displacement of the ST segment;
- negative T-waves and ST-segment elevation;
- prolonged QT interval.
Causes
People are born or "earn" prolapse later. The causes of myxomatous changes in the connective tissue are still not known for certain. Given the fact that MVP is usually combined with other pathologies, it is likely that the disease is genetically determined.
Why is this defect dangerous?
MVP practically does not affect the quality of life, however, the risk of sudden cardiac death in a patient with this diagnosis increases up to 3-5 times.
Table 3. Mitral valve prolapse: what is dangerous, the consequences
| Rupture of tendon chords | With a pronounced MVP, the device holding the valve can be torn off, leading to the separation of the sash |
|---|---|
| mitral valve insufficiency | Acquired heart disease |
| Fibrin deposition on the valve | Increased risk of thromboembolism |
| Arrhythmia | Any heart rhythm other than sinus (tachycardia, bradysystole, etc.) |
| Cerebrovascular pathologies | Ischemic / hemorrhagic stroke, transient ischemic attack, etc. |
| Sudden cardiac death | Only in severe forms of heart failure against the background of prolapse |
Can it disappear on its own?
 Some patients get rid of MVP without effort. When answering the question of whether mitral valve prolapse can disappear, a positive answer should be given.
Some patients get rid of MVP without effort. When answering the question of whether mitral valve prolapse can disappear, a positive answer should be given.
Similar cases are recorded in children. The leaflets get stronger with age, and the valve comes to a normal state. However, such cases are also recorded in adults.
How to treat?
MVP only in rare cases requires special therapy. Basically, no treatment is required.
Preparations
Table 4. Mitral valve prolapse - treatment, drugs recommended by doctors
Folk remedies
Herbal therapy is based on the consumption of drugs that have a sedative effect. Thus, it is strictly forbidden to stop a pronounced prolapse. Treatment with folk remedies should be agreed with the doctor. Mostly used: 
- motherwort;
- peppermint;
- chamomile;
- peony tincture;
- tincture of valerian, etc.
Overview of reviews about the disease and its treatment
People with an established MVP usually live and work without any restrictions. Most do not feel the prolapse. Reviews report that only some patients experience unpleasant manifestations (fatigue, headache). Units were forced to seek surgical care.
Consequences
What kind of restrictions are faced by patients suffering from MVP, we will consider in this paragraph.
Limitation of physical activity
With PMK 1 and 2 degrees with an unexpressed reverse current, no activity restrictions are required. In difficult cases, it is recommended to avoid exercising with increased intensity.
Is childbirth possible with this disease?
During pregnancy, it is worthwhile to conduct ultrasound several times. If during the study no deterioration was found in comparison with past data, and MVP is not higher than degree 2, then it is not dangerous to combine prolapse and childbirth.
Is it possible to play sports?
In order to determine suitability for sports, it is necessary to refer to the recommendations of the All-Russian Society of Cardiology. To understand whether it is possible to play sports with prolapse, the absence of the following symptoms and pathologies will help:
- loss of consciousness;
- arrhythmias (requires Holter and ECG monitoring);
- thromboembolism;
- lethal outcomes among the next of kin caused by prolapse.
If one of the factors is found, then it is permissible to engage in low-intensity sports.
With a slight reverse current, but maintaining normal rhythm indicators, the size and size of the heart muscle, any competitive disciplines are allowed. Therefore, prolapse and sport are quite compatible.
Do they join the army?
Young people of military age who have a valvular anomaly rightly ask the question of whether they take to the army with mitral valve prolapse. If the pathology does not affect the activity of the cardiovascular system, then there are no contraindications for the service.
Useful video
You can learn more about mitral valve prolapse from this video:
Conclusion
Seeing the diagnosis, a person wonders what it is - prolapse. After 40 years, this pathology, indeed, can be aggravated. However, it poses a real danger in isolated cases.
Often severe symptoms are the result of the patient's feelings about his state of health. How to treat mitral valve prolapse and prevent possible complications, the cardiologist determines.
 Mitral valve prolapse of the 1st degree with regurgitation of the 1st degree is a pathological process in which the development of the connective tissue of the heart muscle is disrupted.
Mitral valve prolapse of the 1st degree with regurgitation of the 1st degree is a pathological process in which the development of the connective tissue of the heart muscle is disrupted.
The mitral valve itself has two soft flaps that are regulated by the papillary muscles. The valves regulate the flow of blood so that it only moves in one direction.
When these flaps start to work incorrectly, doctors use the term "prolapse".
Disease pathogenesis
The human heart has two upper (atria) and two lower (ventricles) sections. The valve, which is located on the right, has three shutters. The left valve (mitral) is bicuspid.
E  If the connective tissue loses elasticity and becomes more pliable, the valves protrude towards the atria under the pressure of contractions of the upper chambers. As a result of this phenomenon, a certain amount of blood is thrown back. Thus, the ejection function is reduced.
If the connective tissue loses elasticity and becomes more pliable, the valves protrude towards the atria under the pressure of contractions of the upper chambers. As a result of this phenomenon, a certain amount of blood is thrown back. Thus, the ejection function is reduced.
Mitral valve prolapse with regurgitation is the flexion of the leaflet with the return of blood back. At 1 degree of pathology, the flaps deviate by 3–6 mm.
With such pathological changes, the heart is no longer able to work normally. Mitral valve dysfunction usually leads to stenosis or heart failure.
Types of pathology
The initial stage of the disease is divided into two types - with regurgitation (blood reflux) and without it. Doctors distinguish the following degrees of pathology:
- Zero. The valves only flex, but do not diverge, so there is no return of blood.
- First. With prolapse of the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve of the 1st degree, a slight divergence of the valve flaps is observed, which causes the blood to turn back.
- Second. The blood that is thrown from the ventricle reaches half of the atrium.
- Third. The blood stream is very intense, it reaches the posterior wall of the upper chamber.
Causes
Depending on the causes of occurrence, two types of MVP of the 1st degree are distinguished - congenital and acquired.
 The latter, in turn, can be caused by factors such as:
The latter, in turn, can be caused by factors such as:
- Cardiac ischemia. This disease occurs due to blockage of the lumen of blood vessels with atherosclerotic deposits. With ischemia, pathological changes affect the papillary muscles and chords, which can lead to rupture of the heart tissue during a heart attack.
- Rheumatism. This disease develops as an autoimmune reaction to certain types of bacteria. In parallel with this, other valves are affected, as well as joints.
- Injuries that lead to serious damage to the organ.
It should be noted that congenital prolapse can be without regurgitation, not progress and proceed absolutely safely for the body.
However, this pathology should be identified in childhood in order to know how to take care of your health in the future.
Symptoms
Mitral valve prolapse of the 1st degree with regurgitation of the 1st degree often does not have a pronounced clinical picture. Sometimes there are no symptoms at all.
 And yet, this disease can be confirmed by mild signs:
And yet, this disease can be confirmed by mild signs:
- chronic headaches, dizziness;
- dyspnea;
- fainting states;
- different types of arrhythmia;
- subfebrile temperature;
- vegetovascular dystonia (rare).
The first stage of pathology with minor regurgitation, which passes without complications, as a rule, does not pose a threat to the pathological development of the fetus.
But even if a woman is not worried about anything, before a planned pregnancy, she will need to consult a doctor who should monitor her condition even during childbearing.
PMK in a child
 In children, this pathology is quite common, and in girls more often than in boys. A congenital defect is characterized by a special structure of the connective tissue of the heart muscle. Also, as in adults, in children, MVP manifests itself weakly or pronouncedly.
In children, this pathology is quite common, and in girls more often than in boys. A congenital defect is characterized by a special structure of the connective tissue of the heart muscle. Also, as in adults, in children, MVP manifests itself weakly or pronouncedly.
A third of adolescents diagnosed with MVP complain of chest pain and palpitations. These signs are aggravated under the influence of stress, physical exertion, oxygen starvation of the body.
In children with MVP of the 1st degree, symptoms of a neuropsychological nature are observed. Such patients have a changeable mood, there are nervous breakdowns and even fainting. Often they feel tired even at rest.
Diagnostics
These diagnoses are easily confirmed using known diagnostic measures:
- auscultation (examination of the patient, which consists in listening to the heart with a phonendoscope);
- ECG - electrocardiography (allows you to detect extrasystoles, arrhythmia and other manifestations of pathology);
- Hallper's ECG (monitoring the work of the heart during the day);
- Ultrasound of the heart muscle (allows you to study the condition of the valves, the degree of their death and regurgitation).
Sometimes a specialist can send for additional studies - x-rays and phonocardiography.
Treatment of pathology
People with MVP do not always need drug therapy. Treatment measures depend on the severity of the disease and the severity of its symptoms.
If a person is not bothered by any, even minimal symptoms and the pathology does not progress, he can do the same work and lead the same lifestyle as healthy people.
Young men with mild PMK can be taken into the army. Such people are shown physical activity, with the exception of professional sports.
 If the cardiologist sees the need for treatment, he prescribes conservative therapy. As with other heart conditions, doctors use several groups of heart drugs:
If the cardiologist sees the need for treatment, he prescribes conservative therapy. As with other heart conditions, doctors use several groups of heart drugs:
- sedatives (sedatives) (normalize the work of the autonomic nervous system);
- beta-blockers (taken for arrhythmia, in particular, tachycardia);
- anticoagulants (help fight blood clots);
- drugs for myocardial nutrition (improve the functioning of the heart muscle, supply it with oxygen).
A patient with grade 1 mitral valve disease does not require surgery.
Prognosis and complications
As mentioned above, the progression of the disease can lead to stenosis and insufficiency of the heart valves.
The initial stages of the pathology do not lead to serious disorders of the heart, however, they can develop into more severe forms. With 3 degrees of mitral valve prolapse, a lethal outcome is possible.
WITH  Among the complications of MVP, it is also necessary to highlight:
Among the complications of MVP, it is also necessary to highlight:
- stroke (bleeding into the brain, which is provoked by high blood pressure with weakness of the walls of the vessels of the head);
- cardiac arrhythmias (due to lack of oxygen supply to the heart);
- endocarditis (inflammation of the inner lining of the heart vessels).
As you can see, pathological phenomena in the cardiovascular system are interrelated and entail other, even more severe disorders. Therefore, the forecast can be given only on the basis of the general state of health.
Prevention
L  The best prevention for MVP is the timely detection and treatment of heart diseases that can lead to this disease or complicate its course.
The best prevention for MVP is the timely detection and treatment of heart diseases that can lead to this disease or complicate its course.
Patients with congenital malformations of the mitral valve should adhere to the correct mode of work and rest, give up bad habits, and eat a balanced diet.
People with a mild form of pathology can play sports, but not professional ones. Physical activity should correspond to the capabilities of the body. One should not overwork a heart that cannot be called perfectly healthy.
If the clinical picture does not allow to live fully, physical activity should be reduced, but it is not necessary to completely abandon it. Such patients are recommended physical therapy, selected by the doctor.
Article publication date: 11/25/2016
Article last updated: 12/18/2018
From this article you will learn: what is degree 1, its causes and symptoms. Treatment and prognosis for the disease.
Mitral valve prolapse (abbreviated as MVP) is the most common congenital or acquired pathology of the structure of the valvular apparatus of the heart. This is a deflection (sagging, failure) of one of the valves during the period of contraction of the heart, which may be accompanied by the reflux of blood back into the atrium.
If, according to the ultrasound of the heart, the cusp falls by 3-6 millimeters, then they speak of prolapse (or defect) of the 1st degree. If this situation is joined by the reflux of blood back into the left atrium, then they speak of mitral valve prolapse of the 1st degree with regurgitation of the 1st degree.
Prolapse occurs in men in no more than 2.5% of cases, and in women about 8% - these are data among all people with.
In the older age group of women, the prevalence of prolapse is 4 times lower. In women, this defect disappears with age, for men, the incidence rate of the pathology remains within 2-3%.

Treatment and observation of patients with this diagnosis are carried out by: a cardiologist, an arrhythmologist, a cardiac surgeon, a neuropathologist.
Briefly about the anatomy of the valvular apparatus
Understanding the mechanism and causes of prolapse is impossible without knowledge of the anatomy of the valvular apparatus. The mitral valve consists of two leaflets: anterior and posterior; chords and papillary muscles.


Prolapse is more often in the posterior leaflet, a little less often in the anterior one, but the symptoms are always similar. For this pathology, there is no difference which of the valves bends into the left atrium.
Chords go from the valves, which pass into the papillary muscles and are fixed from the inside of the cavity of the left ventricle to the walls. The valves are covered with connective tissue.
 Parameters on the basis of which the degree of prolapse of the posterior leaflet of the mitral valve is determined
Parameters on the basis of which the degree of prolapse of the posterior leaflet of the mitral valve is determined Causes of pathology
The causes of the development of the defect are congenital and acquired.
Congenital causes
Anomalies in the development of connective tissue (Marfan and Ehlers-Danlo syndromes). This situation is predetermined genetically.
There are family cases of pathology. In such families, all related members confirmed this diagnosis.
Acquired Causes

The most common cause of mitral prolapse is rheumatic malformations. Rheumatism is an autoimmune pathology that leads to a change in the appearance of the valves and the development of prolapse and (or) stenosis - narrowing of the mitral valve opening.
With rheumatism, they speak of a combined defect of the mitral valve, regurgitation (reverse flow of blood into the atrium) in which may prevail over stenosis.
Typical symptoms of prolapse
Complaints that patients present with MVP of the 1st degree without reverse blood flow to the left atrium (that is, without regurgitation) are very non-specific. More often they are scarce, that is, nothing bothers the patients.
Symptoms appear when regurgitation develops, that is, the reflux of blood back into the atrium.
The disease does not interfere with the normal rhythm of life, unless the cause is a myocardial infarction or infective endocarditis of drug addicts.
What are the symptoms of mitral valve prolapse of the 1st degree with regurgitation:
1. Heart signs
- Pain in the region of the heart, short and short-term.
- Rhythm disturbances, which are accompanied by an increase in heart rate. The symptom is characteristic of congenital pathology.
2. Non-cardiac complaints
Non-cardiac causes are associated with disruption of the nervous system.
- Increased sweating.
- Panic attacks. These are attacks of fear that frighten a person (accompanied by an uncontrolled increase in heart rate, sweating, redness of the skin).
- Shortness of breath during physical exertion. It is important to understand that shortness of breath in this case is not, but does not occur due to nerves. This symptom is found in half of patients
- Decreased blood pressure (hypotension), which is accompanied by fainting and pre-syncope states. A symptom is observed in 10–15% of patients among all patients with grade 1 mitral valve prolapse.

Treatment Methods
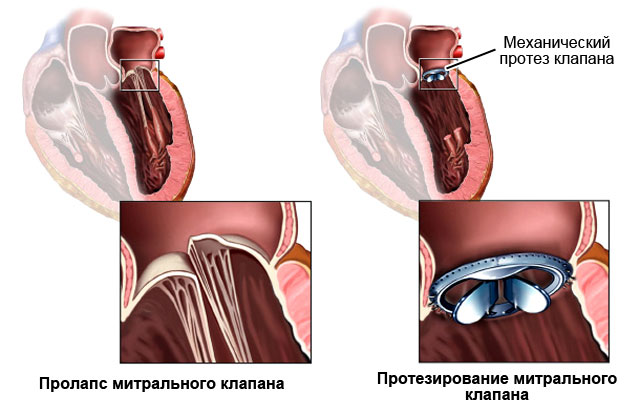
With mitral valve prolapse of the 1st degree, the following are used: general strengthening measures (daily regimen, hardening, physical activity), medications, it is possible to perform an operation to replace the mitral valve.
What drugs are used:
Depending on the cause that led to mitral valve prolapse (we discussed them above), doctors choose treatment tactics:
- If the cause of prolapse is a rheumatic disease, then prophylaxis is needed, which is carried out by rheumatologists in the off-season, so that the damage to the mitral valve does not worsen.
- Mitral valve infection is treated with antibiotics. The disease can be completely cured, the prolapse will go away, and there will be no regurgitation.
- Blunt trauma (a blow to the chest with a fist or a blow with the chest at high speed against the steering wheel of a car) can lead to the separation of one of the chords of the mitral valve leaflet. Then there will also be PMK. Doctors operate on these patients - they sew the chord. The valve ceases to fall into the left atrium and the disease goes away.
- With hypertension (high blood pressure), myocardial infarction (death of part of the myocardium), complex treatment of these diseases is carried out.
Forecast
The prognosis is highly dependent on the cause that caused the disease.
- With hypertension, the prognosis depends on the underlying disease and the severity of heart failure.
- Rheumatic malformations of MK are observed for a long time (maybe a year or decades). They are able to not disturb a person for years. And if there are complaints, then doctors prescribe medications. Medicines are taken in courses (a month or two) throughout life. When medications are ineffective, an operation is recommended - mitral valve replacement (an artificial heart valve is sewn in place of the mitral valve).
- Infective endocarditis can be completely cured even conservatively. Treatment is long - months. The prognosis is good.
- Treatment of drug addicts with infective endocarditis has a very short-term effect. Mortality is extremely high, even after MV prosthetics. Only a few survive for the first two years. The prognosis is bad.
By itself, mitral valve prolapse (without complications) has a good prognosis.
Mitral valve prolapse is one of the most common pathologies of the cardiac system. The essence of the disease is that the blood that comes from the ventricle to the heart comes back.
The halves of the valve, closing with the contraction of the cardiac ventricle, enters the aorta. Many patients are concerned about the question: why is mitral valve prolapse dangerous?
The mechanism of development of the disease
In order to understand the mechanism of the development of the disease, you need to know how the human heart works. Oxygenated blood enters the lungs from the lungs into the left atrium and is then expelled into the left ventricle.
With its contraction, the flow of blood under pressure goes to the right atrium and right ventricle. The blood has already given up all the oxygen that comes to all the internal organs and tissues of the body.
At this stage of circulation, the blood is already saturated with carbon dioxide. From the right ventricle, the blood flow is directed to the artery of the lungs, where it is again enriched with oxygen.
 With the normal functioning of the heart, at the time of atrial contraction, the blood no longer returns back. This process is prevented by the mitral valve of the heart, the valves of which are tightly closed. With prolapse, the halves of the valve bend and sag. As a result, they cannot close tightly enough. This leads to the fact that not all blood enters the aorta. Its part returns back to the left atrium.
With the normal functioning of the heart, at the time of atrial contraction, the blood no longer returns back. This process is prevented by the mitral valve of the heart, the valves of which are tightly closed. With prolapse, the halves of the valve bend and sag. As a result, they cannot close tightly enough. This leads to the fact that not all blood enters the aorta. Its part returns back to the left atrium.
The process of blood flow back in medicine is called regurgitation. When the valve halves are bent 3 mm or less, the blood does not return.
PMK refers to dangerous diseases that are accompanied by severe consequences. With an incorrectly chosen course of treatment or lack thereof, the death of the patient is inevitable.
Classification
From the amount of blood that returns back and from the level of deflection of the halves of the valve, prolapse is divided into several types:

According to the time of development of prolapse, the disease is divided into the following types:
- Primary. It can be either acquired or congenital.
- Secondary. It manifests itself in the form of various heart diseases associated with a change in the structure of the connective tissue of the inner walls of the shell of the heart.
When diagnosing this pathology, an extremely important point is the exact setting of the degree and type of its development.
The choice of the most effective methods of treatment depends on this.
Symptoms
 When diagnosed with MVP, the patient does not feel almost any symptoms.
When diagnosed with MVP, the patient does not feel almost any symptoms.
Only in the later stages of the development of the disease can the following signs of the disease appear:
- feeling of pain behind the sternum - they are felt by about 55% of patients. As a rule, pains are localized in the left half of a thorax. There is no connection with the emotional state of a person or physical activity and pain. They can be both short-term and stretch for the whole day.
A person can feel discomfort both at rest and during exertion; - feeling of insufficiency of air - it seems to the patient that he does not have enough air, and he takes a deep breath;
- violation of the rhythm of the contraction of the heart - it can beat very often or too slowly;
- dizziness;
- fainting state;
- severe headaches;
- unreasonable increase in body temperature.
If one or more symptoms appear, it is urgent to contact a specialist and undergo an examination.
Complications
Mitral valve prolapse, what is it? This question worries almost everyone who has problems with the work of the heart. In most patients, the disease is asymptomatic and does not affect their general condition. But 5-10% of people suffer from the development of complications that occur along with prolapse. Among the most difficult and often encountered are the following:

 From the foregoing, we can conclude that the consequences of mitral valve prolapse can be quite serious.
From the foregoing, we can conclude that the consequences of mitral valve prolapse can be quite serious.
If we talk about the prevention of the disease, it consists primarily in the periodic passage of a medical examination. Even secondary MVP can occur without showing visible symptoms.
A diagnosis can only be made after a thorough examination. Only in this case, it is possible to make a diagnosis at an early stage of the development of prolapse and avoid serious complications, and possibly death. Taking good care of your body and mind is the key to good health.
Valve prolapse is a fairly common, but most often benign disease associated with improper valve formation. This pathology is the protrusion of the valve leaflets. The most commonly diagnosed type of such an anomaly is mitral valve prolapse.
The main cause of this disease, doctors call the lack of strength of the connective tissues of the heart valves. The anomaly is congenital.
Main symptoms
Most often, the anomaly does not manifest itself in any way, but some people may feel:
- intermittent chest pain;
- bouts of general weakness;
- dizziness;
- signs of arrhythmia.
The course of the disease is generally favorable. Special therapy is usually not required.
As a rare manifestation, some patients have minor cardiac abnormalities and valvular insufficiency.
An even rarer occurrence can be called severe forms of prolapse. In this case, a serious course of medical treatment is necessary, and often even surgical intervention.
The structure of the heart valves
For the full-fledged work of the heart muscle, movable dampers, called valves by physicians, are necessary.
In simple terms, the explanation goes like this:
The shutters are made up of a number of elements. These are peculiar flaps, the task of which is to block the holes, so that at certain moments they do not allow blood to enter from one part of the heart to another.
They control the flow of blood.
The heart is a primitive "pump" designed to pump nutrient-rich fluid. The pump can only work if there are valves that let the blood flow in one direction and do not prevent it from returning back.
The heart muscle contracts rhythmically, thereby creating pressure that ejects blood from it. Valves open when contracted. Then comes a brief moment of relaxation of the muscle, which reduces the pressure in it. In this case, the valve closes, and the blood does not reverse.
How many human heart valves and what are they called?
- mitral valve. Its location is the junction of the left ventricle and the left atrium. The valve contains front and rear flaps. They connect to the wall of the left ventricle with tendon filaments called chordae. The chords are also attached to the so-called papillary muscles. If they are in the correct state, then the gap of the mitral valve leaflet is not left. Then there is no sagging or even going out. The main task of the valves is to prevent the blood flow from reversing. Mitral valve prolapse is called
the process of bulging of one or both valves into the cavity of the left atrium. Incomplete, loose closure is carried out. Part of the ejected blood, due to the anomaly, returns back. Prolapse of the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve is one of the most typical phenomena of this kind.
- Tricuspid valve. It separates the right ventricle and the right atrium. Its functionality is similar to the mitral valve.
- aortic valve. Location - the area clamped by the left ventricle and aorta. The task of the aortic valve is to prevent blood flow from the aorta into the left ventricle.
- Pulmonary valve. It connects the right ventricle of the heart and the pulmonary trunk. This valve prevents blood from returning from the lungs to the right ventricle.
For the manifestation of prolapse, the time factor matters.
Primary valve prolapse
This is a congenital anomaly, which depends on the genetic factor and is transmitted to the child from the parents. This is usually a hereditary defect in the connective tissues of the heart valve cusps or tendon chords (the medical term is myxomatous degeneration).
Secondary valve prolapse
This type of prolapse is referred to as acquired anomalies formed for various reasons.
Most often, these are the consequences of such negative factors as:
- chest bruises;
- transferred rheumatism in history;
- myocardial infarction and a number of other reasons.
The valve leaflets may sag directly into the atrial cavity. A common reason for this is inflammatory processes or ruptures of the chords.
signs
As a rule, the course of congenital forms of tricuspid valve prolapse, aortic valve and pulmonary valve is asymptomatic. The disease is detected most often during the examination due to other complaints.
Note. Congenital prolapse does not lead to a significant disruption of the full blood circulation. Special treatment in the presence of such an anomaly is not prescribed.
The most common of all the defects listed above is mitral valve prolapse.
Usually, the course of a congenital disease is not accompanied by bright and painful symptoms.
For a small number of patients, the following symptoms are characteristic:
- The work of the heart is intermittent. As a rule, this is a feeling of "fading", a rapid or slow heart rate, an irregular contraction of the heart muscle.
- Periodic pain in the chest, stabbing or aching. Unpleasant feelings that cause discomfort sometimes drag on for several hours. The pain syndrome manifests itself with or without exercise, during rest hours, and does not subside even after taking nitroglycerin. Psychological pressure and prolonged stress can serve as a provoking factor.
- Feeling of lack of air.
- fluctuations in body temperature.
- Pain in the abdomen, as a pronounced symptomatology of irritable bowel syndrome.
- Pain in the head, sometimes accompanied by dizziness.
- Pre-fainting and fainting, especially in a confined space with lack of air or as a result of nervous overexertion.
- An unjustified feeling of fear.
- The appearance of bruises.
- Bleeding from the nose.
- For women, it is also painful and prolonged menstruation.
Symptoms are due to the wrong structure of collagen fibers.
In some cases, the following factors indicate primary mitral valve prolapse:
- Too tall person.
- Extended upper and lower limbs.
- Excessive thinness and elasticity of the skin.
- Elongated, thin facial features.
- Increased mobility of the joints.
- Some problems related to vision.
Such symptoms are divided into a number of separate syndromes. We are talking about hereditary diseases. Some of them develop along with valve prolapse. In such cases, diagnosis is necessary to exclude Klinefelter's syndrome or Marfan's syndrome.
Signs of acquired mitral valve prolapse
Symptoms of the disease directly depend on the cause of its occurrence:
- Secondary prolapse sometimes develops against the background of myocardial infarction. As a rule, these are sudden manifestations of a number of characteristic signs along with symptoms of myocardial infarction. List of symptoms: severe pain in the chest, shortness of breath, irregular heart beats, dizziness, sudden loss of consciousness, coughing spells, pink foam from the mouth. All of these symptoms are a strong argument about the immediate appeal for emergency medical help. Delay with effective competent treatment is fraught with the risk of death for the patient.
- The second possible reason for the development of an acquired defect is the infliction of a severe or moderate injury to the chest area, if such an action leads to a rupture of the chords that regulate the process of opening and closing the valve. At the same time, the heartbeat may become more frequent, there is a feeling of improper functioning of the heart, shortness of breath and coughing fits with pink discharge. Such symptoms should be the basis for calling an ambulance.
- Secondary mitral valve prolapse sometimes develops due to rheumatism, which often leads to inflammation of the connective tissue in the heart valve. The disease is characterized by slow and sluggish development with symptoms such as increased fatigue, shortness of breath after walking or slight physical exertion, and impaired heart function.
In order to have an accurate idea of the degree of mitral valve prolapse, the patient definitely needs a diagnostic procedure such as echocardiography. The level of sagging of the valve leaflets into the cavity of the left atrium is taken into account.
Characteristics of the three degrees of prolapse:
1 degree
Sagging into the cavity of the left atrium is less than five millimeters.
2 degree
Sagging six to nine millimeters.
3 degree
Sagging ten or more millimeters.
Note. Please note that only doctors in the Russian Federation and in a number of post-Soviet countries use this classification. Note also that the degree of prolapse is not an accurate reflection of circulatory disorders. Therefore, mitral valve prolapse of the first and second degree usually does not significantly impair blood flow and in most cases does not require medical intervention.
Should we be afraid of complications with such a defect?
Possible negative complications:
- Incorrect closure of the valves causes blood to enter the atrial cavity. Sometimes heart failure is a consequence of the pronounced development of mitral valve insufficiency.
- There is a risk of infective endocarditis. It is an inflammation of the inner lining of the heart. You should pay attention to such symptoms - a change in body temperature, weakness, pain in the joints, impaired heartbeat, signs of jaundice, a network of petechial hemorrhages on the skin.
- Signs of arrhythmia are felt, dizziness, fainting are possible.
- The risk of a sudden acute violation of the blood supply to the brain increases. A stroke carries the risk of serious consequences, including death. Such a risk should be excluded, first of all, for people over fifty years old.
How does mitral valve prolapse manifest in children?
For children, defects in the heart valves of the primary type (violation of the structure of the connective tissue) are most characteristic. Symptoms of the disease are sluggish or absent altogether. Usually, anomalies of this kind are discovered during an examination for other medical problems.
Signs of mitral valve prolapse in children and adults
Symptoms in children and adults are practically the same. This disease belongs to the list of minor anomalies in the development of the heart. Such pathologies, as a rule, do not prevent the child from fully studying, relaxing and playing sports.
However, there is a risk of developing arrhythmia or a number of other complications, so children with such anomalies are referred for regular preventive examinations and counseling in the cardiologist's office.
What should pregnant women do if they have mitral valve prolapse?
This type of anomaly in the heart valve of a pregnant woman cannot bring significant harm to her or her child. During the course of pregnancy and childbirth, there should not be any special complications.
In a mother with valve prolapse, children do not differ in body weight and ability to develop from those children who were born by absolutely healthy mothers. Babies are born on time and in the vast majority of cases without specific problems.
Note. If you are planning a pregnancy, be sure to undergo an examination using a special, very informative, simple, painless and affordable study - echocardiography (ECG).
Make sure that the volume of blood that is returned back in a full cycle of circulation is normal. Learn about the degree of mitral valve insufficiency if you have been diagnosed with it. Negative consequences with such anomalies are extremely rare, but this does not mean that you should not consult a specialist about them.
Help for patients with heart valve anomalies is needed in such cases:
- A sharply deteriorating state of health, manifested in weakness, shortness of breath, "bubbling" breathing and the appearance of foam from the mouth. Such symptoms indicate the return of a large part of the blood flow to the left atrium. Regurgitation can lead to pulmonary edema.
- Sudden loss of consciousness, which is possible with insufficient blood flow to the brain (due to malfunctions of the heart muscle), which also indicates an arrhythmia.
- Temperature increase.
- Joint pains.
- Feeling weak, which may indicate infective endocarditis. This is a rather serious complication of valve defects.
- Inability to concentrate while performing work functions.
- Signs of pronounced fatigue, even if there is no reason for this.
- Problems with respiratory function with minor physical exertion.
Important. All of the above signs may be the basis for the need for a comprehensive study of the patient to detect possible heart failure.
Diagnostics. When should research be done?
Symptoms that indicate prolapse of the heart valves require a clarifying diagnosis from your doctor (usually a general practitioner) and a cardiologist. The patient may need an examination of the heart and the cardiovascular system as a whole, as well as additional diagnostics from a neurologist or other related specialist.
In medical practice, a wide range of modern effective methods for diagnosing the mitral valve is used:
- Echo-KG and Doppler echocardiography make it possible to speak with sufficient accuracy about the degree of mitral valve prolapse, to detect insufficiency of this valve and its degree of development, to determine the level of blood entering the atrium.
- Electrocardiography gives a picture of a number of functional disorders of the heart, which sometimes indicates mitral valve prolapse. We are talking about arrhythmias, an increase in non-rhythmic contractions of the heart muscle, etc.
- An ECG (Holter) makes it possible to monitor the work of the cardiovascular system for a long period (for example, a day). Electrodes are placed on the subject's chest, which "remove" information and transmit it to a small recording device. During the day, the patient behaves as usual, excluding bad habits. This technique gives the most complete description of the work of the heart.
Effective treatment measures to eliminate all risks from mitral valve prolapse
Congenital prolapse is a disease that usually does not require special medical intervention.
When is prolapse treatment necessary?
Pay attention to these symptoms:
- Disturbed rhythm of heart beats, which indicates tachycardia and arrhythmia.
- A number of recurring disorders of the autonomic system. We are talking about unpleasant and painful sensations in the heart, dizziness and fainting.
- Signs indicating severe mitral valve insufficiency.
Only a medical specialist determines the necessary measures for the treatment of anomalies of the heart valves, taking into account the individual factors of the patient.
Mitral valve prolapse and medications to restore health:
- Some drugs from a number of adrenergic blockers are recommended for frequent heartbeats (tachycardia), as well as in order to prevent the development of arrhythmia.
- A number of preparations containing magnesium help fight dizziness and fainting, relieve pain in the heart muscle area. Magnesium helps to stabilize the temperature, the functioning of the nervous system and the process of sweating.
- A number of vitamins, including group B and PP.
Such an operation is prescribed only by a certified experienced specialist, based on the history, examination materials of the patient and his individual characteristics.
Surgery is usually prescribed for identified and pronounced valve insufficiency. The patient is changed with symptoms indicating a large regurgitation, the mitral valve to a special prosthesis.
When prescribing treatment and taking effective medical measures to eliminate functional problems of the mitral valve, it is necessary to take into account the causative factor and the degree of blood flow regurgitation.
If a patient has significant mitral regurgitation confirmed by examination, indicating that a large volume of blood has returned to the atrium, the patient will require surgery.
Please note that the following tips will be useful for all people who have signs of congenital mitral valve prolapse:
- Careful oral hygiene. This means that the patient needs to brush his mouth two to three times a day, and also use high-quality dental floss. You should visit the dentist's office at least twice a year. Such precautions are not at all redundant, because we are talking about reducing the risk of infective endocarditis. This is a very dangerous complication that is possible with valve defects.
- Complete or at least partial rejection of a number of bad habits, especially from drinking alcohol, coffee drinks and smoking tobacco products. With this restriction, you will significantly reduce the risk of functional disorders of the cardiovascular system, including tachycardia and arrhythmia.
- Reducing physical stress on the body and psychological pressure on the nervous system.
Note. Modern medicine does not adhere to the outdated opinion that sports games and physical labor inevitably cause irreparable harm to people with heart valve abnormalities. On the contrary, they need moderate exercise in order to maintain the heart in proper tone.
Admission of children with mitral valve prolapse to physical education lessons
This question has the right and due competence to decide only a medical specialist. To reach a verdict, he should accurately assess all possible risks and the individual characteristics of the child. It is also necessary to exclude all negative chances for possible complications.
For most children with symptoms of complicated mitral valve prolapse, exercise, swimming, and aerobic exercise are not only acceptable, but also beneficial.
As for admission to professional sports, this is a matter of individual order. In any case, such a decision requires a consultation of medical specialists with the inclusion of a psychologist.
Since the problems of cardiovascular diseases are closely related to the state of the nervous system, special attention should be paid to this fact.
A child with problems in the functionality of the heart valves should be protected from psychological pressure and stress. This also applies to adult patients to a large extent. Please note that the mental load on the nervous system is one of the main factors in the appearance of a number of complications.
Doctors have long known that a person's mental attitude to a large extent determines his health and comfort of living in any conditions.
A positive attitude, friendliness, love for oneself and loved ones is the only way to a world of harmony, peace and happiness.
Take care of yourself and respect the living space of the people around you. Health is a closed island of your being. This is a collective work in the name of improving the perception of reality.
Conclusions. Mitral valve prolapse most often does not pose a serious threat to health. However, if such a pathology is detected, one should regularly undergo examinations, be observed by specialists and follow their recommendations.
We try to provide the most relevant and useful information for you and your health.

