The course of pregnancy with complete placenta previa. Breech presentation of the fetus during pregnancy. How does pregnancy proceed with a breech presentation of the fetus?
Pregnancy, whether planned or spontaneous, is a physiological process, which means it is not always predictable. Sometimes, up to 35 weeks, the baby changes its position several times, in which case they speak of the unstable position of the fetus. But after 35 weeks, as a rule. position is determined. In most cases, this is a cephalic presentation, less often - a pelvic presentation, and even less often - an oblique and transverse position of the fetus. It is such non-standard situations that we will talk about today.
What are the risks and complications of vaginal delivery?
The following conditions are considered necessary to attempt a vaginal birth. The child shows no signs of distress while his heart rate is closely monitored. The birth process is smooth and steady when the cervix dilates as the baby descends. Supplier medical services calculated that the baby is not too big, or the mother's pelvis is too narrow for the baby to pass safely through the birth canal.
- The child is complete and in a frank representation of the execution.
- Anesthesia is available and a short cesarean delivery is possible.
The position of the fetus in the uterus is determined by many factors, both from the mother and the fetus.
Pregnancy and childbirth with a breech fetus are classified as pathological obstetrics due to possible risks and complications.
Causes of breech presentation of the fetus
Maternal
Anomalies of uterine development. These include malformations of the genital organs, such as saddle uterus, bicornuate uterus, and duplication of the uterus. Sometimes such anomalies are first detected during pregnancy. Pregnancy in these cases is observed in the medium and high risk group.
Sometimes forceps are used to guide the baby's head out of the birth canal. Another potential problem is cord prolapse. In this situation, the umbilical cord contracts as the baby moves towards the birth canal, thereby slowing down the flow of oxygen and blood. For vaginal delivery, electronic fetal monitoring will be used to monitor heart rate child throughout the entire period of work. Or it may be an option if there are signs that the child may be in trouble.
When is caesarean section used with breech delivery?
Most healthcare providers recommend C-section for all babies in the breech position, especially babies who are premature. Because premature babies are small and more fragile, and because the head premature baby relatively larger in comparison to his body, the baby is unlikely to stretch the cervix as much as full-fledged child. This means there may be less head room.
Polyhydramnios. An increase in the amount of amniotic fluid creates the preconditions for repeated movement of the fetus in the uterus; it turns over several times and may remain in a breech presentation. in addition, with polyhydramnios and breech presentation, there is a high risk of the umbilical cord entwining around the neck and torso of the fetus.
Low water. A reduced amount of amniotic fluid compared to normal, on the contrary, limits the movement of the fetus. Normally, the fetus turns head down at full term; in case of oligohydramnios, it has practically no room for this action.
Compiled using information from the following sources. William's Obstetrics Twenty-Second Ed. Danforth Obstetrics and Gynecology Ninth Ed. The crippling idea refers to the position of the baby in the womb. It is normal until the seventh month of pregnancy for the baby to be in the breech or breech position. After the seventh month, any position other than the apex may not only challenge the possibility of vaginal birth, but also introduce abnormal stressors to the developing baby.
The mechanism of natural childbirth
The risk is small; studies show that approximately 4 percent of full-fledged pregnancies are omens. There are several reasons for a crippling presentation. There is likely a structurally altered pelvis; this may be caused by rickets, poor development bones and joints or structural or functional compromise of the pelvis. Additional reasons mutilating anomalies are uterine anomalies, placenta previa, multiple births, excessive amniotic fluid or fetal abnormalities such as hydrocephalus and anencephaly.
Umbilical cord entanglement. Sometimes entanglement occurs spontaneously. If at this moment the fetus was in a breech presentation (for example, at 23-24 weeks, as often happens), then the revolution is limited by the mechanical tension of the umbilical cord loop.
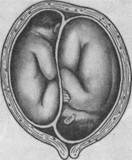 - Multiple pregnancy. If you are expecting not just one baby, but twins or triplets, then you should be prepared for the fact that not all babies will be born with a head. Again, due to the limited space for turning, one of the fetuses more often ends up in a breech presentation. If the first fetus comes with its head, and the second is in a breech presentation, then the birth proceeds more safely, since the first baby manages to expand the birth canal.
- Multiple pregnancy. If you are expecting not just one baby, but twins or triplets, then you should be prepared for the fact that not all babies will be born with a head. Again, due to the limited space for turning, one of the fetuses more often ends up in a breech presentation. If the first fetus comes with its head, and the second is in a breech presentation, then the birth proceeds more safely, since the first baby manages to expand the birth canal.
There are three main types of shutter submissions: frank, full and trap. In a candid display, the baby's legs are pushed upside down next to the head. This is the most common shutter presentation, occurring 65 to 70 percent of the time. Full presentation means that the baby "sits" upright in the uterus, with legs crossed and legs next to the buttocks. The idea of one or both of the baby's legs moving down towards the cervix.
Vaginal caries options were quickly becoming a thing of the past. Not only this, but also medical field, the need for obstetrician training for vaginal births does not exist! However, some midwives are still trained in breech presentation and may be willing to assist in vaginal births. The virtual elimination of vaginal birth has created a generation of obstetricians who are inexperienced and untrained to treat the breech. But what about the woman who knows she's a recluse and doesn't want a C-section?
Uterine fibroids. Myoma large sizes also creates a purely mechanical obstacle to turning the baby head down. Myomatous nodes growing inward into the uterine cavity are especially dangerous.
Decreased tone and contractility uterus. This condition can be observed in multiparous women if there have been several abortions or curettages with medical treatment in the anamnesis. diagnostic purpose. In women who have undergone a cesarean section or myomectomy, scars remain on the uterus, which also reduce the local contractility of the myometrium and may prevent the baby from turning.
Features of the course of labor
There are only a few doctors who offer alternative methods or options for delivering government items. Women need to be educated and empowered to know that there are many options, from prevention to treatment, both invasive and non-invasive. There are many alternative methods, which may promote optimal fetal positioning.
The Webster Technique, as defined by the International Pediatric Chiropractic Association, is a specific chiropractic analysis and adjustment that reduces interference with nervous system and restores balance with maternal pelvic bones, muscles and connections. By aligning the pelvis, stress on the attached ligaments and muscles is reduced. This, in turn, can reduce excessive tension in the uterus. A balanced pelvis provides the optimal environment for the developing baby.
Placenta previa. Placenta previa is the complete or partial obstruction of the internal os by the placenta. Normally, the pharynx is free. the placenta is located at the bottom or at least 7 cm from the internal os. if the pharynx is blocked, then restrictions are created for stretching the lower segment of the uterus, and there is less opportunity for the fetus to turn onto its head.
Thanks to this optimized space, the child has a better chance of getting into best position for birth. Optimal fetal positioning results in safer and more easy birth. There have been several studies showing success regarding optimal fetal positioning and the Webster technique. The Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapy reported an 82 percent success rate in infants who turned down when chiropractors used the Webster Technique.
Features of pregnancy with pelvic location
The conclusion of this retrospective study suggested that chiropractic care may be a valuable adjunct to prenatal care. Indeed, Webster's technique needs further exploration of its role in general care for pregnant patients and safer birth outcomes.
Short umbilical cord. The absolute shortness of the umbilical cord (less than 40 cm) mechanically prevents movement inside the uterus.
Anatomical narrowing of the pelvis or deformation of the pelvic bones. Anatomically narrow pelvis or displacement of the pelvic bones (as a result of injury or past diseases, rickets or bone tuberculosis, severe scoliosis) limit the movement of the fetus and prevent rotation.
The authors discussed their preliminary findings: There is a long tradition in chiropractic care of the pregnant patient. The results of our study demonstrate a certain degree of effectiveness and safety of the Webster method in reducing the effects of intrauterine restriction during pregnancy. We advocate continued research in this area.
Even when the baby's position is properly downward, chiropractic care using the Webster Technique optimizes the neurobiomechanical function of the pelvis. It has been found that the effects of using the Webster method during pregnancy can have a huge impact on maintaining natural birth.
Fruit
Fetal malformations. Defects that interfere with fetal movement must be very pronounced. For example, a large goiter (enlarged thyroid gland) or hydrocephalus with a significant increase in head size. Such defects are diagnosed by ultrasound and in this case the issue of termination of pregnancy is decided. medical indications. It is rare; detection by ultrasound is reliable.
The ideal time to evaluate and begin chiropractic treatment is before or during pregnancy. early stages. Restrictions in the pelvic area may not be sufficient to adversely affect the baby's position, but may affect the mother's comfort, progress and duration of labor and proper development child. One study shows that mothers receiving chiropractic adjustments experience first births 22% faster than those without adjustments and 37% faster in subsequent births.
The purpose of the study was to determine the effectiveness of chiropractic care for a pregnant woman with placenta previa, migraine, neck, and back pain with hopes of a vaginal birth after cesarean section. Placenta predominance is when the placenta lies in the lower part of the uterus, obstructing the cervix, which can cause severe obstetric complications.
Formation disorders vestibular apparatus in the fetus. There is also such a version of the formation of breech presentation, but diagnosing the health of the fetus can only be done after childbirth. There is no threat to the life of the fetus in this condition.
Prematurity (unstable fetal position before 35 weeks)
Constitutionally small fetus or delay intrauterine development. Small fetal size predisposes to active movements and movements of the baby inside the uterus.
Chronic migraines have been reported in 4-8% of first-time pregnant women. In general, the use of additional and alternative medicine is popular for pregnant women to increase their chances of having a positive experience during their pregnancy and birth. The current study focuses on the case report of a 28-year-old woman carrying her second child at 29 weeks' gestation. Her main complaints were a history of chronic migraines due to neck and back pain. Finally, a recent ultrasound revealed placenta previa in her current pregnancy.
Classification
Breech presentation is divided into several types. It is very important for the doctor and the pregnant woman to decide on the type of breech presentation, since the tactics of labor management and the prognosis for the life and health of the baby depend on this.
1. Pure breech presentation. This means that the child lies with his buttocks towards the exit, his legs are bent at the knees and pressed to his stomach. this type of breech presentation occurs in 50 - 70% of cases, more often in primigravidas.
The patient's migraines began as an 8-year-old child with one-time chiropractic care for the past 10 years without permission. She described her headaches as severe and severe pain, while the neck and back pain was a boring pain. The patient said that the only relief for her back and neck pain was massage, which provided only temporary relief.
The Doctor of Chiropractic examined the patient and found that the patient's upper and middle back were misaligned and also exhibited muscle tension. The Doctor of Chiropractic began a plan of care with the patient that included adjustments to her upper and mid back. The doctor had a patient using a pregnancy pillow to support her fetus during an adjustment. She received chiropractic care for six weeks, for a total of six visits. After three visits over ten days, the patient reported that her migraines were resolved.
2. Mixed. In this case, the child seems to squat down. Both the buttocks and feet of the fetus are present at the exit from the pelvis.
3. Foot. Most dangerous look breech presentation. The fetal legs are presented, one (the second is extended and pressed to the stomach or more often bent at the knee and pressed to the stomach) or both. It is observed in 10 - 30% of cases, mainly in multiparous women. Mixed breech presentation accounts for up to 5 - 10%, and occurs equally in multiparous and primiparous women.
After her fourth visit, an ultrasound confirmed that her placenta previa had resolved. The importance of seeking quality chiropractic care for overall well-being is demonstrated in this case study. Case reports in obstetrics and gynecology. The authors present the case of a 38-year-old working woman with four repeated presentations of the fetus in urgently. This rare condition affects the mode of delivery and is a significant obstetric problem as it is associated with increased perinatal morbidity or mortality.
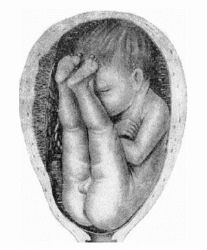
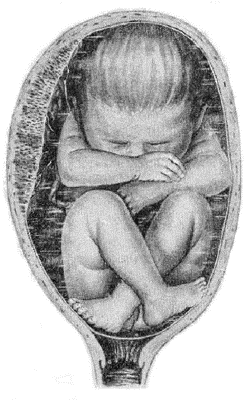
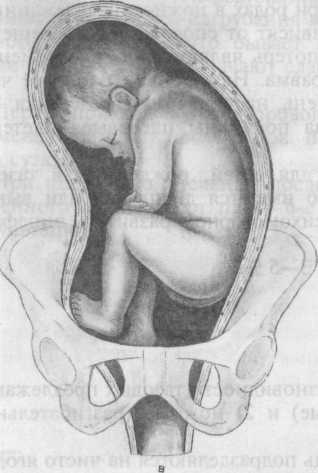
4. Knee. The fetal knees are present at the exit; it is extremely rare. During childbirth it turns into foot pain.
Diagnostics
Primary diagnosis is ultrasound screening. In the second trimester, ultrasound determines the position (longitudinal, transverse) and presentation of the fetus (cephalic, pelvic). The location of the fetus, determined at 20-23 weeks, is not final; the situation in most cases changes to the head position by the third screening.
The authors provide details of the risk factors for execution, its diagnosis, and the controversial issues surrounding the possible causes leading to repeated breeches among working women. Breech presentation is defined as the initial entry of the fetal gluteal region into the maternal pelvis and is the most common abnormal fetal presentation. Team prevalence ranges from 3% to 4% at term. Predisposing factors for predisposition to kazen are prematurity, multiple pregnancy, multiple pregnancy, fetal hydrocephalus, oligohydramniosis, polar placenta, placenta previa, gestational diabetes, history of delivery of execution, short umbilical cord, low weight at birth, uterine anomalies, congenital anomaly, previous cesarean section, and pelvic tumors.
In the third trimester, if breech presentation persists, it can be determined by gynecological examination. During an external obstetric examination, by palpating the abdomen, the doctor can find out the location of the fetal head. When examined in a chair, it is possible to determine with a high degree of probability the presenting part: head, buttocks, feet of the fetus.
Complications of breech birth
1. Premature rupture of water. This happens because there is no pressing of the head and no differentiation of water into front and back.
2. Prolapse of the legs during breech presentation, loss of umbilical cord loops.
3. Weakness of generic forces. Primary and secondary weakness of labor develops due to weaker pressure (compared to the head) of the soft pelvic end on the uterine os, as well as long and ineffective contractions (cannot be stimulated).
4. Intrapartum hypoxia and fetal asphyxia. During childbirth, the umbilical cord loops may be pressed against the walls of the pelvis; if the pressure lasts for more than 5 - 7 minutes, then severe oxygen deficiency develops.
5. Throwing back the arms and hyperextending the head. The pelvic end is soft and narrower than the head, so there is not enough expansion birth canal, and the denser and larger part comes out last. This can lead to difficulty in removing the head and tilting. And then, when providing benefits, there is a high risk of overextension cervical spine spine and damage to the nerve plexuses.
6. Aspiration (inhalation) of amniotic fluid. Inhalation of even normal, light amniotic fluid causes aseptic inflammation to varying degrees gravity. In the case of meconium aspiration (inhalation of green water that is colored by original feces - meconium), the prognosis is significantly worse.
Management of pregnancy with breech presentation of the fetus
Inspection, laboratory and instrumental examinations are carried out according to the standard. Consultation with a geneticist if you suspect birth defects fetal development.
If at 32 weeks or more the fetus has not turned head down, and there are no obvious factors causing breech presentation (for example, large fibroids or complete placenta previa), then special complex exercises. It is aimed at working the abdominal muscles and increases the likelihood of the baby turning into a cephalic presentation.
A set of exercises for breech presentation
Bridge. Lie on the floor, raise your pelvis and place 2 - 3 pillows under your butt. Then, as you lower yourself onto the pillows, your pelvis and knees form a straight line. Lie in this position for several minutes if it does not cause discomfort. Sometimes this exercise helps quickly, but you can repeat it up to 3 times a day. You should not perform this exercise after eating or drinking, if you are already worried about heartburn, or if there is a threat of premature birth.
Breath. Get into the starting position, feet shoulder-width apart, arms down. Inhaling, raise your arms with your palms down to shoulder level, at the same time rise onto your toes and slightly bend your lower back forward. Then slowly lower yourself down. Repeat 4 times at a time.
Turn. Lie down on the floor (the surface should be quite hard, a sofa will not work), turn on the side to which the back of the fetus is facing (in a transverse position, on the side where the head is). bend and pull your legs towards you, lie down for 5 minutes.
then take a deep breath and exhale and turn over your back to the other side, lie down for another 5 minutes, breathing freely and evenly.
Then straighten upper leg(for the pelvic position) or lower (for the transverse position), take a deep breath and bend your leg. Move your bent leg outward without feeling pain or discomfort. If the exercise does not satisfy discomfort, then you can repeat it up to 5 times in one go.
Bridge-2. Lying on the floor, place your feet on the floor, arms along your body. As you inhale, lift your pelvis up, hold for a few seconds, and as you exhale, lower down. Then, while inhaling, tighten the muscles of the perineum, and while exhaling, relax. Repeat several times.
It is better to perform the exercises in this order, so the muscles smoothly start working and there is no sudden overload of the body.
If on the ultrasound you see that the child has turned his head, then continue to perform only the last exercise.
Contraindications to exercises: threat of premature birth, fetal defects, large fibroids, uterine malformations, complete or partial placenta previa, spotting from the genital tract of unknown nature, nagging pain in the abdomen and lower back of unknown origin.
Exercises can only be performed in consultation with your doctor, starting from 32 weeks until birth.
External rotation of the fetus.
This is an obstetric manual that was described many years ago by the Russian doctor B.A. Arkhangelsky. IN lately he attracts increased attention, especially among Western doctors.
The result is achieved in approximately 50% of cases. It is performed at 34 - 36 weeks; the earlier the rotation is carried out, the more likely it is to be successful. But the likelihood of reverse reversion also increases.
Contraindications to taking an obstetric turn: threat of premature birth, bleeding, uterine defects, placenta previa, twins/triplets, oligohydramnios, signs of fetal hypoxia.
Previously, external rotation was not performed in women with a uterine scar, but now it is relative contraindication(individual risk assessment is required, examination by a council of doctors is possible).
External rotation is also not started if leakage of amniotic fluid is detected or the cervix has begun to dilate.
Ultrasound of the fetus with fetometry. Prerequisites: small fruit weight (exclude large fruit 4000 g or more), normal amount waters, absence of obvious defects, normal localization of the placenta.
- Administration of beta-adrenergic agonists (hexoprenaline) intravenously under supervision blood pressure and pulse. Beta-agonists relax smooth muscles uterus and increase the chances of success of the reception. For the mother, the administration of hexoprenaline (gynepral) can be complicated by low blood pressure, tachycardia, weakness and headache.
- It is possible (but not always) to use epidural anesthesia.
- The rotation begins from the presenting part (placing the hand on the pelvic end), as shown in the picture. The movements are smooth, in a circle, without sudden jolts.
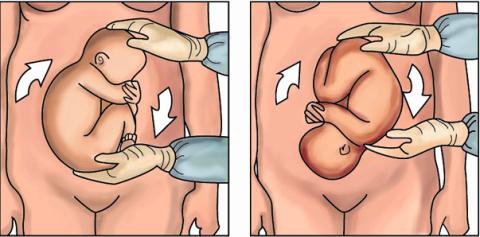
After the rotation, both in case of success and in case of unsuccessful rotation, the condition of the fetus is monitored. First of all, the fetal heartbeat is listened to, then cardiotocography (CTG) is performed. Doppler measurements are monitored according to indications.
Complications of external rotation:
Acute fetal hypoxia (due to impaired blood flow in the umbilical cord, compression of the loops), recorded by CTG (decreased heart sounds, irregularity, muffled tones),
- placental abruption (partial, rarely complete) up to 1.4% of cases. In this case, emergency surgical delivery is indicated.
- injury to the brachial nerve plexus as a result of throwing back the handles.
- antenatal fetal death (acute hypoxia, uterine rupture along the scar and other rarer causes).
With the right tactics, the prognosis for the fetus is favorable. External obstetric rotation, when performed skillfully and competently, is also rarely fraught with complications, but it is impossible to insure against them. Whether or not you agree to this procedure is your choice, you can always think it over, discuss all the risks and benefits with your doctor and make the final decision. Spontaneous childbirth with foot and mixed breech presentation does not always have a favorable prognosis; the risk is high birth trauma and disability of the child.
Birth with breech presentation
In order to determine the tactics of labor management, you need to take into account a number of factors:
1. Age of the patient. Primiparas over the age of 30 and young primigravidas (up to 18 years, and especially up to 16 years) have greater risk traumatism of mother and fetus during childbirth. This occurs due to less elasticity and extensibility of the perineal tissue.
2. Obstetric history. It is important to know: what kind of births there were (primiparas are at greater risk in terms of birth injuries), how the previous births proceeded, whether there were complications, bleeding, trauma to the child, how this pregnancy proceeded.
3. Assessment of the birth canal
- examination of the cervix, assessment of its maturity (readiness for childbirth),
- assessment of the woman's pelvis.
If there is an initial anatomical narrowing of the pelvis (even a slight one), then spontaneous childbirth can be dangerous.
4. Assessment of fetal parameters. If classically large fruit a child weighing more than 4000 grams is considered, then in the case of breech presentation, a fetus weighing 3600 grams or more is already considered a large fetus.
- Compensated condition of the fetus, absence of signs of hypoxia, heartbeat disturbances according to CTG and hemodynamic disturbances according to Doppler measurements
5. Features of breech presentation
- view: gluteal, mixed, leg, knee,
- position of the head: flexion (normal), extension (pathological position).
Independent childbirth
Independent birth in a breech presentation is allowed with a purely breech presentation, a compensated condition of the fetus weighing from 2500 to 3500 grams, normal sizes mother's pelvis, readiness of the birth canal. Prenatal hospitalization is indicated.
Pregnant women with a breech presentation of the fetus are not induced to give birth, do not use tablets or gels to prepare the cervix, and do not undergo amniotomy (opening of the amniotic sac).
Women who have a uterine scar from a previous cesarean section or myomectomy are also more likely to have an operative delivery. In this case, they are guided by the woman’s desire (to give birth herself) and internal protocols medical institutions.
And all the above factors are taken into account.
Only a doctor attends the birth.
During childbirth in the cephalic presentation, obstetric assistance is provided by a midwife, and only if difficulties arise - by a doctor.
IN independent childbirth in case of breech presentation, Tsovyanov's manual is required.
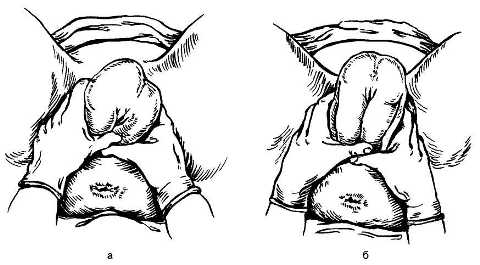
If the Tsovyanov benefit is provided in the event of a planned delivery of a breech birth (manual according to Tsovyanov No. 1), then the goal is to maintain the safest position of the fetal body parts (the legs are extended and pressed to the body), to prevent premature birth of the legs, throwing back of the arms and hyperextension of the head.
The doctor is positioned so that his shoulder girdle is at the level of the woman’s perineum. The hands are arranged in a ring, thumbs below, the rest above. As the fetal buttocks advance, the doctor moves the perineal tissues with “removing” movements and gradually releases the presenting part, while the thumbs tightly press the legs in the fetal abdomen. In 1 - 2 attempts the fetus is born before umbilical ring. Then you have to remove the handles; if they do not fall out on their own, then you need to tilt the fetal body downwards and the front handle falls out from under the pubic arch.
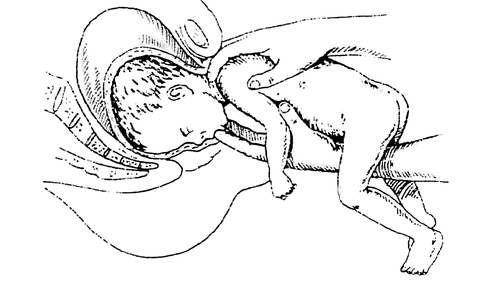
The thinnest part is the removal of the fetal head. If she is not born easily with pushing, then the Morisot-Levre technique is used.
When performing this technique, the fetal body is placed on the obstetrician’s hand, the 2nd and 3rd fingers of this hand are inserted into the vagina, you need to find the fetal mouth and press lower jaw. It turns out that we bend the head. The second hand (index and middle finger) should hold the fetal neck at this time. Extraction is carried out according to the biomechanism of childbirth, depending on which plane of the pelvis the head is located at that time. At the very end, the body is pulled far anteriorly and the head is born.
If the manual according to Tsovyanov (manual according to Tsovyanov No. 2) turns out to be a foot presentation, the pattern of actions is somewhat different. In general, leg presentation is absolute reading for caesarean section, but if the woman was admitted already in labor, with full opening and surgical intervention is impossible, then you have to act according to the situation. Such births should not happen as planned.
The goal in providing benefits according to Tsovyanov No. 2 is to prevent premature birth of the legs, throwing back of the arms and hyperextension of the head. This is achieved by converting leg presentation into mixed presentation.
As soon as the legs begin to be identified in the birth canal, the doctor sits down in the same way as when providing the usual Tsovyanov manual, a sterile napkin is placed on the perineum (to weaken the sliding) and resistance is exerted with the palm of the hand until the buttocks drop and the fetus “sits on squat."
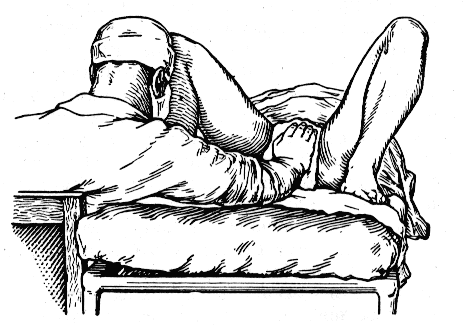
Then the hands are positioned in the same way as with the usual Tsovyanov manual, the fetal body is clasped by the obstetrician’s hands and gradually removed using the force of pushing.
When providing any of these benefits, you should not pull the child’s body, only assist the mother’s pushing and follow the natural biomechanism of childbirth.
If everything is fine, then the birth of the child goes smoothly, but complications may arise: tilting of one or both arms, tilting of the head, difficulty in the birth of the head and shoulder girdle.
In these cases, classic manual assistance is provided.
Classic manual manual produced as follows: the obstetrician's hand is inserted into the vagina from the side of the fetus, with the palmar surface facing the fetus. Find the angle of the shoulder blade and remove the handle with a “washing” motion. The obstetrician moves the left arm with his left hand, and the right one with his right hand. Next, if the head is in an extension position, then the Morisot-Levre technique is performed. During all manipulations, the assistant (midwife) holds the fundus of the uterus.
Indications for caesarean section for breech presentation of the fetus:
mixed breech presentation,
foot and knee presentation of the fetus,
breech presentation of the fetus in a pregnant woman with a scar on the uterus,
breech presentation of the first fetus of twins,
extensor position of the head during breech presentation,
large fruit (more than 3600 grams),
breech presentation of the fetus in a woman with anatomical narrowing of the pelvis and/or deformation of the pelvis (oblique, oblique pelvis),
lack of biological readiness for childbirth, tendency to post-term pregnancy ( immature cervix uterus),
age of primigravida over 35 years ( relative reading),
aggravated obstetric history (recurrent miscarriage, long-term infertility, pregnancy as a result of IVF, perinatal losses or a history of perinatal trauma to the fetus),
low placentation or marginal placenta previa (relative indication).
These are indications for surgical delivery related only to the position of the fetus. Other indications may arise independently (acute fetal hypoxia, indications for the heart or blood pressure, for diabetes in a pregnant woman, and so on).
The cesarean section operation is carried out according to the general canons. As a rule, such operations should be carried out in a 3rd level health facility (in perinatal centers), where there is intensive care for newborns and the second stage of nursing children.
Transverse and oblique position of the fetus
These provisions are rare, approximately 0.5 - 0.7% of all cases. They are classified as abnormal fetal positions.
In the transverse (A) position, all parts of the fetus are above the conventional line connecting the iliac spine.
With oblique (B) - the head or pelvic end intersects this line at an angle.
In both cases, the presenting part is not determined.
The reasons for such positions are the same as for breech presentation. Ultrasound reliably confirms the position of the fetus, and can also identify possible reason- polyhydramnios, fetal or uterine defects, placenta previa.
Complications caused by the oblique or transverse position of the fetus: premature rupture of water, premature birth, increased risk of postpartum hemorrhage.
Delivery is only surgical.
As planned during a full-term pregnancy, or as an emergency when water breaks or any other emergency obstetric situation develops.
Loss of small body parts is specific complication, characteristic only for the transverse, less often oblique, position of the fetus. With the release of water and a large opening of the uterine pharynx, the uterus begins to develop labor and push out the fetus. A fetus that is not positioned correctly cannot be born on its own. Acute fetal hypoxia and loss of an arm or leg occurs. This is an extremely unfavorable prognostic sign. Most often, in this case the fetus is no longer viable.
In this case, the mother has a high risk of infection, including the development of obstetric sepsis.
The unphysiological position of the fetus leads to overstretching of the uterus and increases the risk of rupture, the risk is especially high in multiparous women ( dystrophic changes uterine wall) and in women with a scar. Pregnancy is carried out under careful monitoring, an attempt at an obstetric turn is possible. Prenatal hospitalization is indicated.
If you are carrying a baby who is not positioned the way you and the doctor would like, then this is a reason to take a closer look at your condition, take additional actions and follow the recommendations. But there is no reason for panic and frustration. Take care of yourself and be healthy!
During pregnancy and childbirth, the baby can be in the uterus and then in the birth canal in different positions and presentations. Presentation is determined by the part of the body with which the baby comes into contact with the internal uterine os - the head or buttocks (legs).
What does breech presentation mean?
This is a situation where the child is attached to internal os lower end of the body. It is registered on average in 4 women per 100 pregnancies and can be gluteal or leg. In the first case in lower section the uterus is determined by the buttocks, in the second - the lower legs or feet.
Why is this condition dangerous?
The likelihood of a baby dying during childbirth increases several times compared to a head down position. What does this situation threaten besides perinatal death:
- untimely birth;
- oxygen starvation (hypoxia) of the child when the umbilical cord vessels are clamped;
- trauma at birth, if manual intervention by an obstetrician is used to remove the baby's upper body;
- low weight;
- umbilical cord loops getting into the vagina;
- location of the placenta on the internal os;
- congenital diseases and defects, often deadly.
Consequences of breech presentation for a child - an increase in the number of diseases in postpartum period up to 16%. Therefore, the process of childbirth in such a situation is initially considered pathological.
Predisposing conditions
The factors under the influence of which the breech presentation of the fetus is formed are not completely clear. The uterus during pregnancy has an ovoid shape, and its upper part wider than the bottom one. The fetus adapts to this by placing its wider pelvic part in upper section uterus, and the heavier head pressing against the upper part of the pelvic ring.
At birth, the baby's head moves forward, changing its shape and pushing the tissues apart. However, under the influence of certain factors on the part of the mother, fetus or placenta, this situation may change.
Causes of breech presentation of the fetus on the mother's side:
- violation of the structure of the genital organs (septum in the uterine cavity, bicornuate uterus);
- neoplasms, in particular, especially when they are located in the lower myometrium;
- discrepancy between the size of the pelvis and head;
- neoplasms pelvic organs(ovaries, intestines and others);
- violation of uterine tone (reduced, uneven).
Predisposing conditions from the fetus:
- prematurity or low weight;
- multiple births;
- congenital anomalies (hydrocephalus, myelomeningocele, pathology of the kidneys, heart, bones and muscles, chromosomal diseases).
Causes from the placenta:
- presentation;
- location in the corner or upper part of the uterus;
- shortened umbilical cord;
- little or polyhydramnios.
Half of the women with this pathology have no visible reasons this state does not exist. On the other hand, it has been found that if a woman herself was born in such a presentation, she increases the likelihood of developing it during her own pregnancy. If the first child was in a breech position, then for the next one this probability is about 20%.
Classification
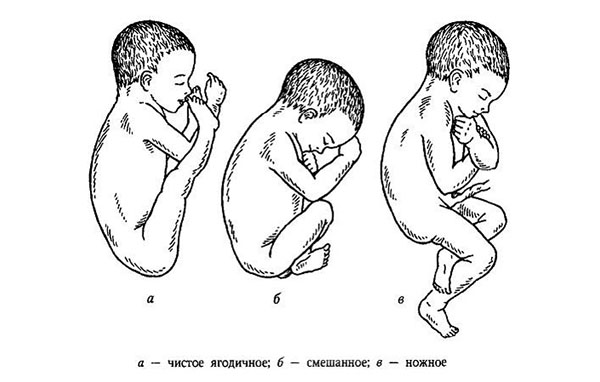
Domestic obstetricians have developed a systematization of pelvic presentation, highlighting the main types - gluteal and leg.
Gluteal
- pure gluteal: the child’s legs are straightened at the knee joints and bent at the hip joints, they press folded arms, the head is tilted forward, towards pelvic ring buttocks are close;
- pelvic mixed presentation: the legs are bent at the hip and knee joints, so the buttocks and one or two feet are adjacent.
Foot
- incomplete: one of the legs is directed downwards;
- full: both legs are directed towards the cervical canal;
- knee: rare, during childbirth it transforms into a leg one.
Transformation of incomplete to full leg presentation leads to increased risk birth complications. Indications for caesarean section arise.
According to the American division, the following forms of breech presentation are distinguished:
- true gluteal: legs bent at the knees and pressed to the chest;
- full pelvic: legs bent;
- incomplete pelvic: the joints of the legs are straightened, so that the legs are presented.
Pure breech presentation occurs in most women; it is determined in 65% of cases. A quarter of the patients have a mixed breech presentation, and a tenth have a leg presentation.
If the baby is lying in a breech position, then by the time of birth he will most likely turn head down. This revolution is especially likely when repeat pregnancy and breech presentation. It is observed in 70% of multiparous women and only in a third of primiparous women. Turning usually occurs before 34 weeks (40% of women), then its frequency decreases (12% at 36-37 weeks of pregnancy). If by this time the child has turned his head down on his own, his turning back is unlikely to happen.
In addition to being positioned head up, the fetus may take an incorrect position in the uterus. Transverse or oblique breech presentation often serves as the basis for operative delivery.
Diagnostics
Signs of breech presentation are determined by obstetric, vaginal and ultrasound (ultrasound) examination.
During an external examination of the patient’s abdomen, the doctor or midwife identifies a dense, displaced head in the upper part of the uterus (its bottom), which is often displaced to the side. The fundus of the uterus is higher than with a cephalic presentation because the baby's buttocks are less tightly pressed to the mother's pelvis. In the lower part of the uterus, a less dense presenting part is determined; it is larger than the head and does not move.
The baby's heartbeat is best determined at the level of the patient's navel.
To independently determine how the baby is positioned in a breech presentation, you need to know where the movements are felt. Since the baby is positioned with his legs down, the most intense movements will be felt in the lower abdomen. In the upper and middle sections, the shocks are weaker - these are movements of the handles.
Presentation cannot always be determined during external examination. This can be prevented by developed abdominal muscles, high uterine tone, twins, developmental defects of the child, and obesity in the mother. Therefore, if in doubt, carry out vaginal examination, during which a large soft formation is palpated - the baby’s buttocks.
The diagnosis is finally confirmed by ultrasound. With its help, the doctor determines the position of the fetus, the placenta insertion, the amount of water, and calculates the child’s weight. There are ultrasound signs that increase the likelihood that breech presentation will persist until the end of pregnancy:
- pure breech presentation;
- extension position of the head;
- small amount of water;
- attachment of the placenta in the area of the corners of the uterus.
Pregnancy management
Normally, the fetus is already positioned head down at 20-21 weeks. However, if at this time a breech presentation is determined, there is no need to worry. In most cases, the baby will roll over to the correct position on its own.
It is important to detect breech presentation only in the third trimester of pregnancy. At the same time, the efforts of doctors are aimed at transitioning from pelvic to cephalic presentation at 30-32 weeks and later, so that the child does not then roll over to its original position. At this time, the woman is prescribed therapeutic exercises according to the methods of Dikan, Fomicheva or Bryukhina. The choice of complex depends on many factors, in particular on the tone of the uterus.
With increased uterine tone, exercises according to Dikan are performed. They can be performed from 29 weeks. Three times a day on an empty stomach, the woman lies alternately on her right and left sides for 10 minutes three times in a row. The fetus begins to move more actively, the tone of the uterus changes, and the head turns downward. After this, the patient should use a prenatal bandage and sleep on the side where the baby's back is facing.
Is it possible to wear a bandage until the baby turns over?
This is allowed up to 30 weeks, since at this time the child can still freely change body position. In more late period During pregnancy, you can only wear a bandage if the baby is turned head down.
What to do with normal or low uterine tone?
Starting from the 32nd week, gymnastics according to Fomicheva is used. The complex is performed in the morning and evening for 20 minutes, an hour after eating. They will need a rug and a chair.
First, a warm-up is performed. For several minutes you need to walk on your toes, on your heels, with your knees raised on the sides of your stomach. Then follows a set of the following exercises:
- exhale: bend to the side, inhale: stand up straight, repeat 5 times;
- exhale: if possible, bend forward with a bend in the lower back, inhale – lean back, repeat 5 times;
- inhale: spread your arms to the sides, exhale: slowly turn your body to the side, simultaneously bringing your arms together and stretching them forward, repeat 4 times;
- hold on to the back of the chair; inhale: raise the bent leg near the stomach, touch the arm with the knee; exhale: lower the leg and bend into lumbar region, repeat 5 times;
- put one knee on a chair, while inhaling we spread our arms, while exhaling we slowly turn our body to the side and bend over, stretching our arms down, repeat 3 times;
- we kneel down, lean on our forearms, raise our straightened leg up, repeat 5 times;
- lie down on your right side; inhale: bend left leg, exhale – straighten it, repeat 5 times;
- from the same position, raise the leg and perform 5 circular movements with it;
- get on all fours; inhale: lower your head and arch your back, exhale: raise your head, bend in the lumbar region, repeat 10 times at a slow pace;
- lie down on your left side and repeat the two exercises above;
- we get on all fours, straighten our legs and stand on our toes, raising our heels, repeat 5 times;
- lie on your back and raise your pelvis, resting on your heels and occipital region, repeat 4 times.
Then, for relaxation, breathing exercises. Quite vigorous bending, turning, and bending the legs increase uterine tone and reduce its length, which helps the fetus to turn over.
In case of uneven uterine tone, gymnastics according to Brukhina is prescribed. It is carried out in the same time frame as the previous complex. The complex is based on relaxation of the abdominal muscles:
- kneeling with support on your forearms, take 5 deep breathing movements;
- in the same position, while inhaling, lower your face to your hands, while exhaling, raise it, repeat 5 times;
- in the same position at free breathing raise the outstretched leg, make a slow swing to the side and lower it so that the toe touches the floor, repeat 4 times;
- repeat the “cat” exercise, the same as in the Fomicheva complex, slowly 10 times.
In conclusion, you should perform, tensing your muscles anus and perineum.
Important to know! Properly selected gymnastics helps correct the child’s position in ¾ of all cases. It is believed that the presentation formed by the 35th week will be final.
External rotation of the fetus
How to turn a baby over in a breech presentation if physical therapy doesn't bring the desired result? IN recent years Obstetricians have regained interest in external rotation of the fetus in the third trimester. This is due to the development of ultrasound diagnostics, assessment of the child’s heartbeat using monitoring and the appearance effective drugs, reducing myometrial tone. Now external rotation is performed even in pregnant women with a scar on the uterus after any surgical intervention and is considered safe and effective.
With the help of this manipulation, a baby in a breech presentation moves his head down in about half of the cases. The frequency of reverse rotation to the starting position is about 10%. However, about a third of women with successful rotation still undergo cesarean section for other indications. Thus, the active use of this technique can reduce the frequency of surgical delivery by 1-2%.
Low hydramnios makes manipulation difficult, overweight the mother has a dilated cervix. It is safer to carry out the procedure between 34 and 36 weeks of pregnancy.
External rotation is performed in the maternity hospital under the control of ultrasound and fetal heartbeat. It is contraindicated in the following situations:
- threat of interruption;
- location of the placenta above the internal os;
- malformations of the genital organs;
- small amount of water;
- twins, triplets;
- small pelvis size;
- oxygen starvation of the fetus.
When performing an external turn, the following complications are possible:
- fetal hypoxia;
- fetal injuries;
- uterine rupture;
- death of a child due to clamping of the umbilical cord.
Therefore, during the procedure, doctors are always ready to perform an emergency caesarean section. The manipulation itself involves turning the fetus through the abdominal wall with the help of the obstetrician’s hands.
Choosing a birth method
How to give birth with a breech presentation? The answer to this question is ambiguous.
Today, caesarean section has the advantage. However, according to some obstetricians, an unfavorable birth outcome is often associated not with the position of the child itself, but with other factors - diseases of the mother and fetus, and the doctor’s limited experience. There is an opinion that the choice of delivery method later than 37 weeks does not affect the child. In addition, the operation is not indicated for rapid labor.
To select the method of delivery, a special scale is used. Natural childbirth can be carried out at a long term, in multiparous women with previous normal birth, pure breech presentation, flexed head, mature cervix, good condition child, normal pelvic size.
However, in case of breech presentation, surgery is considered the method of choice, which significantly reduces the risk of injury, illness or death of the child.
Natural childbirth is possible in the following situations:
- fetal weight 1.8-3.5 kg;
- one fetus in breech presentation;
- there are no indications for surgery;
- normal pelvic size;
- mature cervix.
A third of women have indications for emergency surgery during natural childbirth.
Childbirth takes place in several stages: first the child is born bottom part the body to the navel, then the torso is released up to the shoulder blades, the shoulders are born and, finally, the head appears. Helping a woman requires the experience and skill of an obstetrician.
Possible complications during childbirth:
- early rupture of water and prolapse of the umbilical cord, which leads to oxygen starvation of the child;
- weakness of labor activity;
- difficulties during the birth of the head, most often associated with throwing back the arms.
Natural childbirth
The mechanism of natural childbirth
In the upper, wide part of the pelvis, the buttocks are located in such a way that the axis between hip joints the child coincides with the mother's. At the beginning of labor, the buttocks gradually descend into the narrow part of the pelvis, simultaneously turning 90 degrees. In this case, the buttock, located in front, passes under the woman’s pubic symphysis and is temporarily fixed there.
Based on this point, the child’s spine flexes in the lumbar region and the underlying buttock is born. After that spinal column straightens, and the anterior buttock finally appears. The fetus quickly emerges from the birth canal to the navel.
After birth, the buttocks turn from a straight position to an oblique position, since at the same time the baby’s shoulders are pressed against the entrance to the pelvis. They enter the pelvic cavity according to its oblique size.
When moving along the pelvis, the child’s shoulders turn back to straight size, and the torso turns accordingly. The front shoulder passes under the woman’s pubic symphysis and is fixed there, just as the buttock was fixed before.
The baby's spine bends at the cervical and thoracic regions, the back shoulder is born first, and then the front shoulder.
The nascent head enters the pelvis so that its longitudinal suture is located in a transverse or oblique dimension. As the head passes to the exit from the pelvis, it turns with the back of the head forward. The area below the back of the head is fixed under the pubis.
Then the chin, face, crown of the baby appear above the perineum, and then the baby is born occipital protuberance. The head is not deformed. As a result, significant ruptures of the perineal tissue may occur. Therefore, an obstetrician delivering a baby requires experience and excellent knowledge of the biomechanism of childbirth.
Features of the course of labor
Childbirth is different from normal. A woman should listen to her feelings and be prepared for unexpected situations.
Does the stomach drop during breech presentation?
At the end of pregnancy, if the baby is positioned head down, this presenting part begins to descend into the pelvis and presses tightly against the internal bony protrusions. As a result, the fundus of the uterus becomes lower. With a breech presentation, the larger gluteal part does not descend into the small pelvis, but moves freely above it. Therefore, the belly does not drop until childbirth.
Due to the high position of the presenting part amniotic fluid often pour out prematurely, and in full, because the head does not hold them back. This contributes to further weakness of labor and increases the risk of infection in the uterus.
To prevent such a complication, a woman should lie in bed on her side, without getting up, until her water breaks. This will help save amniotic sac whole for as long as possible. After the water breaks, a vaginal examination is performed to rule out prolapse and compression of the umbilical cord. If the umbilical cord loops are still detected in the vagina, an emergency caesarean section is performed.
The soft presenting part puts less force on the uterine wall from the inside, so the opening cervical canal delayed. The first period lasts longer than normal by an average of 2-3 hours.
The second period is the most dangerous. At this time, a child is born, and maximum attention and effort is needed from the mother and doctors to ensure that this process goes without complications. Contractions during a breech presentation occur as usual, but due to irritation of the pelvic nerve plexuses by the gluteal part of the fetus, they can be stronger than during a cephalic presentation.
In the second period, the baby’s body and legs are born quite quickly. The passage of the head through an insufficiently dilated birth canal may be difficult. In some cases, with the rapid birth of the body, the baby’s arms are thrown back, and then the eruption of the head is hindered by the shoulder girdle. These are the causes of injury to the baby during childbirth.
Sometimes during this period the child swallows amniotic fluid. In addition, there is a danger of the umbilical cord falling out and being pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis by the nascent head, which is accompanied by severe oxygen starvation child.
During the second period, the woman is given some medicines, improving labor and facilitating the birth of a child. A dissection of the perineal tissue is required - perineotomy or episiotomy.
After the birth of the lower part of the body, the doctor delivering the baby holds the baby’s arms, preventing them from throwing back, and also helps the head to be born. With foot presentation, the obstetrician holds the baby's heels at the exit of the birth canal, transferring him to the breech position to sufficiently dilate the cervix and facilitate the birth of the head.
The third period (separation of the placenta) usually passes without any special features. Due to abnormal placental attachment, in some cases there may be a need for manual separation placenta. This manipulation is performed under intravenous anesthesia.
C-section
How is a caesarean section performed in a breech presentation? Preferably elective surgery with the use of epidural anesthesia, when the lower part of the body is numbed. However, let us also general anesthesia when the patient falls asleep. In this case, there is little harm to the child, since it is removed very quickly. The duration of the intervention does not exceed 1 hour, its technique is the same as for cephalic presentation.
Indications for the operation:
- fetal weight less than 2 kg or more than 3.5 kg;
- narrowing or deformation of the pelvis;
- excessively extended head;
- weak labor activity, lack of effect from inducing labor with medications;
- foot presentation;
- child growth retardation;
- death or injury of a child during a previous birth;
- time after the outpouring of water is more than 12 hours;
- post-maturity;
- scars, malformations, neoplasms of the uterus;
- placenta previa or abruption;
- breech presentation with twins, if in incorrect position the first child is born.
In primiparous patients, cesarean section is performed at the age of over 30 years, severe concomitant diseases, myopia, during pregnancy after IVF, hemolytic disease fetus, as well as at the persistent request of the woman.
Perinatal outcomes with breech presentation of the fetus in the case of timely operation favorable. IN further child grows and develops normally, unless he has a pathology that formed before birth.
Complications of childbirth:
- trauma to the cervical spine, spinal cord and brain;
- asphyxia (suffocation) of the fetus;
- prematurity and growth retardation;
- developmental defects;
- intrauterine infection due to early rupture of amniotic fluid;
- respiratory distress syndrome (impaired lung function after birth);
- hip dysplasia.
Birth trauma is associated not only with damage to the cervical spine, but also with excessive pressure on the head during childbirth from the fundus of the uterus. She later calls serious illnesses in a child. Violations noted motor function(paralysis), strabismus, seizures(epilepsy), neuroses, endocrine pathology, hydrocephalus, lagging behind peers in physical and intellectual development.
Affected musculoskeletal system. The baby may develop torticollis, hip dislocation, clubfoot, contracture (limited mobility) knee joints, dysplasia (impaired formation) of the hip joints.
At an older age, in children born in a breech presentation, often, regardless of naturally this happened or with the help of surgery, increased excitability is detected, restless sleep, loss of appetite, hyperactivity syndrome. Subsequently, difficulties may arise when adapting to society and schooling.
To prevent complications during breech presentation, the following measures must be taken:
- formation in antenatal clinic risk groups for breech presentation;
- regular observation by a doctor;
- diagnosis and treatment of complications during pregnancy such as, threat of miscarriage;
- prevention of postmaturity;
- use of therapeutic exercises;
- choosing the right method of childbirth;
- advance preparation for a planned caesarean section;
- proper management of natural childbirth, prevention of premature rupture of water, bleeding, disturbances in uterine contractility;
- diagnosis of complications during childbirth and timely decision about emergency surgery;
- careful delivery;
- thorough examination of the newborn child.
Information is important expectant mother about pregnancy and birth tactics. Psychosomatics - work disorders internal organs associated with prolonged stress, anxiety, fear of the unknown - can negatively affect the baby’s condition.
The more a woman knows about her situation, the less likely she is to develop complications. Therefore, it is recommended not only to ask the doctor about all the details of future childbirth that interest you, but also to read more about this pathology. It is necessary to prepare for a positive outcome in advance.

