Ultrasound of the ovaries preparation for examination. Transabdominal ultrasound of the ovaries. Pathology of gynecological organs detected by ultrasound
Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages - an examination that allows you to determine the anatomy, size, structure and condition reproductive organs women. Such diagnostics are carried out as screening studies, as well as for diagnosing pathologies and monitoring the treatment.
To perform this type of ultrasound, preparation is required. Decoding is carried out based on the comparison results normal indicators with the data obtained as a result of the study.
Who is indicated for ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages?
Ultrasound of the uterus, ligamentous apparatus, fallopian tubes and is performed for the following symptoms:
- stomach ache
- cycle disorder
- bleeding outside of menstruation, heavier periods
- discharge of pus or mucus from the vagina
- pain during coitus
- if you suspect a polyp or tumor (including fibroids) based on the results of the examination.
A routine ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries is performed if there is a desire to become pregnant, including as part of IVF, as well as as an observation – screening or urgent – over the course of pregnancy. 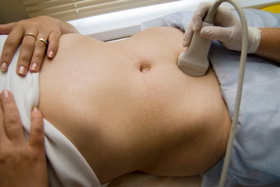
Types of ultrasound examination in gynecology
How is it carried out? this examination? There are three methods for obtaining information about the structure of the female genital organs using ultrasound:
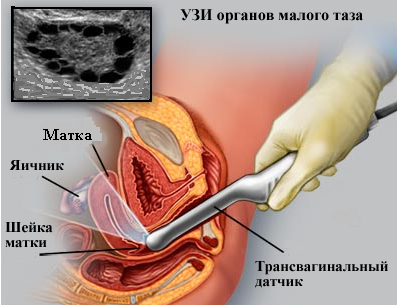
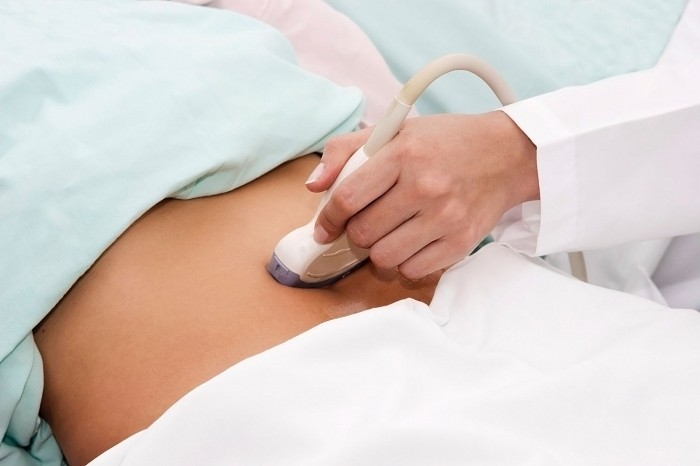
- Study: in this case, a special ultrasound sensor is inserted into the vagina. Ultrasound passes completely shortcut to the organs being studied, therefore this method is considered the most accurate. In addition, it is an important aid in the diagnosis of cervical pathology.
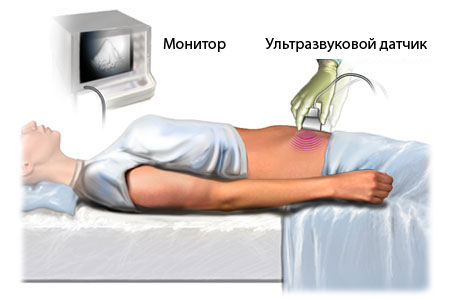
- (transabdominal) method: the sensor is located on the anterior surface of the abdomen and is not inserted anywhere.
- Transrectal examination: used only in virgins with suspected serious pathology gynecological organs. In this case, a thin sensor intended only for such research is inserted into the patient’s rectum.
- Internal research. Used only according to indications (for example, for submucosal localization of myomatous node). It consists of inserting a thin sterile probe with an ultrasound transmitter directly into the uterine cavity.
How to prepare for research
Preparation for the examination is based on the type of method in which this study will be carried out.
1.Preparation for abdominal diagnostics
If this type The ultrasound will be performed transabdominally; before this, the following preparatory measures need to be taken:
- The day before the ultrasound, exclude from your diet cabbage, legumes, carbonated drinks, brown bread and those foods that increase gas formation for you personally
- Fill bladder. To do this, you need to choose the option that is most convenient for you. Or an hour before the procedure, drink about 1 liter of still water, tea or juice; or do not urinate for about 2-3 hours.
2. Preparation for transvaginal diagnosis
Preparation for a transvaginal examination involves emptying your bladder immediately before the procedure. The day before, it is necessary to clear the intestines of gases with the drugs “Espumizan”, “Infacol”, “Smecta”.
3.Preparation for transrectal examination
Preparatory procedures for a transrectal ultrasound examination consist of emptying the rectal ampulla 6-8 hours before the time prescribed by the sonologists. To do this, the girl needs to choose one of several options:
- give an enema of a small volume of cool water
- use a microenema (“Norgalax”, “Microlax”)
- put in anus glycerin suppository
- drink a laxative like Senade.
4. Preparation for intrauterine diagnostics
There is no need to prepare before this type of ultrasound. You need to go to the test with an empty bladder.
How the procedure is performed
Here's how to do this procedure:
- For women, the patient undresses to the waist or simply opens her stomach for examination. She then lies down on her back, facing the doctor. A small amount of a special gel-like substance is applied to the stomach, and the sensor will move along it.
- How do they do it? Such diagnostics are carried out only using a vaginal sensor (in parallel, examination of other pelvic organs is performed). To do this, you will need to remove clothes below the waist, including underwear. Next, you lie down on the couch, bend your legs at the knees, and a special sensor placed in a disposable condom is inserted into the vagina.
- A transrectal type of diagnosis of the uterus and ovaries is done as follows: they use a special sensor that is thinner than a vaginal one. In this case, you will need to undress from the waist down and lie on the couch on your left side. A sensor in a condom, onto which a special gel is applied that improves the conduction of ultrasound waves, is inserted into the patient’s rectum.
- How to do it intrauterine diagnostics: the same as transvaginal, only a thin sensor will be inserted much deeper.
What errors occur during diagnosis?
Diagnostic accuracy depending on the day of the cycle
Q: When is it necessary to do an ultrasound examination of gynecological organs?
A.: This diagnosis is best carried out at the beginning of the cycle, when the mucous membrane (endometrium) of the uterus is still quite thin and will allow you to see existing polyps, even small tumors, and distinguish a cyst from a follicular and endometriotic one.
Q: On what day of the cycle are scheduled diagnostics carried out?A.: On the 3-5th day after the end of menstruation (can be performed on 7-10 days).
In each specific case, you should definitely consult with your doctor when it is better to do such a procedure: there are variants of pathology that will be visible not in the first, but in the second phase (after 12 days) of the cycle.
On the contrary, it is better to do it at the end of the cycle - from day 24 to day 28.
Q.: When to do an ultrasound in case of acute gynecological pathology?A: Immediately after you notice one or more of these signs:
- pain in the abdomen and its lower parts
- bleeding from the uterus
- copious purulent discharge
- sharp pain during sex
- menstruation that began after a delay and a positive test
- reappearance of blood from the vagina in the early postpartum period, after spotting are already over.
Since ultrasound is a harmless method in which visualization is performed using sound waves high frequency, this study can be done as often as necessary. It can even be done every day if necessary.
Decoding the research results
First, about what the uterus looks like on an ultrasound.
- This muscular organ pear-shaped.
- In most women, it has a forward bend (anteflexio), a backward bend (retroflexio) is not considered a pathology, but often creates problems with childbirth and normal function intestines.
- The contours of the organ are smooth and clear. If they are uneven, this indicates a tumor (for example, fibroids); the vagueness of the contours indicates inflammation of the surrounding tissues.
Normal uterus and ovaries according to ultrasound data
Normal description of the uterus
- for women 15-40 years old it has the following dimensions: 4.5-6.7 cm in length, 4.6-6.4 cm in width, 3-4 cm in thickness
- 20 years after the onset of menopause, its dimensions: 4.2 cm (length), 4.4 cm (width), 3 cm (thickness)
- if the size is smaller, they speak of an infantile uterus
- sizes speak more about pregnancy, fibroids
- echogenicity of the walls – homogeneous
- cervical canal – 2-3 mm in diameter
- V cervical canal mucus is detected
- The structure and thickness of the mucous membrane (called M-echo) depends on the phase of the cycle:
Based on this, the doctor indicates whether the size of the uterus is normal and whether the thickness of its endometrium corresponds to the phase of the cycle.
An ultrasound of the uterine cavity is performed in cases where there is its expansion, to clarify the causes of this condition. This allows you to closely examine the intracavitary pathology (most often, this is the submucosal node of the fibroid), determine its size and nature. The method also helps to diagnose the presence of remnants of membranes and blood clots in the organ cavity.
Description of the ovaries is normal
- the sizes of the right and left are approximately equal
- length: 3-4.1 cm, width: 2.0-3.1 cm, thickness: 14-22 mm
- ovarian volume is about 2-8 cm 3
- echostructure – homogeneous
- areas of capsule fibrosis up to several millimeters in size (signs of previous ovulations) should be detected
- uneven contours are normal, this is due to growing follicles
- in the middle of the cycle, a follicle measuring 18-23 mm (dominant) appears in one of the ovaries, several small follicles (up to 6 mm) are visible.
Pathology of gynecological organs detected by ultrasound
Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages helps to diagnose abnormalities in the development of a woman’s genital organs, assess the condition of the walls of the uterus and scars on it, clarify the nature of the existing pathology, and determine the presence and location of the fertilized egg.
Below are the most common questions from women.
About physiological processes in gynecological organs
1. What does mucus in the uterus mean on an ultrasound? The cervical canal should normally be filled with mucus, which prevents infection from entering the uterine cavity. In this case, the diameter of the channel should not be more than 0.3 cm.
2. Ultrasound of the uterine scar after caesarean section held in mandatory after such childbirth, as well as in case of subsequent pregnancy. This is necessary in order to:
- diagnose complications of cesarean section: fistulas, abscesses, formations
- timely detect and terminate a pregnancy that occurred earlier than a year after the operation
- The scar is examined upon the onset of pregnancy in order to detect its failure in time and take steps to terminate the pregnancy or early delivery.
3. After childbirth, a study is necessary in order to assess the nature of uterine contractility, see the number and nature of clots in its cavity, and diagnose inflammation of the uterus in a timely manner. Thus, a routine examination carried out by the third day should show that the clots are still in upper half the uterus, which itself has a spherical shape, decreases in size. 
Atypical location of the ovum
An ectopic pregnancy on ultrasound is visible already from 3 weeks, if the examination is carried out transvaginally, and the woman must take Espumisan at a dose of 2 capsules four times a day for 2 days before the examination.
Q: Does ultrasound show ectopic pregnancy?A.: Yes, some sonologists write that tests carried out using a vaginal sensor help to identify the incorrect location of the fertilized egg already from the second week of pregnancy, that is, the first day after a missed period.
Q: Is it possible to detect an ectopic pregnancy using an ultrasound?A.: In 90% of cases, such a diagnosis is made precisely by direct or indirect signs ultrasound diagnostics. To avoid that 10% chance when the test becomes positive, but the ultrasound does not show ovum in the uterus, it is necessary to conduct a repeated study over time, and also track over time hCG level in the blood.
Now about what an ectopic pregnancy looks like on an ultrasound. A sonologist can describe such signs tubal pregnancy:
- dilated fallopian tube, the embryo is localized in it
- there is a false egg in the uterus - areas of the mucous membrane that have changed due to pregnancy
- if the tubal pregnancy is interrupted, the ultrasound specialist sees free liquid in the pelvis (blood).
A: Sometimes this can be very difficult, since in the case of such a pregnancy the same symptoms occur as with the uterine localization of the embryo: toxicosis, breast tenderness, aching pain V suprapubic region, changes in the perception of taste and smell, delay of menstruation. The development of the ectopic localization of the embryo will be indicated by:
- small amounts of dark, bloody discharge that may appear at term normal menstruation or a little later
- such “periods” are weaker and shorter than usual
- when a tubal pregnancy is terminated, it appears sharp pain V lower sections abdominal cavity, it radiates into the anus, accompanied by nausea, loss of consciousness, and increased heart rate.
Abnormalities of the uterus
Bicornuate uterus. There are many forms of doubling of this organ. They are distinguished by:
- how many uterine horns there are
- Are they hypoplastic or are they both functioning normally?
- how many cervixes
- whether or not there is a septum in the vagina, dividing it into 2 halves.
According to these criteria, 8 forms of uterine duplication are distinguished, which are divided into 2 main types:
- Incomplete duplication of the uterus: it looks like the only organ, but with increased width. They may be the same or have a significant difference in size. One half may be filled with blood, but may still be functional.
- Full doubling. In this case, there are two organs of the same or different sizes, diverging at an angle.
Saddle uterus. It has the following signs on ultrasound scanning:
- M-echo diverges in the area of the uterine fundus during transverse scanning
- the uterine muscle “bulges” by 1.0-1.40 cm during longitudinal scanning (if more than 1.5 cm, this is a sign of a bicornuate uterus).
What do tumors of gynecological organs look like?
Examination of the pelvic organs, including the appendages, can reveal both benign and malignant tumors. Each species has its own characteristic ultrasonic features, but if cancer is suspected, a biopsy is performed under ultrasound guidance. This is the only way to make a diagnosis.
Diagnosis of uterine fibroids
Ultrasound helps diagnose this tumor, its location, condition, size, number of nodes.
Uterine fibroids on ultrasound:
- looks like
- it has an even, but not necessarily clear, contour
- the near contour of uterine fibroids has greater echogenicity than the distant one
- the far contour may not be detected
- there are hyper- and hypoechoic stripes
- Ultrasound for submucosal uterine fibroids shows a significant displacement of the M-echo
- Myomatous nodes may contain cysts and calcifications.
Viral tumor-like formations
These are polyps in the uterus. They are defined as round or ovoid formations that have smooth contours and do not change the shape of the uterus.
Polyps are best seen when injected contrast agent during transvaginal examination.
Malignant formations
Uterine cancer is not only determined using this study, a sonologist can also determine:
- exact location of the tumor
- depth of tumor invasion into the uterine muscle
- How narrowed is the cervix of the uterus?
- visualize damage to the ovaries and regional lymph nodes.
Cervical cancer is determined using transvaginal ultrasound:
- heterogeneous formation in the cervical area
- hyperechoic
- contours are uneven
- growth into nearby structures.
Due to the prevalence and high malignancy of the tumor, screening for cervical cancer should be carried out in all women over 30 years of age. It consists of carrying out colposcopy, ultrasound diagnostics, a smear for the human papillomavirus (it is this that causes this pathology) with a definition of its type.
Especially screening for cervical cancer should be carried out with the following symptoms:
- bleeding outside of menstruation
- hypogastric pain
- vaginal bleeding associated with sexual intercourse
- bleeding during menopause
- watery discharge
- swelling in the legs not related to heart or kidney problems
- difficulty urinating.
Other pathology on ultrasound
- Erosion of the cervix can be visible on ultrasound only during a transvaginal examination. The main method of making such a diagnosis is colposcopy.
- The expansion of the uterine cavity according to ultrasound indicates the development of endometritis, that is, inflammation of the uterus. In addition, an accumulation of gas is detected in the uterine cavity, the thickness of the mucous membrane decreases, and it becomes heterogeneous.
- What does the tone of the uterus look like on ultrasound? The sonologist sees local thickening organ walls.
Where to take the study
An ultrasound examination can be done at any multidisciplinary medical center or a specialized clinic.
The price of ultrasound diagnostics depends on how the study will be carried out. Thus, the cost of a transabdominal examination is within the range of 300-3800 rubles, and the price of vaginal diagnostics is within the range of 500-4000 rubles. You can ask about how much such diagnostics cost in the clinic of your choice by phone or find out on the website.
Thus, ultrasound of the uterus and appendages - informative view diagnosis of a large number of diseases of these organs. It has several subspecies, each of which has its own characteristics and “preferred” pathology. Preparation and execution different types research has its own characteristics.

ATTENTION! The information on the site is for reference or popular information only. Correct treatment and purpose medicines can only be carried out qualified specialist taking into account the diagnosis and medical history.
Successful diagnosis and treatment, health and feeling great!.
UziLabUltrasound of the ovaries visualizes the shape, location and size of the ovaries in women with extreme accuracy. Moreover, the procedure itself is absolutely painless and is performed quickly (about 15 minutes).
Ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries also allows you to examine the follicular apparatus (it contains the right and left ovaries). It is he who is responsible for a woman’s fertility. Its diagnosis can be done on any day of the cycle.
In this article we will talk about what pathologies an ultrasound scan of the ovaries shows, what normal sizes ovaries and why this diagnostic method is safe. We will also talk about how and when it is best to do an ultrasound of the ovaries.
2 Preparation for the procedure
Preparation for ultrasound examination of the ovaries is specific to each of the three methods. But in general, all three methods of preparation are united by their simplicity.
So, preparation before a transabdominal examination consists of a three-day diet before the procedure. Necessary exclude the following products:
- cabbage;
- legumes;
- any carbonated drinks;
- black bread;
- raw vegetables and fruits.
An hour before the test, you should fill your bladder. Volume of liquid required: from 0.5 to 1.5 liters of ordinary water (necessarily without gas!).
Preparation for transvaginal examination is carried out the day before the procedure. It is enough to use “Espumizan” (three times according to age) or any sorbents during the day. This procedure Do it only with an empty bladder.
When preparing for a transrectal examination, the same rules apply as for a transvaginal examination. However, you still need to empty the rectum several hours before the diagnosis.
To do this, use either classic enemas, or microenemas of the “Norgalax” type, or the introduction glycerin suppositories. Laxatives such as Senade and Guttalax are also suitable.
This study, like the transvaginal one, is done only with an empty bladder. Alcohol should be avoided on the day of the test.
2.1 Ovarian parameters are normal
Follicles in the ovaries, the norm of which is that they are approximately the same size relative to each other, are variable in size. That is, there is no universal indicator that can be taken as an absolute norm.
But the size range is known, which in any woman indicates the absence of pathologies. So normal size ovaries the following:
- length: from 30 to 41 millimeters;
- width: from 20 to 31 millimeters;
- thickness: from 14 to 22 millimeters;
- volume: approximately 12 cubic milliliters.
2.2 Conditional pathologies
Conditional pathologies include cystic formations(as with polycystic disease), which does not pose a threat to life. They usually go away on their own, but sometimes surgery is required.
Luteal cyst (interpretation: corpus luteum having a cystic capsule). This cyst may be in the place where the finished egg came out of the follicle on a certain day of the cycle.
A luteal cyst has a diameter of 30 millimeters (sometimes it can be larger). Usually this cyst dissolves by itself without leaving traces (the corpus luteum is not damaged). This can happen on any day of the cycle.
But sometimes a luteal cyst can be present throughout a woman’s pregnancy. In this case, this cyst will disappear only when the corpus luteum stops producing progesterone (the placenta will do this).
But a follicular cyst appears where the follicle appears (matures). This can also happen on any day of the cycle.
Having appeared on a certain day of the cycle, this cyst will gradually increase its volume from that moment on. Sometimes there is a situation when the volume follicular cyst reaches enormous values and rupture occurs.
Such an event is accompanied by sharp dagger pains in the abdominal area. In this case, urgent hospitalization in a surgical hospital (but preferably in a gynecological hospital) is necessary.
2.3 Pathological cysts
Dermoid cyst refers to benign tumors. The reason for its formation is a failure in intrauterine differentiation (interpretation: identification) of tissues. It can form on any day of the cycle.
In its cavity there are those cells that were supposed to form the skin, but got into the ovaries by mistake. The results of this are quite disgusting: the body of the cyst is filled with unformed nails, hair and even cartilage.
It can only be seen with the help of an invasive (penetrating) ultrasound examination (it is better to use the intravaginal method in this case). Results and interpretation of ultrasound for such a cyst has the following parameters:
- number of formations: one, round (sometimes attached to the corpus luteum);
- hyperechoic inclusions are visualized inside the cyst (as in polycystic disease);
- the formation has fairly thick walls (from 7 to 15 mm).
There is no method to prevent the appearance of this formation. It can occur, as mentioned above, on any day of the cycle.
K potentially dangerous formations also include endometrioid cyst. It is formed from the tissues of the uterine mucosa on any day of the cycle, but not in the uterus itself, but in the ovary. Its features:
- Quantity: always one (sometimes attached to the corpus luteum).
- It has variable wall thickness (from 2 to 8 mm).
- The outer contour resembles that of polycystic cysts (smooth, clear).
- The ovary is not differentiated from the side of such a neoplasm.
- In the cavity of the formation there are inclusions measuring less than two millimeters, having a ring or linear shape (reminiscent of a honeycomb).
It is best to look for such a cyst on a transvaginal ultrasound (an abdominal examination will only see its contours). There is no way to prevent the occurrence of such a cyst.
2.4 Detection of ovarian cysts on ultrasound (video)
2.5 Ovarian diseases
Serious and very dangerous diseases ovarian cancer and polycystic disease. The results of transabdominal ultrasound do not always visualize these pathologies, which is why it is always better to use penetrating diagnostic methods.
With polycystic disease, the ultrasound monitor shows large number different sizes neoplasms (cysts). Their size ranges between 2 and 9 millimeters. Such cysts sometimes affect the corpus luteum.
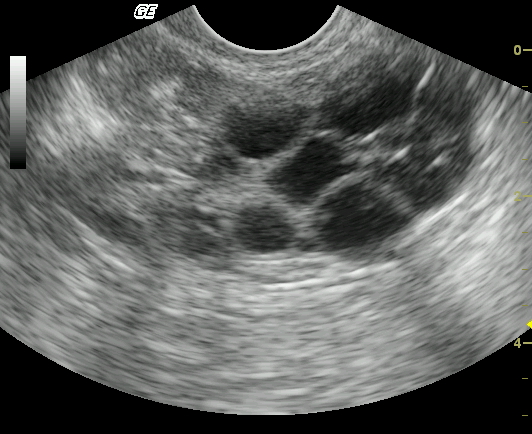
The number of cysts directly affects the course of the disease. With a large number of them, a woman feels worse than with single tumors. Polycystic disease is suspected when the picture shows:
- there is an increase in the size of the ovaries (more than 10 cm 3);
- thickening of the capsule is observed;
- Ultrasound visualizes multiple ovarian tumors.
The most dangerous ovarian disease is cancer. It is important to understand that the corpus luteum can also undergo degeneration into cancer.
Most often, ovarian cancer occurs in women in the so-called menopause. It is extremely rare (as anecdotal evidence) that cancer occurs in young women.
Ovarian cancer is often difficult to distinguish from a cyst. At the same time, ovarian cancer is very similar to a banal cystadenoma. But there is clinical differences, which should alert the diagnostician regarding cancer:
- Multi-chamber neoplasm.
- Spread of this neoplasm to neighboring organs.
- Cyst contents that cannot be analyzed (without biopsy).
- Accumulation of fluid in the pelvis and abdominal cavity.
If cancer is suspected, additional research. Usually this biochemical analysis blood and mandatory biopsy of the tumor.
Ultrasound is a method for diagnosing the condition internal organs, based on the different ability of tissues to absorb short ultrasonic waves. As a result, the doctor sees on the screen of a special monitor the echogenic structure of the organ, which may indicate a particular pathology.
There is no clear answer to the question of when is the best time to do it. It's all about what goals the doctor sets for himself.
Let's start in order. Ultrasound of the ovaries, as a rule, is performed in conjunction with an examination of the entire area of the woman’s internal reproductive system. Indications for this diagnosis include the following situations:
Preventive examination;
Treatment control;
Pregnancy;
Suspicion of gynecological pathology;
Changing the volume allocated menstrual blood;
Suspicion of pregnancy, planning pregnancy, as well as infertility;
At the time of admission hormonal contraceptives, as well as when setting intrauterine device.
Ultrasound of the ovaries can be performed in three main ways:
- Through abdominal tissue, i.e. transabdominal. If a woman is not pregnant, then such an ultrasound must be performed with a full bladder.
- Transvaginally - the sensor is inserted into the vagina, and thus diagnostics are carried out.
- Mixed or combined method - first inspection is carried out through abdominal wall and then through the vagina. This method is optimal because... allows you to see a more accurate picture of what is happening.
Ultrasound of the ovaries to determine normal maturation of follicles and egg formation is performed on days 5, 9, 11-14, 15 menstrual cycle. These days are “indicative” for considering a woman’s folliculogenesis. Most often, diagnosis on such days of the cycle is carried out when planning pregnancy, infertility, or to assess the result of treatment.
In order to identify the viability of the endothelium, diagnostics are best carried out at 20-21 days. In other cases, pelvic ultrasound can be done at any time, and there are no contraindications for this study.
Ultrasound examination is the most inexpensive, simple and informative method diagnosis of gynecological pathology.
As described above, there are three main types of diagnostics of the organs of the female reproductive system using ultrasonic waves. Each woman is warned in advance about how much liquid she should drink before the procedure, and for how long. Modern methods Ultrasound of the ovaries allows this procedure to be carried out with a small amount of liquid drunk an hour before the procedure.
If you are prescribed a combined diagnostic method, then prepare for the fact that the doctor will first look at the pelvic organs through the abdominal muscles, and then you will be asked to urinate (empty the bladder) to continue the diagnosis. A vaginal probe, covered with a condom, is inserted into the vagina up to the cervix - this includes both the ovaries and the uterus. In addition, the state of the Douglas space is determined (fluid sometimes accumulates here). Normal fallopian tubes are not visible on ultrasound, and there should be no fluid or blood in the retrouterine space. The echogenicity of the uterus should be homogeneous, without structural changes.
Ultrasound of the ovaries is performed either as preventative measure, or if there are suspicions of tumors, pathologies and inflammatory processes. Discover this body is not difficult for a specialist. If a woman has pain in the lower abdomen, bleeding outside the cycle, pain during ovulation and others alarming symptoms, you should immediately contact a gynecologist, who will then gynecological examination will be able to make a preliminary diagnosis and, if necessary, refer to ultrasound examination. It's not worth studying self-treatment and diagnosis, since not only her sex life, but also the ability to conceive and bear a healthy child.
 An ultrasound examination is prescribed for a woman if:
An ultrasound examination is prescribed for a woman if:
- Present constant pain lower abdomen.
- She plans to get pregnant in the near future.
- There is pain during sexual intercourse.
- Pain during menstruation is too severe.
- Cycle disturbances are observed.
- There are diseases of the mammary glands.
- Inflammation of the appendages.
- The woman is observed in the process of IVF dynamics.
- The doctor suspects a pathology.
- As a preventive measure.
Ultrasound of the ovaries allows you to identify women a large number of pathologies, diseases at the preclinical stage. The study also helps to diagnose neoplasms, evaluate the follicular apparatus and the structure of the ovaries.
How do?
Ultrasound examination of the ovaries women do in several ways:
- Transabdominal. Transdobinal ultrasound is considered classical method research. Recognized as an informative method if Preparation was carried out according to recommendations. This study is painless and non-invasive. Last no more than 15 minutes. A specialist deciphers the results.
- Transrectal. Data research method do through anal hole. With such an ultrasound there must be a special Preparation. It is considered an informative method. Used in rare cases.
- Transvaginally. Used very often. Helps diagnose diseases early stages, there is an opportunity to carefully study right And left ovaries. It is necessary to prepare in advance, since such a study should be carried out women on a specific day of the cycle.
After the doctor has prescribed an ultrasound examination, you need to clarify how it will take place so that the woman can prepare properly.
Preparing for an ultrasound
It was previously discussed how passes Ultrasound of the ovaries women, and now let’s look in more detail at how it’s done Preparation to each type separately.

How is the procedure done?
The procedure depends on its type:
- Transabdominal ultrasound of the ovaries women carried out in a supine position. The patient is first undressed to the waist. On skin A special gel is applied to the abdomen, which helps the sensor slide smoothly and prevents air from entering under the sensor. Air in such a situation can cause an inaccurate reading from the device. Thanks to this method left and right ovary women more precisely visualized. Ovarian cyst on ultrasound transabdominal type can be seen without much difficulty.
- Transvaginal ultrasound of the ovaries women It is also carried out in a lying position, the legs must be bent at the knees. The patient must first bare bottom part bodies. A condom is placed on the vaginal sensor and inserted into the vagina.
- Transrectal ultrasound of the ovaries women performed in a supine position on the left side. The patient should first expose the lower part of her body. A small sensor is inserted into the anus. The sensor is first lubricated with a special gel and a disposable condom is put on it.
All of the proposed types of ultrasound are considered informative and help the specialist make the correct diagnosis; they are considered painless and non-invasive.

