What does biparietal head size mean? BPR - transcript. Biparietal head size: normal
After each ultrasound procedure, pregnant women receive a study protocol, which contains important information baby development. One of the most important parameters of the fetus is the biparietal head size, or BDP. and why it is needed, how BDP and gestational age are related, what are the norms for biparietal head size by week - you will learn about all this from our article.
BPR - decoding
During ultrasound examination special attention is devoted to the study of the baby's head. This is not surprising: the brain most important organ, the growth and development of which directly affect the condition of the fetus. BDP will help determine the size of the head, and therefore the level of brain development. Biparietal size- this is a kind of “width” of the head, measured along the minor axis, from temple to temple.
In addition to the BPR, the fronto-occipital size (FOR) is also determined - along the major axis, from the forehead to the back of the head. However, the main parameter remains the biparietal size: it is this that is used to determine the duration of pregnancy. With particular accuracy, this can be established in the period of 12-28 weeks.
BPR values are also important for determining the possibility physiological birth. If the size of the fetal head does not correspond to the size birth canal, a decision is made about a planned caesarean section.
Biparietal head size is normal
To assess fetal BPD week by week, special tables have been developed that indicate the average norm for the biparietal size of the fetal head and its permissible fluctuations. In the BDP tables, fetal head size values are presented as percentiles. This is a special way of presenting medical statistics that typically gives the mean (50th percentile) and lower (5th percentile) and upper (95th percentile) limits of normal values.
In order to use such a table and determine the norm of fetal BPD by week, you need to find the value of the 50th percentile, the remaining values determine the boundaries normal readings. For example, at 12 weeks the norm for BPR is 21 mm, with permissible deviations of 18-24 mm. This means that with a BPR value of 19 mm to the expectant mother Don’t worry – this is most likely a feature of the baby’s development.
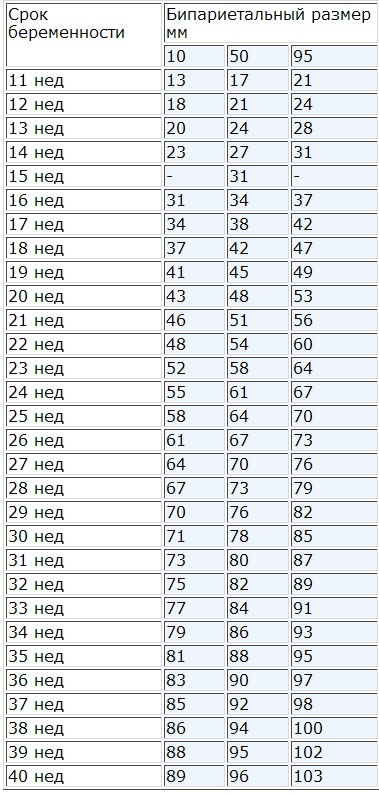
Fetal BPD in the table - deviations from the norm
It happens that the BDP indicators go beyond acceptable limits. What could this mean? Firstly, in order to make sure there is no pathology, the doctor must evaluate other parameters of the fetus (thigh length, abdominal circumference). If they all exceed the norm by one or several weeks, then this may indicate large fruit. If other fetometry values are normal, then perhaps the baby is growing in leaps and bounds, and in a couple of weeks all parameters will level out.
However, significant deviations of BPR values from the norm may indicate serious problems. Thus, an increased biparietal size is observed with tumors of the brain or skull bones, as well as with cerebral hernia, etc. In all these cases, with the exception of hydrocephalus, the pregnant woman is offered to terminate the pregnancy, since these pathologies are incompatible with life. If hydrocephalus is detected, treatment is carried out with antibiotics and only in in rare cases(if there is no effect of treatment) they resort to termination of pregnancy.
A significantly reduced size of the fetal head also does not bode well: as a rule, this means underdevelopment of the brain or the absence of some of its structures (cerebellum or cerebral hemispheres). In this case, the pregnancy is terminated at any stage.
In the third trimester, a reduced BPD indicates the presence of retention syndrome intrauterine development. Treatment is carried out with drugs that improve uteroplacental blood flow (chimes, Actovegin, etc.).

