Can the menstrual cycle change? Changes in menstruation: nature of the cycle, reasons, duration
The concept of “cycle” includes a certain process that has a beginning and an end. Then the cycle repeats from the beginning, and so on continuously. This constant movement is the meaning of cyclicality.
When you are asked at an appointment: “In how many days does your period start?”, they mean the duration of your cycle.
Regardless of the individual duration of menstruation, the first day is precisely the first day of bleeding, followed by the second, third and so on.
After menstruation, the cycle does not end; it continues until the first day of the next menstruation.
What is the normal length of the menstrual cycle?
Variations are possible: from 21 days to 32 days. For most women, 28 days pass from the first day to the first day of menstruation.
If within two to three months the time intervals for the onset of menstruation are different - then after 20 days, then after 30 days– this is regarded as a lack of regularity in the menstrual cycle.
Why do my periods always shift by a few days?
This happens because our official calendar does not coincide with the individual calendar. Otherwise it is called lunar, in which the length of one month is exactly 28 days, that is, is exactly 4 weeks.
If your last period started on the 21st, with a 31-day month, the next menstruation with a 28-day cycle should be expected three days earlier.
What is ovulation, why is it necessary?
- this is the release of an egg formed by the ovary, which can, after fertilization by a sperm, turn into a fertilized egg - the unborn child.
Even if this does not happen, the egg is still needed! And why? Because the entire female body develops cyclically and functions according to a cyclic law.
The processes of maturation and rejuvenation are continuous. In other words, ovulation provides uninterrupted functioning of the entire female body.
The physiological cycle is two-phase. The middle of it just happens to coincide with ovulation. With an average cycle length of 28 days, Ovulation should occur on the 14th day.
First phase(growth of young cells) - before ovulation, second(cell maturation) - after it.
If ovulation does not occur– there is no menstrual cycle, then acyclic bleeding occurs. Pregnancy without ovulation is impossible.
The reproduction of new life is inherent in every woman. And for a new life, a young egg is needed, the formation of which occurs continuously in the ovary under the influence of female sex hormones.
If a woman’s menstrual cycle is not disrupted, it means she has normal hormonal levels. This protects her from serious illnesses that prevent pregnancy, even if it does not occur.
What is the corpus luteum of pregnancy?
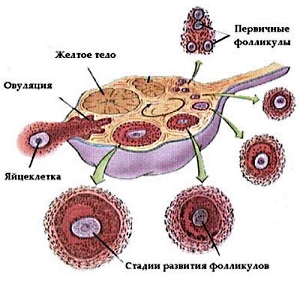 When a mature follicle turns into an egg, in its place a yellow body is formed. This is a cluster of cells that produce gestagens - maturation hormones.
When a mature follicle turns into an egg, in its place a yellow body is formed. This is a cluster of cells that produce gestagens - maturation hormones.
During pregnancy the corpus luteum continues to function until the placenta develops, then it turns into a white body - a small scar like a callus in the ovarian tissue.
Before the onset of menstruation, the corpus luteum stops working if pregnancy does not occur.
Manifestations of ovulation
Sometimes the process of releasing an egg is accompanied by pain. in the lower abdomen during ovulation, due to rupture of the superficial membrane of the ovary.
Causes of pain there may be inflammatory processes in the ovarian tissues, or increased sensitivity of peritoneal receptors to estrogen.
In gynecology this condition is referred to as ovulatory syndrome and requires treatment.
Mood changes and even the life position of women is determined by the replacement of growth and acquisition hormones (estrogens) with gestagens, which are responsible for preservation and further development.
If in the first phase of the cycle a woman wants to buy something, then in the second she thinks differently. Now there is a need to preserve what is available.
This is where the concept of female logic came from, which is not clear for a man whose hormonal background remains unchanged from birth until death.
The menstrual cycle is a reproductive mechanism launched in the body of every healthy woman of fertile (childbearing age), ensuring a woman’s ability to conceive and bear a child.
The stability and regularity of this cycle affects a woman’s overall well-being, her condition, activity and mood.
How does this happen
The functioning of the menstrual cycle depends on the central nervous system and hormonal levels - the balance of sex hormones - progesterone and estrogen, the production of which is responsible for the ovaries. Depending on the hormones produced by the ovaries, hormones of the main gland - the pituitary gland - appear, but if there are few female sex hormones, then the pituitary gland stimulates their greater production, and this also happens in the opposite case.
The pituitary gland, as part of stimulating the normal menstrual cycle (MC), acts in three directions:
- stimulates the release of the follicle, the maturation of the egg in the first half of the MC;
- stimulates the release of the egg and the production of progesterone in the future, if conception has occurred;
- promotes the production of prolactin - to provide the baby with breast milk after childbirth.
The pituitary gland is affected by the central nervous system (CNS) and its department, which corrects the functioning of the endocrine system - the hypothalamus. It is in this area that hormones that inhibit or inhibit, depending on the need, the production of gonadotropic pituitary hormones are not located and are constantly produced. At the head of the entire hierarchy is the cerebral cortex.
Ovarian cyst
Often, due to impaired maturation of the follicular component and accumulation of fluid in the cavity, a benign formation appears - a cyst.
It can often be diagnosed in fertile women. The cyst may disappear and appear on its own. The disease occurs in 70 percent of women. Ovarian cysts are classified according to the area of occurrence:
- follicular;
- corpus luteum cyst;
- paraovarian.
If the cyst does not go away within 1-2 cycles or does not disappear after childbirth in pregnant women, it must be removed surgically.
Failures in the cycle, why they happen
We can observe irregular cycles in most women. Few people can boast that their periods begin on the same day of the month. Why is this happening? The first and obvious reason: ideally, the menstrual cycle lasts 28 days. Therefore, if your period began on January 6, then after 28 days it will begin on February 3–4, and then on March 1–2 and March 31–April 1. After all, each month has a different number of days, and the cycle can normally be delayed by 1–2 days. On average, it is expected that the cycle can be from 24 to 35 days. For many women, their cycle changes every month.
Another reason is disorders in the woman’s body. This includes nervous experiences, malfunction of the pituitary gland, ailments of the hormonal system, infections, inflammation, bad habits, excessive physical activity, heavy lifting, taking certain medications, blood diseases, exacerbations of chronic diseases, oncology, etc. The cycle can be affected by unsuccessful surgical interventions for gynecological problems, as well as trauma and damage to the uterus, diseases of the appendages, hypothermia.
What types of MC violations are there?
Since the mechanism of the cycle’s functioning is triggered by different parts of the body, the classification of MC disorders is based on where exactly the regulation is disrupted. Cycle failures are distinguished at levels:
- cortex and hypothalamus;
- pituitary gland;
- ovaries;
- uterus;
- thyroid gland;
- adrenal glands
If violations occur in one of the listed departments, the MC also fails. After stressful situations, severe fright or prolonged nervous tension, the pituitary gland suffers, not releasing the required amount of hormone for the cyclic maturation of the egg. There is no ovulation - no menstruation occurs either.
If the function of the hypothalamus is impaired, the ovaries may reduce estrogen production, so egg maturation will not occur within a given cycle. Perhaps the malfunction in the MC is associated with damage to the ovaries up to their fibrosis, which results in a decrease in the number of follicles ready to create an egg during the menstrual cycle. Follicles are formed individually during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus.
How to determine that a failure has occurred in the MC
MC disorders are divided into the complete absence of menstruation - amenorrhea and the presence of scanty discharge of a non-menstrual type at inopportune times.
Another intermediate failure is observed if the intervals between previously regularly occurring menstruation have changed, the intensity of bleeding has increased or decreased, and erratic menstruation has appeared.
The main obvious signs of failure:
- the volume of discharge changes – hyper- or hypomenorrhea;
- the period of discharge has shortened - if previously menstruation lasted for 7 days, now this period has been reduced to 3–4, for example;
- the discharge period has increased;
- The usual rhythm of menstruation has been disrupted - periods appear either twice a month, or there is a 90-day break.
Hypomenorrhea - scarcity of discharge occurs due to decreased activity of the pituitary gland and hardening of the ovaries. Menorrhagia is prolonged heavy menstruation, accompanied by pain and blood loss, lasting up to 2 weeks. Such phenomena occur during the formation of a cycle in adolescence and during hormonal decline in the premenopausal period. At fertile age, such disruptions occur from chronic diseases of the uterus, fibroids and the presence of polyps.
Any cycle disturbances require attention and timely consultation with your gynecologist.
Menstruation is a physiological process that normally occurs monthly in women. The duration of the menstrual cycle and the nature of menstruation are individual for each woman, this is due to the structural features of the body, the presence of any diseases of the female reproductive system, genetic characteristics and many other factors.
A healthy woman of childbearing age should have regular periods. The duration of the menstrual cycle (from the beginning of the previous menstruation to the first day of the next menstruation) should be approximately 28 - 35 days.
Why does menstruation occur? Every month, an egg matures in the body of a healthy woman. If fertilization does not occur, the egg is released.
A regular menstrual cycle is the main indicator of the normal functioning of the reproductive function of the body. In other words, a woman whose menstrual cycle is constant is able to conceive and carry a child.
Menstruation is a necessary process for the normal functioning of the female body. However, there are many reasons that can disrupt a woman’s menstrual cycle and cause changes in the nature of her periods. Let's take a closer look at why such violations can occur.
Reasons that can cause disruption in the menstrual cycle and the main clinical forms of disorders
Menstrual irregularities, as a rule, are a consequence of some pathology or arise as a result of the influence of unfavorable factors on reproductive function.
There are three main types of reasons that provoke disruption of the menstrual cycle:
- pathological (cycle disruption due to the presence of diseases);
- physiological (stress, diet, climate change, etc.);
- medicinal (cycle disruption is caused by taking or stopping any medications).

Pathologies that can cause menstrual irregularities:
- One of the main and most common causes of menstrual cycle disorders in women is ovarian pathology.
- Disruption of the hypothalamic-pituitary system.
- Pathologies in the functioning of the adrenal glands.
- Endometrial polyps.
- Endometriosis.
- Diseases of the uterus.
- Oncological diseases.
- Damage to the uterine cavity as a result of curettage or abortion.
- Liver diseases.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the hemocoagulant system.
- Conditions after operations on the female reproductive system.
- Genetic reasons.
As mentioned above, one of the types of reasons that can affect the regularity of menstruation is external factors. This includes work in hazardous industries, a change of place of residence, severe emotional shocks, drinking alcohol and smoking, an unbalanced diet, and sudden weight loss.
In addition, irregular periods are observed in women undergoing drug treatment with hormone therapy drugs, antidepressants, anticoagulants and others. That is why only a doctor should prescribe medications and monitor the patient’s condition during treatment.
The main clinical forms of menstrual cycle disorders are:
1. Cyclic changes in menstruation:
- hypermenorrhea - an increase in the volume of menstrual flow with a normal duration of menstruation;
- hypomenorrhea – scanty menstruation;
- polymenorrhea - normal in terms of volume of menstruation lasting more than a week;
- menorrhagia – a significant increase in the volume of menstrual flow, the duration of menstruation is more than 12 days;
- oligomenorrhea – short menstruation (1-2 days);
- opsomenorea – rare periods, the interval between which can reach 3 months;
- proyomenorrhea - a menstrual cycle of less than 21 days.
2. Amenorrhea – absence of menstruation for more than 3 months.

3. Metrorrhagia (uterine bleeding):
- occurring in the middle of the cycle (anovulatory);
- dysfunctional (independent of the ovulation process).
4. Painful menstruation (algomenorrhea).
Diagnosis
In order to regulate the menstrual cycle and restore it, you first need to understand what caused the disturbances. To do this, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination, based on the results of which a specialist will be able to select the necessary treatment.
Diagnostics includes several stages:
- Taking an anamnesis - you need to tell the doctor about all diseases, the number of births and abortions, medications taken, external factors that could affect the consistency of menstruation.
- Gynecological examination and smear test.
- Blood tests, including determination of hormones.
- Additional tests prescribed by your doctor.
What can cause menstrual irregularities?
Many women do not consider an irregular menstrual cycle to be a big problem. However, such disorders can lead to infertility. Intermenstrual bleeding, for example, can cause apathy, fatigue, and decreased immunity.
How to deal with menstrual irregularities
After diagnosis, the doctor decides on the need for one or another method of therapy, this can be either conservative drug treatment or eliminating the causes of cycle disruption through surgical intervention. Often these two methods are combined during the treatment process.

To normalize the menstrual cycle, it is necessary to eliminate exactly the cause that led to the cycle failure, so anti-inflammatory drugs, hormonal contraceptives, and hemostatic drugs can be prescribed.
Restoring the menstrual cycle after childbirth
Separately, I would like to talk about restoring the menstrual cycle in women during the postpartum period. It is worth considering that menstruation has resumed only after the onset of the first menstruation. But even here you should not hope that the cycle will immediately become regular.
The changes that have occurred in the female body in connection with pregnancy and childbirth, including hormonal ones, can affect the stability, character, and pain of menstruation. Irregular periods are acceptable during the first 2-3 months from the moment they begin to return.
Women whose periods do not come 2 months after giving birth should be concerned, provided that the child is bottle-fed. If your baby is on a mixed diet, then menstruation may be absent for up to six months. Young mothers who breastfeed their baby may not wait for menstruation during the entire first year.
It takes time to restore the menstrual cycle. Often, disruptions in the menstrual cycle occur precisely because of the influence of external factors: try to avoid conflicts, stress, emotional experiences, eat right and get proper rest in the postpartum period.
If your periods after childbirth become more abundant or scanty, long-lasting or short-term, or more painful, you should immediately consult a gynecologist.
Those women who gave birth by caesarean section should be especially careful about the process of restoring menstruation. To avoid complications or identify them at the very beginning, it is necessary to constantly visit a gynecologist.
In conclusion, I would like to emphasize that identifying pathologies that cause menstrual irregularities in the early stages significantly increases the chance of getting rid of them. You should not self-medicate - this can only worsen the situation. Prescription of medications should be carried out only by a doctor, taking into account the diagnosis and medical history of the patient.
Replies
A normal menstrual cycle should last from 21 to 34 days. It is divided into 2 phases: follicular and luteal, during which egg maturation, ovulation and menstruation occur under the influence of sex hormones.
Shortening of the menstrual cycle or proyomenorrhea can occur due to various reasons. Before you begin to correct this condition, you need to understand why this happened.
A short menstrual cycle can manifest itself in different ways. Most often, this looks either like the arrival of menstruation every 15–17 days, or as a strong reduction in the amount of discharge, both in volume and in time.
Physiological reasons
The most common physiological reasons that cause the period between menstruation to become shorter are overwork and stress. Severe emotional shocks can change hormonal levels, causing an increase in the concentration of the hormone prolactin. In this case, dealing with a short menstrual cycle is quite simple. The body needs proper rest, minimizing any stressful situations and increasing resistance.
If the menstrual cycle has become short, then vitamin deficiency may be another reason. A lack of vitamins A, E, B and K can cause metabolic disorders and affect blood characteristics. This also includes a condition of the body that appears with excessively rapid weight loss. Usually, when going on any diet, a woman sharply reduces the amount of nutrients consumed, which can lead to the period between menstruation becoming shorter. Also, excessive thinness often leads to hormonal imbalances.
Physiological causes of cycle changes that are very easy to detect include recent surgery on the reproductive system, childbirth, abortion, and menopause. In these cases, practically no adjustment is required and you just need to wait out this period.
Taking certain medications and flying from one climate zone to another may cause the menstrual cycle to become shorter. But in these situations, the next menstruation should already begin on time.
Sometimes women mistake a spontaneous miscarriage that occurs in the first week of pregnancy for an early onset of menstruation, because the two conditions are very similar. But even in this case, the next menstruation will begin on time; this cannot be said that the cycle has become short.
Pathological causes
Most diseases of the reproductive system affect the duration and nature of menstruation. Therefore, with them, the cycle may well become shorter. But at the same time, pathologies of other body systems can cause changes in menstruation.
- Uterine fibroids and other tumors.
- Inflammatory processes in the organs of the reproductive system.
- Ovarian cyst.
- Diseases associated with blood clotting disorders.
- Endocrine pathologies.
- Kidney diseases.
- Metabolic disease.
All these pathologies, which may be the reason that the menstrual cycle has become shorter, require timely and adequate treatment. Therefore, if you notice changes in the nature and duration of your periods, you should contact your gynecologist.
Accompanying symptoms
If the menstrual cycle has become shorter, then you should pay attention to other changes in the body. After all, a short cycle almost never appears alone; other failures are almost always present. You should also pay attention to the nature of the changes in the cycle: observe which of the phases has become shorter, because this will help the doctor understand why this symptom appeared.
Depending on the reasons for the shortening of the cycle, there are the following varieties:
- biphasic with a short follicular phase, in which ovulation occurs prematurely;
- biphasic with a short luteal phase, in which the corpus luteum disappears prematurely;
- single-phase anovulatory, in which ovulation does not occur.
The danger of the last two varieties is that pregnancy is impossible. With early resorption of the corpus luteum, the reproductive system simply does not have time to prepare to receive the egg, and if this does happen, then there is a high probability of miscarriage. With the single-phase variety, ovulation does not occur, so conception is impossible.
Hormonal imbalances
If the menstrual cycle has become noticeably shorter, then the first reason that comes to mind is disturbances in the balance of sex hormones. Such failures can occur due to physiological factors, for example, during certain periods of life, such as menopausal changes in the body.
It is before the onset of menopause that a natural decline in estrogen synthesis occurs and a decrease in the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle.
A similar condition can occur in a woman after childbirth, since the body needs to rest for some time after bearing a child before it becomes possible to conceive the next one.
During these periods, a short cycle is not accompanied by other symptoms, but both you and the gynecologist understand why the shortening occurred.
Tumors in the reproductive system
The menstrual cycle becomes shorter if a woman has tumor processes in the uterus or ovaries. Other organs of the reproductive system are practically not susceptible to the appearance of neoplasms. Depending on the location and nature of the tumor, other symptoms will appear.
For example, with fibroids or polyps, the duration of menstruation increases, and the periods between discharges decrease.
With an ovarian cyst, one of the phases is shortened, but often during the next menstrual cycle this symptom is no longer observed.
Inflammatory processes
When inflammatory processes appear in the organs of the reproductive system, the cycle almost always changes. If it has become shorter, then you need to pay attention to the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen, itching and burning, discharge that differs from the norm and an increase in body temperature.
Various inflammatory diseases are often accompanied by the appearance of secondary infertility, as adhesions may appear. Also, tumor processes interfere with conception and bearing a child. Therefore, if the cycle has become shorter, then you should find why this happened and begin treatment.
Treatment
If the menstrual cycle has become shorter, you should consult a gynecologist to find the cause and begin adequate treatment. In addition to the reasons for the appearance of a short cycle, it is also important which phase has changed. Most often, doctors prescribe medication, but in some situations surgery may be prescribed.
Drug therapy
Usually, with a short cycle, not one medicine is prescribed, but a complex of drugs. They are designed to normalize hormonal levels, reduce blood loss, if necessary, and improve the functioning of the patient’s immune system.
If the cause is inflammatory processes, then additional antibiotics and antiseptics are prescribed in the form of vaginal suppositories.
Surgical treatment
This treatment is prescribed if the cycle has become shorter due to the fact that tumor processes have begun in the reproductive system. There are several options for surgical treatment.
- Laparoscopy.
- Laparotomy.
- Hysteroscopy.
- Hysterectomy.
The choice of treatment method is based on examination data. Important information is how much the tumor has grown, which organs are affected, and whether the patient wants to have children in the future.
When cycle shortening is normal
Often, women after 35 years begin to notice that their cycle becomes shorter. Why does such a shortening occur, because if we take the average values, then at 25 the duration is 32 days, and at 35 it already lasts 28. This is due to the fact that at a more mature age the corpus luteum begins to produce progesterone in smaller quantities. Therefore, the luteal phase shortens.
Then, a decrease in the number of follicles and a decrease in their quality leads to the fact that estrogen production gradually decreases. All this leads to the fact that the ovulatory phase becomes impossible.
Gradually, all these processes in the female body lead to the onset of menopause. But before the final cessation of menstruation, a woman may notice their irregularity or shortening. We should also not forget that before the onset of menopause, a woman’s body experiences hormonal disruptions that affect the duration of the cycle.
Do not ignore the fact that the menstrual cycle has become shorter. If this happens once, then you should reduce emotional and physical stress, and also pay attention to your diet. If the short menstrual cycle continues, then you should visit a gynecologist to find the cause of such changes. Timely treatment will help to avoid many complications and maintain health at the proper level.
2014-06-02 , 6763
A woman’s life is subject to cyclicality - roughly speaking, beautiful ladies live from menstruation to menstruation. It often happens that menstruation is expected at an inopportune moment, for example, on the day of a special event, during a trip to nature or on an excursion. Unfortunately, the menstrual days for most women do not look like commercials, where cheerful beauties, using ultra-thin padding, wear white trousers and dance merrily in miniskirts at discos. What should ordinary girls do, whose condition is far from ideal? Will you really have to change your plans?
It turns out there are ways that can help in this situation. However, we strongly recommend not to use them without the advice of a doctor, and therefore we deliberately do not publish the names of medications. One visit to the gynecologist will solve all problems and protect against negative consequences!
Hormonal drugs
The easiest way to delay the onset of menstruation is for women who regularly take oral contraceptives to prevent pregnancy. They just need to start taking the next pack immediately after the current one ends, without taking a break for bleeding. Monophasic tablets provide an almost 100% guarantee, while three-phase tablets can fail, and in their case you need to drink the contents of the third phase.
Girls who are not protected by combined oral contraceptives, but really want to change their cycle, are recommended to start taking birth control pills on any day of the cycle, but no later than three days before their expected period. You need to take the pills until all the planned events have taken place - bleeding, as a rule, begins 2-3 days after stopping the drug. However, you should not count on a contraceptive effect - in this mode, the effectiveness of the pills is extremely reduced.
You can also take progestin medications to delay menstrual bleeding. It is advisable to start taking them 2 weeks, but no later than 5 days before the expected threat. It is necessary to stop taking it on the day of the expected end of menstruation. If everything works, your period will start 1-3 days after the last pill.
Natural and folk methods
If you need to delay the onset of menstruation by 1-2 days, this can be done by taking good care of your health. Firstly, you should not increase your physical activity, you should not lift weights, exhaust yourself in the gym or visit a bathhouse or sauna. Secondly, you will have to give up sex - a rush of blood to the genitals can cause your period to start a day earlier. Thirdly, it is advisable to exclude spicy and salty foods, pineapples, papaya, and dates from the diet.

