Narrow blood vessels of the brain. Symptoms and causes of cerebral vasoconstriction, recommended treatment. Traditional medicine methods
Many people experience frequent, sometimes unbearable headaches accompanied by dizziness. Some note memory impairment when it is impossible to remember where an object is placed. The patient thinks that he is simply overtired at work or has developed a problem.
But this condition very often causes a narrowing of the blood vessels in the brain, which is called.
Hamer presented his thesis and was given an ultimatum to abandon his scientific discoveries or be denied a contract extension at the university hospital. Hamer was hunted and persecuted for 25 years, especially by German authorities and factions. But because the Faculty of Medicine at the University of Tübingen supports delaying tactics, patients from all over the world are deprived of the right to benefit from Dr. Reverend's revolutionary discoveries.
Atherosclerosis includes a group of diseases characterized by thickening and thinning of the arterial wall with a progressive decrease in lumen and the occurrence of clinical picture arterial are concerned about ischemic territory. Although the name suggests a condition that only affects older people, atherosclerosis actually begins much earlier. The presence of atheromatous plaque in large arteries was demonstrated after autopsy of young American soldiers killed during the Vietnam War.
Mechanism of the disease
Vasoconstriction occurs due to deposits of cholesterol plaques on the walls of the arteries that supply blood to the brain. The lumen between the walls of the vessels decreases and, as a result, the throughput of the vessels decreases.
Much less blood begins to flow into the brain, the supply of oxygen and other things necessary for brain function becomes much worse nutrients. This condition leads to memory impairment and headaches.
In conclusion, the process of atherosclerosis begins in childhood. What is the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis? The atheroma plate consists of lipids, inflammatory cells, conjunctival test, smooth muscle cells, calcium deposits and blood clots. Arteries are blood vessels consisting of three layers. As a rule, atheromatic plaques form at the bifurcation of arteries, where turbulence is observed in the laminar blood flow. This type of blood flow suppresses nitric oxide, which has anti-inflammatory and vasodilatory effects.
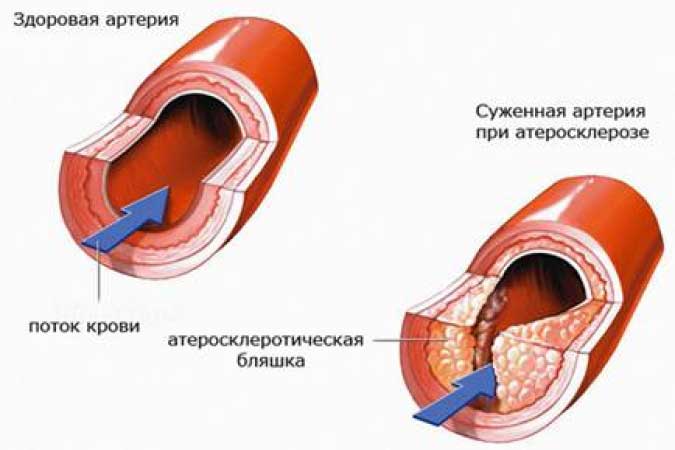
Plaque formation in a vessel
Formation atherosclerotic plaques most often occurs when pathological conditions cerebral vessels and cervical spine. The walls of the arteries become less elastic, because the level of cholesterol in the blood is increased, cracks appear on them, and it is in these cracks that small spots-plaques form.
Endothelial damage causes the accumulation of inflammatory cells. With hypercholesterolemia, lipoproteins accumulate in the intima arteries. Although atherosclerotic lesions are complicated, smooth muscle cells accumulate to form subendothelial fibrous scale. When calcium is deposited, calcification of the inside of the board occurs over time. Atheromatic plaques become stable and unstable. The atheroma plate has a fibrous plug that can collapse over time, causing hemorrhage.
Secondary rupture of platelet plaques, platelets come to defeat. There are five ways that the process can be carried out: obstruction to close embolization of the vessel thrombus embolization of the content of atheroma plaque is broken, modification of atheroma plaques secondary inclusion of thrombus in the plate and fill the plate with blood becomes noticeable, and can cause occlusion of the destination artery.
Plaques attract platelets like a magnet, and they promote blood clotting. At the same time, they begin to grow rapidly, form a blood clot, and the gap between the walls becomes smaller and smaller. Sometimes a blood vessel can be completely blocked by a blood clot, and this is very serious.
Therefore, if a patient has been diagnosed with cerebral vasoconstriction, blood cholesterol levels should be measured more often to prevent progression of the disease.
Symptoms and signs
What are the risk factors for developing atherosclerosis? Among the predisposing factors of atherosclerosis. Male hereditary catheter of premature atherosclerosis. . What are the consequences of atherosclerosis? A pathology that affects all arteries, atherosclerosis, is asymptomatic for a long time. The first clinical manifestations occur when the memorial armor has increased enough to alter normal blood flow. People with risk factors may have blocked arteries in a proportion of 50% without any symptoms.
Causes of the disease
The main reason for vasoconstriction, as mentioned above, is an increase in cholesterol levels in the blood, but it is not alone; the appearance of atherosclerosis is also influenced by the following factors:
- big mental stress, stress, overwork. Many people strive to have a successful career, but nervous fatigue and constant mental work lead to vasoconstriction. After all, all this leads to stress and nervous exhaustion;
- lack of fresh air. Many people spend most of the day in stuffy offices and cars. To modern man there is simply no time to set aside time for a regular leisurely walk on fresh air and this is very sad, because the brain experiences oxygen starvation, a person’s blood pressure rises, but the result is still the same - atherosclerosis;
- poor nutrition . Excessive use too spicy, greasy and high-calorie food and a chronic lack of fish products, fresh fruits and vegetables in the diet leads to the rapid accumulation of cholesterol and its excess is rapidly deposited on internal walls vessels.
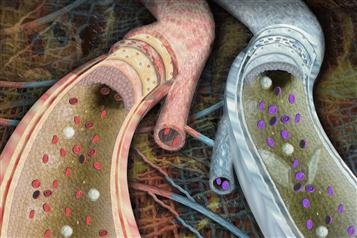
Clinical manifestations occur when the arterial lumen narrows by more than 70%. Among the consequences of atherosclerosis are acute heart attack myocardium, ischemic stroke, obliterating arteriopathy of inferior parotitis. What are the manifestations of atherosclerosis? The clinical manifestations of atherosclerosis depend both on the affected area and on the degree of obstruction of the affected vessel. Atherosclerosis is one of the main causes of the disease coronary artery, stroke and obliterating arteriopathy of the lower extremities.
Cerebral atherosclerosis is the cause of most ischemic stroke. Clinical manifestations depend on the part of the brain affected. Symptoms include aphasia, hemiparesis, somnolence, amnesia, decreased mental capacity, dementia, irritability.
Development of constriction
The course of the disease, its symptoms and stages
Constriction of cerebral vessels can be both acute and chronic form. Acute form is the most severe and leads to cerebral infarction or hemorrhage. Such crisis conditions sometimes lead to the sudden death of the patient.
During chronic course The symptoms of the disease develop slowly, and this form of vasoconstriction has three stages:
Coronary atherosclerosis is the reason coronary disease hearts. Coronary heart disease can manifest as persistent angina or acute coronary syndromes. Pain stable angina usually occurs with effort and manifests itself as chest or atrial pain with claws or pressure, with irradiation on the neck, lower jaw, shoulders, left arm.
Atherosclerosis of the superior or inferior parotitis manifests itself in intermittent claudication and paresthesia. Nephroangiosclerosis causes secondary arterial hypertension. Radiological study of the lithosphere Coronary angiography -. Coronary atherosclerosis is the cause of coronary artery disease.
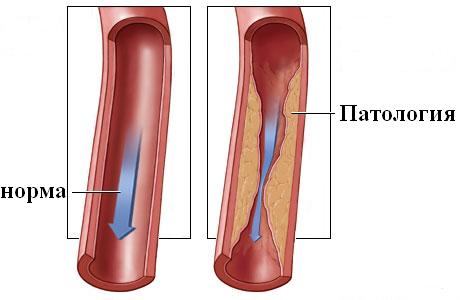
1 - stage. It is the mildest, usually there are no symptoms. Happens slight decrease disability, which quickly passes and the patient believes that he is simply tired or did not get enough sleep. It is clear that no one even thinks about going to the doctor;
2nd stage. There may already be violations here normal functions individual organs. For example, if the functioning of the musculoskeletal system is disrupted, a person’s gait changes; he himself does not notice how he shuffles his feet when walking, or simply minces while walking. From time to time, the legs become numb and eventually the patient becomes irritated by this. A person’s mood changes constantly and because of this, quarrels with family and friends occur.
An objective physical examination for the presence of atherosclerosis includes xanthelasmas, xanthomas, bruises and impulses reduced or eliminated in large arteries. To assess the location of atherosclerosis, paraclinical studies are necessary. Research methods. Doppler ultrasound - no invasive method, allowing you to evaluate the speed and uniformity of arterial blood flow, as well as the contour and linearity of the vessel. Also, using Doppler ultrasound, we can see both the affected area and the degree of obstruction to the vessel.
Doppler sonography is the first step in diagnosing atherosclerosis. Radiological examination - radiological presence on arterial level calcinators is an indicator of the presence of atherosclerosis. On an x-ray of the umbilical gland, you can see calcification of the aortic button. Ophthalmological examination showed the presence of atherosclerosis in the reticular arteries. Coronary angiography is an invasive method that allows you to accurately view the affected coronary vessel, as well as assess the degree of stenosis. Coronary angiography also allows for a therapeutic gesture by placing stents in the affected vessel.
Present headache, sometimes very strong, a person feels tinnitus, there is constant fatigue and decreased performance. Such signs of illness may go away in a day or a little more, but this is already quite serious reason go to the clinic;
3rd stage. At this stage, the symptoms of vasoconstriction become even more pronounced, and brain function begins to be seriously impaired. A person cannot coordinate his movements, so he moves very slowly. The patient can walk by touch to find the way. With further progression of the disease, control centers musculoskeletal system cease to perform their functions completely, and the patient cannot not only walk, but also stand on his feet. Speech is often impaired and vision is lost.
Traditional methods of treating cerebral vasoconstriction
Membrane angiography is an invasive method that emphasizes the presence of atheromatous plaques and the degree of vessel stenosis. Allows dilatation with or without stents. Scintigraphy is a method using radionuclides. Provides data about coronary blood flow and its reduction. Thus, these methods visualize myocardial perfusion defects. In the face of all methods for detecting atherosclerosis, the diagnosis often occurs when the vessel is more than 50% stenotic. The clinical manifestations that bring the patient to the doctor are secondary to decreased percussion in the organ due to atherosclerosis present at this level.
The danger of vasoconstriction lies in self-medication and late treatment. medical assistance. The patient does not pay attention to the signs of a progressive disease and treatment begins very late, which can lead to a stroke or pre-infarction condition.
Drug treatment
Atherosclerosis - multifactorial degenerative disease. Many of the risk factors that lead to worsening atherosclerosis change. Thus, we can alleviate its worsening by eliminating and controlling one or more risk factors. Risk factors such as smoking, sedentary behavior, diets with high content fat, obesity, can be avoided. Other risk factors, such as high blood pressure or diabetes, can be controlled through diet and medical treatment.
Prevention of atherosclerosis should be taken more seriously by both patient and physician. Optimizing the risk factor profile before the onset of atherosclerosis should be one of the goals of the treating physician. Prevention of atherosclerosis should begin in childhood through a lifestyle diet, including regular physical activity and a balanced diet. These measures should be applied in particular to children with a family history of cardiovascular events. Hygienic and dietary measures are aimed at regression of atheromatous plaque.
Narrowing of cerebral vessels is treated by neurologists, cardiologists and therapists. Consultation with other specialists may be required. Treatment consists of long-term use prescribed medications, sometimes the patient has to take them for the rest of his life.
Treatment is selected individually for each patient depending on the age, condition of the patient, test results and may be as follows:
Neck vasoconstriction
Stop Diet Diet - balanced diet - important step in maintaining healthy body. It is recommended to reduce consumption and simple carbohydrates, and increase your consumption of fruits and vegetables. Consuming at least 5 servings of fruits and vegetables per day appears to have beneficial influence to reduce the risk of developing atherosclerosis. Flavonoids found in black and red grapes, red wine, and black tea appear to have a protective role in blood vessels. Moreover, given the increased cardiovascular risk obese patients, a low-calorie diet is indicated for additional kilograms. The most dangerous type of male obesity is the accumulation of fat at the level abdominal cavity. This type of obesity is associated with decreased glucose tolerance. Reduced lipid levels - low diet in animal fats should be indicated in all patients with known hyperlipidemia vascular disease or multiple cardiovascular risk factors. Low products lipids include vegetables, lean meats, eggs, cow's cheese, yogurt, fish, fruits and grains. Blood pressure should take into account the patient's age and associated comorbidities. Control of diabetes - control of blood glucose levels, diet, oral medications or insulin slows down the process of atherosclerosis and the occurrence of microvascular complications. Therefore, for statin therapy it is necessary to use transaminase every 1 month every three months. Adverse reactions include elevated transaminases, myositis phenomena and decreased libido. It is administered subcutaneously once every two weeks. Because atheroma plaque is complicated by cracking or rupture, with subsequent platelet activation and thrombosis, the role of these drugs in the prevention of cardiovascular events is well established. Aspirin, the most commonly used antiplatelet aggregator, is recommended for both primary prevention in patients with high cardiovascular and secondary risk.
- The diet should be low in animal fat.
- Side effects of these medications include myositis and liver enzymes.
- Fibrates - recommended for patients with hypertriglyceridemia.
- It has effects similar to statins, but without the side effects.
- Platelet antiplatelet agents - prevent platelet aggregation.
- Folic acid is used to prevent hyperhomocysteinemia.
- prescription of statin drugs. These are Lovostatin, Mefacor or Mevacos. These drugs have a beneficial effect on the brain;
- administration of fibrates. These may be medications such as Clofibrate, Atromidine, Zocor, Simvastatin;
- taking medications that dilate narrowed blood vessels. This is Eufillin, Papaverine. Cerebrolysin may also be prescribed;
- prescription of antioxidants. The doctor prescribes vitamins C, E and A, microelements and general vitamin complexes.
Iodine therapy is popular; the antidepressant Amitriptyline can be prescribed to lift a patient out of depression. If vasoconstriction occurs due to diabetes or hypertension, the patient is prescribed medications that will help eliminate the symptoms of these diseases.
Among the plants used are artichoke, blackcurrant, quail, grass, macaw, birch, hawthorn, dandelion, small squash, patlagagina, clover and hay. Typically drink 2 daily infusions, decoctions or macerations, depending on the plant used. Although this natural treatment, it should not be accompanied by the ear for a long time. Plants used for a long time may cause some harmful effects. Particular care should be taken for plants such as grass, marshes, and field clover.
Plants can be used separately or mixed, depending on the recommendations of the herbalist. A patient with risk factors for atherosclerosis should be evaluated and treated for early stage. Education on the right way feeding should begin already at adolescence, especially in the case of hereditary history cardiovascular pathology. We also need to understand the need for daily exercise. By introducing the right preventive measures and by applying appropriate therapy, we can prevent secondary complications of atherosclerosis.
Radical treatment methods
If drug treatment does not provide positive effect or the disease is too advanced - treatment is carried out using surgical methods:
- endarterectomy. During such an operation, the problematic vessel is removed from the dissected cholesterol plaque. The operation is performed under local anesthesia, and the vessel wall is restored using sutures. Most often, the patient leaves the hospital a couple of days after the operation;
- angioplasty. In this case, a catheter is inserted into the artery, due to which the problem area expands, the plaque is pushed through, and blood supply to the brain is restored;
- carotid bypass. During this operation, a frame made of small thin wire is fixed between the vessel wall and the plaque.
A person’s condition and performance are related to the condition of the vessels that supply blood to the brain. The narrowing of the blood vessels in the brain leads to an insufficient supply of oxygen and nutrients to the parts of the brain, and this, in turn, leads to a lot of health problems.
Causes of cerebral vasoconstriction
Experts are sounding the alarm: the number of patients who experience narrowing of cerebral vessels is increasing every year. This is largely due to the fact that people have to pay for the benefits of civilization with their own health.
There are several causes of the disease:
- – defeat large vessels involved in the blood supply to the main parts of the brain, occurs due to the accumulation of cholesterol plaques on the walls blood vessels. Predisposing factors are an excess of meat and fatty foods, overconsumption alcohol and smoking.
- Arterial hypertension usually associated with age-related changes. Due to clogging and deformation of blood vessels, blood microcirculation decreases.
- Living in an environmentally unfavorable area and working in hazardous enterprises.
- Sedentary image life, insufficient exposure to fresh air.
- Significant mental and psychological stress.
- Metabolic disorders, including those associated with diabetes.
Symptoms of cerebral vasoconstriction
Negative changes in blood vessels usually occur over several years before the disease becomes apparent. There are three stages of disease development:
A sharp narrowing of the blood vessels in the brain causes a stroke - serious condition leading to disability and even death.
Treatment of cerebral vasoconstriction
The chronic form of the disease requires systemic medication. When the blood vessels in the brain are narrowed, the following medications are prescribed:
- statins (Mefacor, Mevacos);
- fibrates (Clofibrate, Atromidine, Zocor);
- drugs that dilate the lumen of blood vessels (Eufillin and Papaverine).
In addition, for the purpose of therapy for narrowing of cerebral vessels, antioxidant drugs are prescribed:
- vitamin and mineral complexes;
- lecithin;
- iodine-containing products.
An additional element of therapy is therapeutic exercises, aimed at increasing vascular tone, and, as a result, blood flow in them. But the decision on expediency exercise therapy classes only taken by a specialist, since in the presence of blood clots or aneurysm physical exercise prohibited.
In severe cases, bypass surgery is recommended, when a stent is placed in the vessel, serving as a frame for vascular walls. Another effective method surgical intervention– endarterectomy. It involves removing atherosclerotic plaques.
A supportive measure in treatment is taking medications based on folk recipes. To prevent and reduce the manifestations of the disease, the following are used: