Normal size of ovaries. Normal ovarian size in women
The best way to check internal organs is ultrasound examination. It is very often used in gynecology. After all, the result can be obtained quickly, safely and accurately.
Why do you need an ultrasound?
The reasons why a doctor prescribes an ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries are varied. So, for example, they could be as follows:
- a woman may be bothered by pain in the uterus and ovaries;
- constant cycle disorders;
- strong painful sensations that appear during menstruation;
- when suspicious discharge from the vagina, but not related to menstruation;
- in addition, such a study should be done by women in order to determine the presence of pregnancy and to exclude ectopic pregnancy.
Thanks to this method, it is possible to identify any deviations from the norm and the onset of diseases.
Process
Many women are interested in how an ultrasound scan of the uterus and ovaries is performed. Two methods are commonly used for this study.
- Transabdominal ultrasound. This method is based on examining organs through the abdomen. To do this, the doctor applies bottom part belly with a little special gel that allows the sensor to glide better over the skin. In addition, if the doctor prescribes this type of ultrasound, it is necessary that the bladder is full. The fact is that ultrasound waves penetrate well through the aquatic environment, but through air - on the contrary.
- Transvaginal ultrasound. In this case, a special device is inserted into the woman’s vagina, with the help of which the examination is carried out. In order to avoid infections, a special condom is put on it. In this case, on the contrary, you need the bladder to be empty. This method is considered more accurate than the previous one.
The process itself does not cause any pain at all and has no negative influence on the body and passes quite quickly.
Uterus parameters
During such an examination, the doctor evaluates certain parameters of the uterus in women.
- Position. The normal position is when the uterus is tilted to the side bladder or rectum, i.e. forward. If the organ has a backward deviation, then this may well become a problem during pregnancy, because This situation is not considered the norm.
- External contours. The outer shell of the organ should be smooth and have a clear border. For fibroids or tumor diseases the contours will, on the contrary, be uneven. If the boundaries are not clear, then this may indicate inflammation.
- Size. It is considered normal when the length of the uterus is between 45 mm and 70 mm, depending on the woman’s age and the number of pregnancies. The width of the organ ranges from 45 mm to 60 mm and also depends on these indicators. Anterior-posterior size – from 34mm to 44mm. If the size of the uterus is smaller than normal, this indicates its underdevelopment. If, on the contrary, the values are higher, then this may be a sign of pregnancy or tumor diseases.
- Endometrial thickness. The doctor will definitely examine this indicator. The fact is that the thickness of the endometrium varies depending on what day of the cycle the ultrasound is performed. Therefore, the doctor looks at the correspondence of this value to the day on which the procedure takes place. Immediately after menstruation ends, the thickness of the endometrium is approximately 1-2 mm, but after ovulation occurs, its size varies from 10 to 15 mm.
- Echogenicity. This indicator shows the density of the fabric. For the uterus, homogeneous echogenicity is considered normal. If any other indicators are present, this may indicate the presence of fibroids or tumors.
- Structure of the uterine cavity. The cavity of this organ in healthy women is homogeneous, with clear contours. Its blurriness indicates that endometrial diseases are present. In addition, any neoplasms may be visible on ultrasound.
- Cervix. A normal size is 35 to 40 mm. At the same time, it must be homogeneous. The diameter of the cervical canal is approximately 2-3 mm. There must be liquid inside it. If the canal or the cervix itself is dilated, then this indicates possible diseases.
- Presence of free liquid. After ovulation, women may have some fluid in the retrouterine space. However, on any other day of the cycle, the presence of such fluid indicates possible diseases caused by sexually transmitted infections.
Ovarian parameters

In addition to examining the uterus, doctors must examine the ovaries. These are paired organs, and during the procedure the condition of both is assessed. What parameters does the specialist consider, and what values are considered normal?
- Location and form. Both organs are located on the sides of the uterus. Moreover, this arrangement is most often asymmetrical. In healthy women, the ovaries have oval shape. The follicular apparatus is clearly defined, the follicles are clearly visible in it. If an ultrasound is done on days 8-9 of the cycle, the specialist will determine the dominant follicle, which at this time can be from 15 to 25 mm in size. If its size exceeds this value, then this indicates the possibility of a follicular cyst.
- Ovarian size. A normal indicator is when the width of the ovary is 25 mm, the length is approximately 30 mm, and the thickness is 15 mm. If these values differ greatly, then inflammation or even inflammation may be present. serious illnesses these organs.
- External contours and echogenicity. The outer lining of the ovaries should be clear and lumpy (due to the growth of follicles). Echogenicity should normally be homogeneous. If the contours are blurred, then this indicates inflammatory processes.
- Structure. The ovaries consist of follicles and a capsule. The number of the former may differ in the left and right organs.
Fallopian tubes
With ultrasound, the fallopian tubes, if they are in in good condition, should not be visible. If a specialist nevertheless detects them, then we can talk about inflammatory processes present in them.
Diseases
Often, when comparing the data obtained with the examination results, the doctor can determine the presence of any disease. What diagnosis can there be?
- Myoma. In this case, the size of the uterus is larger than normal, its contours are blurred, and a node is detected in the myometrium.
- Endometriosis. This disease occurs when endometrial cells begin to grow outside the uterus. On ultrasound it is visible as a number of bubbles, which can be located in the uterus, and in its cervix, and in fallopian tubes Oh.
- Improper development of the uterus. These may be deficiencies in its development, for example, a bicornuate uterus or hypoplasia of this organ.
- Endometritis. In this case, the endometrium becomes thicker, and swelling may occur. The size of the uterus also increases in size.
- Uterine cancer. In this case, ultrasound determines large formations in the cavity of this organ.
- Cervical cancer. At the same time, the specialist sees that the size of the cervix is much larger than normal, and it itself is deformed due to the disease.
- Cyst. If a formation is found in the ovary, filled with fluid and exceeding 25 mm in diameter, then most likely there is a disease such as an ovarian cyst.
- Polycystic disease. The size of both ovaries exceeds normal indicators, they become thicker. In addition, fibrosis is determined.
- Adnexitis. If this disease is present, then an ultrasound can clearly see that the fallopian tubes have fairly thick walls, the ovaries become larger in size, and their boundaries become unclear.
Pregnancy
Ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries is mandatory during pregnancy. Their sizes vary. For example, the uterus stretches to a length of approximately 40 cm. The ovaries also increase in size, but not much. And the reason for this is increased blood flow to the pelvic organs during pregnancy. Besides, Ultrasound examination will help identify pathologies of organs and the fetus, if suddenly they appear. After childbirth, the uterus returns to normal size, and the ovaries begin to function normally again.
Ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries - necessary procedure if you suspect any disease or pregnancy. This is not a scary study at all, but it is the one that provides the most complete and accurate answer to many questions.
The female reproductive glands located in the pelvis and performing a generative function are the ovaries. They have a huge impact on the state of hormonal balance in the female body. The size of the ovaries indicates the possible presence of deviations in their development and functionality. These are oblong-shaped glands, whitish in color, with a heterogeneous bumpy surface. The proper production of eggs and the reproductive function of the female body depend on the condition of the ovaries. Ultrasound examination will help to identify problems in the health of these glands, during which the size of the ovaries in women is determined, which varies depending on the age and state of health of the woman.
Ovaries are formed already in the second month intrauterine development fetus and continue to form until the onset of menstruation. They perform several important functions:
- generative, on which the formation of eggs depends;
- vegetative, influencing the development and formation of primary sexual characteristics, as well as the development of the mammary glands, skeletal features and hair growth, related to secondary sexual characteristics;
- hormonal, thanks to which a woman’s body produces female sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone) and male sex hormone (androgen).
Thanks to proper development ovaries and their functionality in a woman’s body maintains hormonal balance. Eggs are produced, pregnancy is maintained, and the necessary muscle layer and a normal fat layer is formed.
The functional activity of the ovaries begins from the moment of puberty and continues until the woman reaches menopause. First changes in work of this body can be noticeable already at the age of 40, when women notice a failure menstrual cycle. The purpose of the paired gonads is to prepare everything necessary for pregnancy. This period in life is the most responsible, influencing the state of the entire organism and leading to significant changes in it.
Normal ovarian size
A change in the size of the ovaries does not always indicate a violation of the patient’s health condition. Their dimensions vary depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle and the level of hormones. In addition, the size of the right ovary often differs from the parameters of the left organ, but in most cases such a discrepancy does not exceed 0.2 mm and does not cause concern.
The normal size of the ovaries in women is:
- volume – 4-10 cm3;
- thickness – 16-22 mm;
- width – 18-30 mm;
- length – 20-37 mm.
These parameters are determined on the fifth or seventh day of the menstrual cycle. The range is quite large, and when conducting an ultrasound examination, the specialist takes into account the individual characteristics of each woman. This includes age and the presence of children or inflammatory diseases, and disorders in the development of the organs of the reproductive system, and the woman’s age.
During the entire menstrual cycle healthy woman the size of the ovaries remains within normal limits, minor changes in certain parameters are associated with the individual characteristics of the woman’s body and does not require medical intervention. However, if a significant deviation from the norm is detected, you should immediately consult a doctor who will determine the cause and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Determination of normal parameters of the gonads is required to confirm or cancel a diagnosis such as ovarian depletion or the presence of a tumor. Often, during the examination, the doctor discovers a cyst, which is recognized as physiological and goes away with changes in hormonal levels.
Determine hormone levels and decide on the need for prescription hormonal drugs Maybe experienced doctor. Such treatment can not only relieve the patient from these diseases, but also restore the functionality of the glands, eliminating the cause of ovarian depletion and the onset of early menopause.
Normal ovarian size during menopause 
The active activity of the glands continues until 40-50 years old; with the onset of this age, the production of eggs stops and female body spends what has been accumulated in advance.
While it's fading reproductive function, the size of the glands also changes. The normal size of the ovaries in menopausal women is noticeably reduced and both organs become the same size:
- volume ranges from 1.5 to 4 cm3;
- width is reduced to 1.2-1.5 cm;
- length – 2-2.5 cm;
- the thickness becomes no more than 1 -1.2 cm.
Slight fluctuations in the size of the ovaries during menopause are possible due to the fact that at first in the postmenopausal period the production of individual follicles still continues, despite the fact that there is no longer menstruation.
Ovarian size during pregnancy
All parameters of a woman’s reproductive system change during pregnancy. The size of the uterus and ovaries increases, and the glands may become displaced.
The reason for the enlargement of the glands is active blood flow, and the displacement is associated with the growth of the uterus and the forced rise of the glands under its pressure from the small pelvis upward.

Ultrasound examination
A doctor can determine the cause of changes in parameters during an ultrasound examination. It will accurately determine the onset of pregnancy or the presence of dysfunction, which also causes enlargement of the glands. Changing the parameters may lead to benign tumor or malignant neoplasm, inflammatory process, corpus luteum cyst of the ovary.
The most important indicator is the volume of the gland, indicating the presence pathological process requiring urgent medical intervention. gonads may indicate the development of pathologies such as:
- cyst or ;
- benign tumor;
- malignant neoplasm;
- presence of metastases.
However, it is equally important to promptly detect such pathology as gland depletion. Small ovaries indicate premature decline of reproductive function in women aged 35-40 years. Ovarian wasting syndrome is associated with the cessation of follicle production, leading to the cessation of ovulation and a decrease in the production of female sex hormones. An ultrasound examination will also allow you to notice such changes, during which the doctor not only measures the size of the glands, but also studies their shape and location.
The first sign of ovarian failure is scanty menstruation. They can be repeated several times a month and differ in a small amount bloody discharge. In some cases, menopause occurs suddenly. Only a qualified gynecologist can decide what to do to restore the functionality of the ovaries and prescribe appropriate treatment using hormonal medications.

To make an accurate diagnosis, specialists carry out:
- Transabdominal examination. Using a sensor located on the surface of the anterior wall of the abdomen, it studies the parameters of the gonads and is able to identify gross pathology of the glands, determine the normal size of the uterus and healthy ovaries.
- Transvaginal examination allows you to establish the normal size of the ovaries in women or identify pathology by inserting a sensor into the vagina.
- The transrectal method allows for a full examination of virgins who turn to a gynecologist with complaints about severe pain lower abdomen or menstrual irregularities.
As a rule, best time for the study - 5-7 days of the cycle, but if necessary, the procedure is carried out several times. On days 8-10, 14-17, 22-25 of the menstrual cycle. If dysfunction or the development of severe pathology is suspected, such studies should be carried out at least twice a year.
Maintaining a woman’s health and reproductive function largely depends on timely consultation with a doctor and preventive examination. Such an examination will help to timely detect changes in the structure of the gonads, an increase or decrease in their size, indicating the development various diseases. Modern methods diagnostics allow for early stages detect pathology and take measures to prevent the development of diseases.
Discomfort, pain, and strange discharge should always be a reason to visit a gynecologist who can diagnose accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Very often, after receiving the results of an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, women wonder how their genital organs correspond to the norms. This article will discuss what the normal size of healthy ovaries should be.
Ovaries are reproductive female glands, in which eggs are formed and mature. The ovaries are located on both sides of the uterus and are usually easily identified by ultrasound, and in cases where their detection is difficult, the iliac vein serves as a landmark. Healthy ovaries are well mobile and have a flattened shape. In a woman reproductive age most of the cycle, right and left ovaries different sizes, which indicates their normal functioning. The size of the ovaries depends on the woman’s age, the number of pregnancies and births, the phase of the menstrual cycle, and contraception by taking oral contraceptives and can fluctuate within significant limits. In order to identify pathological changes size of the ovaries, their ultrasound examination should be carried out from the fifth to the seventh days of the menstrual cycle. In this case, the decisive role in determining pathology is played by measuring not so much linear dimensions as volume.
The normal sizes of the ovaries range from:
- volume – 4-10 cm3;
- thickness – 16-22 mm;
- length – 20-37 mm;
- width – 18-30 mm.
The internal anatomy of the ovaries is examined taking into account the phase of the menstrual cycle. The ovaries consist of a tunica albuginea, under which are the outer (cortex) and inner (medulla) layers. In the outer layer of women of reproductive age there are follicles varying degrees maturity – primary immature (primordial) and mature prevoulatory.
- In the early follicular phase (days 5-7), ultrasound reveals a white capsule and 5-10 follicles measuring 2-6 mm, which are located along the periphery of the ovary.
- In the middle follicular phase (8-10 days), the dominant (12-15 mm) follicle is already clearly defined, which continues its development further. The remaining follicles stop developing, reaching 8-10 mm.
- During the late follicular phase (days 11-14), the dominant follicle reaches 20 mm, increasing by 2-3 mm per day. ABOUT imminent arrival Ovulation is indicated by the follicle reaching a size of at least 18 mm and a change in its external and internal contour.
- The early luteal phase (days 15-18) is characterized by the formation of the corpus luteum (15-20 mm) at the site of ovulation.
- During the middle luteal phase (days 19-23) corpus luteum increases its size to 25-27 mm, after which the cycle enters the late luteal phase (24-27 days). The corpus luteum fades away, decreasing in size to 10-15 mm.
- During menstruation, the corpus luteum completely disappears.
- If pregnancy occurs, the corpus luteum continues to actively function for 10-12 weeks, producing progesterone and preventing the release of new eggs.
The size of the ovaries during pregnancy increases due to more active blood flow, while the ovaries change their position,  shifting under the influence of the growing uterus from the pelvic area upward.
shifting under the influence of the growing uterus from the pelvic area upward.
The ovaries are the reproductive organs in women, located on both sides of the uterus. They are egg producers. During an ultrasound of the uterus, the ovaries are also necessarily examined - their size is checked. If inflammation or any pathology occurs, this leads to impaired reproductive function.
In women, the size of this organ may vary, everything will depend on the level of hormones and health status. It must be remembered that the right and left ovaries differ in size from each other, but the difference should normally be no more than 0.2 cm. The size may vary depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. It is recommended to conduct the examination on days 5-7 of the cycle. The date may be adjusted based on individual characteristics every woman.
The main indicator that may indicate the presence of any diseases is volume. Ultrasound indicators of the ovaries of the uterus are normal:
- Volume – 4-10 cubic meters. cm.
- Length – 2-3.7 m.
- Width – 1.8-3 cm.
- Thickness – 1.6-2 cm.
It follows from this that the “dispersion” of sizes depends on age, inflammatory processes and the menstrual cycle. Therefore, a non-specialist will not be able to make a correct diagnosis, since other factors are also taken into account when making the diagnosis.
Causes of changes in ovarian size in women
Normal size and the volume of the ovaries is constantly changing. U nulliparous woman unlike the one giving birth, she will be in to a large extent the size of the ovary varies. Somewhere from 15-17 years of age until the end of life, this organ is subject to constant changes, which are considered the norm.

A particularly important period is pregnancy, when the ovaries become larger in size and can change their location. This occurs due to the increase in size of the uterus due to the growing fetus. After childbirth, the size of the uterus and the location of the ovaries return to normal. If a woman does not breastfeed her baby, the overall blood flow to the ovaries decreases and estrogen synthesis resumes.
Gradually, with age, reproductive function decreases and this affects the parameters of the organ. The ovaries begin to become smaller. Sizes of the ovaries on ultrasound during this period:
- Volume – 1.5-4 cubic meters. cm.
- Length – 2-2.5 cm.
- Width – 1.2-1.5 cm.
- Thickness – 0.9-1.2 cm.
Ovarian pathologies in women
To determine pathological condition or deviations from the norm, the woman is sent for an ultrasound. If everything is normal and the body functions well, then the size of the uterus and ovaries should be within permissible norm. If on an ultrasound the doctor discovered an enlargement of one ovary two or more times, then this indicates serious violations. Also, if there is a deviation in the volume of this organ by 1.5 centimeters or more.
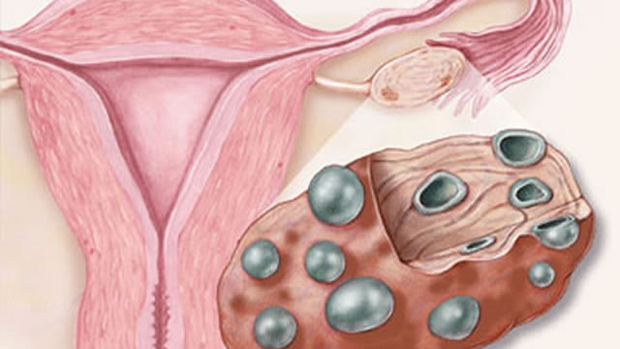 Enlarged ovaries in women, shown on ultrasound, indicate the following diseases:
Enlarged ovaries in women, shown on ultrasound, indicate the following diseases:
- Cyst.
- Polycystic disease.
- Benign tumor.
- Malignant tumor.
- Metastases.
In case of serious deviations, purulent condition and resection, the doctor prescribes an urgent surgery. If the patient refuses the operation, then such an act can even lead to fatal outcome. During an ultrasound, the presence and stage of the disease can be detected. If the tumor has reached significant parameters, then this can end disastrously for the patient. Very often, ovarian cancer can be accompanied by uterine cancer. Therefore, experts recommend regularly undergoing preventive ultrasound of the uterus to detect the disease on initial stage and prevent its development.
Also, a sudden decrease is not considered normal. reproductive organs uterus. Doctors call this condition “premature menopause,” which negatively affects the normal functioning of the reproductive organs. Most often, this pathology is observed in women aged 36-41 years. As for the size of the uterus, they also change slightly - they decrease, and the walls become thinner. Menstruation gradually begins to stop, and then menopause occurs. If discovered in time this pathology on ultrasound, it can be prevented by taking hormonal drugs. After such therapy, a woman even has a chance of becoming pregnant.
Every woman is advised to pay attention to even minor changes or pain that may appear in the lower abdomen. If it starts to bother you unpleasant sensation during sexual intercourse, you should immediately consult a gynecologist for advice, since the disease is easier to prevent than to treat last stage, which can also negatively affect reproductive function especially at a young age.
The ovaries are one of the organs of the reproductive system that is located in the pelvis. They are located symmetrically on the right and left sides of the uterus. Follicles develop in the ovaries and eggs mature. Accordingly, disruption of the functioning of this organ can result in infertility. One of important indicators What is taken into account during the examination is the size of the ovaries in women.
In a female fetus, the ovaries develop towards the end of the third trimester of pregnancy. By the beginning of the 7th week of embryogenesis, the development of the oocyte stalk occurs; during this period, the ovary contains only the cortex with follicles. Complete structure and medulla will appear much later.
The general structure of the ovary consists of a cortex with follicles, an extracellular matrix with cells different types, as well as fibrous compounds. The tunica albuginea, which covers top layer oocytes, combines elastin, collagen and muscle cells. Microvilli are located in certain areas of these glands.
The cortex contains structural components ovaries, which are surrounded by a membrane of epithelial cells and two layers connective tissue on different phases development.
Only with absolute compliance of anatomical indicators is the correct functioning of the woman’s reproductive organs realized.
Normal ovarian size

The normal size of the ovaries in women, which is indicated below, will not be identical for all girls. This indicator changes under the influence of hormonal levels and general condition body. The right and left ovaries may also differ in size, but only by 2-3 millimeters. A sudden change in the size of one of the ovaries indicates the development of a tumor or inflammation.
Various factors can affect the size of the ovaries throughout all phases of a girl’s MC. In order to conduct the study correctly and obtain reliable information, an ultrasound is performed between the 4th and 8th day of the ovarian cycle. The main parameter that indicates the presence of neoplasms is the volume of the ovary.
Normal ovarian parameters in a woman of reproductive age should be:
- Thickness – 15-21 mm.
- Length – 19-36 mm.
- The normal volume of the ovaries is 3-9 cm3.
- Width – 17-29 mm.
Normally, the variation in size is large, so one size is not enough to make a diagnosis. To find out whether there are health problems, it is necessary to conduct a complete examination of the ovaries.
Factors influencing ovarian size

Throughout life, the size of the ovaries can change. Size depends on various factors: number of pregnancies and births, age, duration of MC or use of hormonal contraceptives.
From the moment of the first menstruation, the size of the ovaries changes under the influence natural factors. After pregnancy, these glands will increase significantly due to increased blood flow for transfer nutrients to the fruit. In addition, the ovaries move upward as the fetus grows.
The size of the ovaries during pregnancy will increase to 3 mm. During this period, the glands do not synthesize estrogen and the development of eggs is suspended. However, endocrine function persists and the ovaries produce progesterone. After the baby is born, the ovaries and uterus will decrease in size.
Please note: Placental circulation will change, and the blood flow will become less intense. Over the course of two months, the volume will return to normal, and the production of estrogen will begin, which will restore the possibility of conception. If a woman long time breastfeeds the baby, the functioning of the ovaries will return to normal only after completion of lactation.
As menopause approaches, reproductive function declines, and this will also be reflected in size. The size of the glands decreases, but not at the same time. After postmenopause, the volume of the ovaries will be the same.
Standard parameters during the postmenopausal period are:
- Volume – 2-4 cm3.
- Thickness – 8-11 mm.
- Width – 11-14 mm.
- Length – 19-24 mm.
In the first few years and after menopause, the size of the ovaries fluctuates within 3 mm. This is related to periodic development pairs of follicles in these phases.
Pathological changes in size

During the examination of the ovaries, in order to find out whether there are pathological changes, it is worth taking into account normal parameters. Alarm about problems with reproductive health is an increase in the size of the gland by two times or more. The presence of pathology provokes an increase in the volume of the ovary by 2 cm or more.
If an ultrasound revealed such an increase in the size of the ovary, this is the first indicator of the following diseases:
- Different types of cysts in the ovary.
- Polycystic disease (with the presence large quantity formations).
- Benign education.
- Malignant tumor.
- Presence of metastases.
- Genetic or congenital abnormalities.
If the situation worsens and illnesses result serious complications, such as a purulent inflammatory process or ovarian torsion. Timely surgery will help improve reproductive function.
Please note: One of the life-threatening diseases is malignant neoplasms in the ovary. If treated in the early stages of the disease, the chances of recovery are high, but not everyone manages to diagnose the tumor on time. Therefore, for every woman, especially after childbirth, it is important to regularly conduct ultrasound of the breast and pelvic organs.
The first sign of problems with reproductive system considers both a reduction in size and strong increase one or two ovaries. If the ovaries decrease in size, this may be a sign of premature menopause. Occurs most often in women over 36 years of age. At the same time, the uterus will also shrink and its walls will become thinner.

