High lipoprotein cholesterol. HDL - high density lipoprotein ("good cholesterol")
We'll find out what the risks are associated with low HDL cholesterol. We explore the symptoms and causes of low cholesterol values well, and we see how to return values to the level of a physiological diet.
What is HDL cholesterol
A low HDL level is said to be when concentration V peripheral blood turns out below 40 mg/dl for men and 50 mg/dl for women.
It would seem low level cholesterol may be interpreted as a sign good health However, in the case of HDL, the opposite is true.
Why low levels of good cholesterol are harmful
Of course, you know that high cholesterol levels are the enemy of health cardiovascular system. But this axiom does not apply to all types of cholesterol. In fact, in the case of HDL, the higher its concentration, the lower the risk of developing atherosclerotic changes and, as a result, heart disease.
Cholesterol is an essential component of the proper functioning of the body (component cell membranes, predecessor important hormones, for example, steroids). To move freely with the bloodstream, cholesterol is packaged in special proteins that increase its solubility.
Basic information about lipoproteins:Low density lipoproteins. They are also known as “bad” cholesterol and are produced in the liver. Under normal physiological conditions, this process is balanced. In the sense that each cell is able to maintain the level of cholesterol necessary for its functioning, and return the excess to the liver. If this natural balance will be upset, there will be an increase in the level of LDL in the blood, which can be deposited on the walls of the arteries and lead to the formation atherosclerotic plaques. L hypoproteins high density . Also known as “good” cholesterol. They are involved in the reverse transport of excess cholesterol. That is, they obtain excess lipoproteins circulating there from the cells and transfer them to the liver. In addition, HDLs perform other important functions: protect the body from atherosclerotic deposits, from the occurrence cordially- vascular diseases such as heart attack and stroke. |
High HDL values not only prevent plaque deposition by preventing LDL oxidation, but also promote the removal of existing plaques by preventing the adhesion of monocytes to the vessel wall and, as a result, prevent possible obstruction of blood vessels.
Optimal levels HDL concentrations are:
- Men: 60 mg/dL or more
- Women: 60 mg/dL or more
What are the symptoms of decreased HDL?
A decrease in HDL values occurs asymptomatic and few people notice this, only with routine periodic medical monitoring.
Symptoms occur when health has already been damaged and diseases are developing.
Reasons for lower cholesterol values
But what are the reasons that can lead to decrease in HDL values?
There are many of them, and they are not always associated with diseases:
- Pregnancy and menopause are the most common causes of physiological decreases in HDL cholesterol values. The reason should be sought in hormonal changes. Latest Research showed noticeable decrease cholesterol levels are observed for two years after pregnancy.
- During menopause lower cholesterol is associated with the absence of estrogen, which regulates cholesterol synthesis.
- Birth control pills can reduce HDL cholesterol levels because they contain progestin, which leads to increased levels LDL cholesterol, thus increasing the value total cholesterol.
- Poor nutrition : rich fatty foods and low in vegetables, fiber and monounsaturated fats, which leads to an increase in the proportion of LDL cholesterol and a decrease in the proportion of HDL cholesterol.
- Misbehavior: sedentary lifestyle life leads to an increase in the level of “bad” cholesterol and a decrease in “good” cholesterol.
- Smoking: The mechanism that links smoking to HDL cholesterol is not entirely clear, but quitting smoking has been shown to markedly increase good cholesterol levels.
- Obesity: with obesity, an excess of triglycerides occurs, which leads to an increase in the concentration of very low-density lipoproteins and a number of changes in the cholesterol chain: high-density lipoproteins become smaller and lose their atherogenic functions.
Diseases that lead to a decrease in good cholesterol levels:
- celiac disease or food allergy lower cholesterol levels because the body does not absorb foods, and therefore does not receive HDL in the diet.
- hypothyroidism and liver disease such as hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver; excess hormones thyroid gland leads to an increase in metabolism.
- Medicines, such as beta blockers, diuretics, interferon, or statins, used to lower cholesterol.
Risks of Low HDL Levels
Considering protective function HDL in relation to the arteries, low HDL cholesterol, exposes the body high risk cardiovascular diseases.
When HDL cholesterol levels fall far below optimal levels, the total cholesterol ratio is above 5, then damage to the arteries can lead to:
- Atherosclerosis: body fat in the arteries, which entail a decrease in blood flow.
- Stroke: obstruction or rupture of an artery in the brain, which leads to the death of brain tissue.
- Heart attack: reduction or cessation of blood flow, which leads to the death of the heart muscle.
- Coronary heart disease: complete or partial stoppage of blood flow to the heart.
What to do to increase HDL levels
Quit smoking. Elimination of smoking entails an increase in HDL levels by approximately 10%. Especially if you add physical activity (at least 5 days a week for 30 minutes): swimming, cycling, running, brisk walking, gardening - anything that increases your heart rate.
Lose extra pounds . Losing weight by 3 kg increases HDL level per 1 mg/dl of blood.
Follow the rules rational nutrition . The basis of such a diet should be the consumption of healthy fats. Specifically, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated, in the latter case omega 3, found in hard-shelled fruits and fatty fish.
Drinking one or two glasses of red wine per day. Not everyone agrees with this recommendation, but wine certainly helps maintain high HDL levels. It is possible that this is the reason that explains the French paradox. The French, being heavy consumers of saturated fats ( butter, fatty meats) have a low incidence of cardiovascular disease.
Taking drugs that increase HDL the most common is niacin. There are also supplements based on this ingredient. It should not be used without consulting a doctor because there may be side effects on liver function.
Diet to increase cholesterol values
To reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, you need to eat foods that help increase HDL cholesterol and reduce LDL cholesterol.
In particular:
- Fish omega-3 (fats) rich foods such as salmon or swordfish.
- Cereals, especially whole grains such as bread and pasta.
- Low-fat boiled sausage or low-fat ham.
- Low-fat cheese, such as mozzarella, ricotta, goat cheese.
- Milk and yogurt.
- Lean meat, such as turkey, chicken and rabbit.
- Dried fruits such as hazelnuts, walnuts and almonds because they contain omega-3.
- Antioxidant Rich Foods, such as vitamin C, which is found in kiwis, broccoli, oranges and lemons.
- Some legumes, such as soybeans, which contain phytoestrogens, substances that can mimic the effects of estrogen and reduce cholesterol levels.
A diet that can help you keep your bad cholesterol levels low - vegetarian diet , since it excludes the consumption of animal fats and involves the consumption of large amounts of fruits and vegetables rich in vegetable fats, containing sterols that have a structure similar to cholesterol and stimulate the reduction of total cholesterol.
Lipids, including cholesterol (CH), are the most important and irreplaceable building material for the cells of our body. They ensure the integrity of membranes and also participate in the synthesis various substances, such as steroid hormones, etc. At the same time, fats cannot be independently transported in the blood due to their insolubility in plasma. Therefore, there is a class of special proteins - lipoproteins (another name is lipoproteins) that allow their transportation. High-density lipoproteins (HDL or HDL) move lipids (cholesterol, etc.) from peripheral tissues and blood vessels to the liver, where it can be metabolized in the required direction, which helps cleanse the artery walls of cholesterol and helps prevent the development of atherosclerosis. Low-density lipoproteins (LDL), on the contrary, move lipids from the liver into the blood - to the tissues and cells of the body. This leads to increased cholesterol levels and increases the risk of developing atherosclerotic processes and related diseases.
Deposition of cholesterol and some fractions of lipoproteins in the lumen of the vessel
Good or bad cholesterol
There is an opinion among the population and some doctors that cholesterol is a lipid harmful to the body, leading exclusively to negative processes. However, discoveries in biochemistry and other biological sciences have shown that cholesterol (cholesterol) is essential component cell membranes, participates in the synthesis steroid hormones, as well as in various metabolic processes, which, undoubtedly, does not allow it to be characterized only as a negative substance.
Cholesterol is a key component in maintaining cell activity human body.
When someone talks about “bad” cholesterol, it is necessary to understand this as low-density lipoproteins, which contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and various vascular diseases. The level of cholesterol plays only an indirect role and does not directly indicate disorders in fat metabolism. Lipoproteins consist of a complex protein complex connected to various lipids, which makes it possible to achieve the solubility of the latter in the blood plasma and transport it to the tissues of our body. However, such a process sometimes does not meet the needs of the cells, and cholesterol and other fats begin to be deposited in the walls of blood vessels, leading to the appearance of atherosclerotic plaques. That's why increased level LDL with simultaneous low levels of HDL is associated with the appearance of atherosclerosis in humans.
“Good” cholesterol is represented by high-density lipoproteins. These protein-fat molecules transport cholesterol and other lipids from vascular wall and body tissues to the liver, where they can be metabolized according to the body's needs. HDL cholesterol is not deposited in the arteries and even helps to clear them of lipids, which helps prevent the appearance of atherosclerotic plaques. Reduced HDL levels increase the risk of developing atherosclerosis and related diseases. This fact is widely used in cardiological practice when assessing the risk of such a condition in patients.
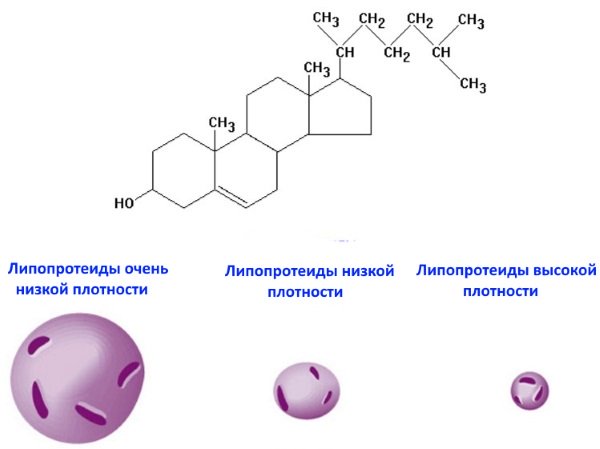
Lipoproteins of various densities
HDL norm
High density lipoprotein levels are measured using biochemical research blood. The table below shows the HDL norm in accordance with the gender and age of a person:
|
Person's age (year) |
HDL content in blood (mmol/l) | |
| Men | Women | |
| From birth to 15 | 0,8-1,7 | 0,77-1,7 |
| From 16 to 20 | 0,8-1,7 | 0,8-1,8 |
| From 21 to 30 | 0,8-1,8 | 0,8-1,9 |
| From 31 to 40 | 0,8-1,8 | 0,8-2,0 |
| From 40 and more | 0,8-1,9 | 0,8-2,2 |
From the table above, it can be noted that the level of high-density lipoproteins in women is higher than in men, particularly during the period after puberty. This feature is associated with the ability of female sex hormones (estrogens) to normalize fat metabolism in the body, lowering the amount of LDL and cholesterol, and increasing the level of HDL.
Normal ranges may vary slightly depending on the specific laboratory in which the test was performed.
Interpretation of HDL level results

Your doctor will help you interpret your lipid profile.
The amount of high-density lipoproteins in the blood can be either increased or decreased. It is important to note that only the attending physician should interpret the results of the study.
Low HDL
If your HDL level is below normal, what does that mean? This situation may mean disturbances in the body’s lipid metabolism and is associated with an increased risk of developing atherosclerosis and the diseases caused by it ( ischemic disease heart, Leriche syndrome, ischemic stroke etc.). A similar situation may arise as a result of the following reasons:
- Genetic disorders in the processes fat metabolism(familial forms of hyperlipidemia, etc.).
- Dietary disorders (predominance of fatty and carbohydrate foods), low physical activity.
- Diseases in endocrine system(diabetes mellitus).
- Chronic kidney and liver diseases, etc.
In any case, a decrease in HDL cholesterol is associated with the risk of atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels, which can be complicated by various diseases.
High HDL
Elevated or normal level High-density lipoprotein is associated with a low risk of atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease and other cardiovascular diseases. HDL allows you to remove lipid deposits from the walls of blood vessels, as well as prevent the formation of plaques in them.
However, there are a number of diseases in which HDL values in biochemical analysis blood levels increased significantly:
- Biliary cirrhosis of the liver.
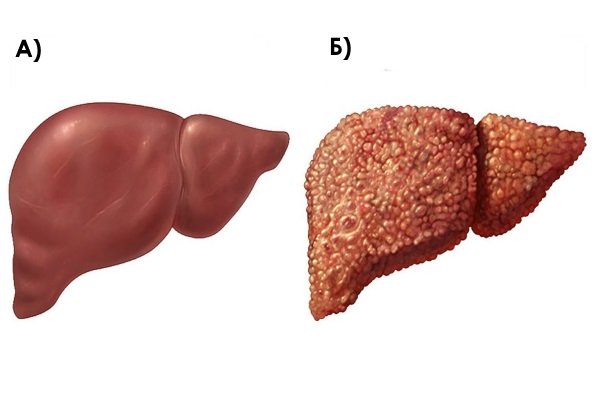
A) normal liver; B) cirrhosis
- Chronic hepatitis of viral or toxic (alcoholic) nature.
- Reception medicines (hormonal drugs based on estrogens, statins, etc.).
- Pregnancy period.
In each specific situation it is necessary to carefully analyze the data of a biochemical study and interpret them in accordance with the patient’s past and existing diseases.
Atherogenic coefficient
Changes in the content of low- and high-density lipoproteins do not accurately reflect the state of lipid metabolism in the body. In this regard, to facilitate the process of interpreting their values, an atherogenicity index was introduced: atherogenic index=(total cholesterol-HDL)/HDL
The atherogenic index is normally 2-3, and changes with various diseases. An increase in the index is observed when:
- Severe liver damage.
- Diabetes mellitus.

All diabetics need to monitor their cholesterol levels.
- Chronic renal failure.
- Eating disorders and decreased physical activity, etc.
In this case, the risk of developing an atherosclerotic process in the patient is very high and requires the adoption of certain preventive and therapeutic measures.
A decrease in the atherogenic index is considered positive news, as it reflects a low risk of atherosclerosis and related diseases. However, special significance this result does not have, due to the low information content in this particular case.
How to increase HDL?
Increasing the level of high-density lipoproteins helps prevent the development of diseases of the cardiovascular system, and is indicated for all people in old age or with a predisposition to similar conditions. As a rule, an increase in HDL levels is closely related to a decrease in LDL and cholesterol levels in the blood.
For normalization lipid profile There are a few simple recommendations:
- Must be included in your daily routine various types physical activity, in the form of aerobic exercise - light jogging, exercise bike, etc. Sports activities have a positive effect on fat and other types of metabolism in the body. At the same time, the frequency of classes should be at least three times a week, lasting at least half an hour.

Cycling has a beneficial effect on lipid metabolism in the body
- It is necessary to exclude fatty meats and fish from food, avoid cholesterol-rich egg yolks, and also remove sour cream, milk, cream and cottage cheese with high fat content.
- A person needs to give up smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- Increase consumption plant food(fresh and boiled vegetables, fruits and berries) and freshly squeezed fruit juices.
- Exclude from the diet bakery and confectionery products that increase blood glucose levels, etc.
In cases of serious changes, it is necessary to additionally use medicines, normalizing the fat composition of the blood (statins, fibrates, cholesterol absorption blockers, etc.).
Assign medications only the attending physician should, after medical examination person.
A decrease in HDL content is important factor risk of developing coronary heart disease and stroke. In this regard, it is necessary to pay great attention periodic assessment of this parameter and conducting preventive examinations with correction of nutrition and level of physical activity during the day. Correct prevention helps prevent the development serious illnesses and increases general level human life.
Sometimes during examination lipid spectrum it is discovered that the level of HDL is increased or decreased: what does that mean? In our review, we will analyze what differences exist between high- and low-density lipoproteins, what causes deviations in the analyzes of the former from the norm, and what methods of increasing it exist.
Good and bad cholesterol
Cholesterol is a fat-like substance in the human body that is notorious. There is a lot about the dangers of this organic compound. medical research. All of them link high levels of cholesterol in the blood and such a terrible disease as atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis today is one of the most common diseases in women after 50 years and men after 40 years. IN recent years the pathology occurs in young people and even in childhood.
Atherosclerosis is characterized by the formation of cholesterol deposits on the inner wall of blood vessels - atherosclerotic plaques, which significantly narrow the lumen of the arteries and cause disruption of blood supply. internal organs. First of all, systems that perform a large amount of work every minute and require a regular supply of oxygen and nutrients– cardiovascular and nervous.
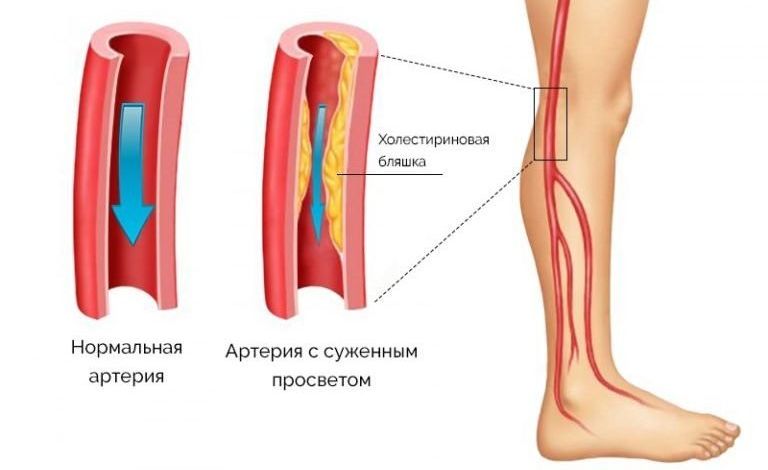
Common complications of atherosclerosis are:
- dyscirculatory encephalopathy;
- ACVA of ischemic type – cerebral stroke;
- coronary heart disease, angina pain;
- acute heart attack myocardium;
- circulatory disorders in the vessels of the kidneys.
It is known that elevated cholesterol levels play a major role in the formation of the disease. To understand how atherosclerosis develops, you need to learn more about the biochemistry of this organic compound in the body.
Cholesterol is a substance with a fat-like structure, chemical classification related to fatty alcohols. When you mention him harmful influence on the body, do not forget about important biological functions which this substance performs:
- strengthens cytoplasmic membrane every cell of the human body, makes it more elastic and durable;
- regulates the permeability of cell walls, prevents the penetration of certain substances into the cytoplasm toxic substances and lytic poisons;
- is part of the production of the adrenal glands - glucocorticosteroids, mineralocorticoids, sex hormones;
- participates in the synthesis of bile acids and vitamin D by liver cells.
Most of the cholesterol (about 80%) is produced in the body by hepatocytes, and only 20% comes from food.
Plant cells They do not contain saturated lipids, so all exogenous cholesterol enters the body as part of animal fats - meat, fish, poultry, milk and dairy products, eggs.
Endogenous (own) cholesterol is synthesized in liver cells. It is insoluble in water, therefore it is transported to target cells by special carrier proteins - apolipoproteins. The biochemical compound of cholesterol and apolipoprotein is called lipoprotein (lipoprotein, LP). Depending on the size and functions, all drugs are divided into:
- – the largest fraction of cholesterol, consisting mainly of triglycerides. Their diameter can reach 80 nm.
- - a protein-fat particle consisting of an apolipoprotein molecule and large quantity cholesterol. The average diameter is 18-26 nm.
- High-density lipoproteins (HDL, HDL) are the smallest fraction of cholesterol, the particle diameter of which does not exceed 10-11 nm. The volume of the protein part in the composition significantly exceeds the volume of fat.

Very low and low density lipoproteins (LDL - especially) belong to the atherogenic fractions of cholesterol. These bulky and large particles are difficult to move through peripheral vessels and can “lose” some of the fat molecules during transportation to target organs. Such lipids settle on the surface inner wall blood vessels, strengthen connective tissue, and then calcifications and form a mature atherosclerotic plaque. Due to their ability to provoke the development of atherosclerosis, LDL and VLDL are called “bad” cholesterol.
High-density lipoproteins, on the contrary, are able to clean blood vessels from fatty deposits that accumulate on their surface. Small and nimble, they capture lipid particles and transport them to hepatocytes for further processing into bile acids and excretion from the body through the gastrointestinal tract. For this ability HDL cholesterol.
So, not all cholesterol in the body is bad. The possibility of developing atherosclerosis in each individual patient is indicated not only by the TC (total cholesterol) indicator in a blood test, but also by the ratio between LDL and HDL. The higher the fraction of the former and the lower the fraction of the latter, the development is more likely dyslipidemia and the formation of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels. The inverse relationship is also true: increased rate HDL can be considered a low risk for developing atherosclerosis.
How to prepare for analysis
A blood test can be performed as part of a lipid profile - comprehensive examination fat metabolism in the body and independently. To ensure that the test result is as reliable as possible, patients should follow the following recommendations:
- High-density lipoproteins are examined strictly on an empty stomach, in the morning (from approximately 8.00 to 10.00).
- The last meal should be 10-12 hours before donating the biomaterial.
- 2-3 days before the examination, eliminate all fatty foods from your diet. fried foods.
- If you are taking any medications (including vitamins and biological supplements), be sure to tell your doctor about this. He may advise you not to take pills for 2-3 days before the test. Taking antibiotics especially affects the test results, hormonal drugs, vitamins, omega-3, NSAIDs, glucocorticoids, etc.
- Do not smoke at least 30 minutes before the test.
- Before entering the blood collection room, sit for 5-10 minutes in a calm environment and try not to be nervous.
To determine the level of high-density lipoproteins, blood is usually taken from a vein. The procedure itself takes one to three minutes, and the analysis result will be ready the next day (sometimes after a few hours). Along with the obtained data, the reference (normal) values accepted in a given laboratory are usually indicated on the analysis form. This is done for ease of deciphering the diagnostic test.
PAP norms
What should the high density lipoprotein level be? healthy person? The norm for women and men for this fraction of cholesterol may be different. Standard lipid profile values are presented in the table below.
| Age, years | HDL norm, mmol/l | Norm HDL, mg/dl | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimal level | Average permissible level | Prognostically unfavorable level | |||
| Men | 0-14 | 0,78-1,68 | 55-65 | 40-54 | <40 |
| 15-19 | 0,78-1,68 | 55-65 | 40-54 | <40 | |
| 20-29 | 0,78-1,81 | 60-70 | 45-59 | <45 | |
| 30-39 | 0,78-1,81 | 60-70 | 45-59 | <45 | |
| Over 40 | 0,78-1,81 | 60-70 | 45-59 | <45 | |
| Women | 0-14 | 0,78-1,68 | 55-65 | 50-54 | <50 |
| 15-19 | 0,78-1,81 | 55-70 | 50-54 | <50 | |
| 20-29 | 0,78-1,94 | 60-75 | 50-59 | <50 | |
| 30-39 | 0,78-2,07 | 60-80 | 50-59 | <50 | |
| Over 40 | 0,78-2,20 | 60-85 | 50-59 | <50 | |
According to the NICE research center, a decrease in high-density lipoprotein levels by 5 mg/dl increases the risk of developing an acute vascular accident (heart attack, stroke) by 25%.
To assess the risk of developing atherosclerosis, as well as its acute and chronic complications, it is important to take into account the ratio of high-density lipoproteins to total cholesterol.
If HDL is low in the context of high levels of atherogenic lipids, the patient probably already has manifestations of atherosclerosis. The more pronounced the symptoms of dyslipidemia, the more active the formation of cholesterol plaques in the body.
What does increased value mean?
Elevation is not diagnosed very often. The fact is that there is no maximum concentration of this fraction of cholesterol: the more high-density lipoproteins in the body, the lower the risk of developing atherosclerosis.
In exceptional cases, severe disturbances in fat metabolism are observed, and HDL levels become significantly elevated. Possible reasons for this condition are:
- hereditary dyslipidemia;
- chronic hepatitis;
- cirrhotic changes in the liver;
- chronic intoxication;
- alcoholism.
In this case, it is important to begin treatment of the underlying disease. Specific measures designed to reduce HDL levels in medicine have not been developed. It is this fraction of cholesterol that can clear blood vessels of plaque and ensure the prevention of atherosclerosis.
What does reduced value mean?
Low levels of HDL in the body are much more common than high levels. Such a deviation from the norm in the analysis may be due to:
- diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism and other hormonal disorders;
- chronic liver diseases: hepatitis, cirrhosis, cancer;
- kidney pathology;
- hereditary (genetically determined) hyperlipoproteinemia type IV;
- acute infectious processes;
- excessive intake of atherogenic cholesterol fractions with food.
It is important to eliminate the existing causes and, if possible, increase the concentration of HDL cholesterol to the proper level. We'll look at how to do this in the section below.
How to increase HDL
Lifestyle correction

Lifestyle is the first thing that patients with low HDL levels need to pay attention to. Follow the doctors' recommendations:
- Eliminate bad habits from your life. Nicotine from cigarettes has a damaging effect on the inner wall of blood vessels and promotes the deposition of cholesterol on its surface. Alcohol abuse negatively affects metabolism and destroys liver cells, where lipoproteins are normally formed. Quitting smoking and alcoholic beverages will increase HDL levels by 12-15% and reduce atherogenic lipoproteins by 10-20%.
- Fight excess body weight. Obesity in medicine is usually called a pathological condition in which the BMI (a relative value reflecting the ratio of the patient’s weight and height) exceeds 30. Excess weight is not only an additional burden on the heart and blood vessels, but also one of the reasons for the increase in the level of total cholesterol due to its atherogenic fractions. A decrease in LDL and VLDL compensatory leads to normalization of high-density lipoprotein levels. Losing 3 kg of weight has been shown to increase HDL cholesterol by 1 mg/dL.
- Engage in sports approved by your doctor. It is better if it is swimming, walking, Pilates, yoga, dancing. The type of physical activity should be approached with full responsibility. It should bring positive emotions to the patient and not increase the load on the heart and blood vessels. In case of severe somatic pathology, the patient’s activity should be expanded gradually so that the body adapts to daily increasing loads.
And, of course, visit your doctor regularly. Working together with a therapist will help normalize the disturbed metabolism faster and more efficiently. Do not ignore appointments prescribed by the therapist for medical examination, take tests for the lipid spectrum once every 3-6 months and examine the vessels of the heart and brain if signs of insufficient blood supply to these organs occur.
Therapeutic diet

Nutrition is also important in dyslipidemia. The principles of a therapeutic diet to increase HDL levels include:
- Meals are fractional (up to 6 times a day), in small portions.
- The daily caloric intake of food should be sufficient to replenish energy costs, but not excessive. The average value is at the level of 2300-2500 kcal.
- The total amount of fat entering the body throughout the day should not exceed 25-30% of total calories. Of these, it is recommended to allocate most of them to unsaturated fats (low cholesterol).
- Exclusion of foods with the highest possible content of “bad” cholesterol: lard, beef fat; offal: brains, kidneys; aged varieties of cheese; margarine, cooking oil.
- Limiting products containing LDL. For example, during a hypocholesterol diet, it is recommended to eat meat and poultry no more than 2-3 times a week. It is better to replace it with high-quality vegetable protein - soy, legumes.
- Adequate fiber intake. Fruits and vegetables should be the basis for patients with atherosclerosis. They have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and indirectly affect the increase in HDL production in the liver.
- Inclusion in the daily diet of bran: oat, rye, etc.
- Inclusion in the diet of foods that increase HDL levels: fatty sea fish, nuts, natural vegetable oils - olive, sunflower, pumpkin seeds, etc.
You can also raise HDL with the help of dietary supplements containing omega-3 – polyunsaturated fatty acids rich in “exogenous” good cholesterol.
According to statistics, about 25% of the world's population over 40 years of age suffers from atherosclerosis. From year to year, the incidence is increasing among young people aged 25-30 years. Violation of fat metabolism in the body is a serious problem that requires an integrated approach and timely treatment. And changes in HDL levels in tests should not go unnoticed by a specialist.
Found an error in the text? Select it and click Ctrl+Enter, and we will fix everything soon!

